Key Terms
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Management, Leadership and Decision Making
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
1
New cards
authority
Authority is defined as institutionalised and legal power inherent in a job, function, or position that enables the job holder to successfully carry out his/her responsibilities.
2
New cards
Autocratic Leadership
A leadership style in which leaders dictate without consultation of subordinates.
3
New cards
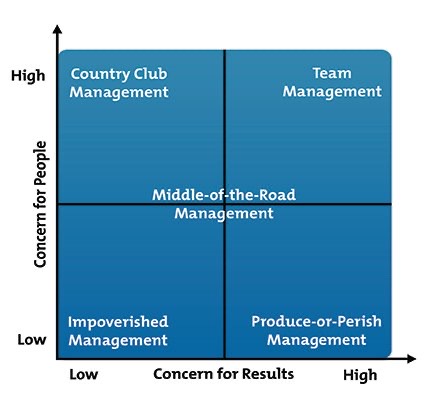
Blake Muton Grid
The Blake Mouton grid was created by Robert Blake and Jane Mouton in 1964.
It’s a way of determining a person’s leadership style, based on their concern for people, and their concern for production
It’s a way of determining a person’s leadership style, based on their concern for people, and their concern for production
4
New cards
communication
Business communication is communication that is intended to help a business achieve a fundamental goal, through information sharing between employees as well as people outside the company. It includes the process of creating, sharing, listening and understanding messages between different groups of people
5
New cards
consultation
Taking into account the views of employees further down the hierarchy
The action or process of formally consulting or discussing.
Meeting with an expert in order to seek advice
The action or process of formally consulting or discussing.
Meeting with an expert in order to seek advice
6
New cards
Decentralisation
In a decentralised structure, decision-making is spread out to include more junior managers in the hierarchy, as well as individual business units or trading locations
7
New cards
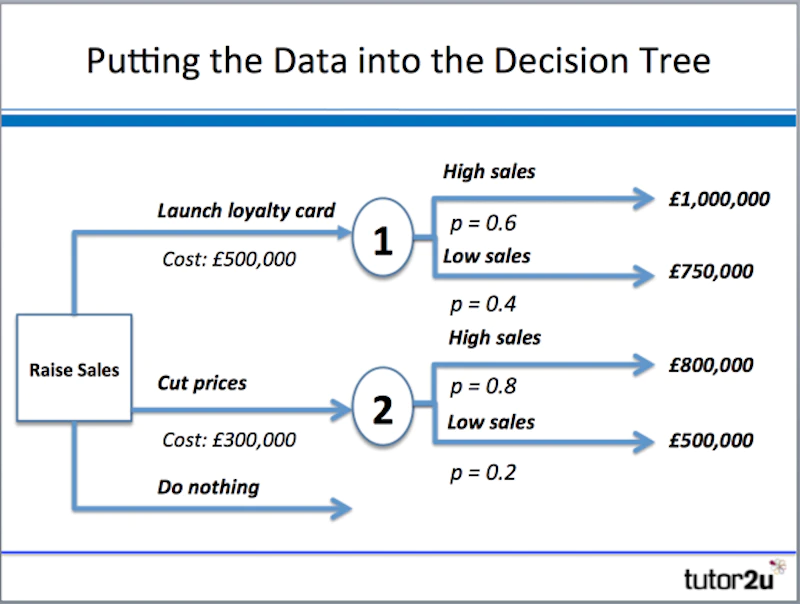
Decision Trees
A decision tree is a mathematical model used to help managers make decisions.
-A decision tree uses estimates and probabilities to calculate likely outcomes.
-A decision tree helps to decide whether the net gain from a decision is worthwhile.
-A decision tree uses estimates and probabilities to calculate likely outcomes.
-A decision tree helps to decide whether the net gain from a decision is worthwhile.
8
New cards
Delegation
Delegation involves the assignment to others of the authority for particular functions, tasks, and decisions.
9
New cards
Democratic Leadership
Style involving consulting with subordinates and evaluating their opinions before making a decision.
10
New cards
Directing
Direction is telling people what to do and seeing that they do it to the best of their ability. It includes making assignments, corresponding procedures, seeing that mistakes are corrected, providing on-the-job instructions and, of course, issuing orders
11
New cards
Empowerment
Empowerment is giving employees the power to do their job.
