Enzymes and Activation Energy
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
Enzymes
Biological catalysts that speed up the rate of reaction
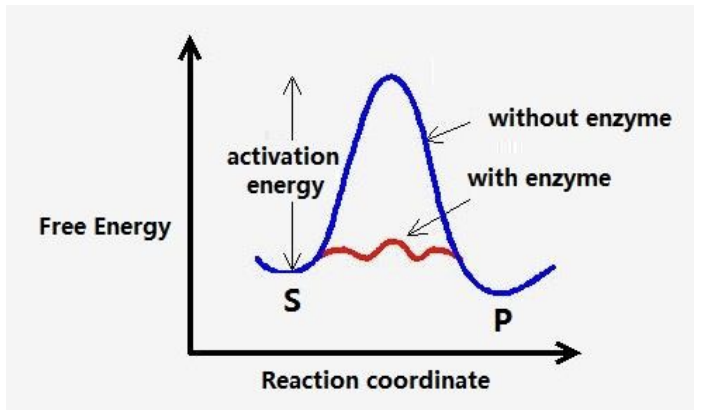
Does this by reducing the potential energy of the transition state
Activation energy (Ea) is lowered
Products can be produced a
t a faster rate
The catalyst does not alter the physical composition of the products
Requirements for a Chemical Reaction
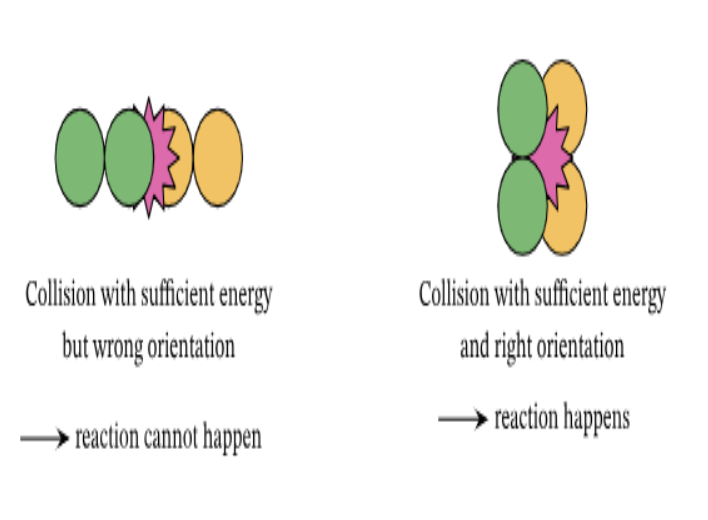
Activation energy is the minimum amount of energy required to break the bond in a chemical reaction
For this to occur, two requirements must be met:
Molecules must be in correct orientation
Molecules must collide with enough force
Effects of Temperature on Chemical Reactions
Temperature can increase the collisions between molecules
Causes the molecules to move at a high speed, forcing more collisions
In turn, new bonds can form
However, high temperatures can also lead to denaturation
It can also increase the rate of all chemical reactions (not just one) which can overwhelm the cell
Lowering activation energy
Enzmes can lower the activation energy of a reaction
Reactants can reach the transition state at a faster rate
Free energy remains unchanged as enzyme does not alter the composition of the reactants or products
How do Enzymes Lower Activation Energy
Promotes Collisions
Enzymes bind to molecules to bring them closer together
Exposure to Charged Environments
The active site contains ionic group that either attract/repel substrates
Encourages bonds to favour catalysis
Changes Shape to Substrate
Can strain bonds, allowing for reactions to occur