ECAD - Thorax, respiratory system, mediastinum {2.06, 2.07, 3.01-3.02}}
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
203 Terms
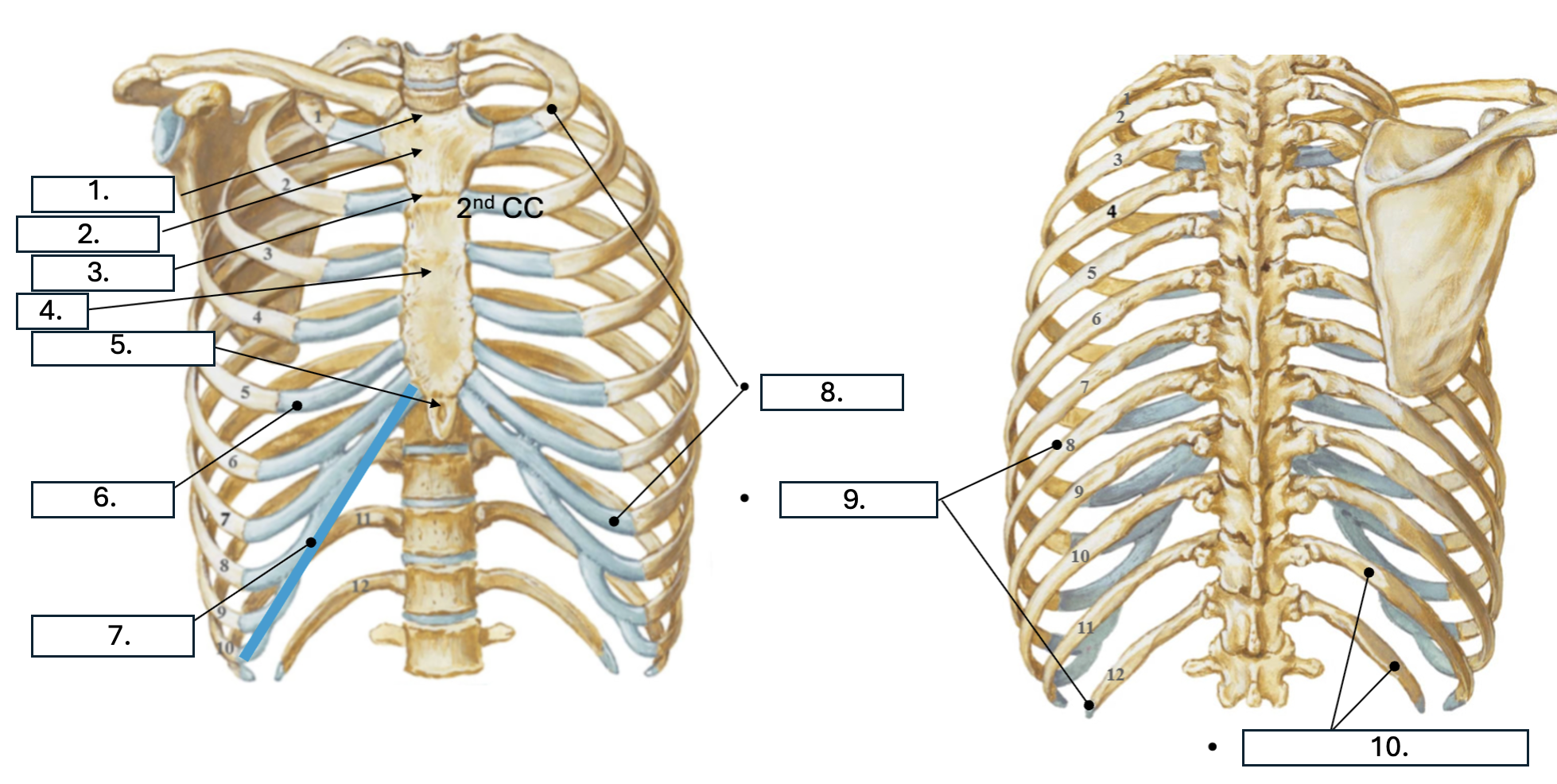
What is number 1?
Jugular notch
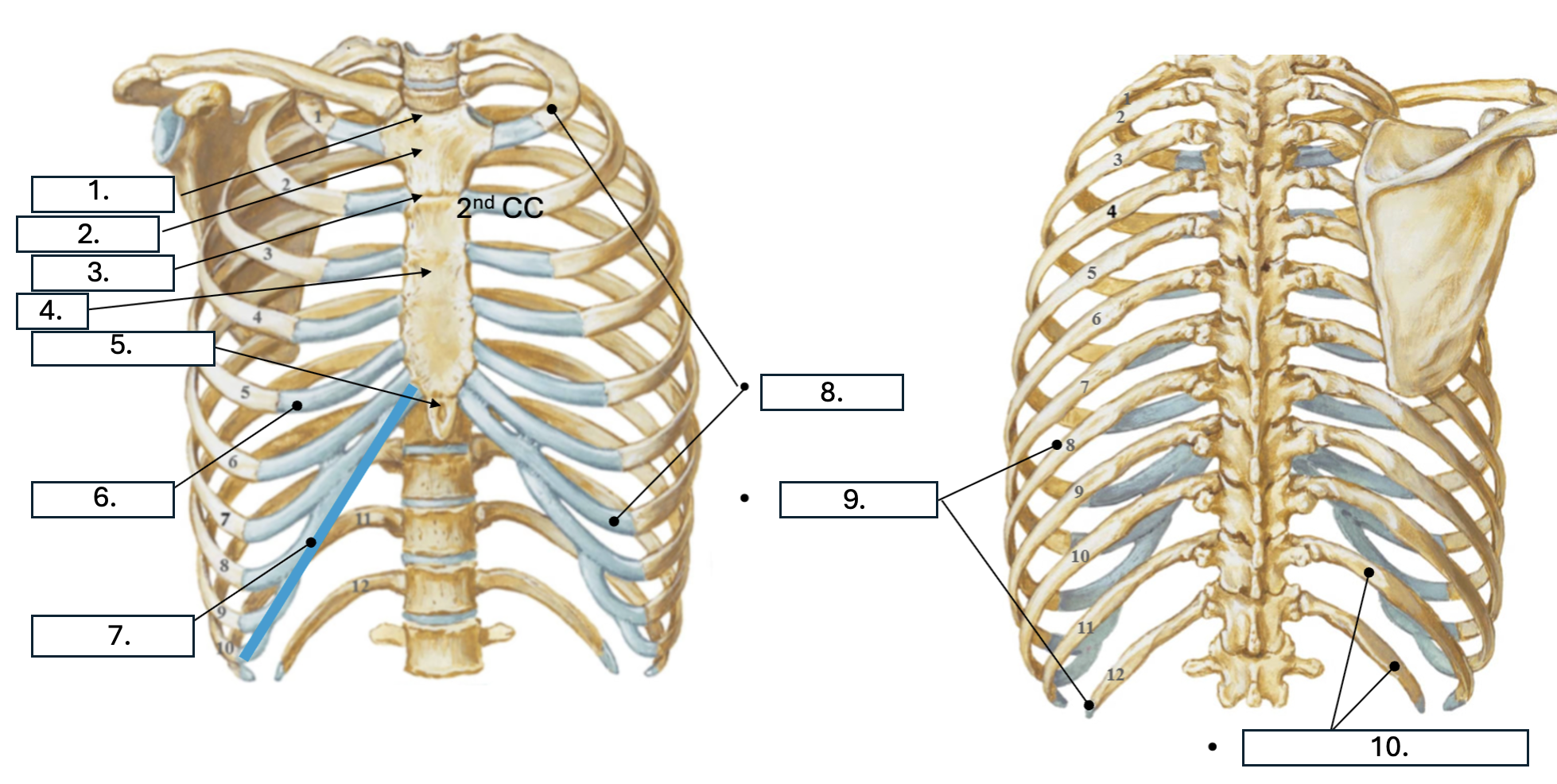
What is number 2?
