Unit 4 ; The Financial Sector, Money, and Monetary Policy
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:08 AM on 2/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
Identify the reasons why our money has value
It is accepted by other people for goods and services.
It holds it’s value, stability with predictable levels of inflations
It holds it’s value, stability with predictable levels of inflations
2
New cards
Describe functions of money
Medium of exchange
Store of Value
Unit of accounting
Store of Value
Unit of accounting
3
New cards
Explain the definitions of money used in the U.S. (M1, M2)
M1 = physical money (cash and coins), checkable deposits (aka demand deposits or checking accounts), travelers checks
\
M2= M! + savings accounts, money market accounts, time deposits under $100,000.
\
M3= M2 + time deposits over $100,000.
\
M2= M! + savings accounts, money market accounts, time deposits under $100,000.
\
M3= M2 + time deposits over $100,000.
4
New cards
Explain the concept of near monies
M2 and M3 are both near monies because they have a definite intrinsic value but cannot be immediately spent, must be liquidated to spend.
Benefit is better interest growth.
Benefit is better interest growth.
5
New cards
Define the variables in the equation of exchange. (MV = PQ)
MV = PQ (both must be equivalent to eachother)
\
M = money supply (M1)
V = velocity of money, how many times a dollar moves in the economy
\
P = average price level
Q = Quantity of output of all goods and services
\
M = money supply (M1)
V = velocity of money, how many times a dollar moves in the economy
\
P = average price level
Q = Quantity of output of all goods and services
6
New cards
Explain how changes in the money supply are translated into changes in nominal GDP, prices and output.
When money supply grows, interest rates drop, investment and consumption go up (AD)
When AD increases GDP, Price, and Output all go up. Reserve effect of AD decreases
When AD increases GDP, Price, and Output all go up. Reserve effect of AD decreases
7
New cards
Explain the fractional reserve system (how banks “create money”)
When money is deposited to banks they lend a portion of it out (excess funds) and hold a portion to be available to cover withdrawals (required reserves)
This occurs over and over effectively multiplying the amount of money deposited.
This occurs over and over effectively multiplying the amount of money deposited.
8
New cards
Explain the process by which banks create or destroy money and the factors that affect the increase or decrease in the money supply
By holding onto money as reserves and not lending it, its not multiplied out
Banks can also purchase treasury securities (bonds) from the Fed which also takes money out of the supply. Works in reverse too.
Banks can also purchase treasury securities (bonds) from the Fed which also takes money out of the supply. Works in reverse too.
9
New cards
Define the required reserve ratio, required reserves, excess reserves, and deposit expansion multiplier
__Required Reserves Ratio__: % of every dollar a bank must hold and not lend
__Required Reserve__: Amount of money held that cannot be lent
__Excess Reserve__: Amount of money that can be lent out
__Deposit Expansion Multiplier__: 1/RR is the expected amount of money to be grown through fractional reserve banking
__Required Reserve__: Amount of money held that cannot be lent
__Excess Reserve__: Amount of money that can be lent out
__Deposit Expansion Multiplier__: 1/RR is the expected amount of money to be grown through fractional reserve banking
10
New cards
Tools of the Fed
Adjusting __reserve requirement__ - (very powerful) but will allow for change to multiplier effect
Adjusting the __Discount Rate__ - Interest charged to banks that borrow money from the Fed, signals to banks if it’s a good time to loan more $
__Open market operations__ - Used often, buying and selling of government securities (bonds)
Adjusting the __Discount Rate__ - Interest charged to banks that borrow money from the Fed, signals to banks if it’s a good time to loan more $
__Open market operations__ - Used often, buying and selling of government securities (bonds)
11
New cards
Discuss the motive for holding assets as money
Very stable in value, not increasing but also not dropping during economic downturns.
Real estate does grow over long time amounts but does occasionally drop temporarily
Real estate does grow over long time amounts but does occasionally drop temporarily
12
New cards
Identify the factors that cause the demand for money to shift and explain why the shift occurs
1. Changes to price levels (cost more/ less to buy stuff)
2. Changes to income levels
3. Changes to interest rates (encourage or discourage borrowing → spending)
4. Changes in wealth of assets
5. Changes in future expectations
13
New cards
Explain how interest rates are determined in the money market
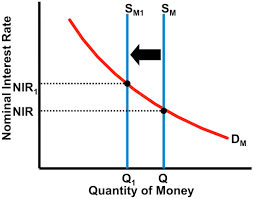
14
New cards
Explain how interest rates affect monetary policy
The Fed examines the economic status to try to correct problems (unemployment or inflation) then adjust the money supply to impact interest rates to stimulate or contract AD.
15
New cards
Explain the relationship among the real interest rate the nominal interest rate and the inflation rate. This is known as the Fisher Equation
Nominal is what we see on a daily basis in banks, there is inflation in this rate
Real excludes inflation and used on loanable funds graph by banks to determine their own interest rates
Fisher equation: Nominal Interest Rate - Inflation Rate = Real Interest Rate
Real excludes inflation and used on loanable funds graph by banks to determine their own interest rates
Fisher equation: Nominal Interest Rate - Inflation Rate = Real Interest Rate
16
New cards
Explain loanable funds money
Used to show how bans determine the interest rates.
