Microbiology Lab 1A
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What is Parfocal
When the microscope is in focus at low magnification, it will remain, approximately in focus as you change to a higher magnification objective. Only minor adjustment of the fine knob should be required to bring the specimen into focus..
What type of light does a light microscope use to focus on a specimen
Visible light
What is visible light?
A form of electromagnetic radiation that travels in waves with wavelengths between 400nm and 750nm
Energy ______ as wavelength decreases
increases
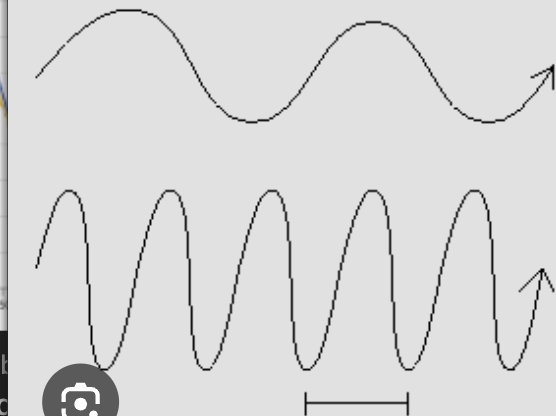
which wavelength has more energy? Top or bottom
Bottom
Which types of electromagnetic radiation are more energetic than visible light?
Ultra violet rays, X-rays, gamma rays
Which types of EMR are less energetic than visible light?
Infrared light, microwaves, radio, and television rays
Name Each color in the spectrum of visible light
Red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet.
Refraction
bending of light as it passes through one state of matter to another (gas, liquid, solid, plasma)
With the compound light microscope, light must pass through
glass to air and back again multiple times, being refracted each time before it reaches our eyes.
Fill in the blank and answer the question :
The microscope has ____ objectives, each containing a ____ lens capable of what?
four objectives; biconvex lens; capable of magnifying a specimen to differing degrees and focusing light from that image on a single point
Immersion oil function
reduce/eliminate refraction of light and increase the resolution of light as it passes through the glass slide and into the glass 100x objective lens.
Why can immersion oil reduce refraction when sliding the objective lens?
Since oil has the same refractive index as glass it allows the light to pass straight from the glass slide through the oil and into the glass high-power objective lens, rather than being bent as it passes from the glass slide through air to the glass
If correctly focused at 10x, the objective lens should rotate directly into the drop of immersion oil. True or false
True
Which objective has the following traits?
Lowest power for large microorganisms
Not strong enough to view bacteria
Used as a way to scan for large microorganisms via the coarse focus knob
Used with lowest amount of light controlled by the condenser diaphram
Shortest length objective lens and largest working distance
Largest diameter lens
4x
Which objective has these traits?
Lowest power for small microorganisms before moving to higher power
Used to quickly scan large areas of interest on the slide
used with the lowest amount of light
With bacteria focused on this magnification before moving directly to 10x
10x
Which objective lens has these traits?
Has moderate power and high dry lens
Highest magnification used without immersion oil
Used with the fine focus knob
Used with a moderate amount of light
40x
Which objective lens has these traits?
Highest power obective and must be used with immersion oil
Used to fine focus on the smallest microorganisms
Smallest diameter lens
Is put into immersion oil
100x
What is Resolution
The ability to distinguish between two very close objects
What is Field of View
the circular viewing area an organisms.
What does Paracentric mean?
organisms located in the center of the field of view at one magnification will remain in the center when using any other magnification objective.
When would you need more immersion oil?
When the field of view starts going in and out of focus
What is working distance?
The distance between the objective lens and the specimen
What is the function of the ocular lens
The lens you look through that provide an additional 10x magnification
Function of Coarse adjustment knob
Make large adjustments to focus microscope
Function of Fine Adjustment Knobs
Makes small adjustment to focus on organism
Function of the objective lens
Lens with different magnification ranging from 4x-100x that helps you see organism closer
What is the mechanical stage
where you put your slide
Function of condenser/condenser adjustment knob
Helps focus light onto specimen and located on the left side of the stage. Controls light passing through condenser
Function of Iris Diaphragm
Adjusts amount of light passing through condenser. It controls depth of field, improves contrast, and maximises resolution
Function of mechanical stage control knob
A spring clip that allows you to move the slide left and right and up/down.
What is the difference ebtween a compound light microscope and a microscope
A compound light microscope uses light to pass through a specimen and uses two lens to form an image while a simple microscope uses a single magnifying lens to produce an enlarged image.
