Skin integrity (Pearls) - Lacerations, Stasis Dermatitis, Pressure ulcers (Smarty PANCE)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
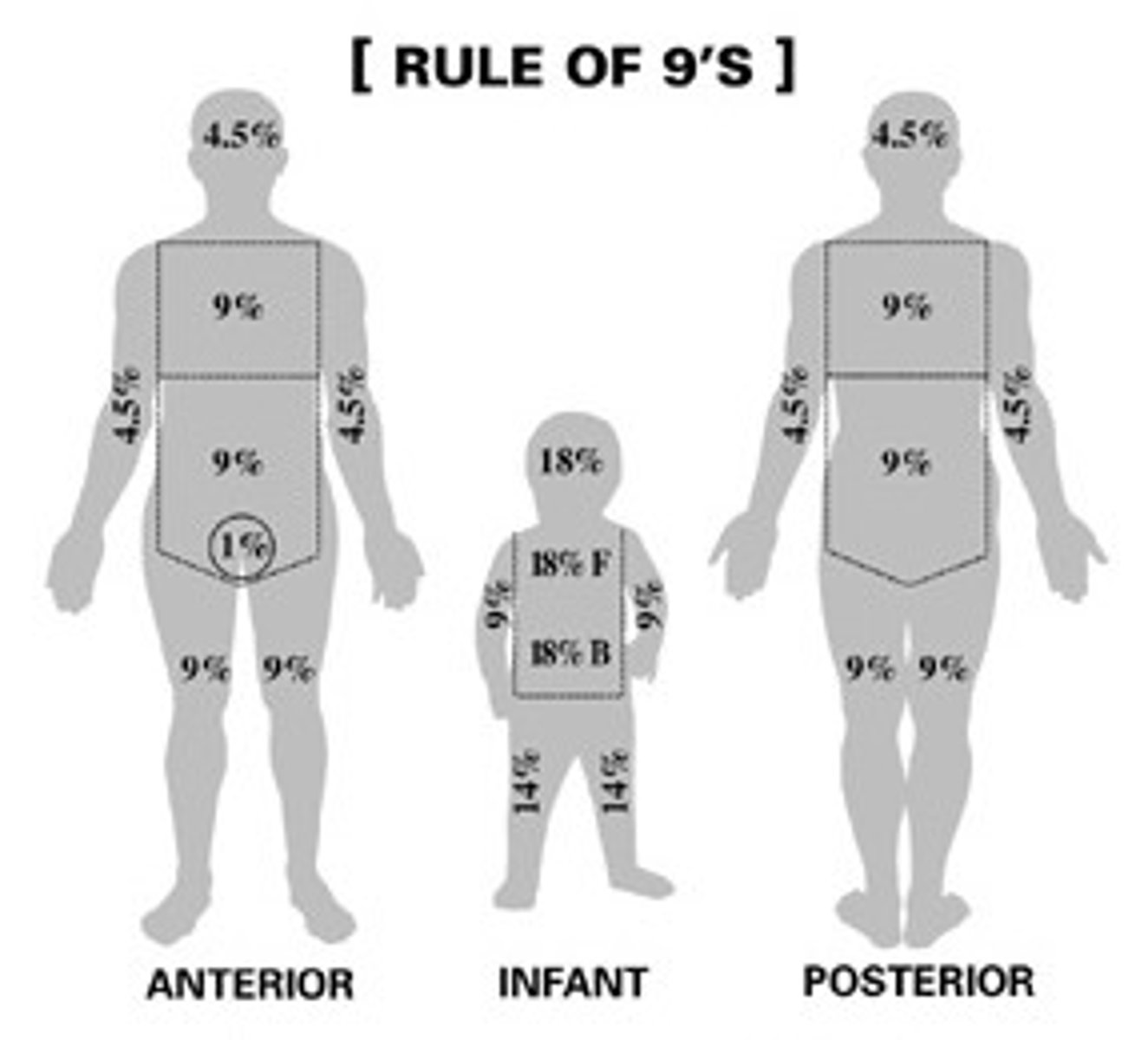
A patient is first seen with burns to the entire right arm, the anterior right leg, and genitals. What is the estimated burn surface area?
The total burn surface area would be calculated as 19%: 9% for the entire right arm; 9% for the anterior right leg (half of 18%); and 1% for the genitalia. The Rules of Nines (first degree not included in calculation) is used to determine the extent of injury: head and neck, 9%; arm (each), 9%; trunk (anterior), 18%; trunk (posterior), 18%; leg (each), 18%; and genitalia, 1%.
