Huerta Exam 1: Pain Evaluation and Management
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
pain definition
unpleasant sensory or emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage
is pain objective or subjective
subjective
even though pain is a subjective experience, we can
get an objective measurement of that subjective experience
pain is multifaceted, as such, what are some variables that affect our experience with pain?
Individual variables such as mood, attention, prior pain experiences, and familial and cultural factors are known to affect one's experience of pain
2 categories of pain
1) acute
2) chronic
typically caused by tissue irritation or damage due to injury, disease, disability or medical procedures
a) acute pain
b) chronic pain
acute
acute pain
Acute pain and its associated physiologic, psychological, and behavioral responses are typically caused by tissue irritation or damage related to injury, disease, disability, or medical or rehabilitative procedures
has a well defined onset
a) acute pain
b) chronic pain
acute
serves as a biological alarm system
a) acute pain
b) chronic pain
acute --> directs attention to damaged structures
usually responses to medication and tx of underlying cause
a) acute pain
b) chronic pain
acute
acute pain can develop into:
chronic pain
endures beyond post of identification of underlying pathological condition:
a) acute pain
b) chronic pain
chronic
- serves no purpose, no alarm
does not appear to serve a biological purpose (no alarm)
a) acute pain
b) chronic pain
chronic
chronic pain tends to produce changes in:
personality
lifestyle (sedentary vs active)
functional ability
mood (irritability)
examples of pain syndromes
1) low back pain syndrome
2) Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS)
3) myofascial pain
4) fibromyalgia
5) cancer pain
6) disability related pain (cp, sci, ms)
The most common causes of LBP are
injury (eg, lifting) and stress, resulting in musculoskeletal and neurologic disorders (eg, muscle spasm and sciatica).
may also result from infections, degenerative diseases (eg, osteoarthritis), rheumatoid arthritis, spinal stenosis, tumors, and congenital disorders.
