Unsaturated Hydrocarbons in Organic Chemistry
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
Contain double or triple bonds between carbon atoms.
Alkenes
Hydrocarbons with one or more double bonds (C=C).
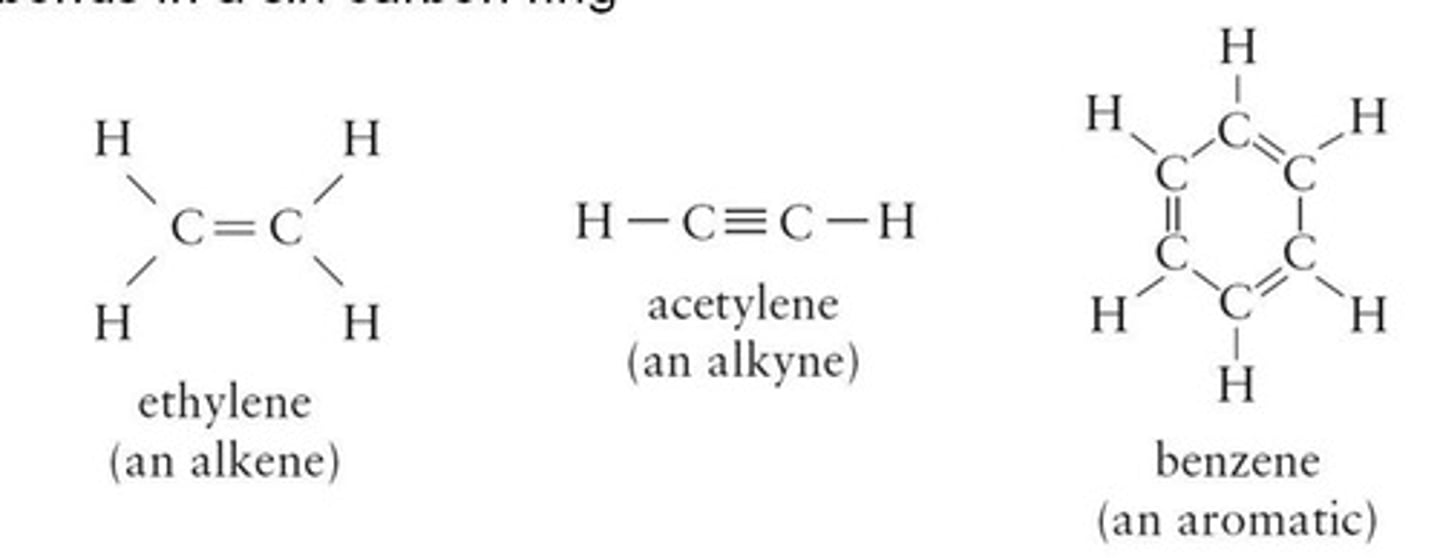
Alkynes
Hydrocarbons with one or more triple bonds (C≡C).
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Contain alternating double and single bonds in a ring.
General Formula for Alkenes
CnH2n, where n is the number of carbons.
IUPAC Naming
Systematic method for naming organic compounds.
Geometric Isomers
Isomers differing in spatial arrangement around double bonds.
Cis-Isomers
Similar groups on the same side of a double bond.
Trans-Isomers
Similar groups on opposite sides of a double bond.
Markovnikov's Rule
Predicts major products in addition reactions of alkenes.
Addition Reactions
Reactions where atoms are added to a double bond.
Addition Polymerization
Process of forming polymers by adding monomers together.
Uses of Addition Polymers
Commonly used in plastics and synthetic materials.
Naming Alkenes Steps
Identify longest chain, number carbons, locate double bond.
Multiple Double Bonds
Use -diene, -triene to denote number of double bonds.