Bases on Supply (saver) and demand (debtors/borrowers)
Equilibrium is the interest rate
Bases on Supply (saver) and demand (debtors/borrowers)
Equilibrium is the interest rate
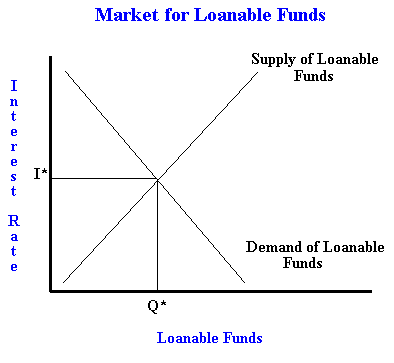
17
New cards
What is crowding out within loanable funds and how can monetary policy correct this
Result of expansionary FISCAL POLICY that increases interest rates (high Gov’t demand on loanable funds). Private investment drops (bad for GDP and future growth)
Expansionary Monetary (adding money into the economy) will lower the interest rates back down and encourage private investment (with cheaper interest rates)
Expansionary Monetary (adding money into the economy) will lower the interest rates back down and encourage private investment (with cheaper interest rates)
18
New cards
Define Financial Sector
The part of the economy made up of institutions (like banks) that focus on pairing lenders and borrowers.
19
New cards
Define Assets
Any item of economic value that can be converted into cash. Something owned
20
New cards
Define Liabilities
A legal or financial obligation that must be paid back. Something owed
21
New cards
Define Liquidity
The ease in which asset can be converted into medium of exchange. Cash and money in checking accounts is very liquid. A car or a home is not.
22
New cards
Three Functions of Money
1. A Medium of Exchange -Money can easily be used to buy goods and services. Dont have to barter
2. Unit of Account - Money measured the value of goods and services and measures value
3. Store of Value - Money allows you to store purchasing power for the future
23
New cards
Types of Money; Commodity Money
Something that performs the function of money and has an alternative use (ex: mark in prison)
24
New cards
Types of Money; Fiat Money
Something used for exchange but has no other important use (ex: $20 bill)
25
New cards
What is the transaction demand for money?
People demand money to make everyday purchases. This is not affected by the interest rate
26
New cards
What is the asset demand for money?
When people demand as a liquid asset because they prefer it to other non-liquid assets like bonds
27
New cards
Interest rates ↑, then quantity of money demanded ______
↓
28
New cards
Interest rates ↓, then quantity of money demanded ______
↑
29
New cards
Shifters of Money Demand
1. Changes in prices level - Inflation requires consumer o hold more cash for financial transactions
2. Changes income - Sustained economic growth in the economy leads to an increase in the demand for money
3. Changes in taxation that affects personal investment - Government policies such as changing the capital gains tax would change the demand for money
30
New cards
Shifters of Money Supply
1. Reserve ratio- the percent of deposits that bank must hold in reserve (the % they can NOT loan out)
1. To increase money supply, decrease the reserve ratio
2. To decrease money supply, increase the reserve ratio
2. Discount Rate - The interest rate that the FED charges commercial banks
1. To increase money supply, decrease discount rate
2. To decrease money supply, increase discount rate
3. Open Market Operations - when the FED buys or sells government bonds (securities)
1. To increase money supply, the FED buys bonds
2. To decrease money supply, the FED sells bonds
31
New cards
Unexpected inflation causes the demand for money to _ and the interest rate to _ .
Unexpected inflation causes the demand for money to INCREASE and the interest rate to INCREASE.
32
New cards
If the supply of money increases, the interest rate will _ and investment will _
If the supply of money increased, the interest rate will DECREASE and investment will INCREASE
33
New cards
True or False: When the interest rate is high, the opportunity cost of holding money increases so the quantity of money demanded will decrease.
True
34
New cards
True or False: The money supply includes all assets like cash, demand deposits, bonds, and real estate.
False
35
New cards
True or False: Monetary policy is when the central banks changes the interest rates by changing the money supply
True
36
New cards
What is the Federal Reserve and what does it do?
The Fed is the central bank of the US and it regulates commercial banks and adjust the money supply to adjust interest rates to meet economic goals. This is called Monetary Policy
37
New cards
Money Multiplier Equation
1/ Reserve Requirement
\
Ex: Assume reserve requirement is .10. If the Fed buys $10 billion worht of bonds money supply will increase by $100billion
(1/.10) \*10 =100
\
Ex: Assume reserve requirement is .10. If the Fed buys $10 billion worht of bonds money supply will increase by $100billion
(1/.10) \*10 =100
38
New cards
What is bond maturity?
A borrower issues a bond that must be paid back by a certain amount of time. That time is its maturity. A bond can be sold early at an agreed upon price.
39
New cards
Define Fractional Reserve Banking
Process where banks hold a portion of deposits in reserve and loan the rest of the money out.
40
New cards
Define excess reserves
The amount banks are legally free to loan out. Excess reserves and required reserves make up total reserve.
41
New cards
Define demand deposits
Banks deposits that can be withdrawn at anytime (ex: checking accounts)
42
New cards
Define Owner’s Equity
The amount of money owners have put into a company or bank. It doesn’t need to be held in reserve
43
New cards
Shifters of Demand for Loanable Funds
1. Changes in perceived business opportunities
2. Changes in government borrowing
44
New cards
Shifters of Supply for Loanable Funds
1. Changes in private savings behavior
2. Changes in public savings
3. Changes in foreign personal investment
4. Changes in expected profitability
45
New cards
What happens to the real interest rate if the government runs a deficit?
Demand increases so interest rate increase