The Rule of 9's
Each arm= 9%, Anterior leg=9%, Posterior leg=9% Head=9%, Back=18% Chest=18%, Perineum=1%
The palmar method
1%, the size of the patient's palm, not including the surface area of the digits, is approximately 1% of the TBSA. Method used to estimate the extent of a small or scattered burn injury,
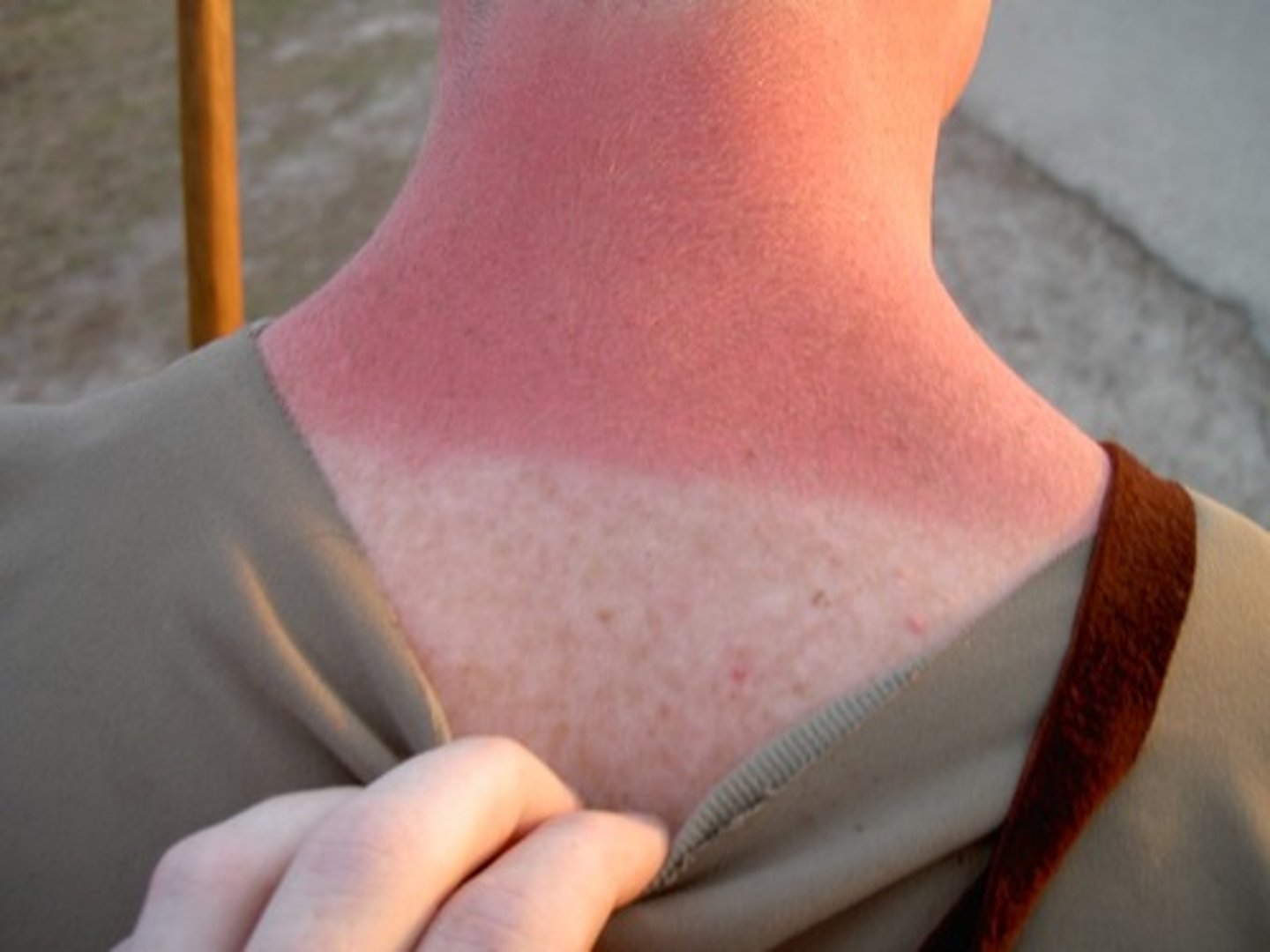
Erythema of involved tissue, skin blanches with pressure, the skin may be tender
1st degree burn (sunburn)
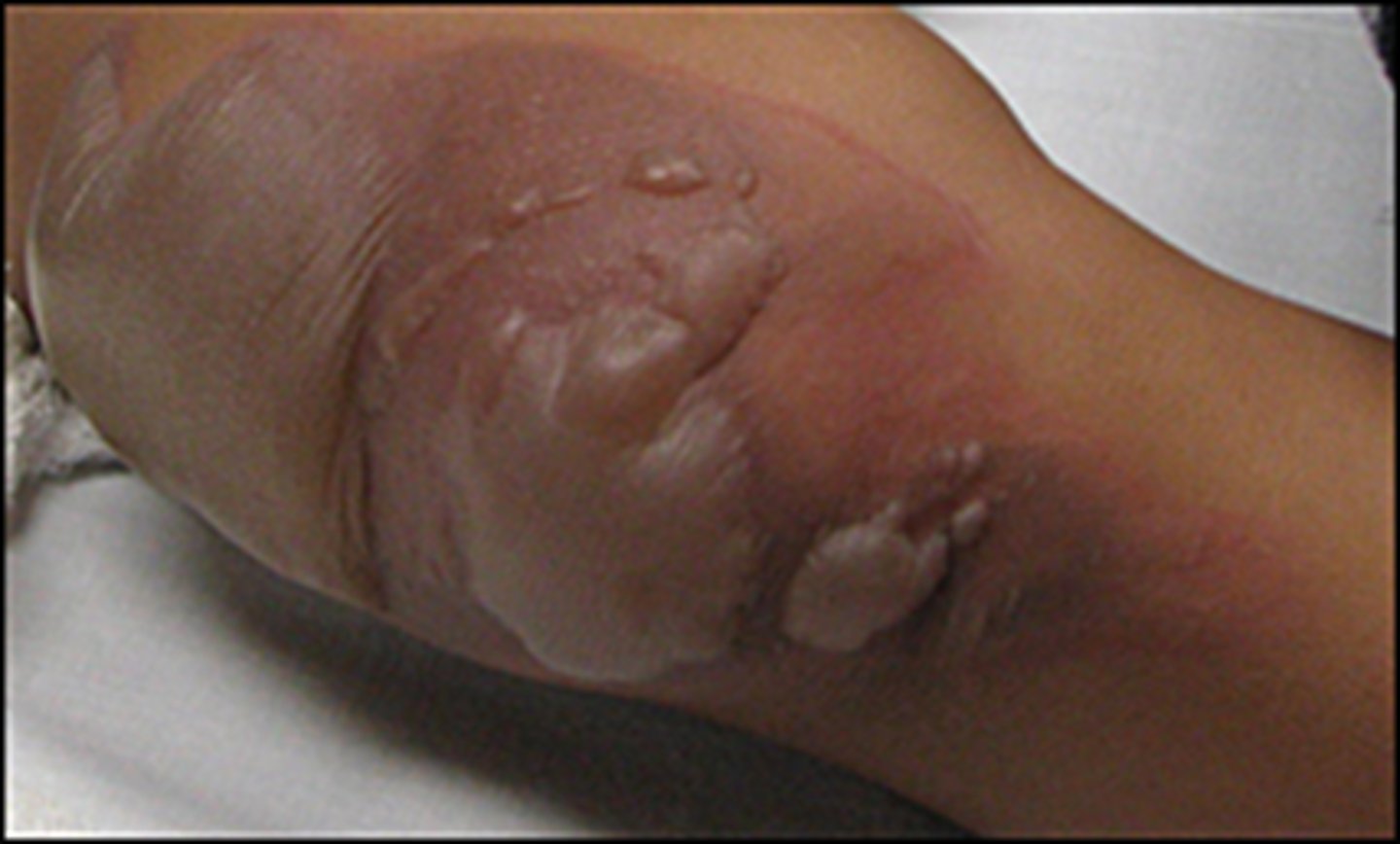
Involves the top layers of skin. Skin is red, usually painful. Has blisters that may open and seep clear fluid.
