Covalent bonding
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
1
New cards
How is a covalent bond formed
Atoms share a pair of electrons
2
New cards
Covalent bonding in terms of electrostatic attractions
A strong electrostatic attraction between the shared electrons and the two nuclei
3
New cards
Understand how to draw covalent bonds for diatomic molecules
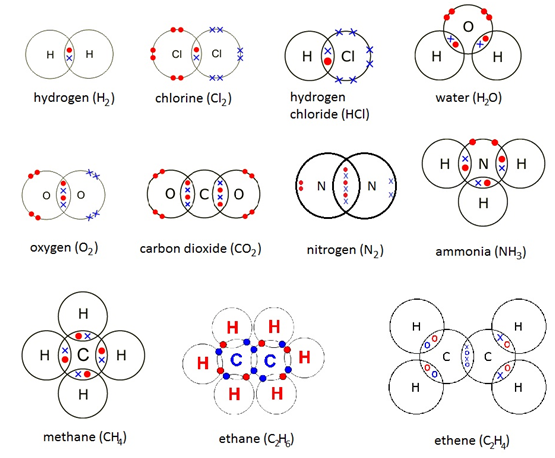
4
New cards
Why do substances with simple molecular structures have low melting and boiling points
Covalent bonds between atoms are strong but between each molecules are weak intermolecular forces that require little energy to overcome
5
New cards
Why do melting and boiling points of simple molecular structures increase with relative atomic mass
Larger molecules tend to have higher boiling points. This is because molecules with more atoms have more forces of attraction between them. Intermolecular forces also get stronger/increase in number so they need more energy to overcome
6
New cards
Why are giant covalent structures solids with high melting and boiling points
Substances such as diamonds are have a giant covalent structure which contain many strong covalent bonds, these need a lot of energy to overcome so it has a high boiling point
7
New cards
How do the structures of diamond, graphite, and c60 fullerene influence their physical properties
Diamond → is made up of only carbon atoms, these atoms have strong covalent bonds to 4 other carbon atoms. This causes diamonds to be extremely hard. This means it is used in high speed cutting tools
Graphite → is made up of only carbon atoms. Each carbon atom is covalent bonded to 3 other carbon atoms. One atom is delocalised in every 4 carbon bonds and is free to move and carry charge, this is why graphite can conduct electricity without being a metal. Graphite is soft and slippery because there are weak forces of attraction between layers
C60 fullerene → is made up of only carbon atoms, has weak intermolecular forces of attractions which take little energy to overcome so it has a low boiling and melting point. It cannot conduct electricity despite having delocalised electrons
Graphite → is made up of only carbon atoms. Each carbon atom is covalent bonded to 3 other carbon atoms. One atom is delocalised in every 4 carbon bonds and is free to move and carry charge, this is why graphite can conduct electricity without being a metal. Graphite is soft and slippery because there are weak forces of attraction between layers
C60 fullerene → is made up of only carbon atoms, has weak intermolecular forces of attractions which take little energy to overcome so it has a low boiling and melting point. It cannot conduct electricity despite having delocalised electrons
8
New cards