Manubrium
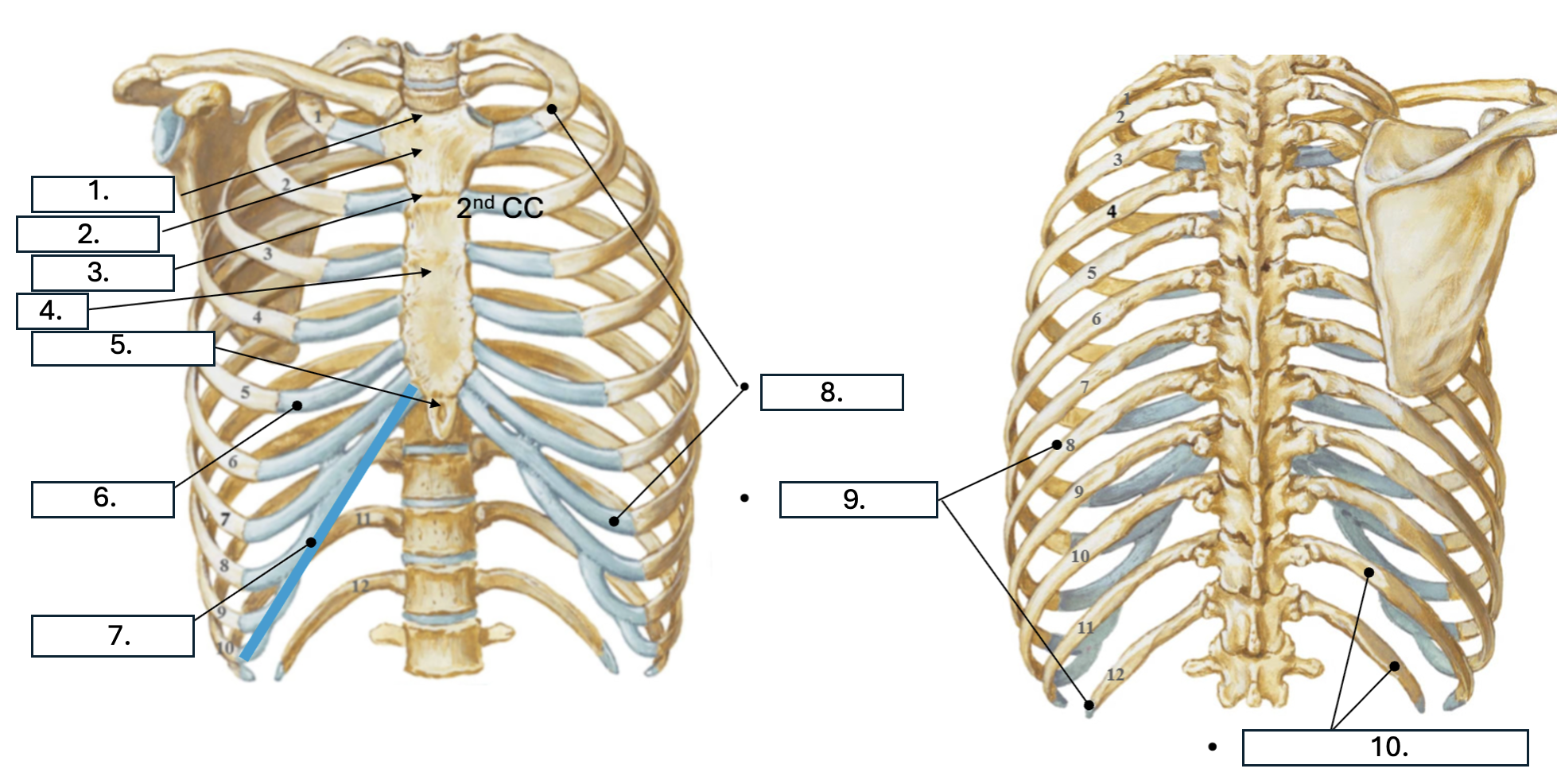
What is number 3?
Sternal angle
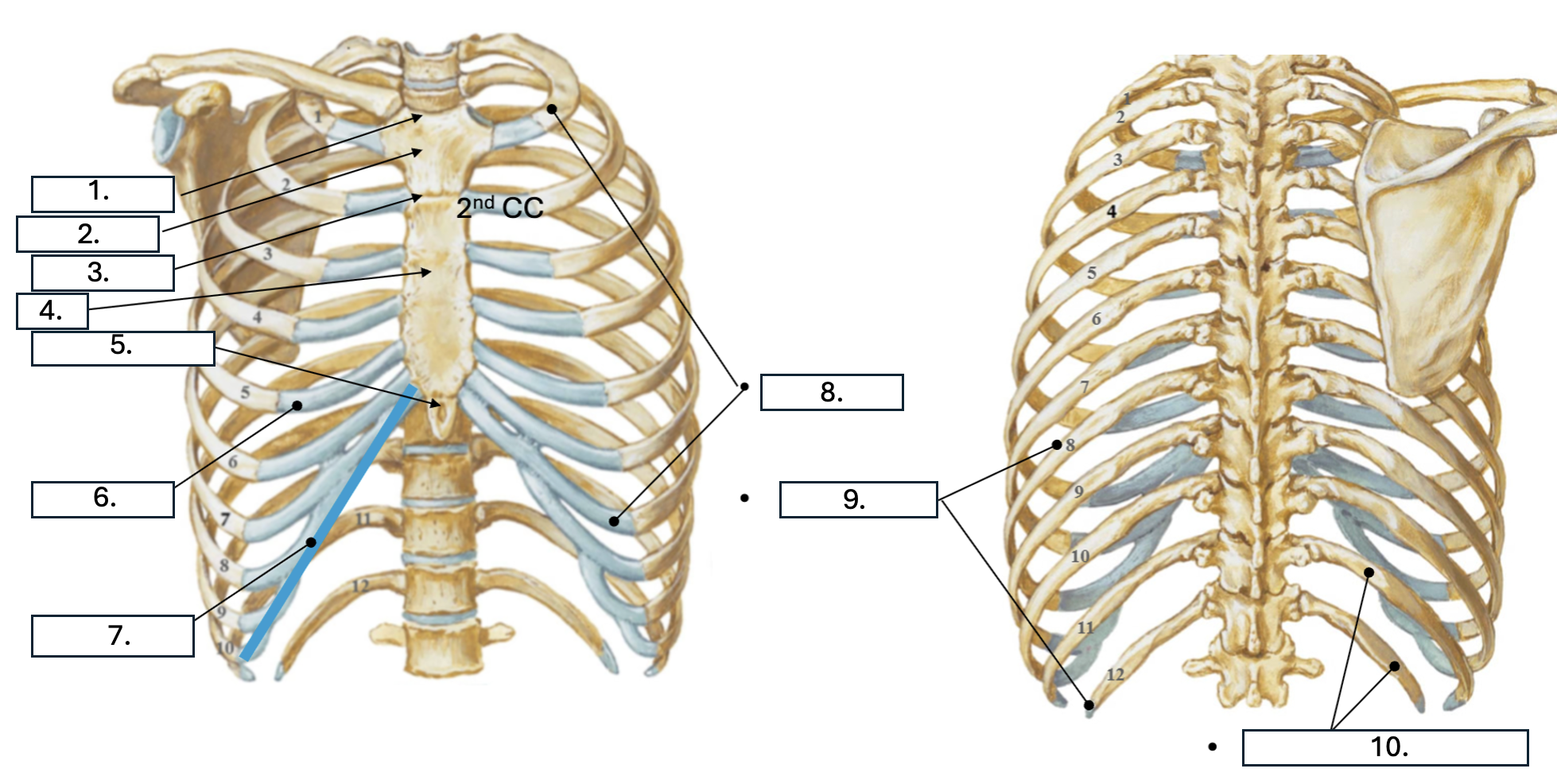
What is number 4?