When in pain, clients may restrict occupational engagement due to:
a fear that the etiology of pain, the interventions, and the restricted social consequences can be harmful.
characterized as a continuous, severe burning pain that results from trauma, postsurgical inflammation, infection, or laceration to an extremity, causing a cycle of vasospasm and vasodilation
CRPS - complex regional pain syndrome
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
• Continuous, severe, "burning" pain
• Out of proportion to severity of injury
• Sometimes referred to as "shoulder/hand syndrome"
OT treatment for CRPS
Occupational therapy (OT) treatment strives to normalize sensation, reduce edema, and increase mobility, strength, and endurance while decreasing guarding and restoring routine activities.
a large group of muscle disorders defined by the presence of trigger points (ie, localized areas of deep muscle tenderness)
myofacial pain
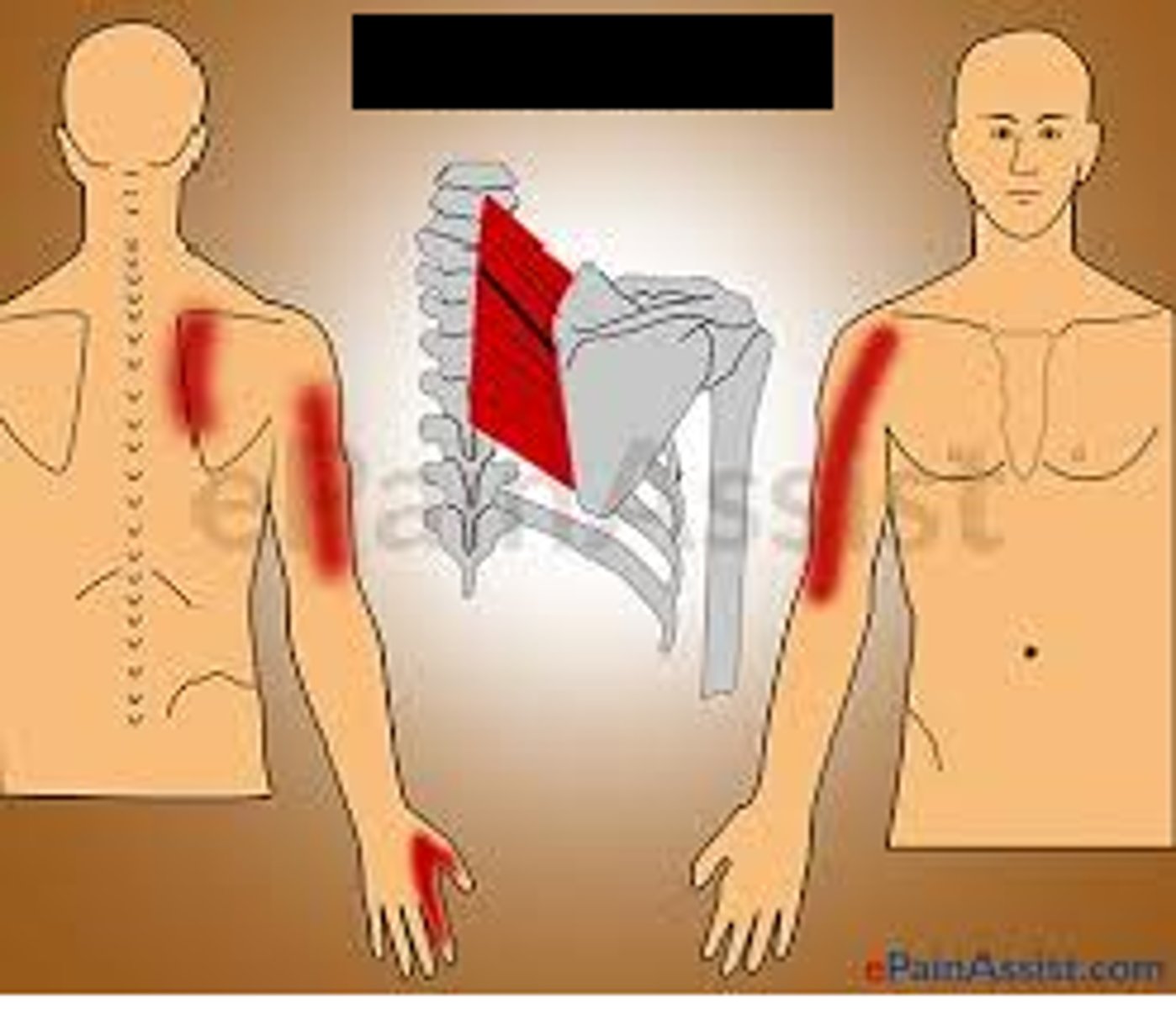
Myofascial pain is perceived as a continual dull ache often located in the
head, neck, shoulder, and low back areas.
Pressure on the trigger point elicits pain to a well-defined distal area
widespread musculoskeletal pain in the muscles, ligaments, and tendons.
fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia
generalized body pain
cancer pain may result from
tumor progression
interventions (eg, surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation)
infection, or muscle aches when clients decrease their activity
when evaluating pain, what should we identify?
1) factors that contribute to pain and aggravate it (time of day, movements, positions)
2) occupational role dysfunction
3) decreased occupational performance
4) diminished quality of life (mood, emotions, physical well-being, participation in life)
Referral for an OT evaluation is made when
pain interferes with the client's occupational performance.
the evaluation of pain consists of assessing:
◻ Pain onset
◻ Location(s)
◻ Frequency
◻ Intensity
◻ Duration
◻ Exacerbating factors
◻ Relieving factors
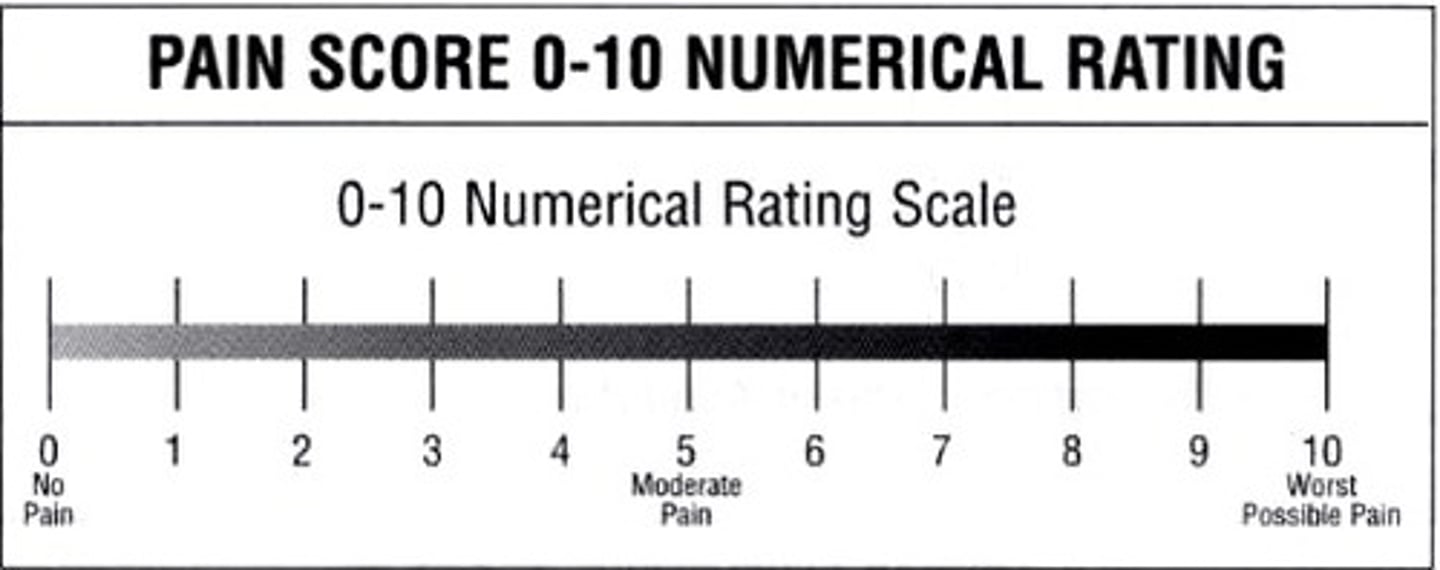
how do we measure pain intensity?