2nd degree burn (partial thickness)
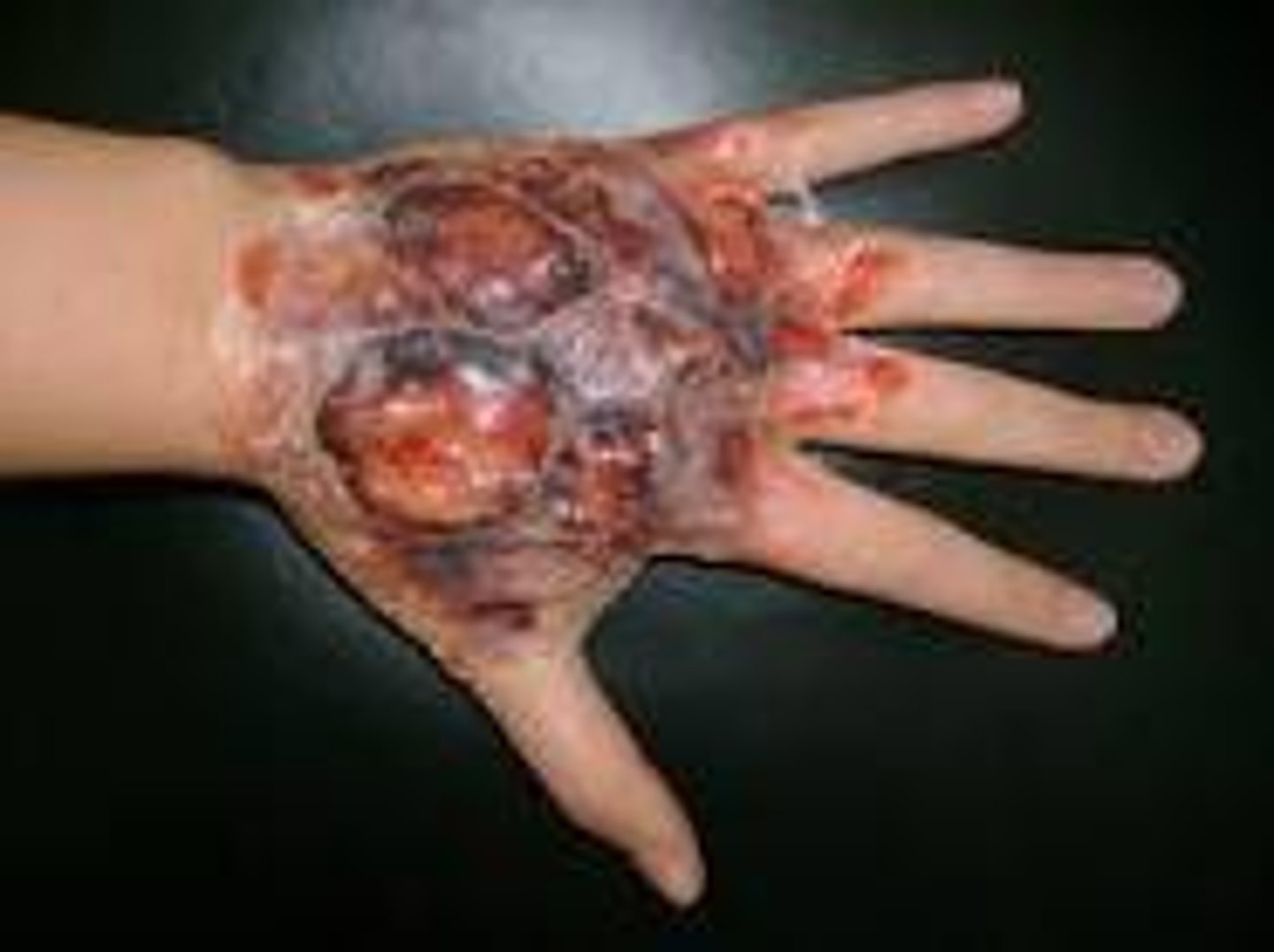
Into the bone and muscle
4th degree burn
Burned skin is tough and leathery, skin non-tender
3rd degree burn
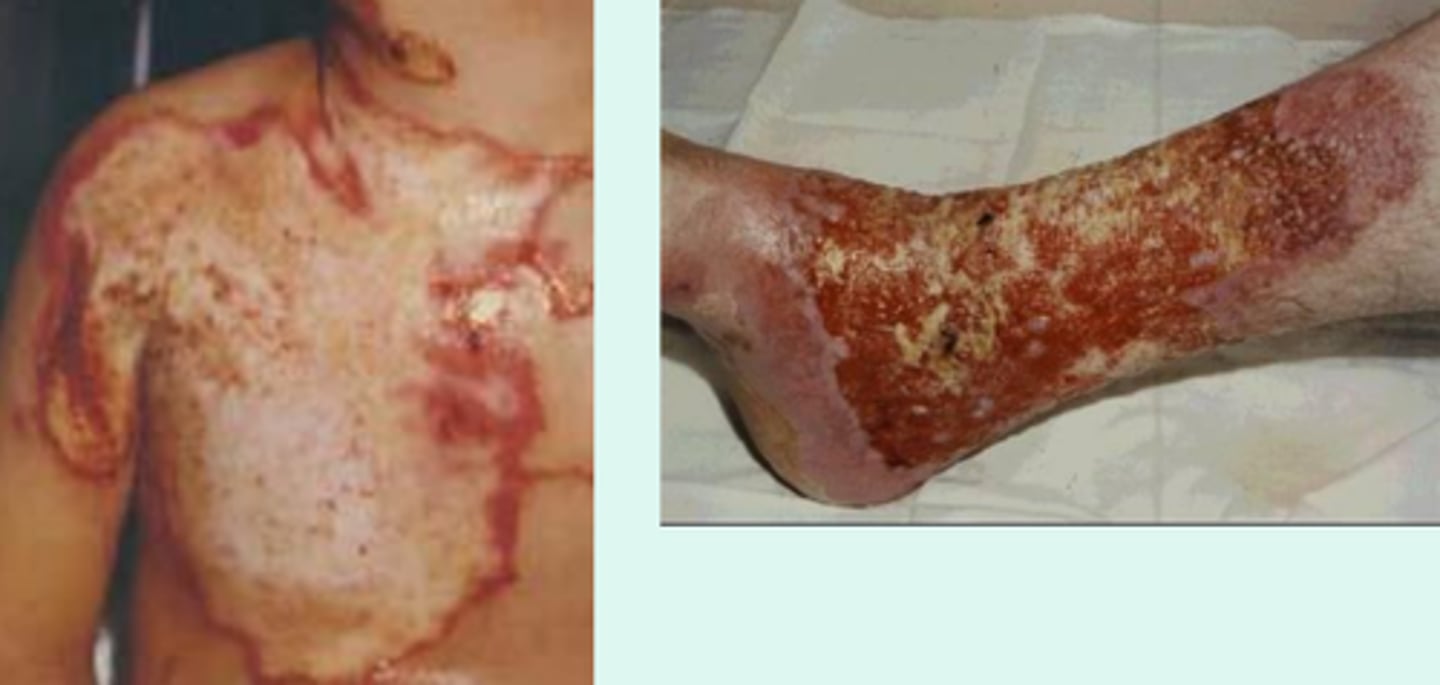
Definition of minor burns?
< 10 TBSA in adults
< 5% TBSA in young/old
< 2% TBSA full-thickness burn
Must not involve face, hands, perineum, feet, cross major joints or be circumferential
Definition of major burns?
> 25% TBSA in adults
> 20% TBSA in young/old
> 10% TBSA full-thickness burn
Burns involving face, hands, perineum, feet, cross major joints or be circumferential
Burns, eg. from cigarettes, and especially on the buttocks and thighs, can be a sign of what?
Burns, eg. from cigarettes, and especially on the buttocks and thighs, can be a sign of child physical abuse.
Burns are a cause of what type of shock?
Burns are a cause of hypovolemic shock
Is UVA or UVB dominant in sunburns?
UVB is dominant in sunBurn, UVA in tAnning and photoAging
Wounds in burn victims are more prone to be infection by what bacteria?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa can cause wound infection in burn victims
Burns are associated with what consumptive coagulopathy?
Burns are associated with disseminated intravascular coagulation which is a consumptive coagulopathy.
Treatment of major burns
