firestine intro/ med chem
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
are charged or uncharged molecules absorbed
uncharged
configurational vs conformational isomers
conform= single bond rotation
config= double bond (e/z) OR have a chiral center
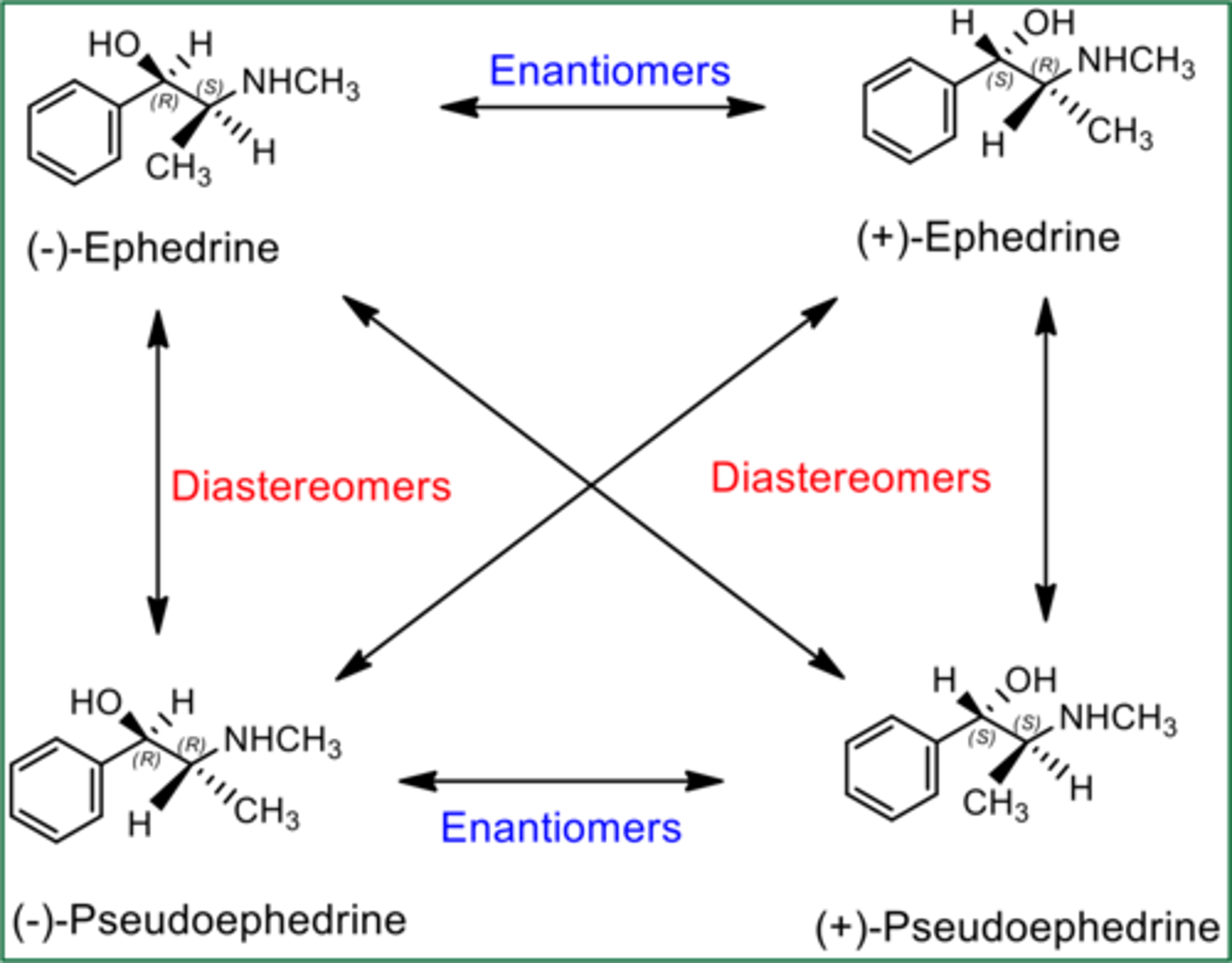
Enantiomers vs. Diastereomers
-enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other
-diastereomers have 2+ chiral centers and are NOT mirror images