body of sternum
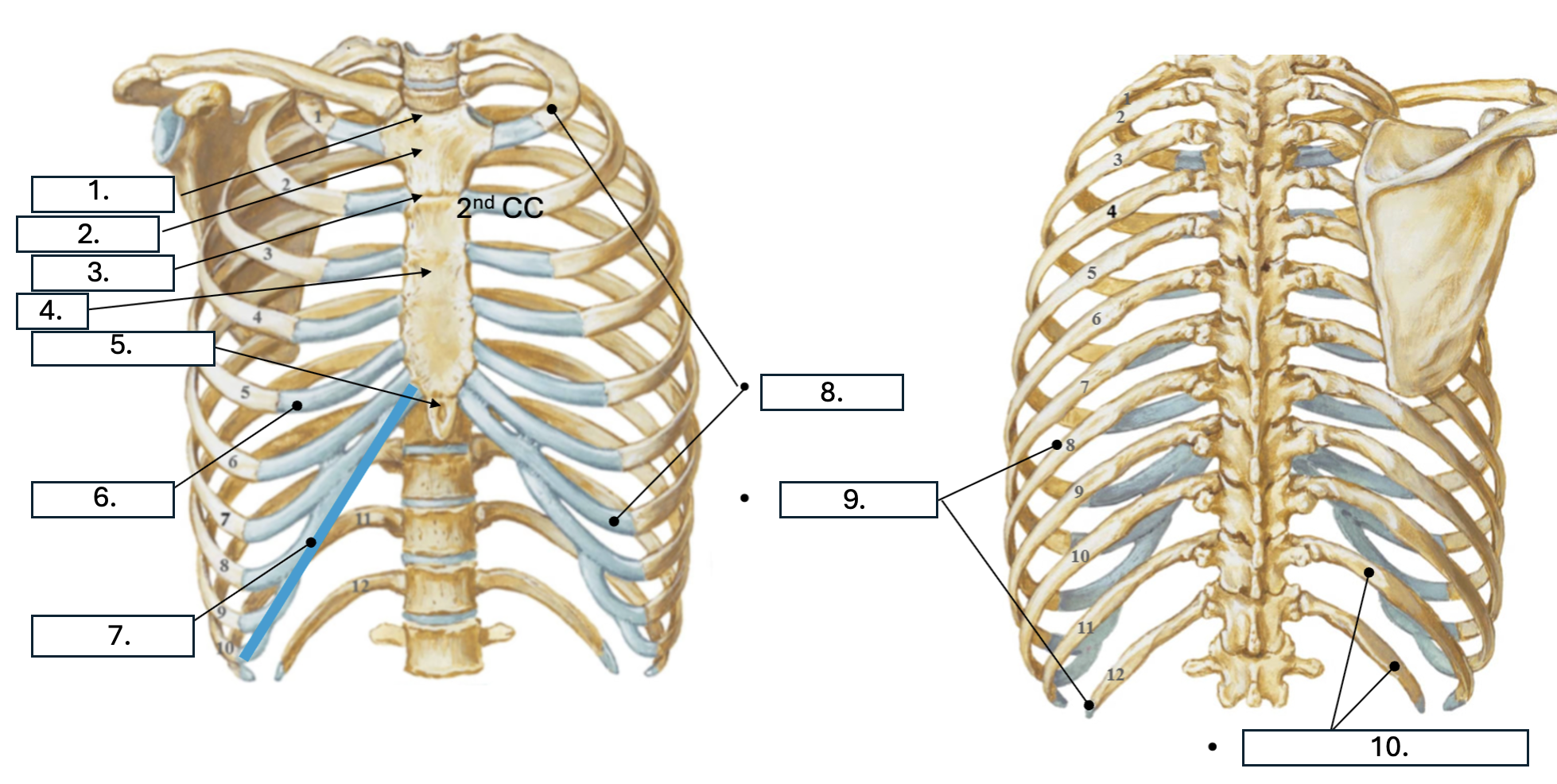
What is number 5?