-decrease burn fluid loss
-preventing infection
-controlling pain
-promoting nutrition
-salvaging viable tissue
Suture removal face
5 days
Suture removal leg
8-10 days
Suture removal scalp
7-10 days
Suture removal palm/digits
10-14 days
Suture removal thorax
7 days
Clean and minor wound
Do we give Tetanus prophylaxis:
1. Uncertain or <3 dose
2. >3 doses
1. Uncertain or <3 dose - YES give prophylaxes
2. >3 doses - Only if last dose given ≥10 years ago
Major or unclean wound do we give immune globulin if < 3 doses or unknown?
Yes - give immune globulin and tetanus toxoid containing vacine
Is nylon (Ethilon) suture absorbable or nonabsorbable?
Nonabsorbable sutures - Skin closure anywhere
Vicryl Suture
Absorbable braided suture - Face, scalp, under cast/splint
Polypropylene (Prolene)
Nonabsorbable sutures - Skin closure anywhere. Blue dyed suture useful in dark-skinned individuals.
Gut suture
Absorbable sutures - Face
What is stasis dermatitis?
Stasis dermatitis occurs with venous insufficiency and valvular incompetency. The proximal skin appears thin and brown, and may occur with distal macules, papules, red irritation, skin thickening and edema.
How does stasis dermatitis present?
Stasis dermatitis typically presents with erythematous, scaling, and eczematous patches or plaques on chronically edematous legs.
