12 Glass and Glazing
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Glass
A hard, brittle, usually transparent or translucent substance, produced by fusing silica together with a flux and a stabilizer into a mass that cools to a rigid condition without crystallization
Sheet Glass
A flat, soda-lime-silica glass fabricated by drawing the molten glass from a furnace (draw glass) or by forming a cylinder, dividing it lengthwise, and flattening it (cylinder glass); The fire-polished surfaces are not perfectly parallel, resulting in some distortion of vision
Plate Glass
A flat, soda-limed-silica glass formed by rolling molten glass into a plate (rolled glass) that is subsequently ground and polished after cooling
Float Glass
A flat, soda-lime-silica glass that is extremely smooth and nearly distortion-free, manufactured by pouring molten glass onto a surface of molten tin and allowing it to cool slowly; Successor to plate glass and accounts for the majority of flat-glass production
Annealed Glass
Glass that is cooled slowly to relieve internal stresses
Heat-Strengthened Glass
Annealed glass that is partially tempered by a process of reheating and sudden cooling; Twice the strength of annealed glass of the same thickness
Tempered Glass
Annealed glass that is reheated to just below the softening point and then rapidly cooled to induce compressive stresses in the surfaces and edges of the glass and tensile stresses in the interior; Three to five times the resistance of annealed glass to impact and thermal stresses but cannot be altered after fabrication; Breaks into relatively harmless particles
Laminated or Safety Glass
Two or more plies of flat glass bonded under heat and pressure to interlayers of polyvinyl butyral resin that retains the fragments if the glass is broken
Wired Glass
Flat or patterned glass having a square or diamond wire mesh embedded within it to prevent shattering in the event of breakage or excessive heat; Considered a safety glazing material
Security Glass
Laminated glass having exceptional tensile and impact strength, consisting of multiple plies of glass bonded under heat and pressure to interlayers of polyvinyl butyral resin
Patterned Glass
Glass having an irregular surface pattern formed in the rolling process to obscure vision or to diffuse light
Obscure Glass
Glass having one or both sides acid-etched or sandblasted to obscure vision
Spandrel Glass
An opaque glass for concealing the structural elements in curtain wall construction, produced by fusing a ceramic frit to the interior surface of tempered or heat-strengthened glass
Insulating Glass
A glass unit consisting of two or more sheets of glass separated by hermetically-sealed airspaces
Tinted or Heat-absorbing Glass
Glass having a chemical admixture to absorb a portion of the radiant heat and visible light that strike it
Blue-Green Tint
What kind of tint does iron oxide impart?
Grayish Tint
What kind of tint does cobalt oxide and nickel impart?
Bronze Tint
What kind of tint does selenium impart?
Reflective Glass
Glass having a thin, translucent metallic coating bonded to the exterior or interior surface to reflect a portion of the light and radiant heat that strike it
Low-emissivity Glass
