CHAPTER 1: Data Collection and Presentation
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Statistics is derived from the Latin word “___” meaning state
status
In plural sense, it is defined as any set of numerical data (e.g. vital statistics, monthly sales)
STATISTICS
In singular sense, it is defined as a branch of science that deals with the collection, presentation, analysis, and interpretation of data
STATISTICS
without drawing conclusions or inferences from it
tables, graphs, frequency, mean, etc.
Descriptive Statistics
utilizes sampled data to make inferences about the population
hypothesis testing, determining relationships, making predictions
Inferential Statistics
facts or figures from which conclusions may be drawn
Data
collection of facts and figures or data
Data Set
entities on which data are collected
Elements/Units
a characteristic or attribute of elements which can assume different values or labels under statistical study
Variable
set of measurements collected for a particular element
Observation
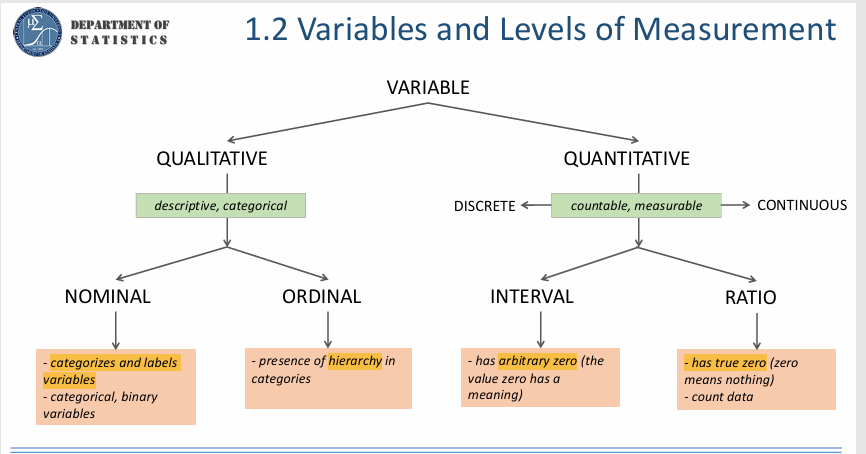
Types of Variables
Qualitative
Quantitative
outcomes of the variables expressed non numerically or categorically
example: name, gender, eye color, religion, etc.
Qualitative
• outcomes are expressed numerically that are meaningful or indicate some sort of amount
• example: age, allowance, number of students, height, etc.
Quantitative
Kinds of Quantitative Variables
Discrete
Continuous
a variable which can assume finite, or at most , countably infinite number of values
usually measured by counting
answers the question “how many”
example: # of students, # of children
Discrete
a variable which can assume infinitely many values corresponding to a line interval
gives rise to measurement
answers the question “how much”
example: weight, allowance, height
Continuous
Scale/Levels of Measurement of Variables
1. Nominal
2. Ordinal
3. Interval
4. Ratio
classificatory scale
weakest level of measurement where numbers or symbols are used simply for labeling or categorizing subjects into different groups
Nominal
classificatory with ordering scale
numbers assigned to categories of any variable may be ranked or ordered
Ordinal
has the properties of the nominal and ordinal levels
Interval •
highest level of measurement
has the properties of the nominal, ordinal, and interval levels
anything that is countable or measurable
has absolute zero or true zero
Ratio
Variables and Levels of Measurement
acquired directly from the original source of information
Primary Data
data taken from published or unpublished data which have been previously gathered by others
Secondary Data
means “from someone’s point of view”
Subjective Data
fact-based, measurable, countable, and observable
Objective Data
there is a person-to-person contact or exchange of information between the interviewer and interviewee
Interview
data are collected by means of written responses based on a list of questions which are relevant to the problems of the study
Questionnaire
used when the objective is to determine the cause-and-effect relationship of certain phenomena under controlled conditions
.Experimental
the researcher observes the behavior of persons and their outcomes
Observation
this method of collecting data is enforced by certain laws such as registration of births, deaths, licenses, etc.
Registration
entire group of observations or elements where inferences and conclusions are made
Population
a numerical characteristic of the population
Parameter –
subset of the entire group of observations or elements where data is collected
Sample
a numerical characteristic of the sample
Statistic
process of gathering information from every unit or all the units of the population
Census/Complete Enumeration
process of obtaining a part or subset of the population
Sampling/Survey Sampling
Types of Sampling Methods
Probability Sampling
Nonprobability Sampling
have equal chances of being selected as a sample
uses some chance mechanism
Probability Sampling
do not have equal chances
without regard for some chance mechanism
Nonprobability Sampling
is used because there is no objective way of assessing the reliability of inferences under non probability sampling
probability sampling
a listing of all individual units in the population, is required in the execution of probability sampling methods
The sampling frame,
2 Types of Simple Random Sampling (SRS)
SRS with Replacement (SRSWR)
SRS without Replacement (SRSWOR)
Method of selecting n units out of N units in the population where all elements in the population have an equal chance of being included in the sample
Simple Random Sampling (SRS)
a chosen element is always replaced before the next selection is made
SRS with Replacement (SRSWR)
a chosen element is not replaced before the next selection is made
SRS without Replacement (SRSWOR)
Systematic sampling with a “random start” is a method of selecting a sample by taking every kth unit from an ordered population, where the first unit being selected at random
__ is called the sampling interval
Systematic Sampling
k
It is done if the population is heterogeneous and can be subdivided into non-overlapping (𝑁1, 𝑁2,…,𝑁𝑘) called____
Stratified Sampling
strata.
A method of sampling where a sample of distinct groups, or clusters, of elements is randomly selected and then a census or all elements in the selected clusters is taken
Cluster Sampling
___are non-overlapping subpopulations which together comprise the entire population
Clusters
Types of Non-probability Sampling
1. Purposive Sampling
2. Convenience Sampling
3. Quota Sampling
4. Snowball Sampling