a lower Kd means ________ affinity
greater
van der Waals
attraction btwn hydrocarbon chains
3 point attachment rule
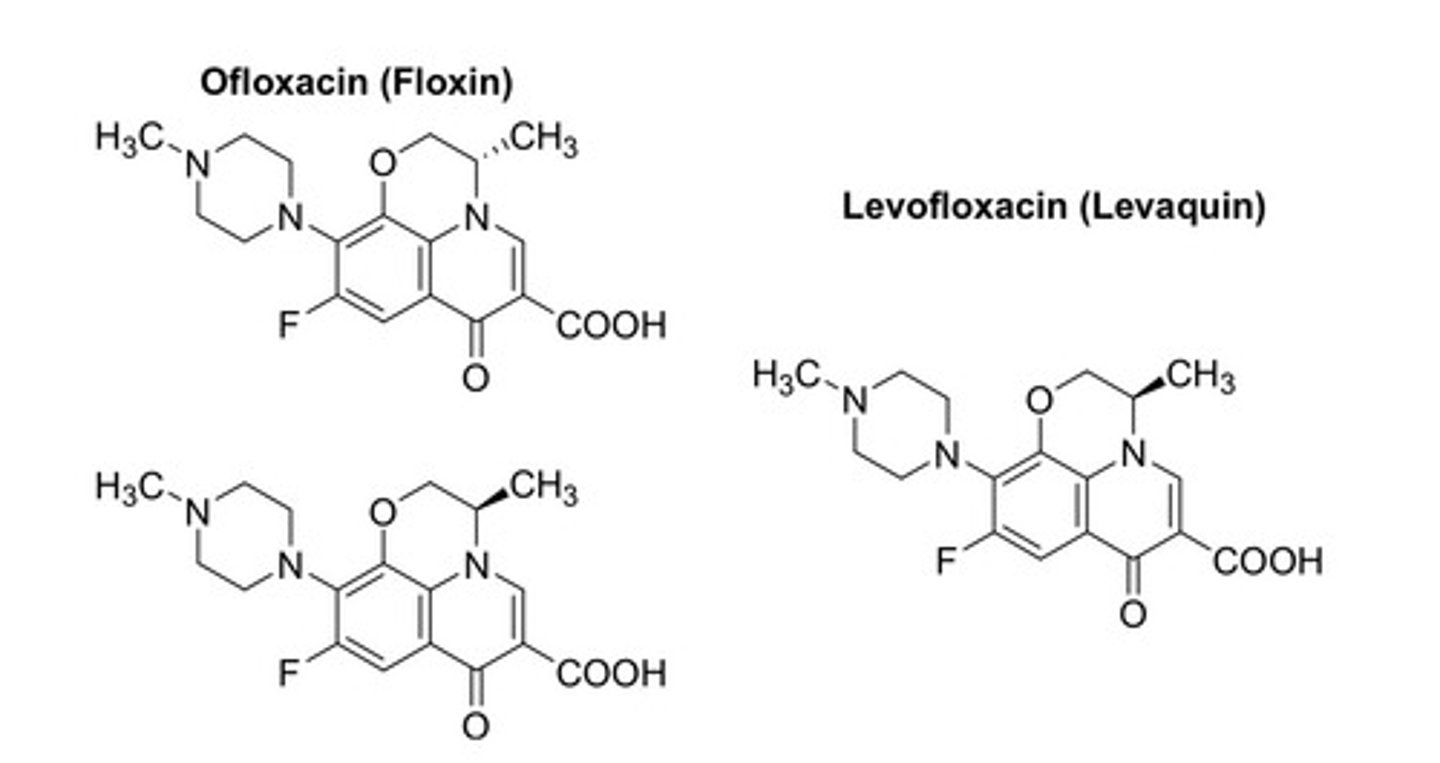
3 points of contact are needed to select btwn 2 enantiomers and determine stereospecificity
racemates
a mixture composed of equal amounts of R and S enantiomers
racemic switch
A drug that is already sold as a racemate is patented and sold as a single enantiomer (the eutomer)
