clas 430: exam 1
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
167 Terms
Mesopotamia
events?
age?
land between the rivers
Sumerian cities → Akkadian empire
early bronze age
Minoan civilization
fertility goddess, bulls, rish lands and cities, Linear A script
not defense, believe god of protection
Michael Ventris
deciphered the language of the clay tablets found on the Greek mainland
divine myth?
legends?
etiological tale?
folktales?
types? motifs?
divine myth: stories of gods/supernatural
legends: stories of heroes (greet deeds)
etiological tale: explains world’s existence (i.e., creation myth)
folktales: stories of regular people
note: folktale types & motifs
Erinyes
female spirits who punish broken oaths
Parent: Uranus (blood drops on earth)
Metamorphoses (ovid)
transformation of chaos into cosmos
stories united by the theme of the transformation of shape
Roman myth
Ovid?
Vergil?
Ovid: 43 BC-AD 17, Metamorphoses
Vergil: 70-19 BC, Aenid, [heracles, Troy]
Greek myth
Aeschylus: Prometheus Bound
classical
Sophocles: Oepidus/king of Thebes
Euripedes:
Homer: Oepidus, Iliad, Odyssesy, Homeric hymns
archaic
Hesiod: Prometheus at Meconê
humanism
choral song
tragedy
epic
e.g., Iliad & Odyssey (Homer, archaic period)
Sumerians
unique language, near Tigris & Euphrates rivers (note: mesopotamia)
all gods are anthropomorphic
first city-states (3000 BC)
irrigation agriculture
cuneiform writing (34000 BC)
Inanna
queen of heaven, [goddess of love, curiosity, war]
adjacent to Aphrodite lust, Athena war
Parent: Anu/Anu
Enlil
who?
parent?
Sumerian storm god
Parent: Anu/An (mesopotamian sky god)
Enki (Ea)
Sumerian freshwater god
Parent: Anu/An (mesopotamian sky god)
Children: Marduk
semites
nonunited, semi-nomadic
akkadians (capital akkad) took over south sumerian cities
akkadians adopted sumerian myths and culture
preserved through cuneiform script on clay tablets
babylonians (capital babylon, 2000 BC)
hebrews = best known semites
southern mesopotamia (abraham)
abraham → egypt → became pharaoh’s slaves
moses <3 yahweh, universal flood adapted from mesopoatmian myth
phoenecian alphabet = hebrew writing system
Akkadians
early bronze age (from mesopotamia?)??
Hebrews
Hittites
powerful and important in late bronze (!!)
controlled central anatolia (turkey, 1600-1200 BC)
preserved through hittite cuneiform clay tablets
language from sumerian → indo-euro
egypt
language include semitic and egyptian influence
important (!!) murder of osiris
resurrected by daughter isis
myth told by greeks (?)
etiological tale
folktale types
folktale motifs
soft vs hard G & C
final E & Es
Chi (x) or Ch
pronunciation: Patroclus
pa-trok-lus
pronunciation: Actaeon
ak-tē-on
pronunciation: Danaë
dān-a-ē
diphthong (ae, oe, au, ei)
dieresis (ë) indicates…
two vowels pronounced as one, long vowel
…not a diphthong, pronounced as separate syllable
Neolithic (New Stone) Period
When: 10,000 BC
Where: Near East
What: development of agriculture and sedentary communities
EARLY BRONZE AGE
When: 3000-2000 BC
Where/What:
Greece (bronze metallurgy)
Mesopotamia: Sumerian cities
Crete: Minoan civilization (Linear A script),
Mesopotamia: Akkadian Empire
MIDDLE BRONZE AGE
When: 2000-1600 BC
Where/What:
Balkan Peninsula: arrival of Indo-European Greeks (kings, nobles, etc.)
Mesopotamia: Old Babylonian Empire
LATE BRONZE (MYCENAEAN) AGE
When: 1600-1150 BC
Where/What:
Anatolia: Hittite Empire rules
Phoenician syllabic writing (1500)
Trojan War (1250)
DARK (IRON) AGE
When: 1150-800 BC
Where/What:
Greece: destruction of Mycenaean cities
Asia Minor: Greek colonies settle
ARCHAIC PERIOD
When: 825-480 BC
Where/What:
Invention of Greek alphabet (825)
Iliad & Odyssey (epics, attributed to Homer)
Southern Italy and Sicily: Greek colonies (polis)
Greek vs Greek conflict
Writing!!
CLASSICAL PERIOD
HELLENISTIC PERIOD
ROMAN PERIOD
MEDIEVAL PERIOD
Hesiod
who?
known for?
period?
aoidos (oral poet)
Theogony & Works and Days
archaic period (700 years before Roman myth)
Homeric Hymns
Period: Archaic
Cyclic poets
Period: Archaic
Bacchylides
Period: Archaic
Sophocles
Period: Classical
Herodotus
Period: Classical
Euripides
Period: Classical
Socrates
Period: Classical
Peloponnesus
event?
period?
