Chapter 4 - First Law of Thermodynamics
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
What is a thermodynamic system
A fixed amount of substance or volume of space that forms the subject of investigation
What are the two type of thermodynamic systems
Open or closed
What is the condition for a closed thermodynamic system
No substance is allowed to flow in or out
What does an open thermodynamic system allow
Transfer of mass
How is a thermodynamic system distinguished from its surroundings
A system boundary
The boundary of a system can either be
Real or imagined
What type of boundary does a closed thermodynamic system have (including 2 subtypes)
An impermeable thermodynamic wall which is either fixed or dynamic
How is a open thermodynamic system bound
By a control volume which can include impermeable thermo dynamic walls
What is an impermeable thermodynamic wall
A boundary which does not allow mass though
What are the two types of thermodynamic walls
Adiabatic and a diathermal wall
What is a adiabatic wall
A wall that does not allow heat transfer
What is a diathermal wall
It allows heat transfer
What type of wall is said to be thermally isolated
Closed adiabatic
What kind of wall is said to be in thermal contact
diathermal
What is the state of a thermodynamic system defined by
Its thermodynamic variables
What are the two kinds of thermodynamic properties
Intensive and Extensive
What is an intensive property
They are defined at any given point within a system, it does not change will mass or size
What is a example of a intensive property
Temperature/pressure/density
What is an extensive property
It reflects the system size
What is an example of an extensive property
Mass/volume
How can extensive properties be made into intensive variables, and what are these variables called
By dividing by the mass, specific properties
When is a system in thermodynamic equilibrium
When the variables are not changing with time
When are two system in thermal contact in thermal equilibrium
When there is no heat transfer between them, they are at the same temperature
When are two systems in mechanical contact said to be in mechanical equilibrium
When there is no exchange of work between them, when they are both at equal pressure
When is a system in chemical equilibrium
When the chemical composition does not change, there is no chemical reactions
When is a system in phase equilibrium
When the mass of each phase reaches an equilibrium level and stays there
What does the state postulate say
How many independent properties are needed to uniquely define the state of a system
How can the state of a simple compressible system be given according to the state postulate
The state of a simple compressible system is completely specified by two independent intensive properties
What is a process
A sequence of changes
What is an isothermal process
A process at a constant temperature
What is an Isobaric process
A process at a constant pressure
What is an isochoric process
A process at a constant volume
What is a cyclic process
A sequence of process which return a process to its initial state
What is a quasi static process
A process that takes place infinitely slowly so that the system passes through a continuous sequence of equilibrium states
What is a pure substance
A substance with a homogeneous chemical composition through out the whole thermodynamic system
What do the relationships between properties in equilibrium
The kind of substance and the phase
What type of substance can air be considered as
Pure
In what conditions does the ideal gas law hold true
Moderate temperatures and low pressures
What 2 observations does the ideal gas law come from
Boyles law and charle’s law
What is Boyle’s Law
The volume of a fixed mass of gas at a constant temperature
What is Charle’s Law
The volume of a fixed mass of gas at a constant temperature is proportional to its pressure
What is an ideal gas
A gas which obeys the ideal gas law
What is an isotherm
Curves along which the temperature stays constant
What is an isochore
Curves along which the specific volume stays constant
What is an isobar
Curves along which pressure stay constant
What does the zeroth law of thermodynamics state
Every thermodynamic system in equilibrium has a property called temperature and two systems in thermal equilibrium if and only if they have the same temperature
What does the ideal gas temperature scale define
An absolute zero at which an ideal gas would have zero pressure
What is the triple point of water
The temperature and pressure at which the solid liquid and vapor phases of water can coexist in mutual equilibrium
What is heat
Energy transferred between a system and its surroundings due to temperature difference
Is heat positive or negative when transferred into the system
Positive
Is heat positive or negative when transferred out of the system
Negative
What is work
Energy transfer between a system and the surroundings that does not involve heat
When work is done on a system is is positive or negative
Positive
When work is done by system is is positive or negative
Negative
What is a P-V system
A system with the primary interest being pressure and volume
What is a referable process
When a system and its surrounding’s can be resorted to their original state with no net transfer of work
What are the conditions for reversible work in a P-V system
Frictionless and the pressure difference between the system and the surroundings must be infinitely small so quasi static
What are two examples of a boundary phenomena
Heat and work
Why are heat and work boundaries phenomena
As they cross the systems boundary
What type of functions are heat and work and why
Path as their magnitudes depend on the path followed not just the end state
What kind of functions are properties
Point
What is work done graphically
The area under a P V curve
How is the path of an irreversible process depicted on a graph
As a dashed line
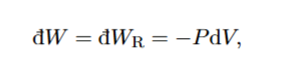
How do you use this equation
Get P in terms of v using ideal gas law and integrate between the two pressures
Give a statement about amount of work in a reversible process
Reversible processes maximise the amount of work that my be done by or on a system
What do the process paths for a cyclic process do
Form a closed path
What makes a cyclic process a reversable one
When each subpath is reversible
Work is done by the system if the path C is traversed in….
Clockwise direction
Work is done on the system if the path C is traversed in…
Anticlockwise direction
In a P-V system, what is the work done equal to
Area enclosed by the closed path
What is internal energy
The total energy in a thermodynamic system
What does internal energy depend on
The state of the system only
What is an Ideal monatomic gas
A gas where particles are single atoms
What does internal energy of a system not include and why
Potential or kinetic energies as these are external
What is heat capacity
The ratio is head supplied to the change in temperature
What does heat capacity depend on
Type of substance and the process by which heat is added
What is specific heat capacity
The energy needed to raise a 1kg substance by 1k
When a gas is heated at a constant pressure, what happens to some of the heat energy
It is used to perform work to expand
What is an isothermal process
One at a constant temperature
What are isotherms
Paths for isothermal processes on a graph
What happens in a gas expansion if the gas is thermally isolated, and what about the work done
Heat transfer is not possible so it expands adiabatically
Tell me about work done in adiabatic expansion
When a gas expands adiabatically the work it does comes directly out of its internal energy, so the gas cools down
What is an adiabatic process
Where there is no heat exchange between a system and its surroundings
What is a adiabatics
Paths for a adiabatic process
What are isothermal and adiabatic expansions examples of
Polytrophic expantions
What is a polytrophic process
One where pressure and volume are related by the polytrophic equation of state
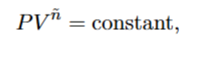
What is n
The polytrophic index
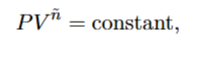
What is n for an isobaric process
0
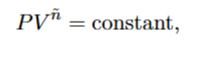
What is n for an isothermal process
1
What is n for an adiabatic process
gamma