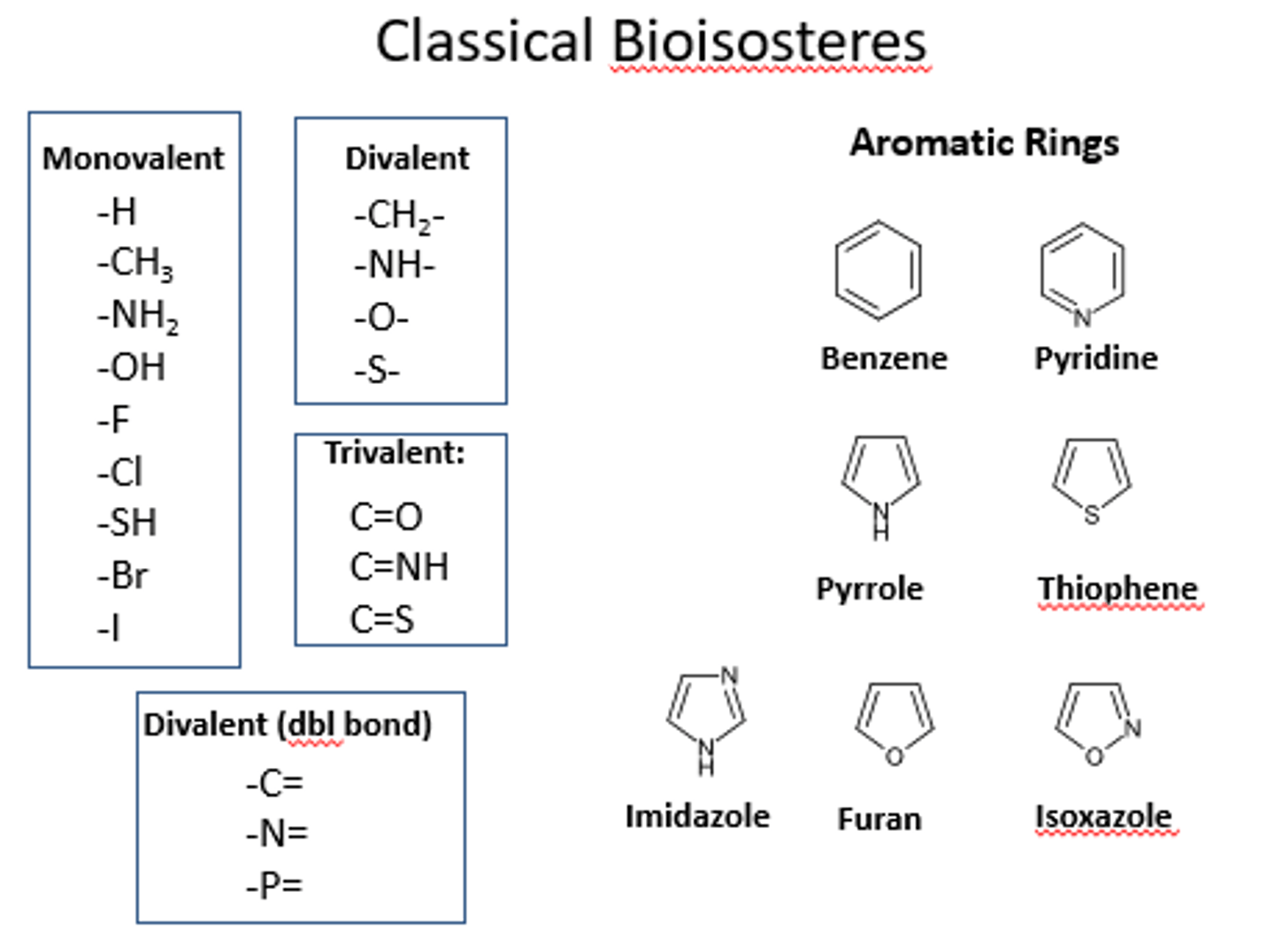
bioisosteres
classical and nonclassical; adding functional group to change a drug property while keeping effect
describe aromatic and benzylic oxidations
OH added to para position/ least substituted spot
omega oxidations
OH added to longest aliphatic chain

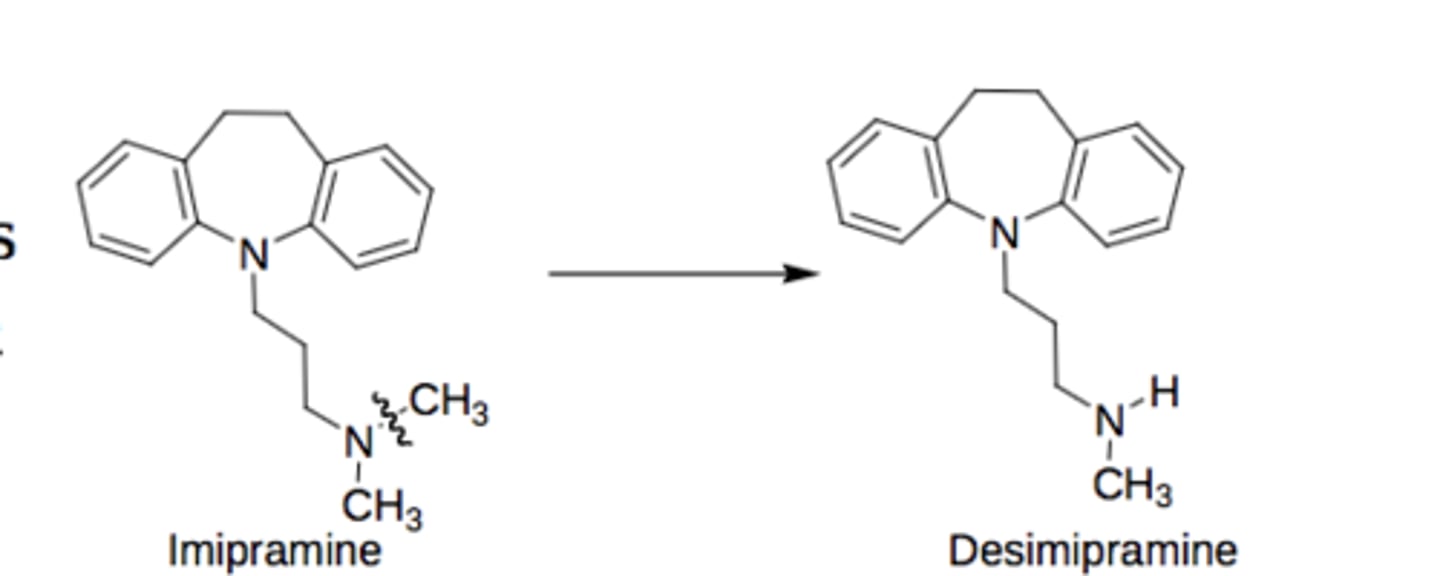
describe 3/2/1 amine dealkylation