The concept of empowerment is closely linked to motivation and customer service. Employees need to feel that their actions count – and empowerment is about making this happen.
The concept of empowerment is closely linked to motivation and customer service. Employees need to feel that their actions count – and empowerment is about making this happen.
12
New cards
Ethics
Business ethics is the system of acceptable business behaviours and principles that are applied in the commercial world
13
New cards
Expected Value
The expected value (EV) is an anticipated average value for an investment at some point in the future. Investors use expected value to estimate the worthiness of investments, often in relation to their relative riskiness.
Used in decision trees, formula: Outcome A + Outcome B = total expected value
Used in decision trees, formula: Outcome A + Outcome B = total expected value
14
New cards
hunch
the use of intuition as a key part of decision making
15
New cards
Laissez-faire leadership
A hands off approach to management
16
New cards
leadership
The process and methods of influencing others to take desired actions
17
New cards
Management
Management is the administration of an organization, whether it is a business, a non-profit organization, or a government body. It is the art and science of managing resources of the business.
18
New cards
Market Conditions
Market conditions relate to the attractiveness (or otherwise) of the overall market in which a business operates.
Market conditions tend to affect all businesses in an industry, although their ability to take advantage or, or respond to changes in market conditions will vary. Two key indicators of market conditions are:
Economic Growth (GDP)
Market Demand
Market conditions tend to affect all businesses in an industry, although their ability to take advantage or, or respond to changes in market conditions will vary. Two key indicators of market conditions are:
Economic Growth (GDP)
Market Demand
19
New cards
Net Gains
Used in Decision trees
Net gains = total expected value - cost of option
Net gains = total expected value - cost of option
20
New cards
Non-programmed decision making
Non-programmed decisions are unique. They are often ill-structured, one-shot decisions. Traditionally they have been handled by techniques such as judgment, intuition, and creativity. Used for unexpected and unique issues.
21
New cards
opportunity cost
The cost of a decision as measured by the benefits foregone of the next best alternative
22
New cards
Paternalistic leadership
A managerial approach where there is a dominant figure that decides what is best for employees.
23
New cards
planning
The business plan sets out how the owners/managers of a business intend to realise its objectives. Without such a plan a business is likely to drift
the cognitive process of thinking about what you will do in the event of something happening
the cognitive process of thinking about what you will do in the event of something happening
24
New cards
pressure groups
A pressure group is an organisation with shared aims which seeks to influence policy through political means, without seeking political office itself
25
New cards
probability
a measure of how likely it is that some event will occur; a number expressing the ratio of favorable cases to the whole number of cases possible
26
New cards
Programmed Decisions
Programmed decisions are those that are traditionally made using standard operating procedures or other well-defined methods. These are routines that deal with frequently occurring situations, such as requests for leaves of absence by employees
27
New cards
risk
The probability or chance that hoped-for outcomes will not occur
28
New cards
Scientific decision making
All business decisions involve some uncertainty. However businesses and managers increasingly want to reduce that uncertainty and risk by applying logic to decision-making, supported by relevant data.