Xiphoid Process
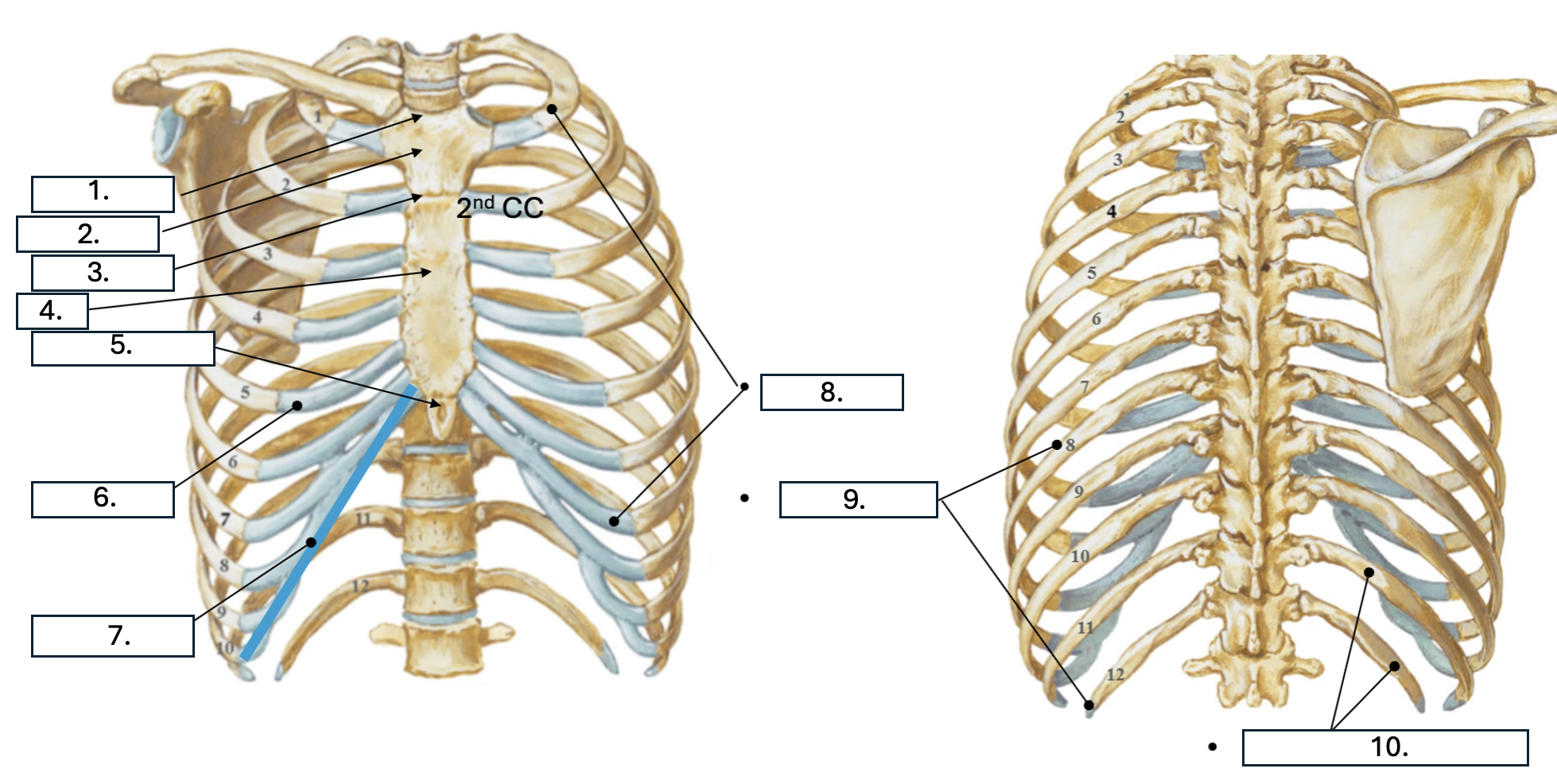
What is number 6?
Costal cartilage (CC)
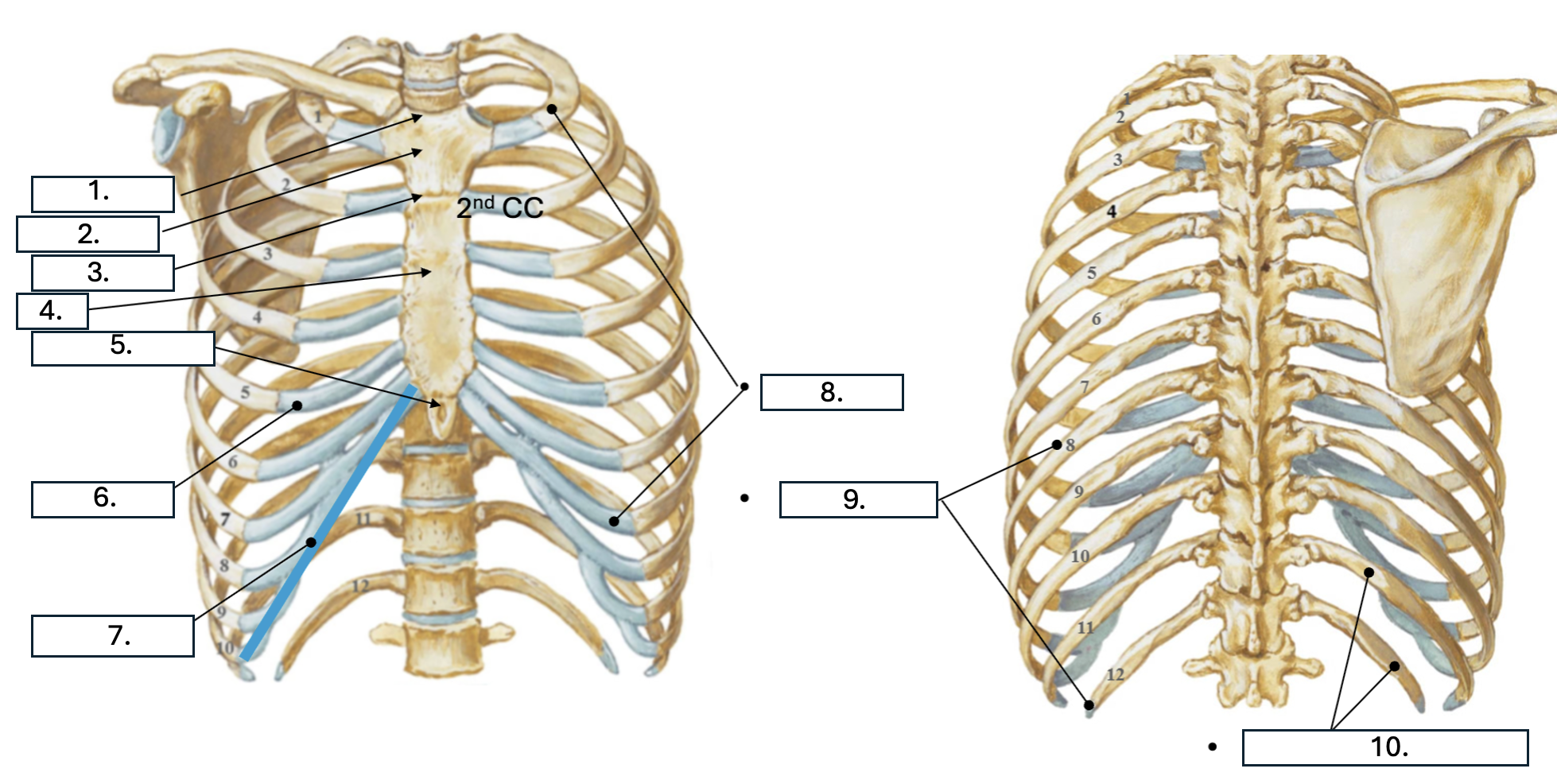
What is number 7?