numerical rating scale (NRS)
or
visual analog scale (VAS)
most frequent scale used
NRS
Numerical Rating Scale (NRS)
a pain scale in which a pt rates their pain on a line scale from 0 to 10
1-4 = minimal impact
5-6 = moderate impact
7-10 = severe impact
visual analog scale
◻ 0 - 10 scale presented with descriptors
◻ Sometimes presented with "emoticons"
◻ Clients tend to prefer NRS, but useful for:
----Difficulty with abstract quantification of pain
---Pediatric clients
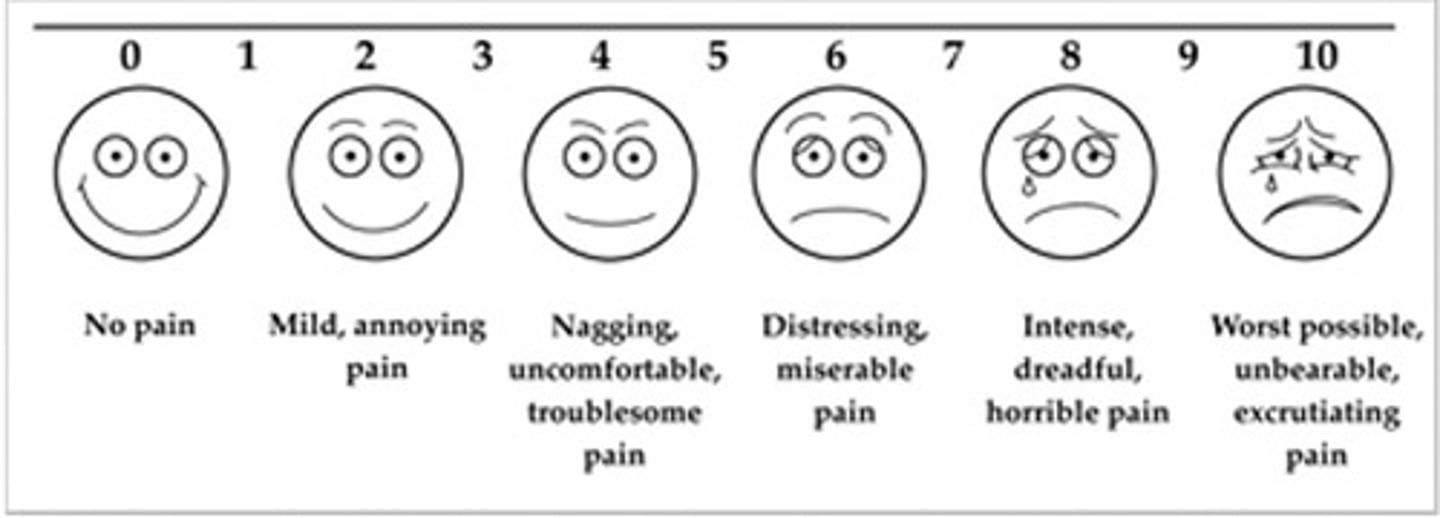
pediatric clients tend to prefer what pain scale?
VAS
the elder population tend to prefer what pain scale?
VAS
overall, clients tend to prefer what scale?
NRS over VAS
observable pain behaviors include:
◻ "Guarding"
◻ Bracing
◻ Posturing
◻ Limping
◻ Rubbing
◻ Facial grimacing
what scale is an example of a standardized rating scale that is a reliable, valid, and easy method for documenting observable behaviors?
The University of Alabama Pain Behavior Scale
pain intervention:
1) medication management
2) activity tolerance (graded)
3) body mechanics and postural training
4) energy conservation, pacing and joint protection
5) splinting
6) AE
7) relaxation
8) PAMS
PAMs for pain
-cold packs
-estim