Scientific decision-making involves the use of:
-Data mining and big data to source relevant data to inform decisions
-Application of software logic and predictive models to analyse scenarios
-Forecasts to consider the possible implications of business decisions
Scientific decision-making involves the use of:
-Data mining and big data to source relevant data to inform decisions
-Application of software logic and predictive models to analyse scenarios
-Forecasts to consider the possible implications of business decisions
29
New cards
Social Responsibility
Corporate social responsibility is where businesses address social and environmental considerations as part of their normal business activities
30
New cards
Stakeholder engagement
Stakeholder engagement is the process by which an organiation involves people who may be affected by the decisions it makes or can influence the implementation of its decisions. They may support or oppose the decisions, be influential in the organization or within the community in which it operates, hold relevant official positions or be affected in the long term.s
31
New cards
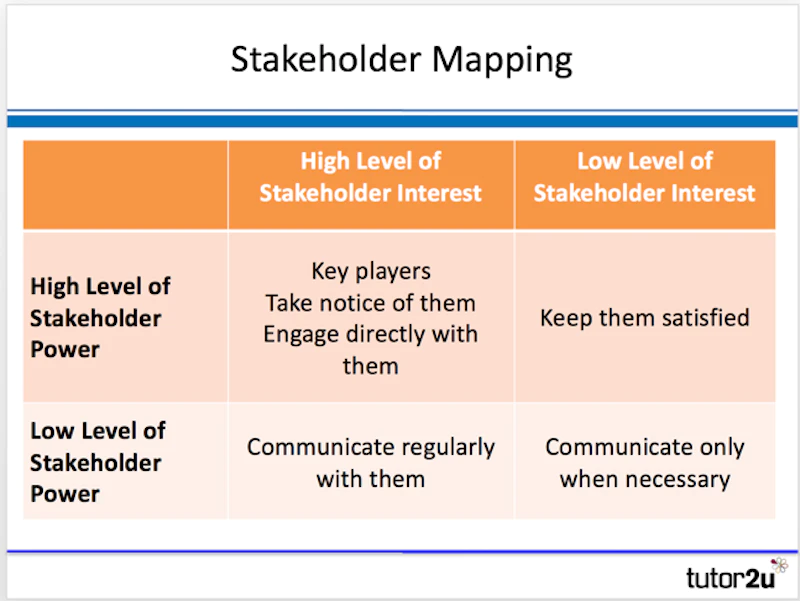
Stakeholder Mapping
To manage its stakeholders well, a business effectively to make choices. It is very difficult to meet the needs of every stakeholder group and most decisions will end up being “win-lose”: i.e. supporting one stakeholder means another misses out.
How should a business respond to variations in stakeholder power and influence? The matrix (stakeholder map) below provides some guidance on the approach often taken:
How should a business respond to variations in stakeholder power and influence? The matrix (stakeholder map) below provides some guidance on the approach often taken:
32
New cards
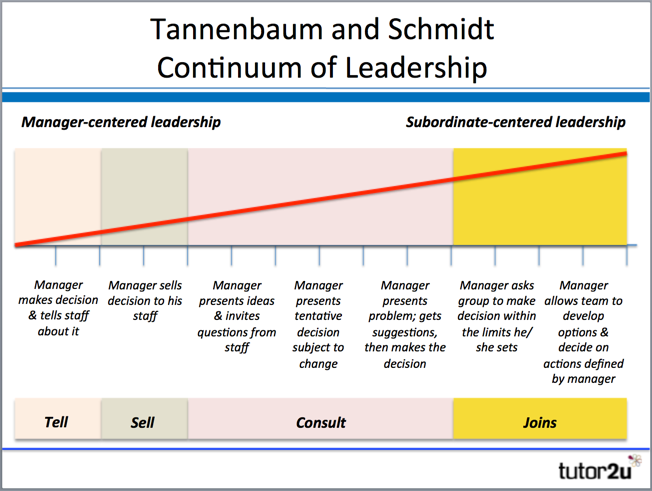
Tannenbaum and Schmidt Continuum
Tannenbaum and Schmidt devised their continuum that illustrates a range of potential leadership and management styles
Tannenbaum and Schmidt Continuum of Leadership
The Tannenbaum and Schmidt Continuum recognises that the chosen leadership style depends on a variety of factors, including the leader's personality, the perceived qualities of subordinates.
It also allows for "situational" factors such as the need for urgency in leadership and decision-making.
The continuum represents a range of action related to the:
– Degree of authority used by the leader or manager
– Area of freedom available to non-managers
Tannenbaum and Schmidt Continuum of Leadership
The Tannenbaum and Schmidt Continuum recognises that the chosen leadership style depends on a variety of factors, including the leader's personality, the perceived qualities of subordinates.
It also allows for "situational" factors such as the need for urgency in leadership and decision-making.
The continuum represents a range of action related to the:
– Degree of authority used by the leader or manager
– Area of freedom available to non-managers
33
New cards
Theory X
McGregor’s Theory X that states that employees generally have little ambition, avoid responsibilities, and are mostly extrinsically motivated.
34
New cards
Theory Y
Theory Y that states that employees are intrinsically motivated, enjoy their job, and want to work to better themselves without a direct reward in return.
35
New cards
Uncertainty
The unpredictable and uncontrollable events that affect business decisions and actions
e.g.Will a business achieve its break-even output?
e.g.Will a business achieve its break-even output?