Costal margin (7th-10th CC)
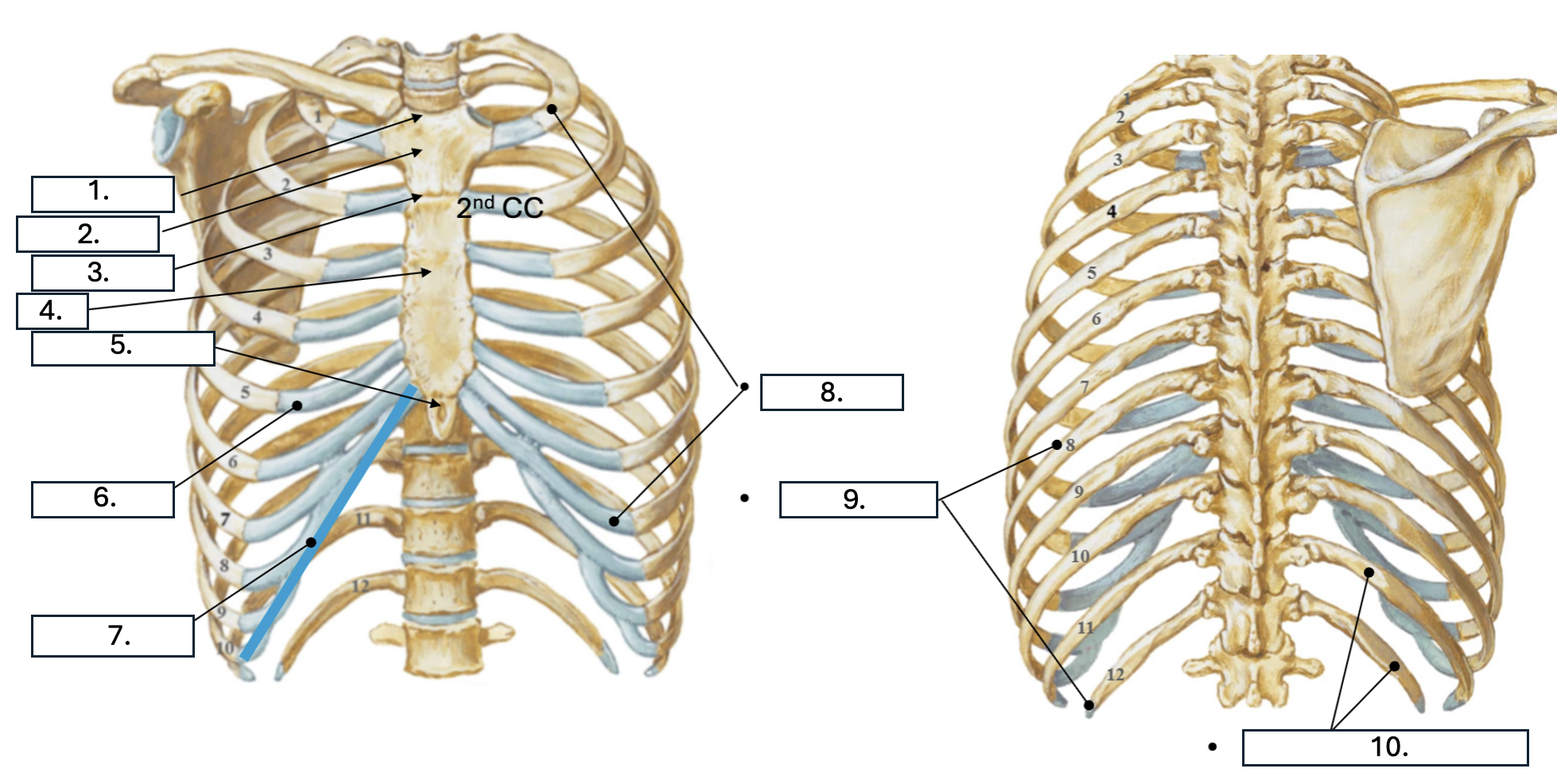
What is number 8?
true ribs (1st-7th)
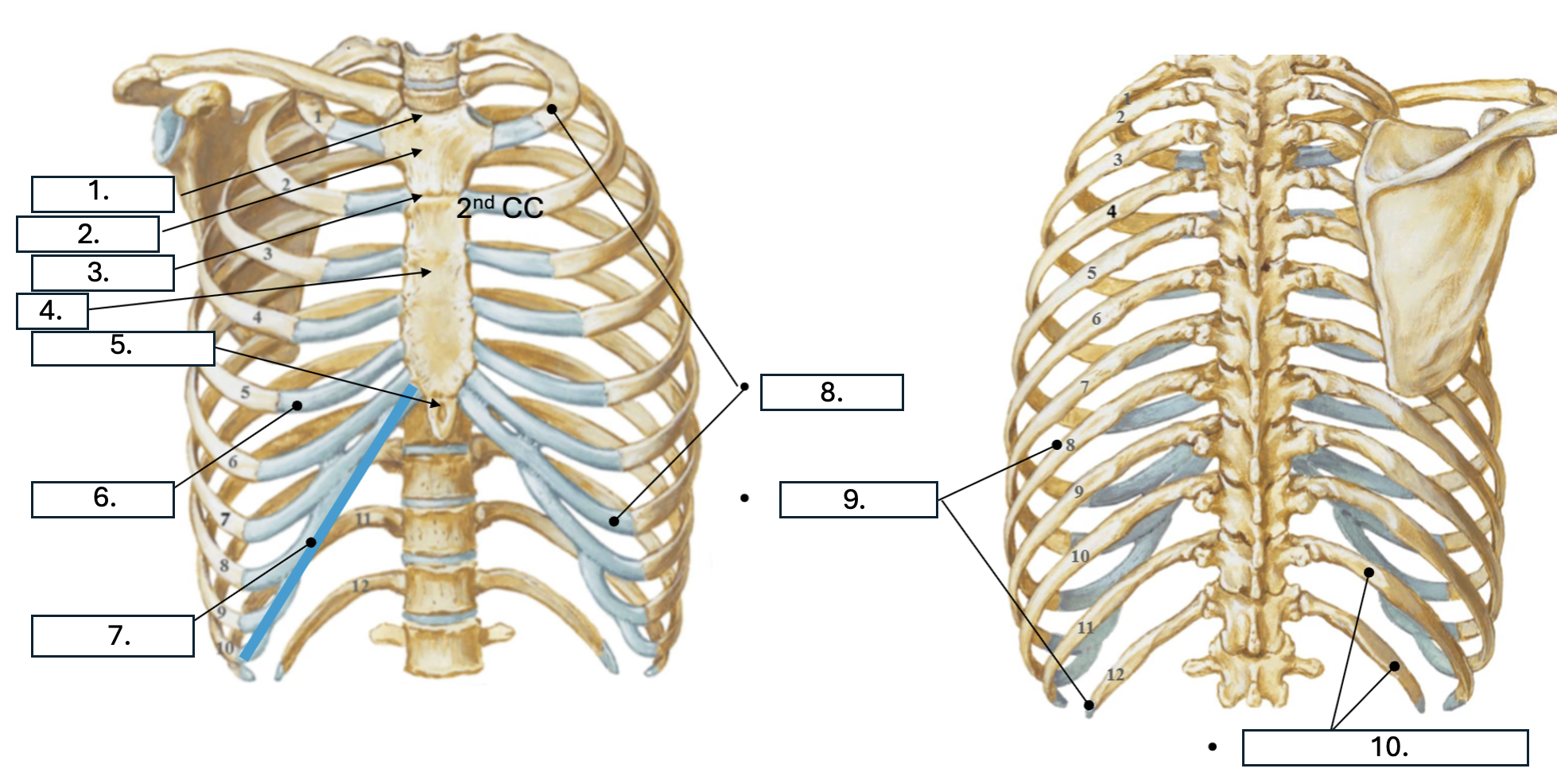
What is number 9?