Glass that transmits visible light while selectively reflecting the longer wavelengths of radiant heat, produced by depositing a low-emissivity coating either on the glass itself or over a transparent plastic film suspended in the sealed air space of insulating glass
Photochromic
Changes color properties when sunlight (photon) hits the surface of the glass
Thermochromic
Glass changes when the surface reaches the prescribed temperature
Electrochromic
The color of the glass is regulated by a DC power applied to the electrochromic layer sandwiched between two panes of glass
Glazing
Process of installing glass into a building; Panes or sheets of glass or transparent material made to be set in frames— windows, doors, mirrors
Face Glazing
The setting of a glass pane in a rabbeted frame, holding it in place with the glazier’s points, and sealing it with a beveled bead of putty or glazing compound
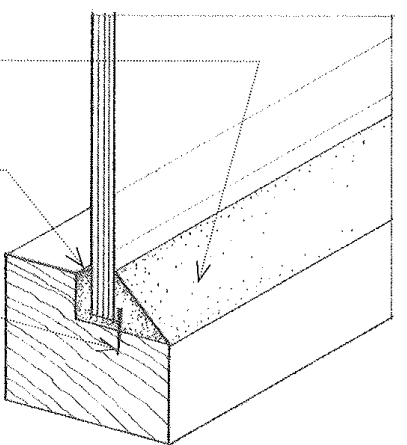
Wet Glazing
The setting of glass in a window frame with glazing tape or a liquid sealant
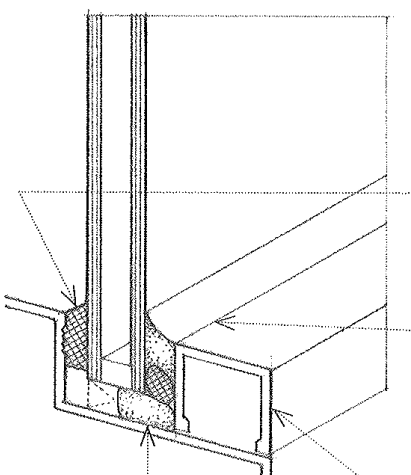
Dry Glazing
The setting glass in a window frame with a compression gasket instead of glazing tape or a liquid sealant
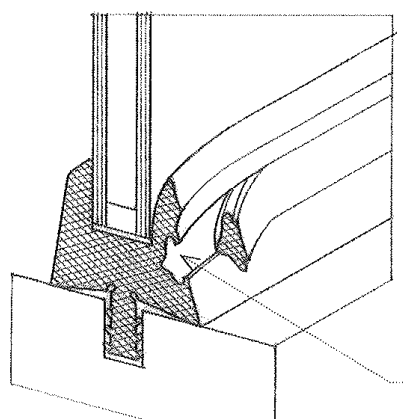
Putty
A compound of whiting and linseed oil, of dough like consistency when fresh, used in securing windowpanes or patching woodwork defects
Double Glazing
The installation of two parallel panes of glass with a sealed air space between to reduce the transmission of heat and sound
Glazing Tape
A preformed ribbon of synthetic rubber having adhesive properties and used in glazing to form a watertight seal between glass and frame
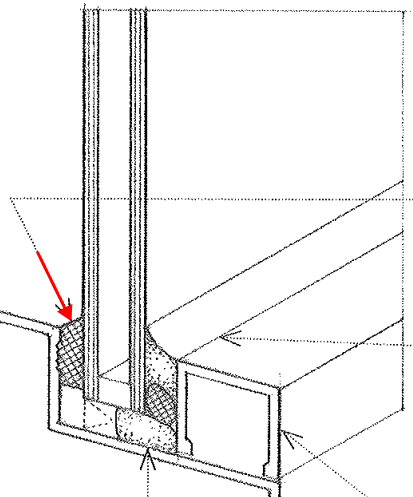
Glazing Bead
Also called glazing stop; A wood molding or metal section secured against the edge of a glass pane or unit to hold it in place
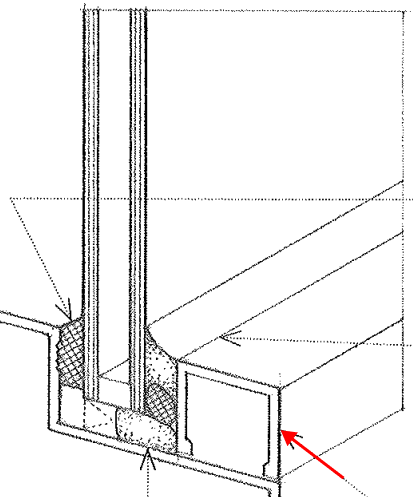
Cap Sealant
Also called cap bead; An adhesive liquid of synthetic rubber injected into the joint between a glass pane or unit and a window frame curing to form a watertight seal
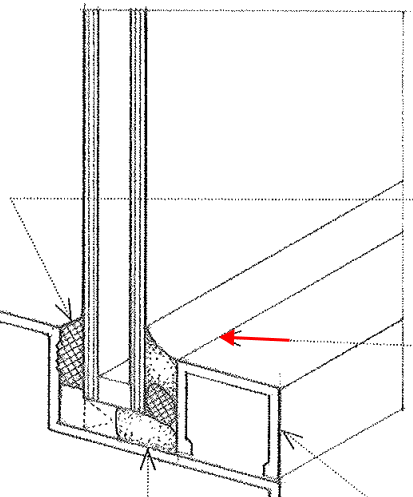
Heel Bead
An adhesive liquid of synthetic rubber injected between a glass pane or unit and a glazing bead, curing to form an airtight seal
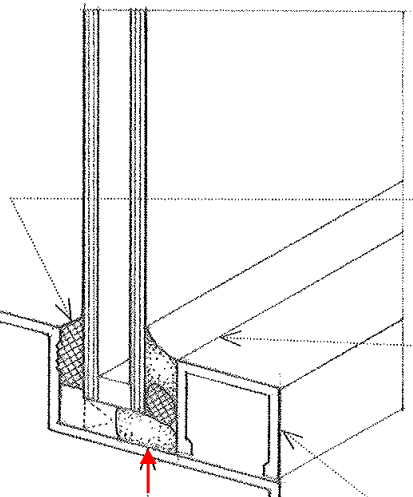
Butt-Joint Glazing
A glazing system in which the glass panes or units are supported at the head and sill in a conventional manner, with their vertical edges being joined with a structural silicone sealant without mullions

Compression Gasket
A preformed strip of synthetic rubber or plastic compressed between a glass pane and a window frame to form a watertight seal and cushion for the glass
Lockstrip Gasket
A preformed gasket of synthetic rubber for securing a glass pane in a window frame or opening, held in compression by forcing a keyed locking strip into a groove in the gasket
Flush Glazing
A glazing system in which the framing members are set entirely behind the glass panes or units to form a flush exterior surface, the glass adhering to the framing with a structural silicone sealant
Structural Sealant
A high-strength silicone sealant capable of adhering glass to a supporting frame
Glass Mullion System
A glazing system in which sheets of tempered glass are suspended from special clamps, stabilized by perpendicular stiffeners of tempered glass, and joined by a structural silicone sealant and sometimes by metal patch plates