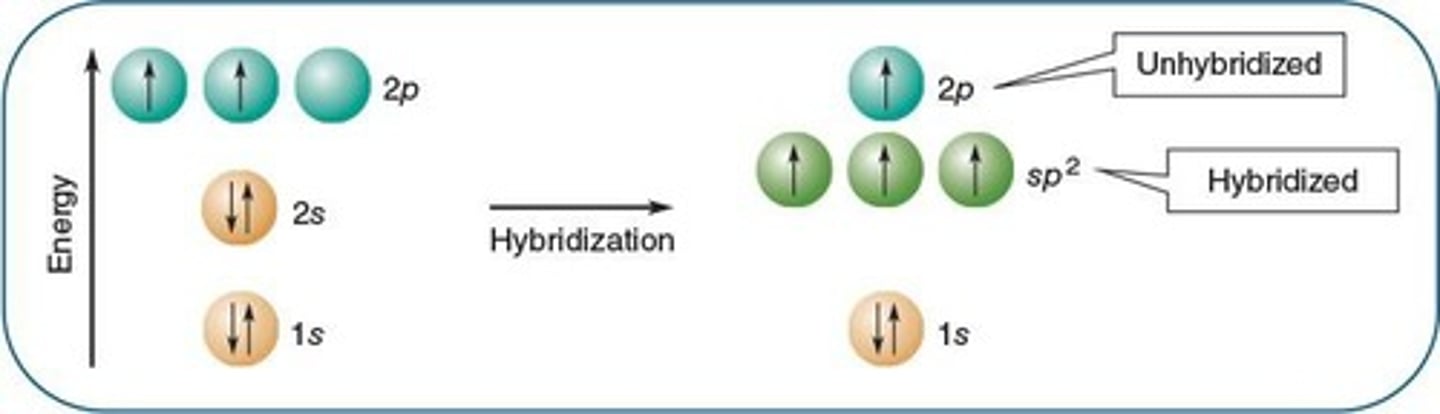
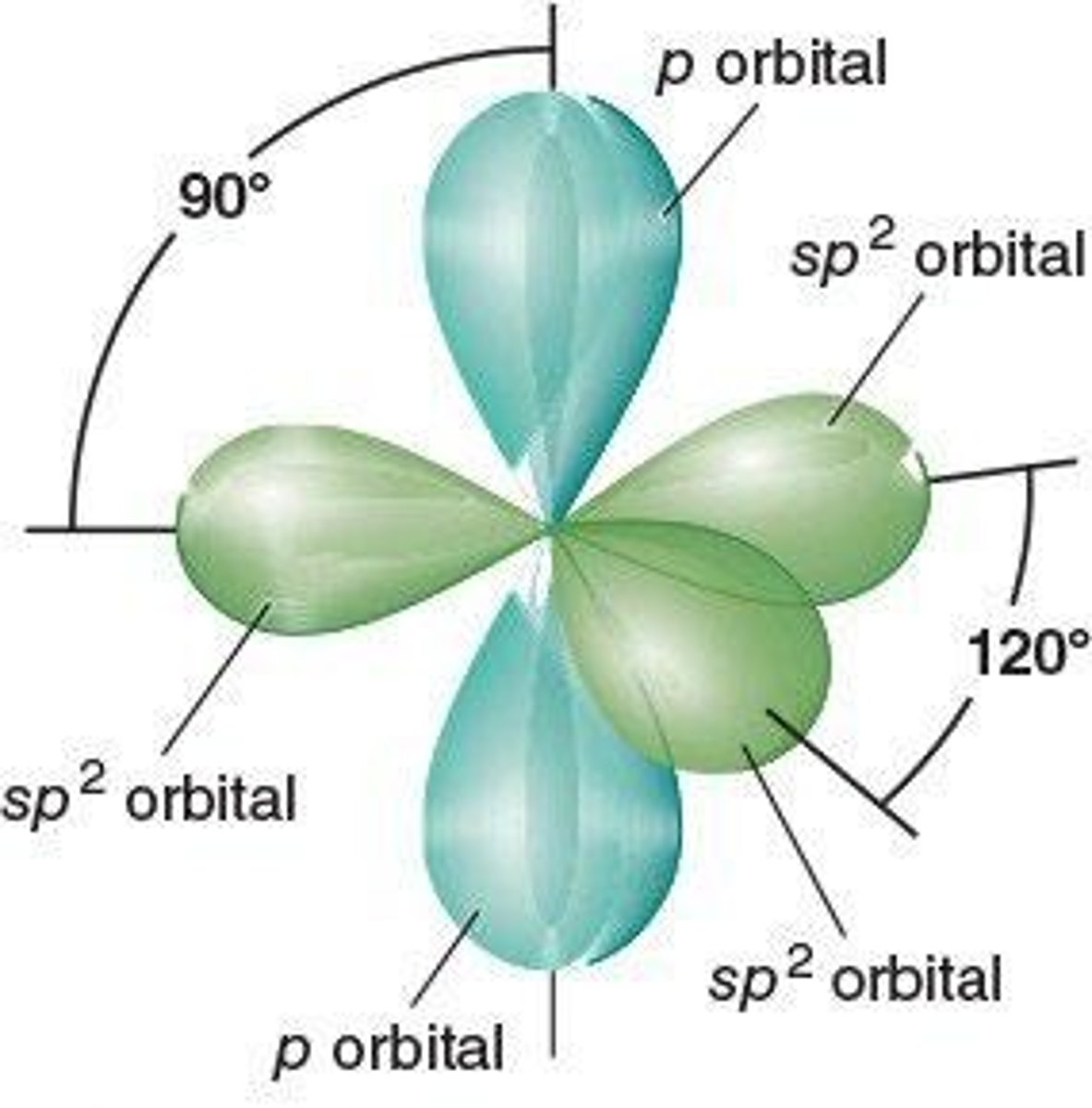
sp2 Hybridization
Formation of three hybrid orbitals from one s and two p orbitals.