False ribs (8th-12th)
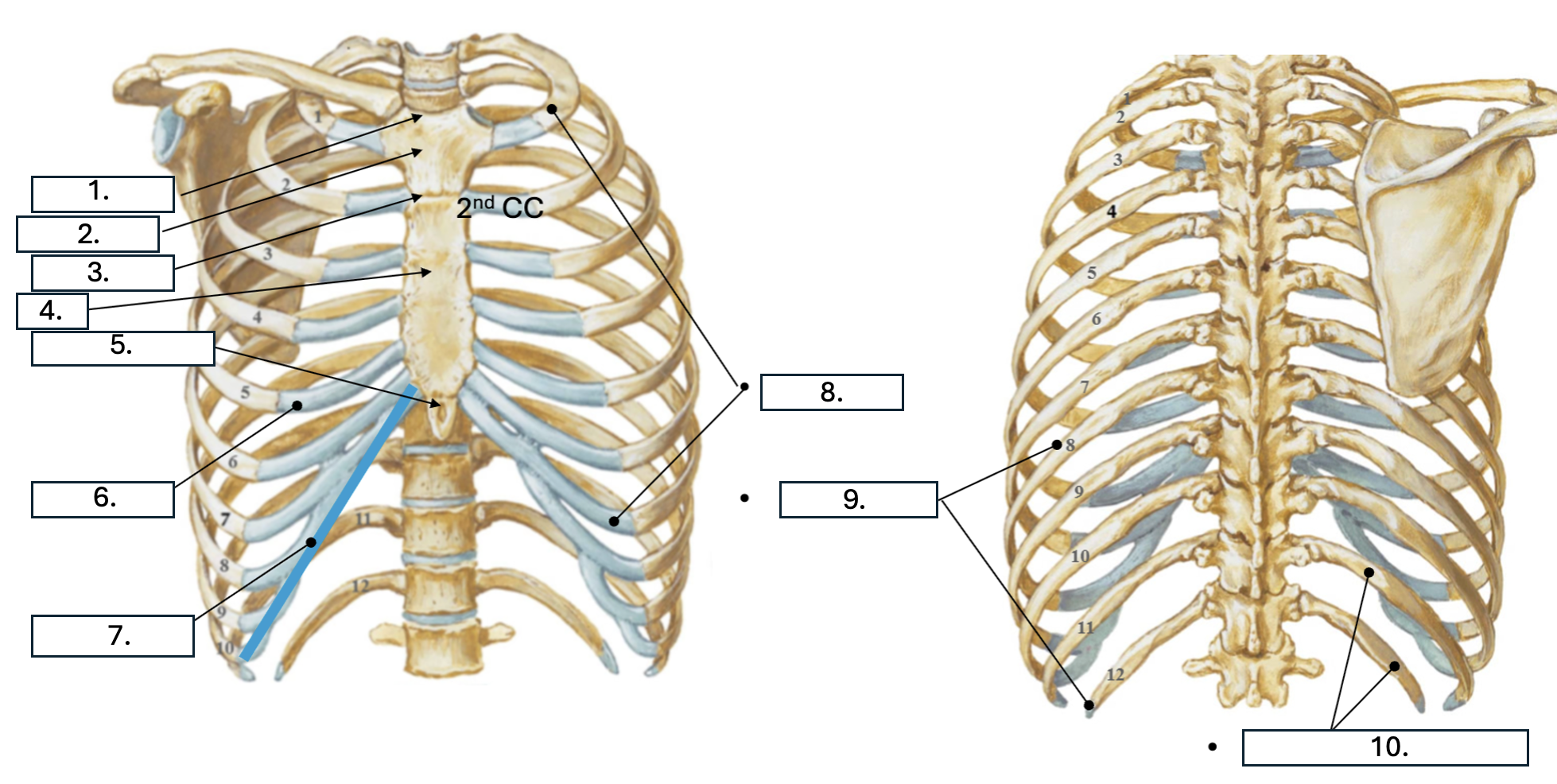
What is number 10?
floating ribs (11th-12th)
What are the attachments of the external and internal intercostals?
From the upper to the lower rib
What is the function of the EIC + interchondral part of IIC?
elevates ribs
What is the function of the Interosseus part of IIC?
depresses ribs
What is the function of the deep layer of Intercostal Muscles?
All muscles depress ribs
What three muscles make up the deep layer of Intercostal Muscles?
