Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Steps of Eukaryotic Gene Expression
Chromatin modification (DNA unpacking)
Transcription regulation
RNA processing (cutting out exons)
Degradation of mRNA
Degredation of protein
Step 1: Chromatin Modification
what step of eukaryotic gene regulation does this picture represent?
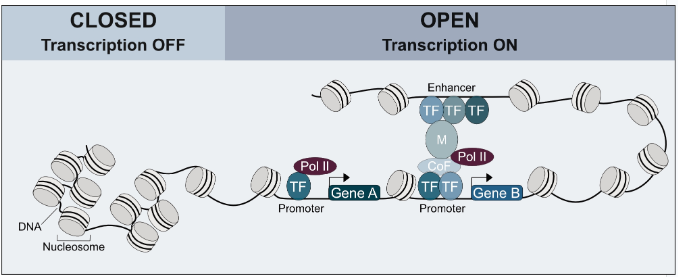
Step 2: transcription regulation (on / off)
what step of eukaryotic gene regulation does this picture represent?
this is operons in prokaryotes
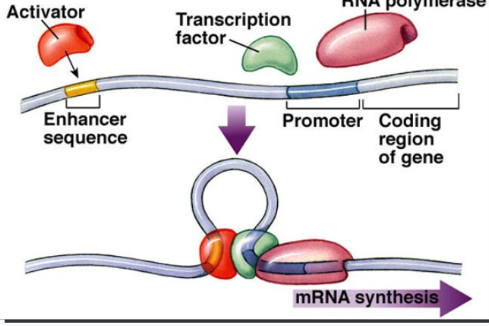
promoters
DNA sequences upstream of transcription start site
signals transcriptional start point / initiation
TATA box
an important promoter in DNA is the ?
transcription factors
mediates the binding of RNA polymerase and initiation of transcription
binds before RNA polymerase binds
rate
transcription factors control the ? of transcription and turns genes on / off
(GO) activators, enhancers
(STOP) repressors, silencers
RNA processing (cutting out exons)
translation occurs during Step 3 ?
introns, 5’ GTP cap, 3’ Poly-A tail
during Step 3: RNA modification / processing, ? are spliced out and the ? cap and ? tail are added
5’ GTP Cap
attachment to mRNA that helps ribosomes attach to the mRNA
3’ Poly-A Tail
attachment to mRNA that helps export from nucleus by making RNA stable
protein synthesis, hours, weeks, prevent
during Step 4: Regulation of mRNA degradation, the life span of mRNA can determine the amount of ?
mRNA can last from ? to ?
5’ cap and 3’ tail ? degradation
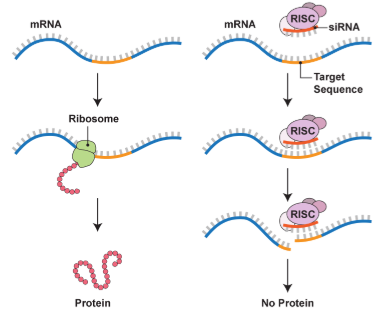
RNAi (RNA interference)
specific type of RNA that can turn down or shut off specific genes at critical times
ex: small interfering RNAs (siRNA)
ex: microRNAs (miRNA)
block, golgi
during Step 5: control of translation / protein processing
regulatory proteins ? initiation of translation
? helps process proteins for transport
proteins degrade