Bond Angles in Alkenes
120° angles between sp2 hybrid orbitals.
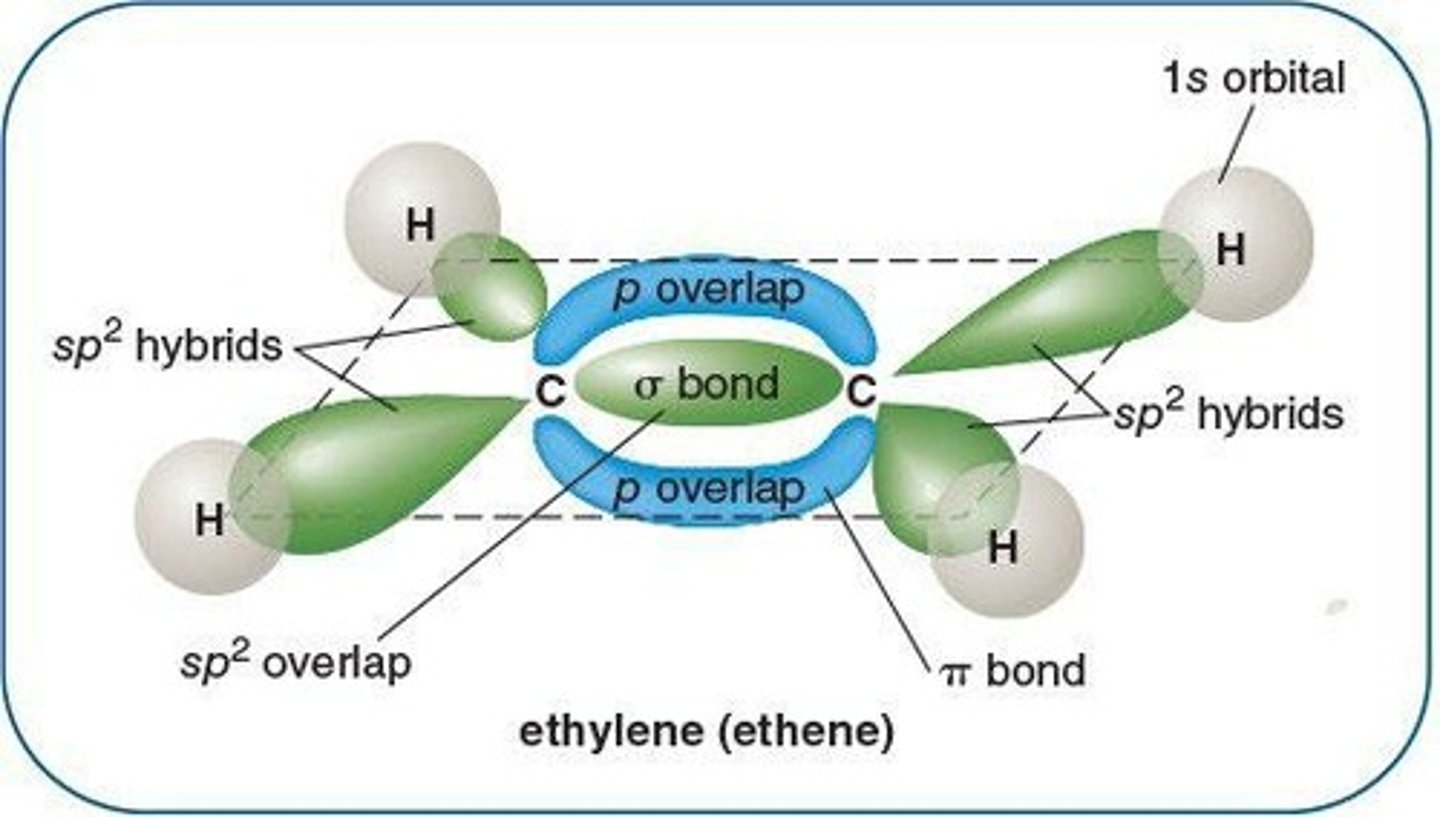
Sigma (σ) Bond
First bond formed by overlapping orbitals.