What is the difference between bright field microscopy and dark field microscopy.
In bright field microscopy, the sample is above a condenser that shoots a light and the central beam isn’t blocked. In dark field microscopy, the central beam is blocked and leads to a dark background with a light sample
What is the difference between bright field microscopy, dark field microscopy, and phase contrast microscopy?
Phase contrast microscopy has a phase shifter above the objective lens which is used for thicker organisms and can increase contrast with light. Bright field has no phase shifter while dark field has a shifter below
What separates transmission electron microscopy from other forms of microscopy
It uses beams of electrons to interact with samples. Through this, it can look at viruses, blood cells, have a resolution of 0.2 and can magnify much higher than other microscopes
What separates fluorescent microscopy from other types of microscopy
It uses laser as a light sources, uses fluorescent dyes and stains, and can visualize autofluorescent cellular structure. Additionally, it’s light waves go through a different tradjectory
As magnification increases, which factors of a microscope decreases
Field of view, depth of field, working distance
As magnification increases, these factors increase
resolution (with immersion oil), Size of image, amount of light required, length of objective
which relationships are directly proportional to an increase in magnification
Length of objective, amount of light required, resolution (with oil)
Which relationships are inversely proportional with an increase in magnification
working distance, depth of field, field of view
Which is the only objective lens that should come into contact with immersion oil
100x
How to calculate total magnification
objective lens x 10
why is immersion oil necessary to view very small organisms such as bacteria
to reduce the refraction of light that would happen and increase the resolution
What does the term function mean?
What something does whether it being an organism, part, or a part of something bigger.
Which property of light is most important for microscopy?
refraction
Write the correct choice for each of the following statements:
As wavelength decreases/increases, energy increases.
As wavelength decreases/increases, energy decreases.
Shorter/longer wavelengths have higher energy.
Shorter/longer wavelengths have lower energy.
Therefore, wavelength and energy are directly/inversely proportional.
Decreases
Increase
Shorter
Longer
Inversely
Common units of measurement in microbiology include ‘mm’, ‘μm’, and ‘nm.’ These are abbreviations, what is the full term for each?
nm=nanometer
mm=millimeters
µm=micrometers
1 millimeter equals how many micrometers?
1 micrometer equals how many nanometers
1 millimeter equals how many nanometers?
1 millimeter=1000 micrometers
1 micrometer=1000 nanometers
1 millimeter=1000000 nanometers
how do the common units of measurement relate to 1 meters
1 m= 10^-9 nanometers
1 m = 1000 millimeters
1m= 1000000 micrometers
Which is the most energetic color in the visible lght spectrum? Least energetic?
Most energetic is violet. Least energetic is red.
Why does a ‘red’ sweater look red when it is seen in visible white light, which contains all of the colors of the spectrum?
It’s absorbing all the other colors and reflects red.
What does the term ‘mnemonic’ mean? Give an example
A way letters are arranged to aid in recalling information. Example is ROY G GIV
What does X mean in 10x or 100x oil
The magnification
Other than magnification, what is different about the ‘100X Oil’ objective lens from the other objective lenses
It’s the only one that uses oil and has the highest resolution. It uses the most amount of light. This is what is needed for it to be able to see the most smallest microorganisms or prokaryotes.
What is a scientific protocol?
a detailed, written plan for conducting a scientific experiment or study
What does the index of refraction/refractive index measure?
a measure of how light refracts through a material or The speed of light in another material.
What important parts, located under the stage, are not shown in this figure? Hint: One is a lens that controls the amount of light of the other and the other controls the amount of light passing through the lens and onto the specimen.
Condenser (latter) and iris diagram (former)
iris diaphram controls amount of light passing through the condenser. Condenser controls the amount of light passing through the lens and onto the spcimen.
What is the type of relationship between magnification and the amount of light passing through the specimen?
Inverse proportional
Why is the total magnification 400x when using a 40x objective
Because of the ocular. lens, there is a 10x increase to an objective.

Name Every piece of the microscope
A. Eyepiece
B. Observation Tube
C. Neck
D. Coaxial Stage controls
E. Coarse Focus knob
F. Fine Focus knob
G. Base
H. Light source
I. Iris Diaphragm
J. Condenser lens
K. Mechanical stage
L. Objective lens
M. Nose piece
Larger Eukaryotic Cells (molds, protozoa, helminths) use _____ magnifications like
lower; 4x,10x,40x
Smaller prokaryotic cells (bacteria) uses ______ magnification like
100x