OH replaces H on the C of one of the R groups, becomes carbonyl, breaks off
3amine-> 2 amine + ket/ald
2amine-> 1 amine + ket/ald
1amine-> NH3 + ket/ald
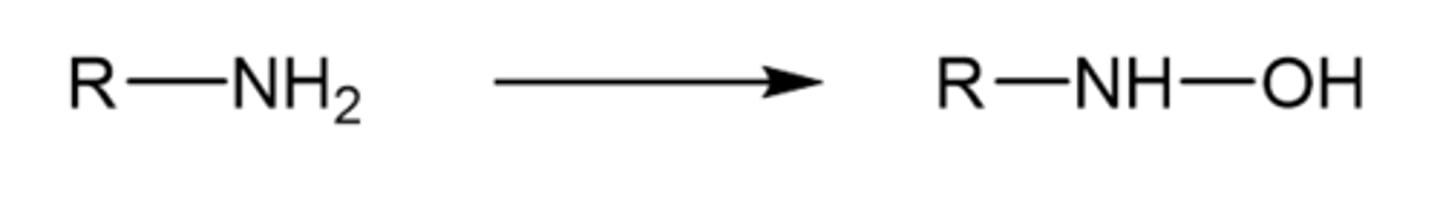
primary amine N-oxidation
if R group on primary amine does not have H, OH can be added without carbonyl breaking off
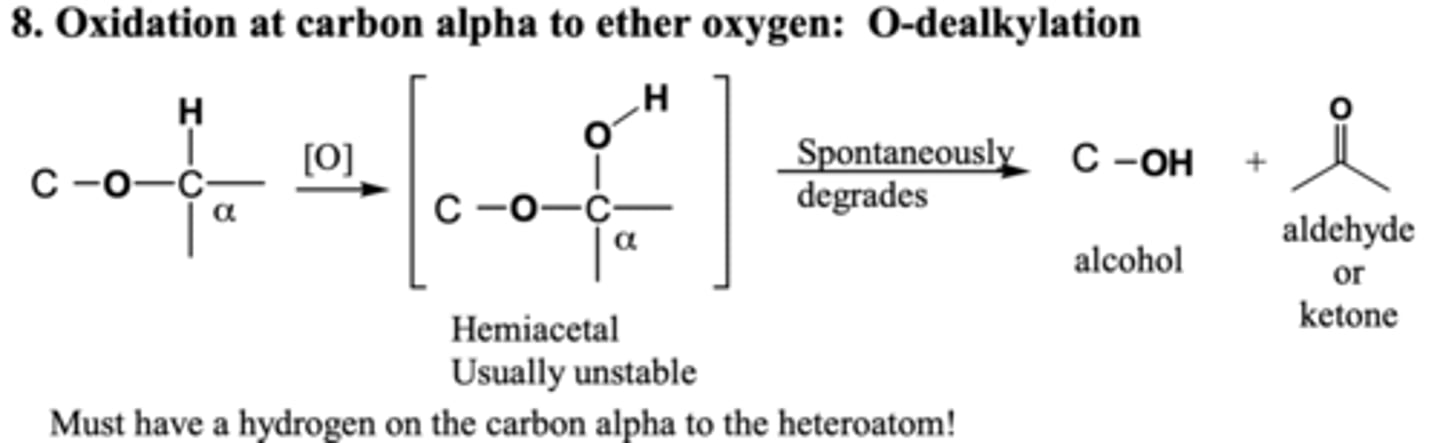
ether o-dealkylation
OH added to R group attached to O, breaks off