Pi (π) Bond
Second bond formed by overlapping unhybridized p orbitals.
Cis-Trans Stereoisomerism
Occurs in alkenes with two different groups on carbons.
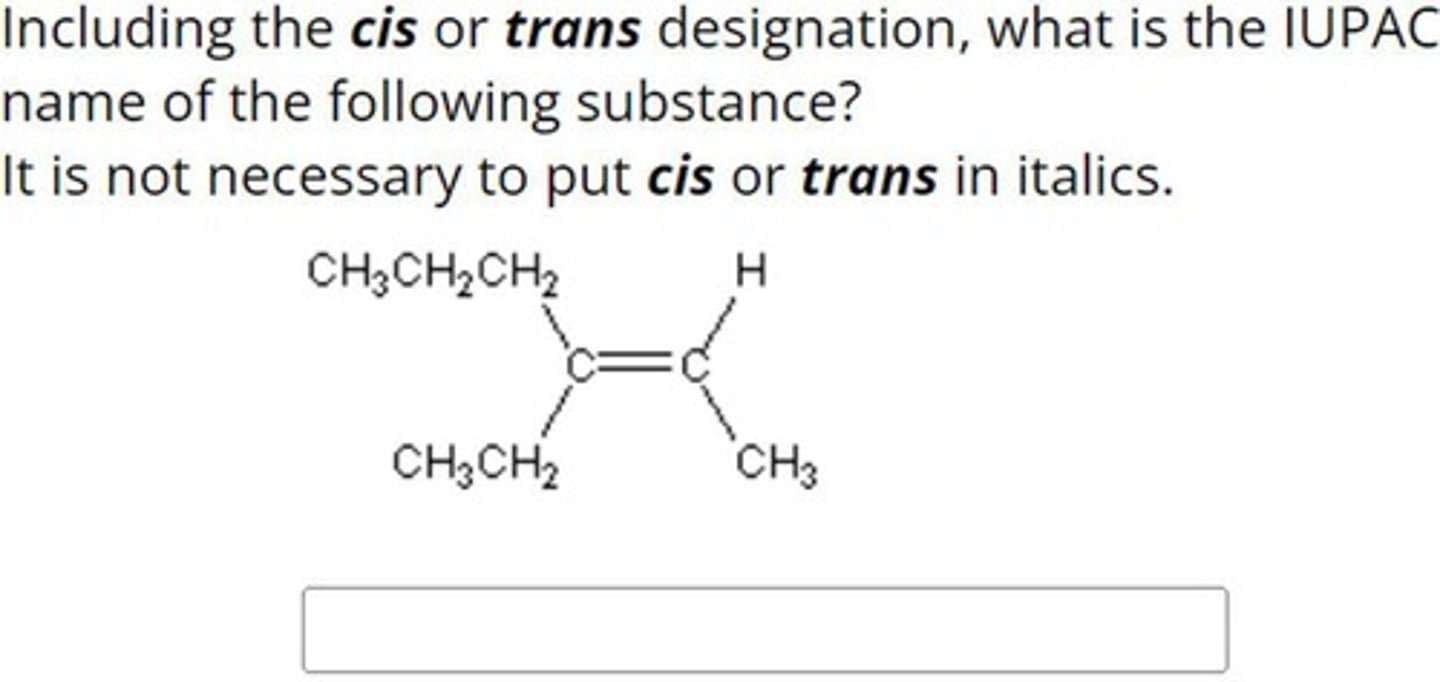
Calculation of Isomers
Number of cis-trans isomers is 2^n, where n is double bonds.
Structural Formulas
Visual representations of molecular structures.
Physical Properties of Isomers
Cis and trans isomers have different physical properties.
Alkenes
Hydrocarbons with at least one double bond.
Physical Properties
Similar to alkanes; nonpolar, insoluble in water.
Alkene States
Gases with 4 C atoms; liquids 5-17 C; solids 18+ C.
Density
Alkenes are less dense than water.
Gasoline Odor
Low molecular weight alkenes smell like gasoline.
Alkene Reactivity
Alkenes are chemically reactive due to double bonds.
Addition Reactions
Compounds add to alkenes at double bonds.
