Antibody Titration
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
Antibody Titration Principle
measures antibody conc. in serum or compare antigen strength on different red cells samples
Estimating antibody activity in allo-immunized pregnant women
Elucidating autoantibody specificity
Characterizing antibodies with high titer and low avidity (e.g. Knops and Chido/Rodgers systems)
Antibody titration
Determines alloantibody concentration
Serum serially diluted, tested against RBCs
Includes indirect antiglobulin phase (anti-IgG)
Result: reciprocal of endpoint or titer score
Critical titer levels set by each lab
Titer of 16-32 generally significant
What specimen is used for Antibody Titration?
Serum or plasma antibody
What reagents are used for Antibody Titration?
Red cells expressing corresponding antibody specificity(ies) in 2-5% saline suspension (uniformity crucial)
Saline
Procedure: Dilution Technique

Antibody Titer Grading Interpretation:
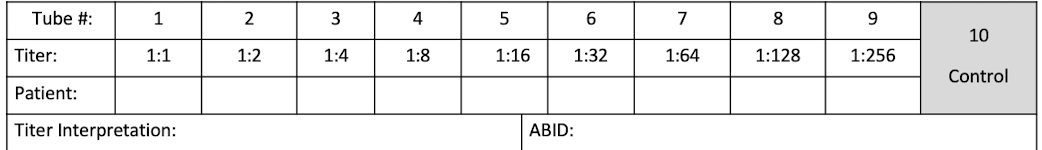
Observe the highest dilution with 1+ agglutination. Titer is the reciprocal of that dilution (e.g., 32). If agglutination occurs in the most dilute tube, continue dilutions.