ROR-> ROH and O=C
does N-dealkylation only happen at amines or other groups like imides/amides
ONLY AT AMINES
t/f: hydrolysis can happen at any carbonyl
true
t/f: reduction only happens at aldehydes and ketones
true
reduction
aldehyde/ketones gaining H, become alcohol
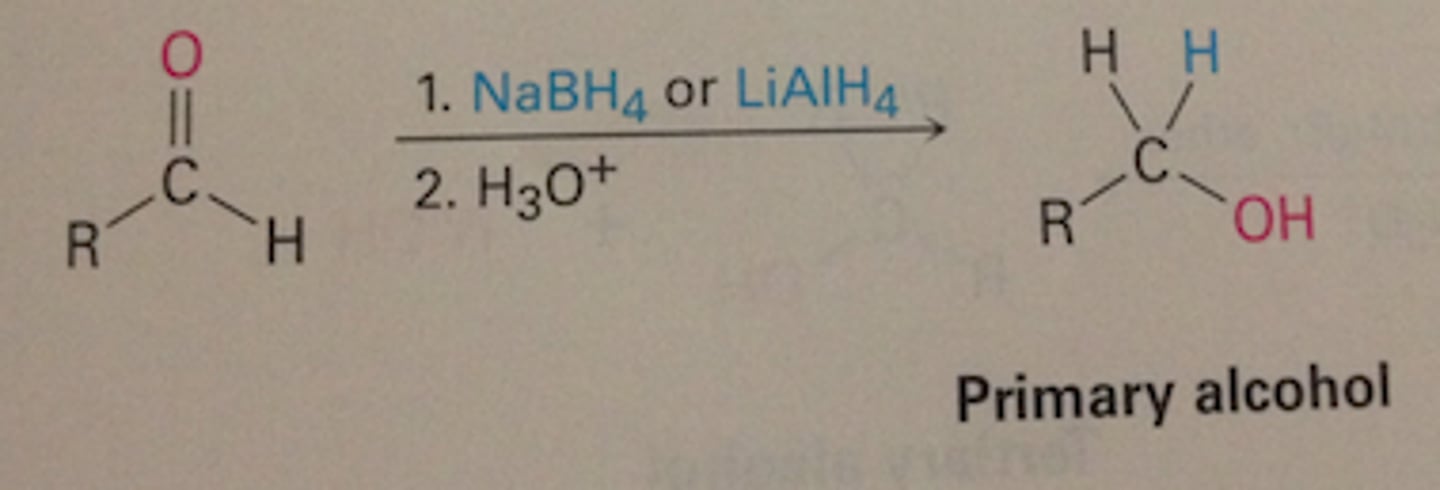
ester hydrolysis
ester reacts with H2O to produce a carboxylic acid and an alcohol
(this can happen to any carbonyl!)