Peloponnesian war
Classical period
Thucydides
Period: Classical
Plato
Period: Classical
Aristotle
Period: Classical
Alexander the Great
Period: Classical
Apollonius of Rhodes
Period: Hellenistic
Catullus
Period: Hellenistic
Vergil
Period: Hellenistic
Livy
Period: Hellenistic
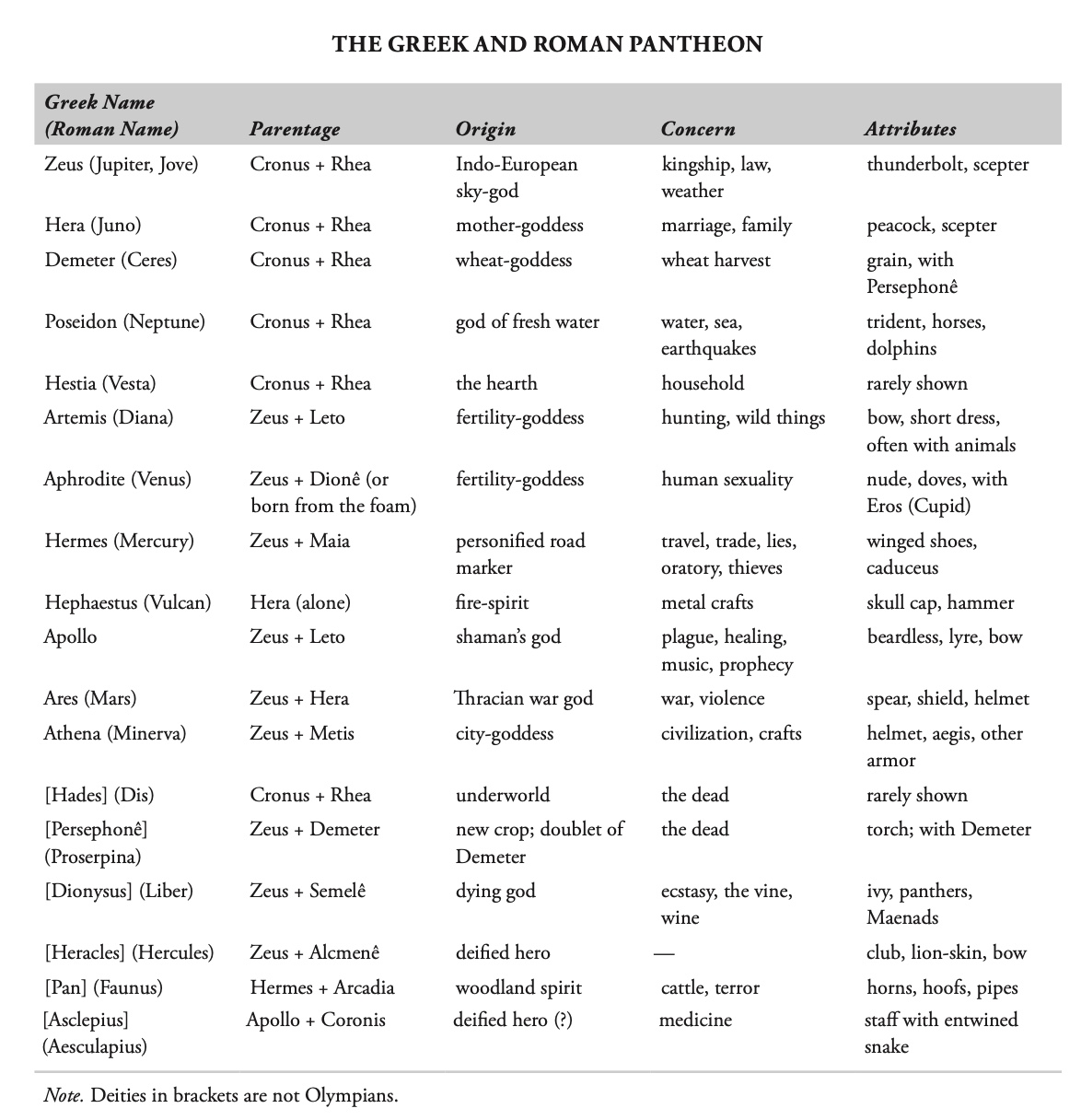
The Greek and Roman Pantheon
Period: Hellenistic
Julius Caesar
Period: Hellenistic
Ovid
Period: Hellenistic (700 years after Greek myth)
Augustus Caesar
Period: Roman
Apollodorus’ Library
Period: Roman
Plutarch
Period: Roman
Apuleius
Period: Roman
Hyginus
Period: Roman
Gaea
Earth, fertility, feminine
Children: Uranus, Mountains, Pontus, Erinyes*, Giants*
*from Uranus’ blood
Chaos
chasm
Children: Erebus (darkness), Nyx (night)
Tartarus
underworld, confinement
Children (+ Gaea): Typhoeus/Typhon (monstrous)
Eros
desire, attraction, lust; more of a concept
succession myth
all gods proceed each generation
for the current generation to be overthrown by the next, they must be banished to underworld
immortal gods who cannot be killed, must be confined & controlled
reason that gods do not want their children to come to fruition, to avoid being overthrown
e.g., uranus, cronus, etc.