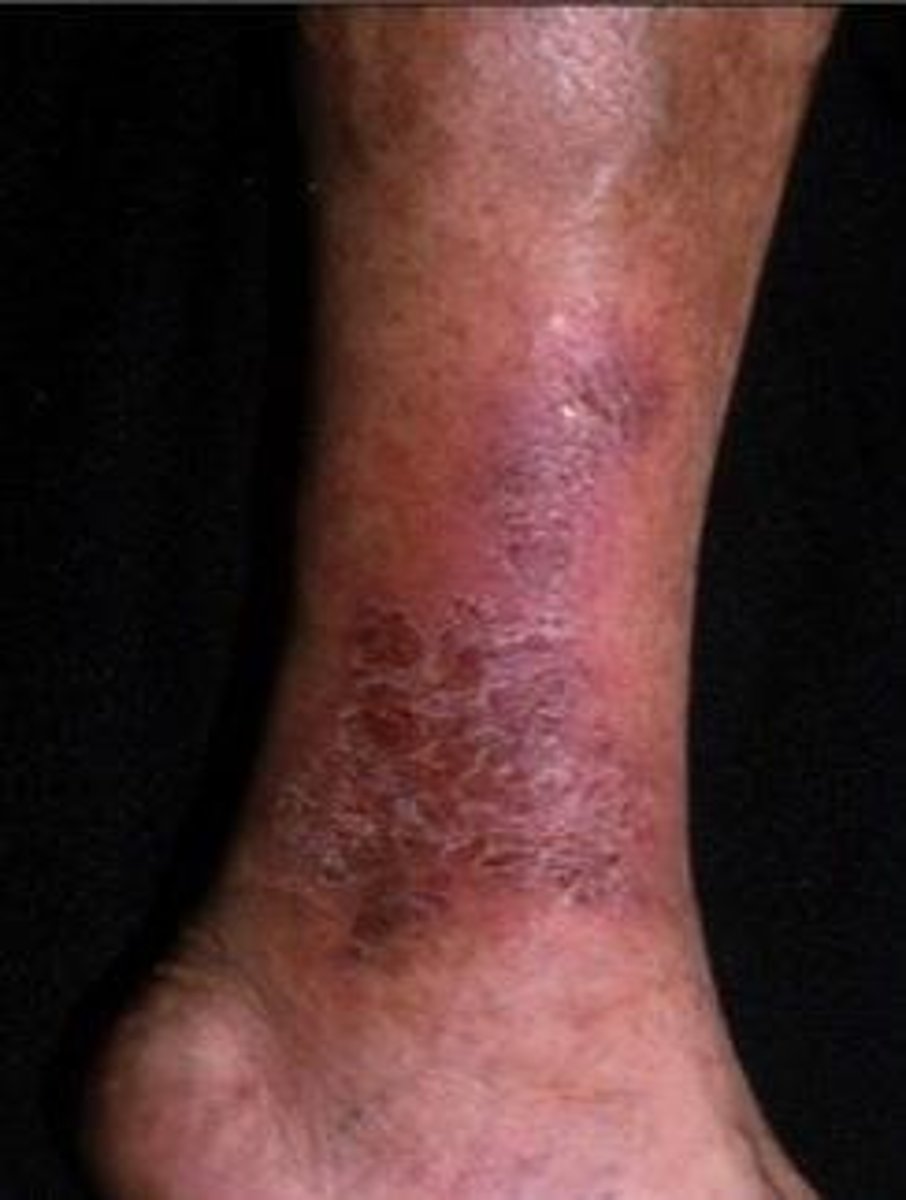
What part of the body is most frequently and severely involved?
The medial ankle is most frequently and severely involved
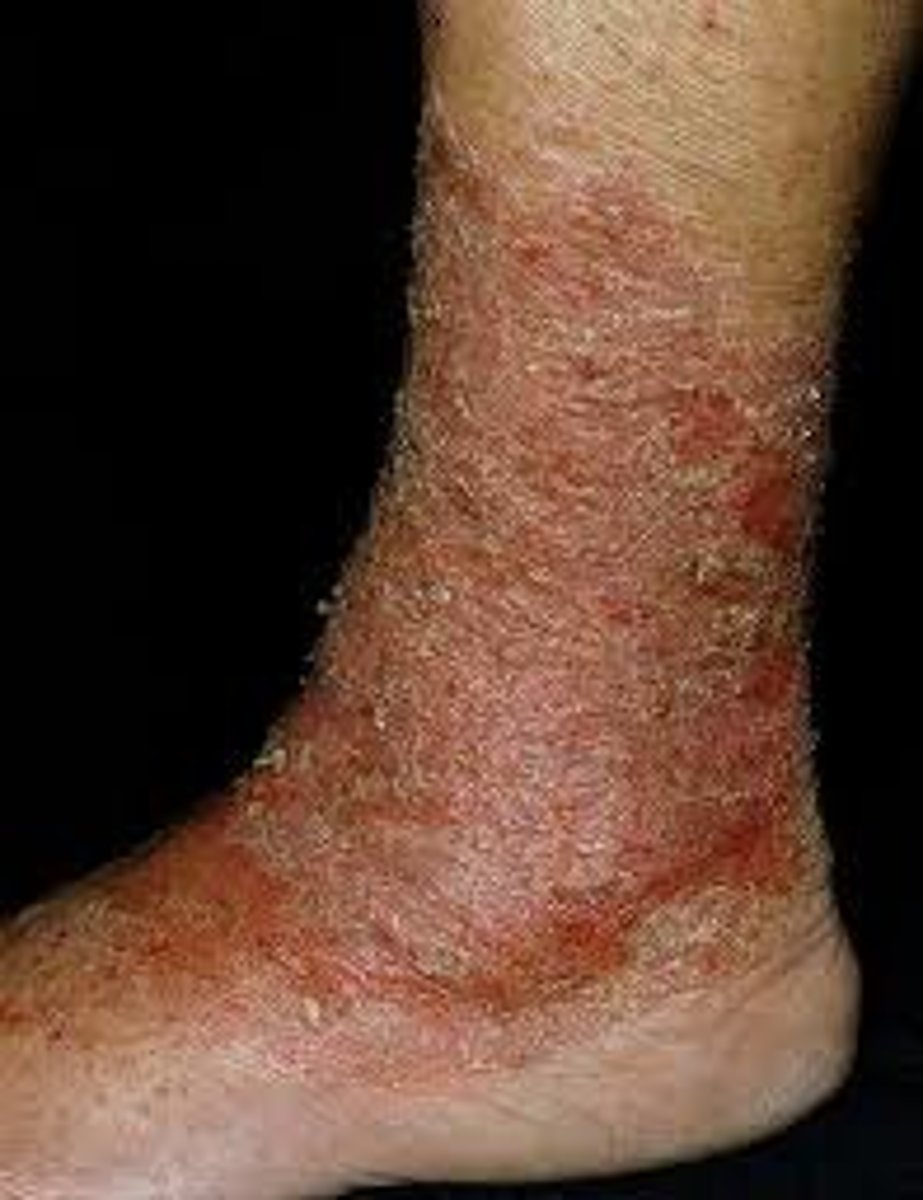
How is stasis dermatitis diagnosed?