amide hydrolysis
Amide + Water --> Carboxylic Acid + Amine
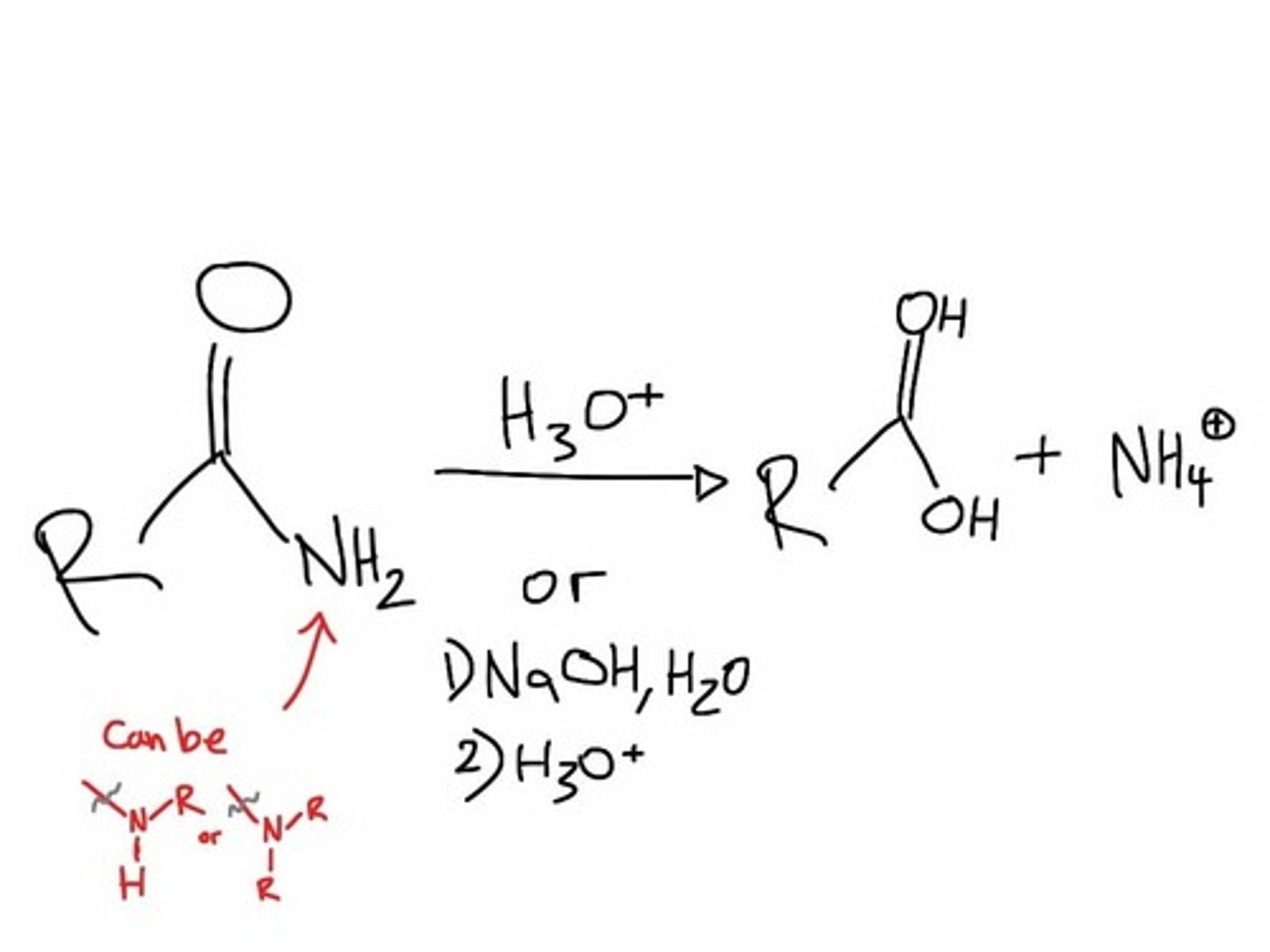
which hydrolysis is faster: esters or amides
esters is faster
phase 2 metabolism
CONJUGATION. Acetylation, Glucuronidation, sulfation. Add groups to increase excretion