Uranus
sky
Parent: Gaea
Children (+ Gaea):
12 Titans: Cronus, Rhea, Oceanus
Cyclopes
Hecatonchires
Children (genitals): Aphrodite (goddess of beauty, sexual attraction)
Cyclopes
produces lightning source for Zeus
Brontes (thunderer), Steropes (flasher), Arges (brightener)
Cronus
cunning, last born of titans
Children (+ Rhea): Hestia, Demeter, Hera, Hades, Poseidon, Zeus (Olympians)
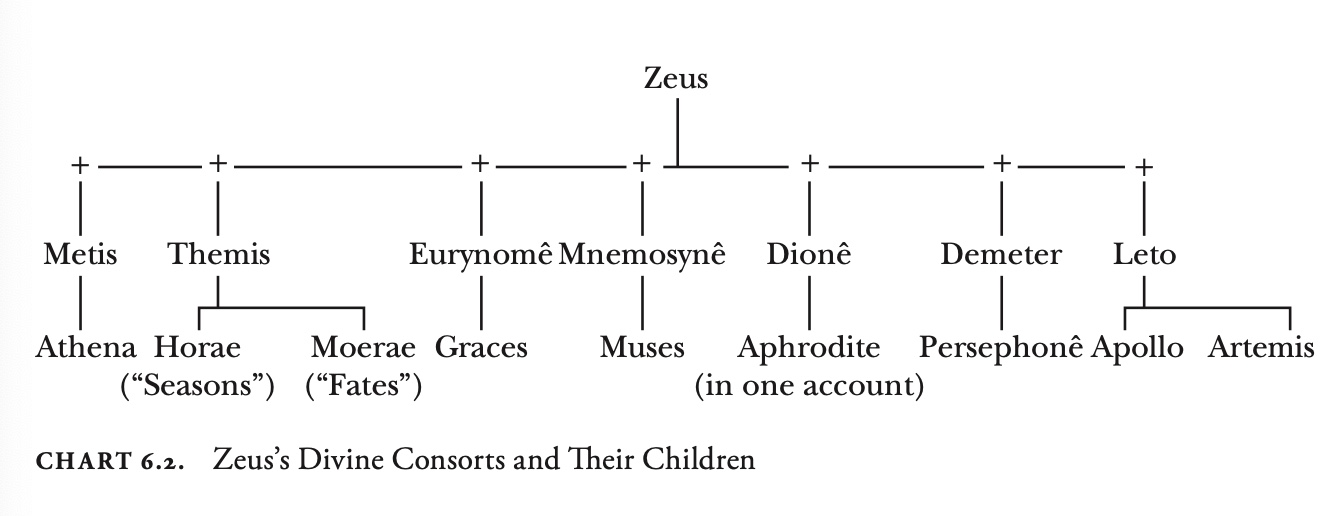
Zeus
who? roman equivalent?
parent? raised by? where?
children? sexual metaphor?
god of lightning, ruler of gods, maker of all things
roman equivalent: Jupiter
Parent: Cronus + Rhea
raised by curetes and dactyls on crete island
Children: note: sexual metaphor of “rain and earth”
Metis: Athena
Themis: Horae (seasons, x3), Moerae (fates, x3)
Eurynomê (Oceanid): Graces (x3)
Mneumosynê (memory): Muses
Donê: Aphrodite (one account)
Demeter: Persephonê
Leto: Apollo, Artemis
Hera: Hephaestus (smith god), Ares, Hebê (youth)
Alcmene: Heracles
Maia: Hermes
Hera
who?
parent?
(formal) spouse? seduction?
children?
gold-sandled, goddess of marriage and women’s fertility
roman equivalent: Juno
Parent: Cronus + Rhea
Spouse: Zeus (seduces himint he Iliad)
uses Aphrodite’s magic girdle to seduce Zeus → female cunning
Children (+Zeus): Hephaestus, Ares, Hebê (youth)
Hades
who? roman equivalent?
parent?
spouse?