Innermost intercostal, Subcostalis and Transversus thoracis (Sternocostalis)
What is the order, from superior to inferior, of the intercostal arteries, nerves and veins
vein, artery, nerve
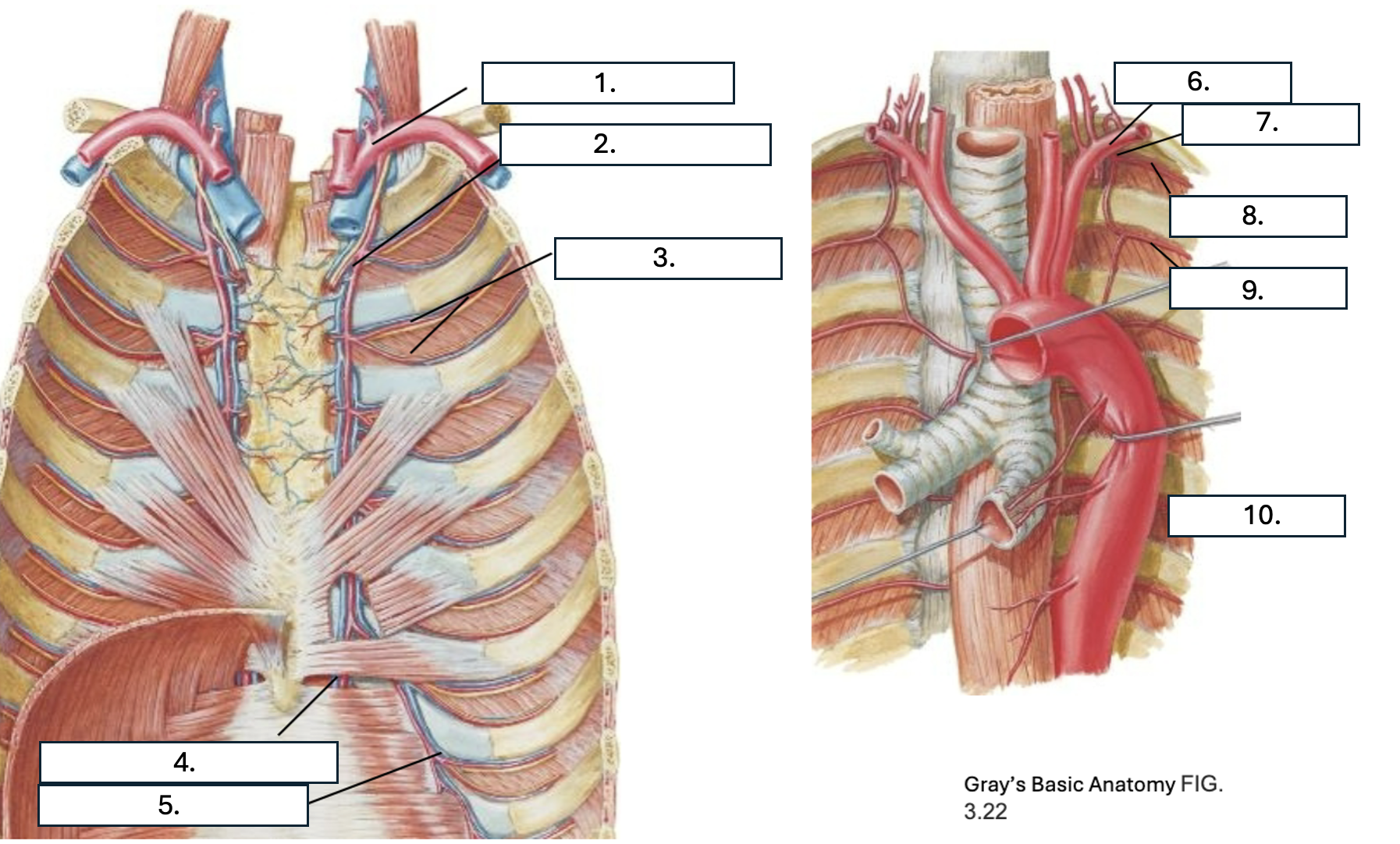
What is number 1?
subclavian artery
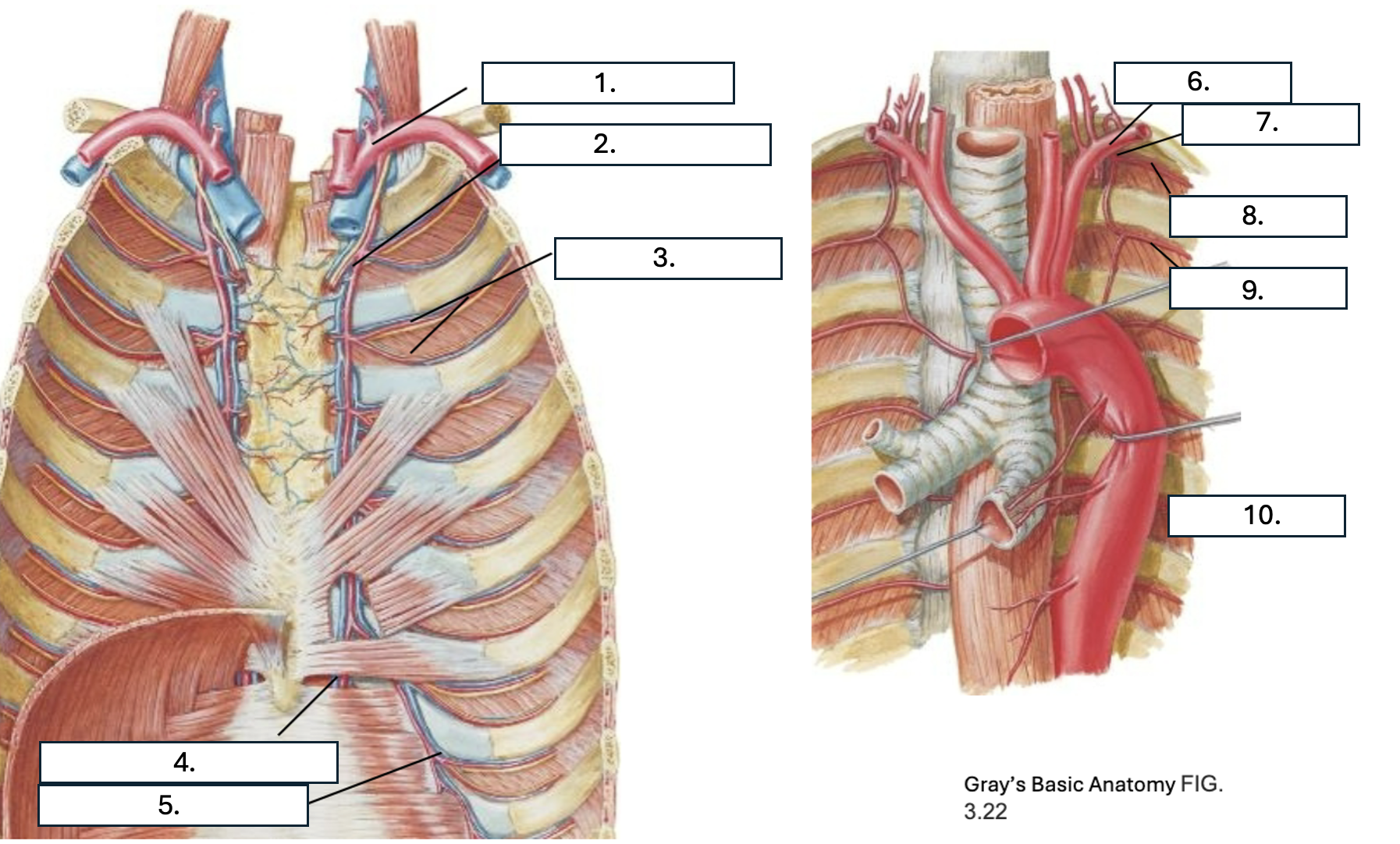
What is number 2?