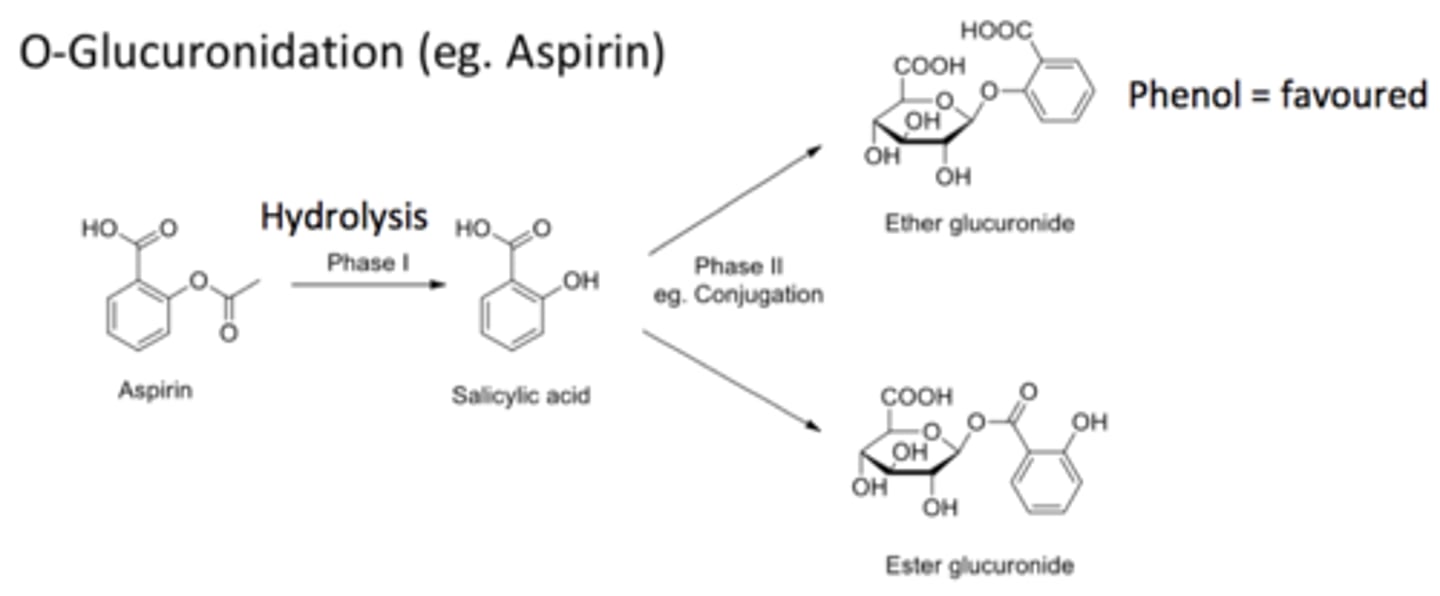
glucuronidation
MOST COMMON PATHWAY
adds gluc to phenols, COOH, and nitrogens
sulfation
MOSTLY WITH PHENOLS; common in children
adds SO3- to phenol

which amino acids are used in phase 2 metabolism
glycine and glutamine; added to COOH (makes new amide bond)