“invisible,” ruler of the underworld, technically not an Olympian
roman equivalent: Pluto
Parent: Cronus + Rhea
Spouse: Persephonê
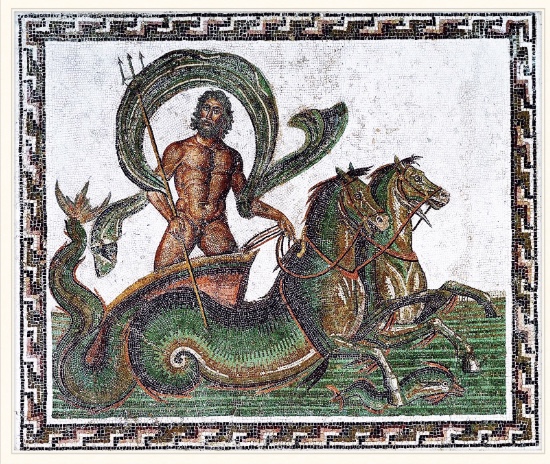

Poseidon
who? roman equivalent?
parent?
children?
ruler of the seas, shaker of the earth → horses!
roman equivalent: Neptune
Parent: Cronus + Rhea
Children (+Medusa): Pegasus, Chrysaör
Children (+Amphitritê, Nereid): Triton
Children: cyclops Polyphemus
Children (+Demeter): Arion
Titanomachy
What is it?
Who sided with Zeus?
battle of the Titans; Titans battled Olympians on Mt Olympus in resentment of Zeus’ rule
Titan Themis and son Prometheus
Hecatonchires
translation?
parent?
names?
hundred-handed ones (+ 50 heads)
gaea (+ uranus)
Cottus, Briareus, Gyes
Atlas
Titan OR Giant
Parent: Gaea (+Uranus) OR Iapetus (+Oceanid)
banished by Zeus to the edge of the world (following titanomachy)
held up the heavens ot separate gaea (earth) and uranus (sky)
Typhoeus (Typhon)
who?
typhonmacy?
parent?
massive, muscular, monstrous roar of several animals
typhonomachy: battle with Zeus
Parent: Gaea (+Tartarus), last of Gaea’s children
Athena
masculine, virgn but infertile (does not want to submit to males)
olive tree: gift to Athens (stomped on by Poseidon’s son, as opposed to his saltwater…)
Parent: Metis (+Zeus)
born from curing Zeus’ headache
Heracles
what did he do for prometheus?
parent?
freed titan prometheus from bound pillar
Parent: Zeus (+ mortal Alcmene)
Divine Myth
subject of myth is gods’ actions and grand events + consequences
Olympians
Who are they?
Where do they reside?
Children of Cronus + Rhea: Zeus, Hera, Hestia, Demeter, Hades, Poseidon
Mt Olympus
Hyperion (titan)
who?
parent?
children?
sun god
Parent: Gaea + Uranus (since titan)
Children: Helius (sun god), Selene (moon), Eos (dawn)
Phaëthon
Parent: Helius (+Clymene, Oceanid)
requested paternal confirmation, since Clymene also married to king of Ethiopia
Helius granted wish to ride chariot, although dangerous, to confirm paternity (Zeus had to blast him, lol)
note: Ovid stories
Helius
sun god
Parent: Hyperion
Children: Phaëthon
Eos
dawn
Parent: Hyperion
Spouse: Tithonus (trojan prince)
Zeus granted immortality, but not anti-aging, lol
Selene
moon
Parent: Hyperion
Children (+shepard Endymion): 50 daughters
Endymion placed in eternal sleep by Zeus
Sphinx
human-headed lion, symbolized divine power of Pharaoh
greeks changed sex M→F, added wings, “strangler”/deadly
Parent: Echidna + Orthus (descendants of Gaea + Pontus)
Harpies
egyptian blessed dead, human-headed birds
greeks changed to “snatchers”/hostile/sirens
Parent: Thaumas (wonder) (descendants of Gaea + Pontus)
Pontus
Parent: Gaea
Children (+Gaea): Nereus, Ceto, Thaumas (wonder)
Nereus
Parent: Gaea (+Pontus)
Children: Nereids (Thetis, Peleus)
Thetis
changes shape at will
Parent: Nereus
Children (+Peleus): Achilles
Ceto
sea monster, whale
Parent: Gaea (+Pontus)
Children: Graeae (gray ones), gorgons (Medusa)
Medusa
who?
parent?
children? with who?
gorgon
Parent: Ceto
Children (+Poseidon): Pegasus, Chysaör
Chysaör
enemy of Heracles, three bodies joined at waist
Parent: Medusa (+Poseidon)
Children (+Oceanid): Geryon, Echidna
Echidna
half woman, half serpent
Parent: Chysaör + Oceanid
Children (+Typhoeus): Orthus (two-headed dog)
Children (+Orthus): Cerebus, Hydra, Chimera, Sphinx