Clinical presentation + US
* remember that it is related to chronic venous insufficiency
Treatment of stasis dermatitis?
1. Cool water dressing x 15 min BIX
2. Topical steroids BID x 2-3 weeks
3. PO anti-histamines as needed for itching
4. Lubricate w/ bland emollients daily (Aveeno, aquaphor, and cetaphil are preferred)
5. Compression (20-30 mmHg) with stockings
Who gets pressure ulcers?
People in nursing homes or people who are in the hospital for a long time.
What areas are most prone to developing pressure ulcers?
Sacrum and hip most often affected. Prevent by repositioning every 2 hours.
Stage I pressure ulcer?
Superficial, nonblanchable redness that does not dissipate after pressure is relieved
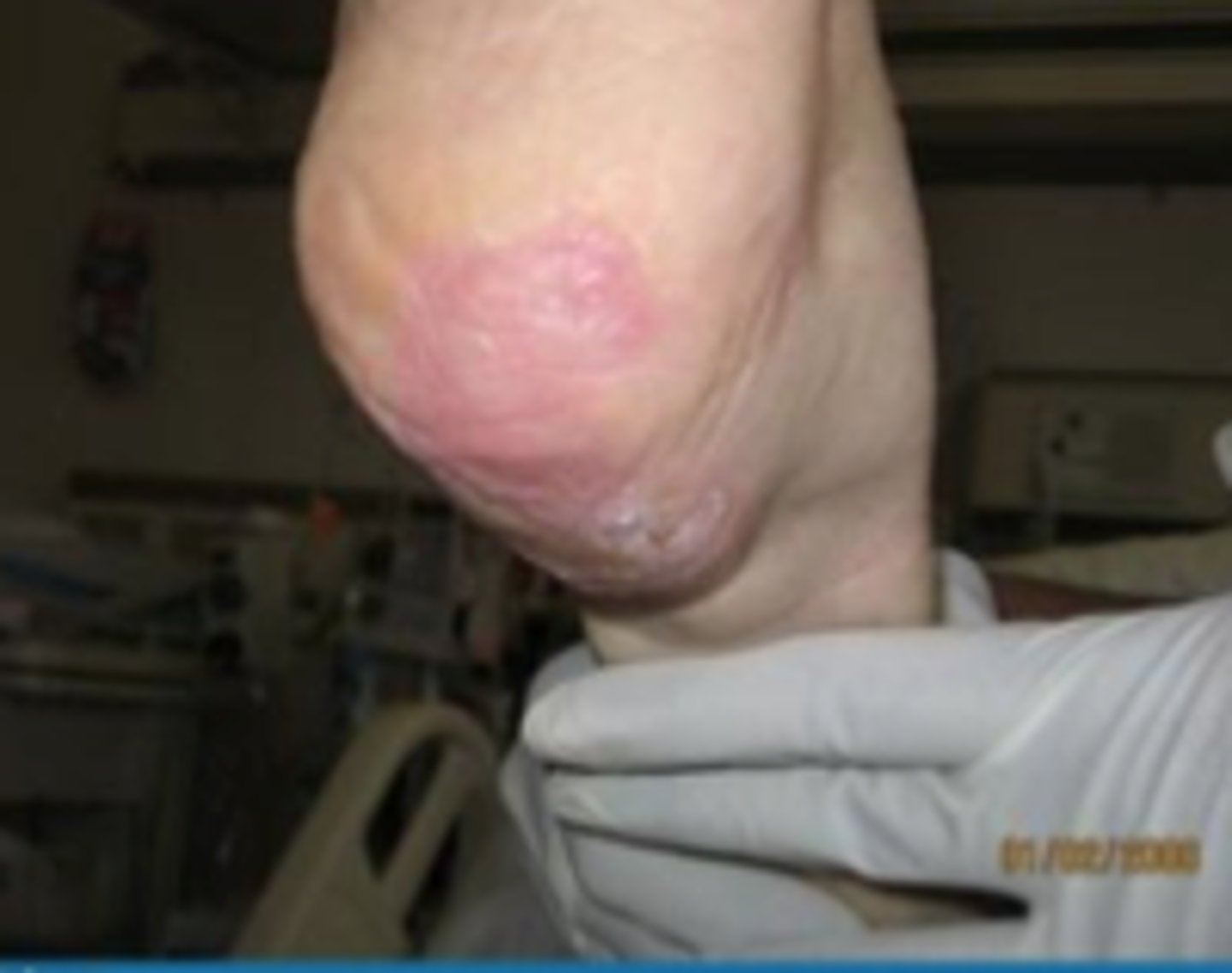
Stage II pressure ulcer?