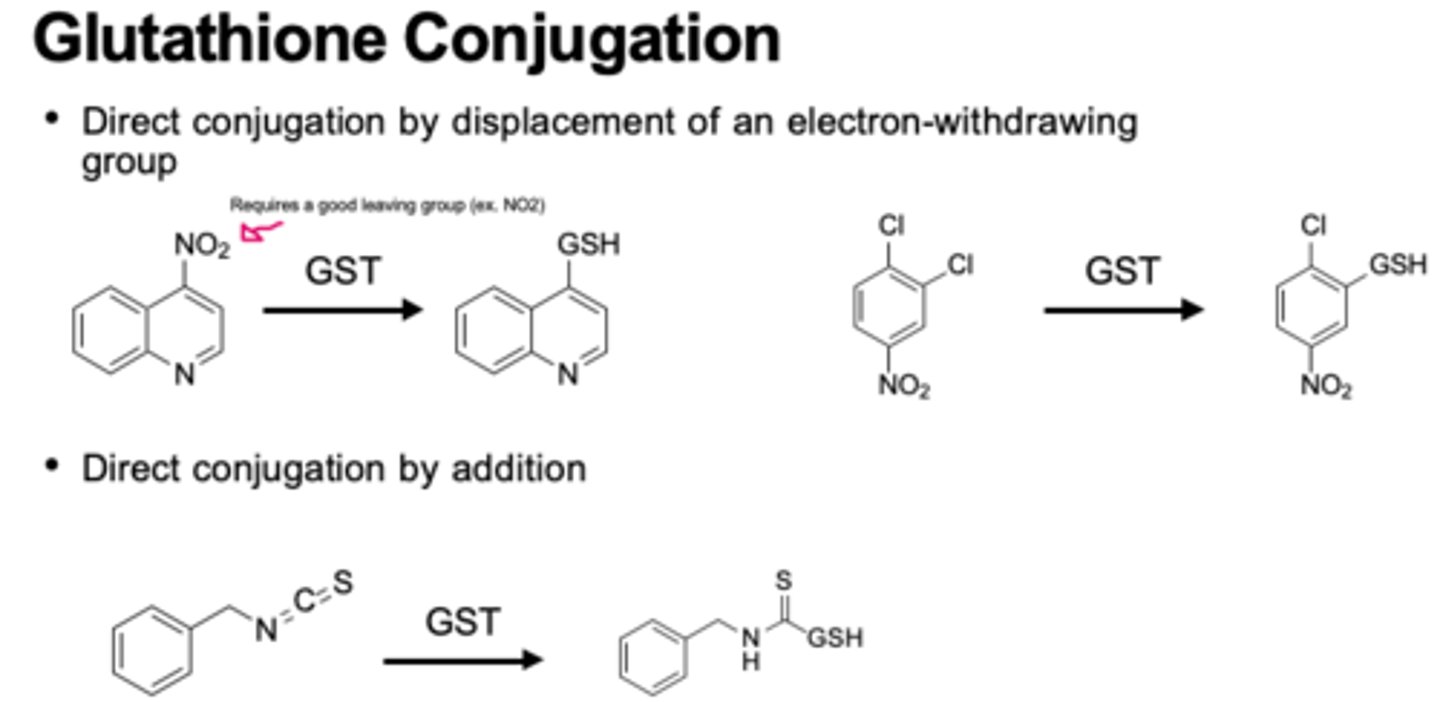
glutathione phase 2
glutathione (nucleophile) added to electrophilic groups
1) good leaving group
2) e- withdrawing group
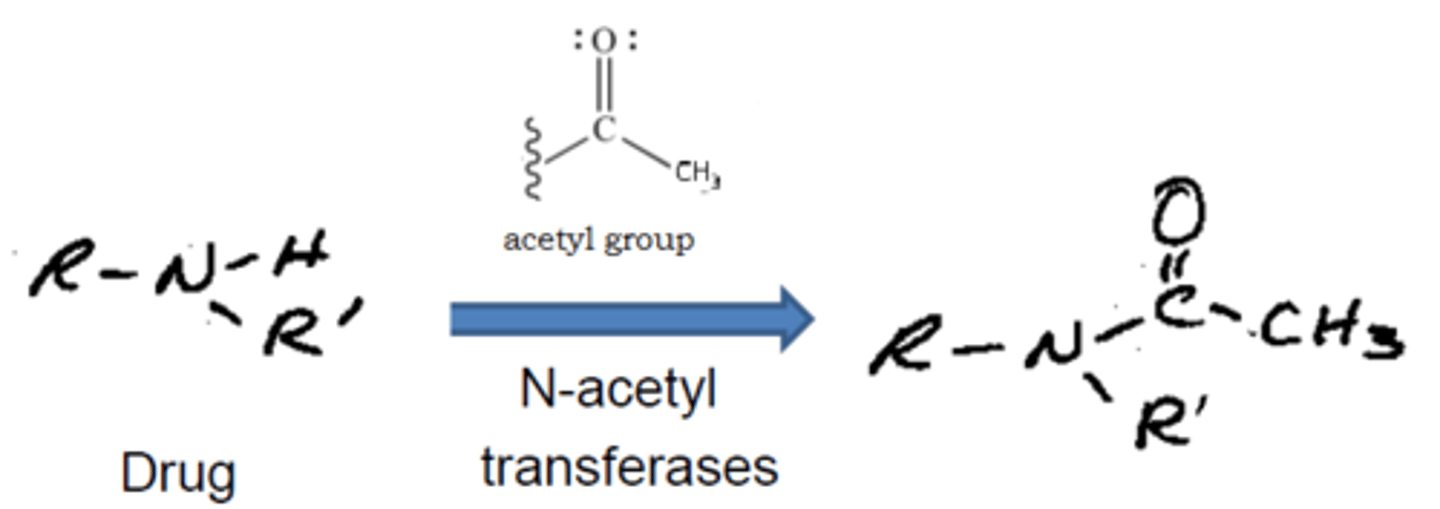
acetylation mainly happens at
primary aromatic or aliphatic amines