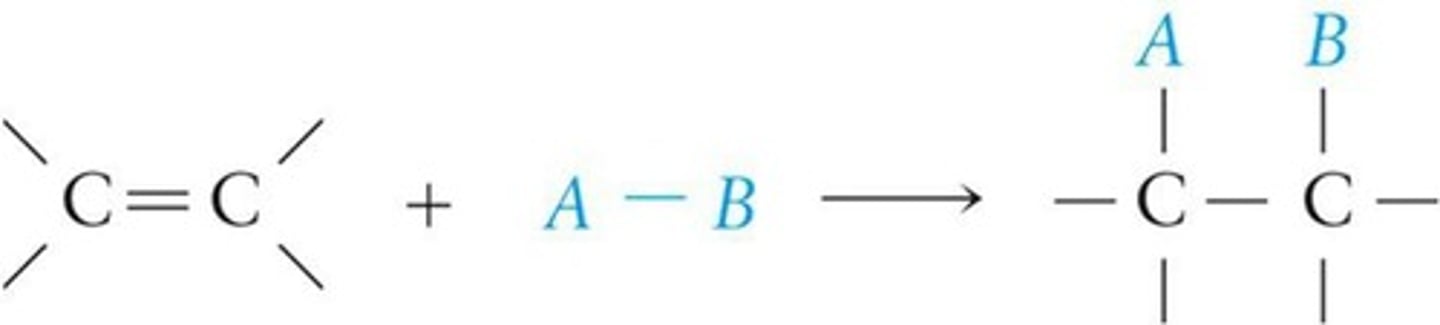
Halogenation
Reaction with halogens forming haloalkanes.
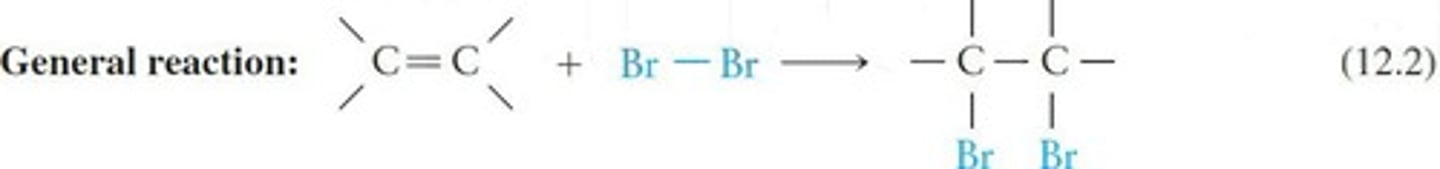
Hydrogenation
Addition of hydrogen using catalysts like platinum.
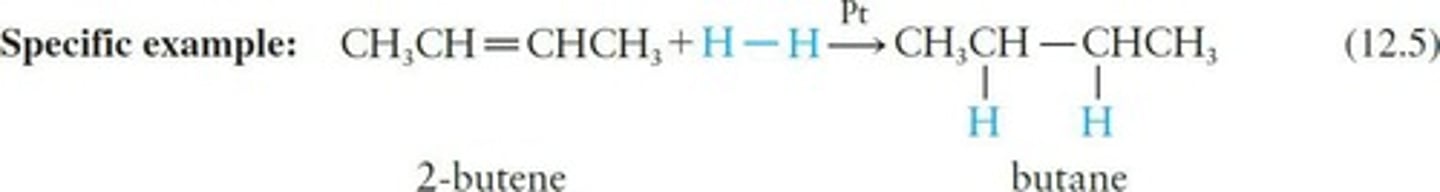
Hydration
Water splits; H and OH attach to carbons.
Markovnikov's Rule
H attaches to carbon with more hydrogens.
Addition Polymers
Polymers formed from alkene addition reactions.
Polyethylene
Example of an addition polymer from alkenes.
Monomer
Starting material for polymer repeating units.
Copolymers
Polymers from two different monomers.
Alkynes
Hydrocarbons with at least one triple bond.
Ethyne
Simplest alkyne, used in torches and plastics.
sp Hybridization
Mixing of orbitals in alkynes for bonding.
Linear Shape
Alkynes have a linear geometry due to sp hybridization.
Alkyne Nomenclature
Alkynes named with -yne suffix.
Aromatic Compounds
Contain benzene rings or structural relatives.
Aliphatic Compounds
Non-aromatic organic compounds including alkenes.
Benzene Structure
Alternating single and double bonds in a ring.
Delocalized Electrons
Electrons move freely around benzene's double ring.
Phenyl Group
Benzene ring as part of a larger hydrocarbon.
Ortho, Meta, Para
Prefixes for substituent positions on benzene.
Substitution Reactions
Aromatic rings replace hydrogen with other groups.
Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds
Carcinogenic compounds with shared carbon atoms.
Aromatic Uses
Solvents and starting materials for valuable compounds.