Epidermal damage extending into dermis; looks like blister or shallow crater
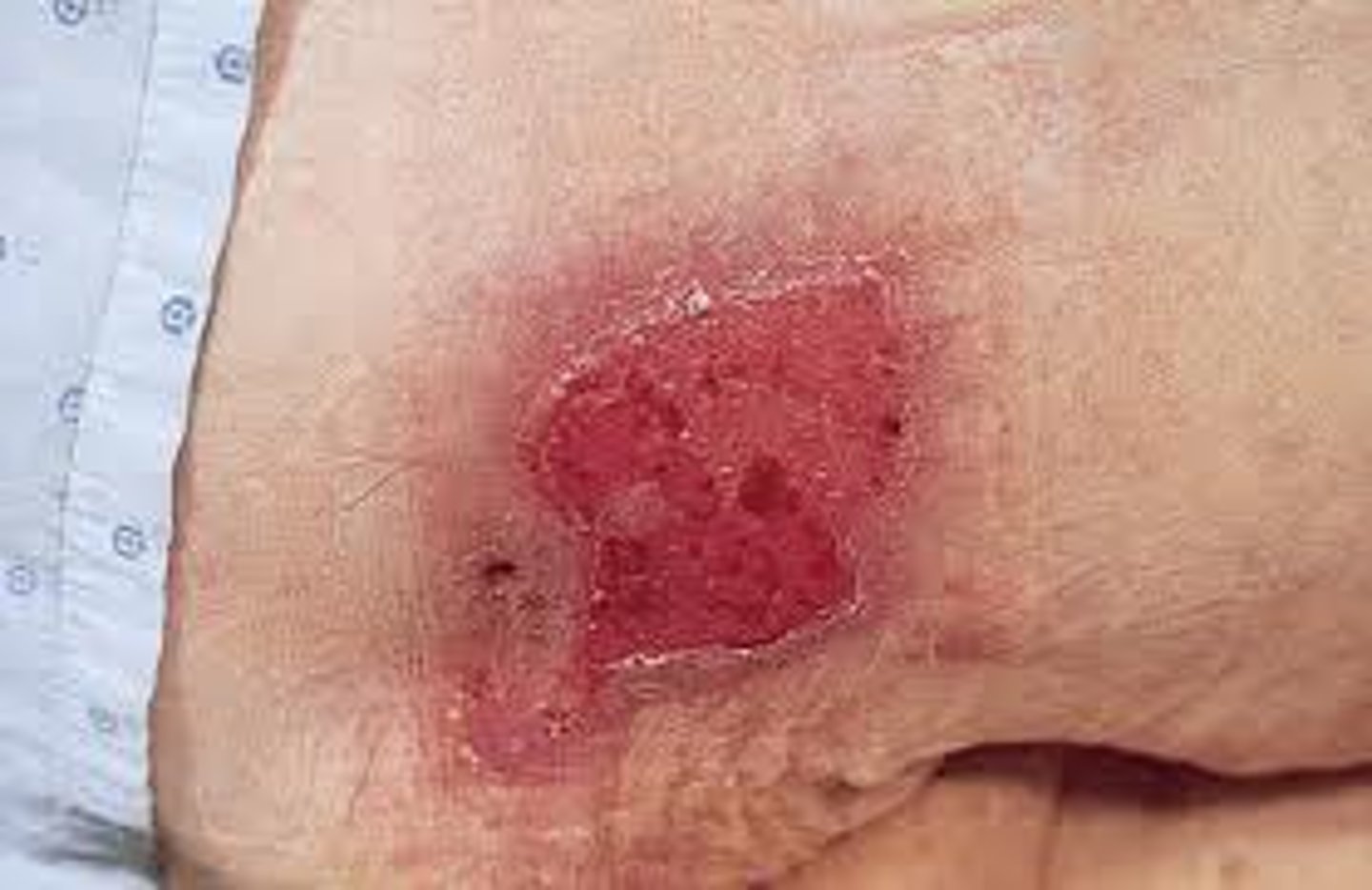
Stage III pressure ulcer?
Full thickness into the subq tissue
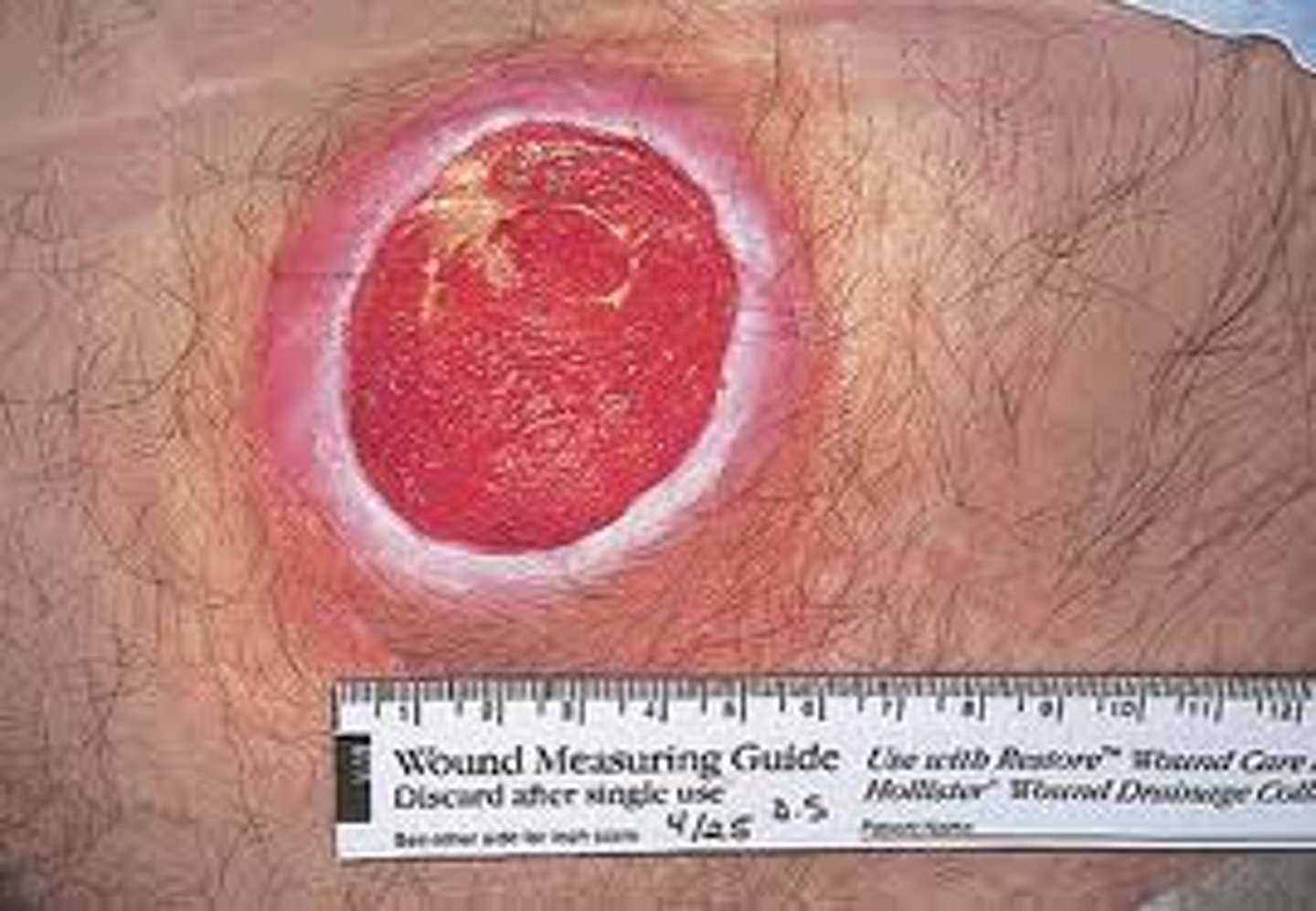
Stage IV pressure ulcer?
Extends BEYOND the fascia, into the muscle or tendon or bone
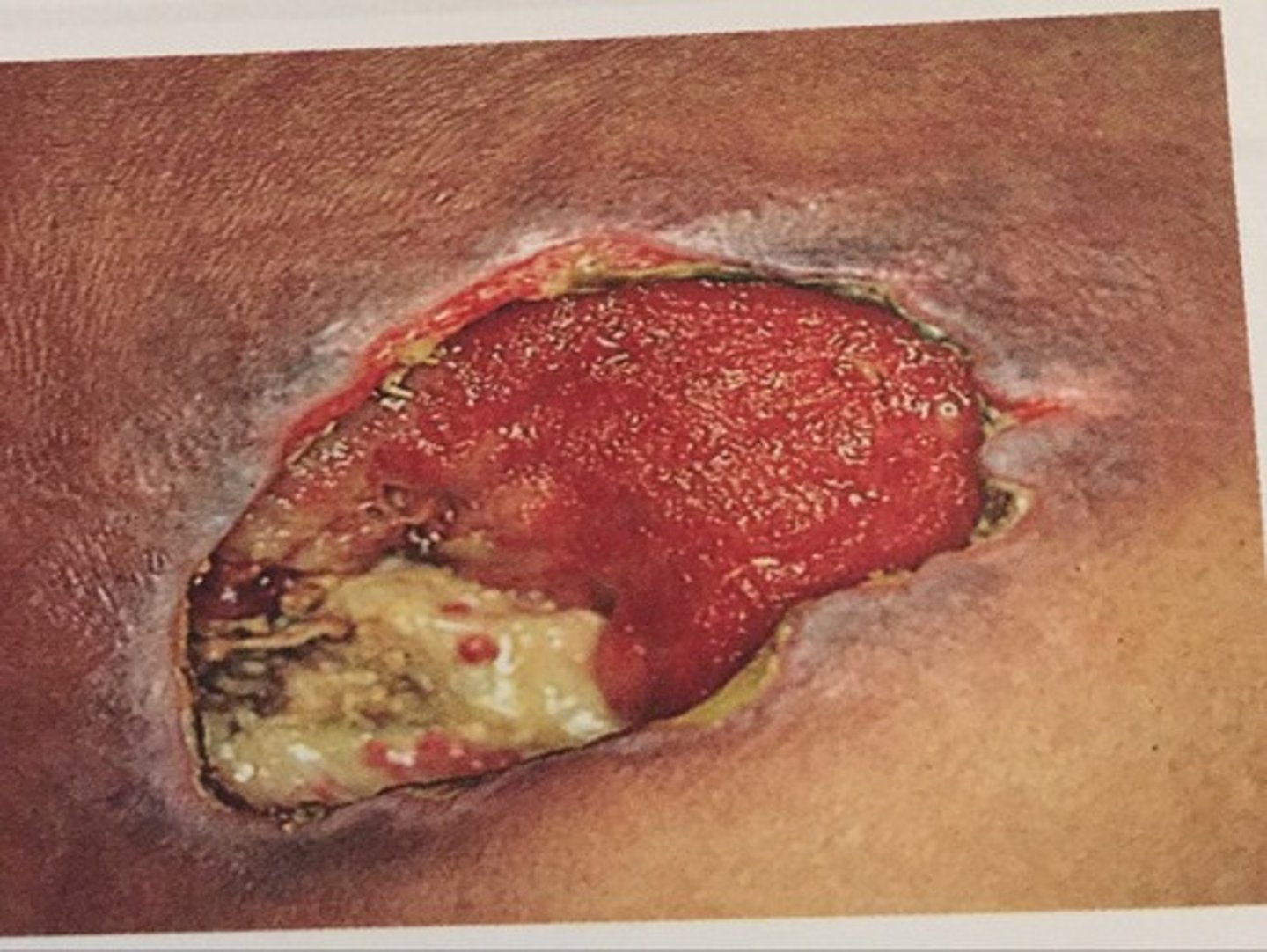
Management of pressure ulcers?
1. Turning the patient more often
2. Wet to dry dressing
3. Stage III and IV may needs surgical debridement