Internal thoracic artery
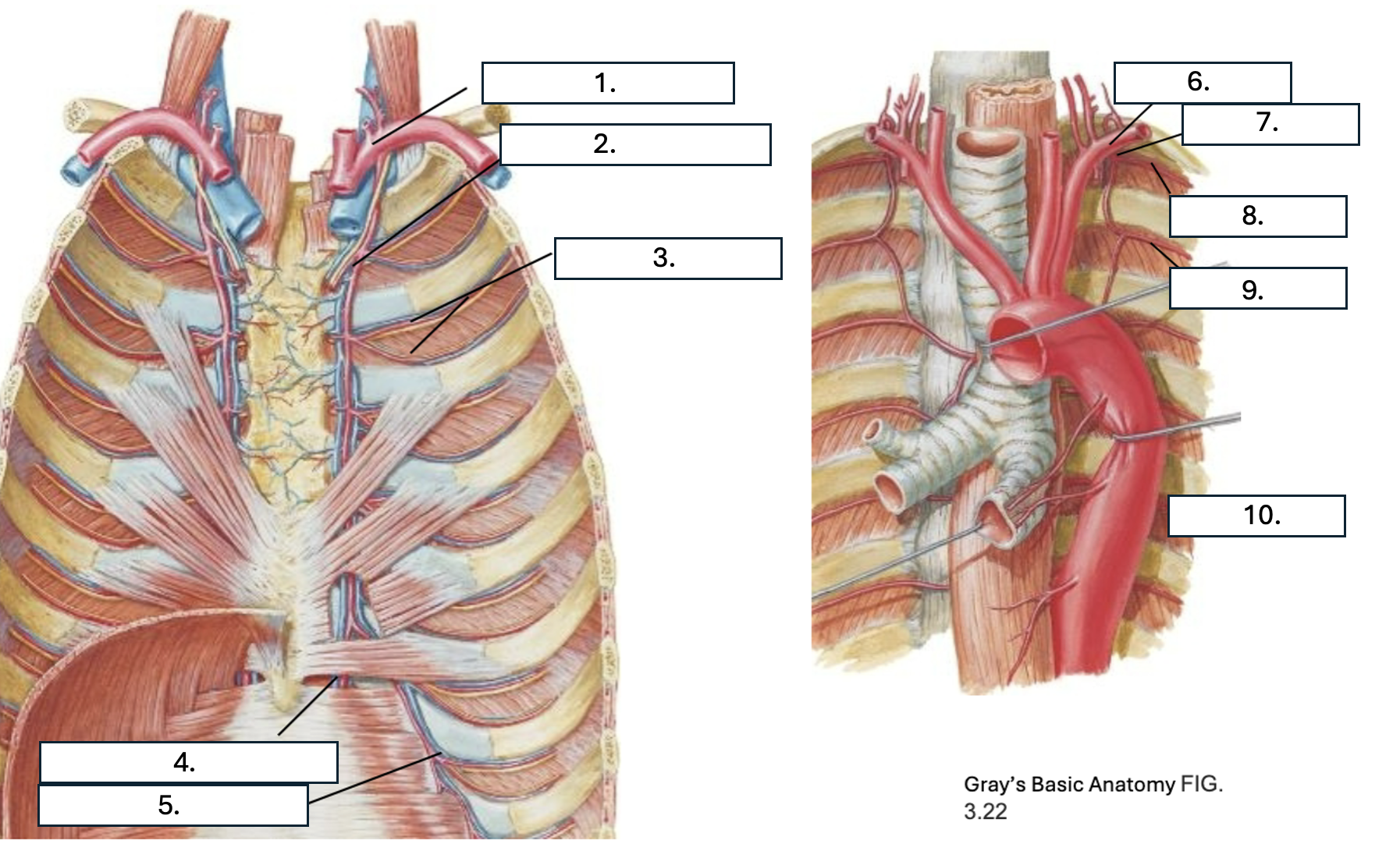
What is number 3?
Anterior intercostal artery
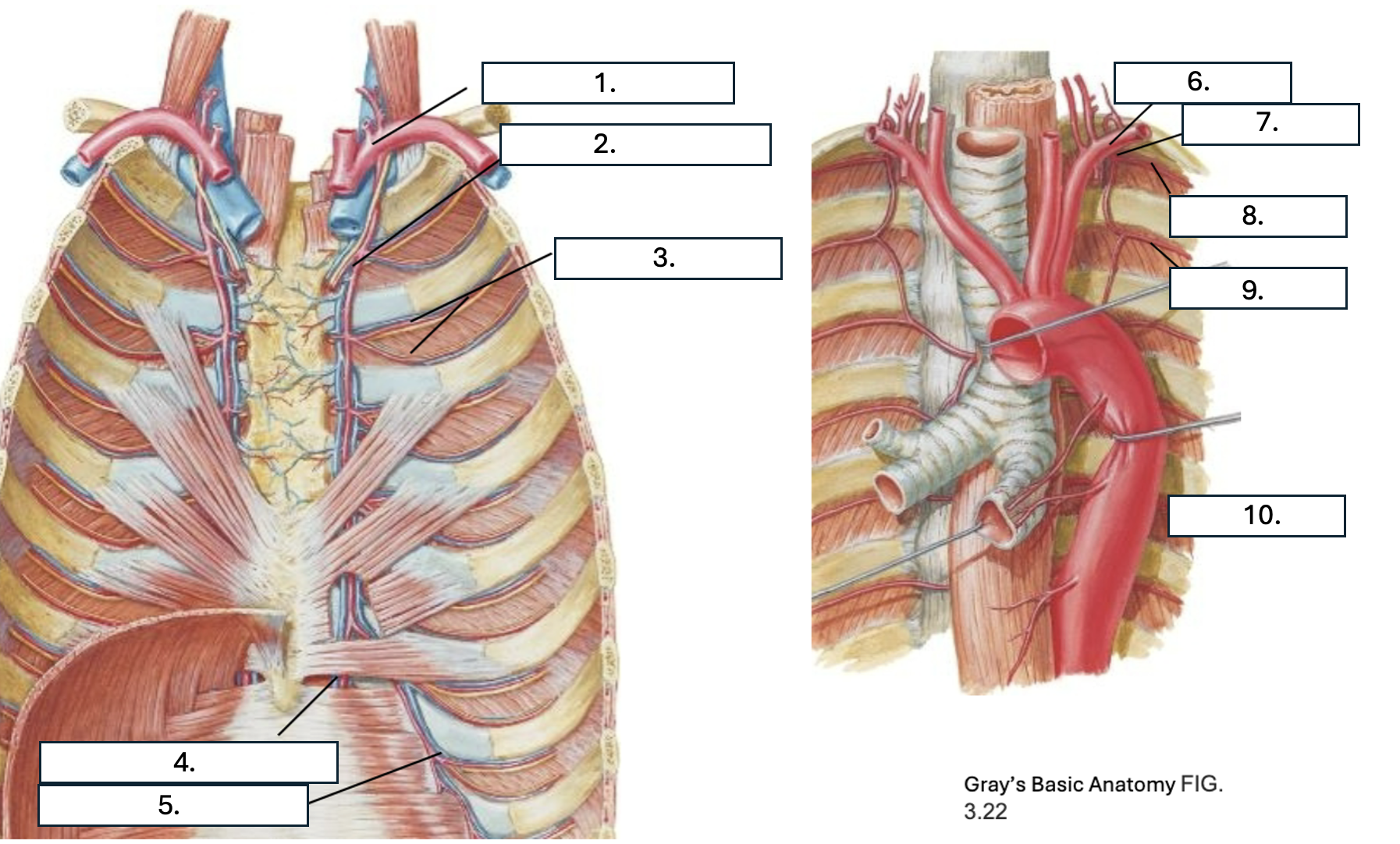
What is number 4?
Superior epigastric artery
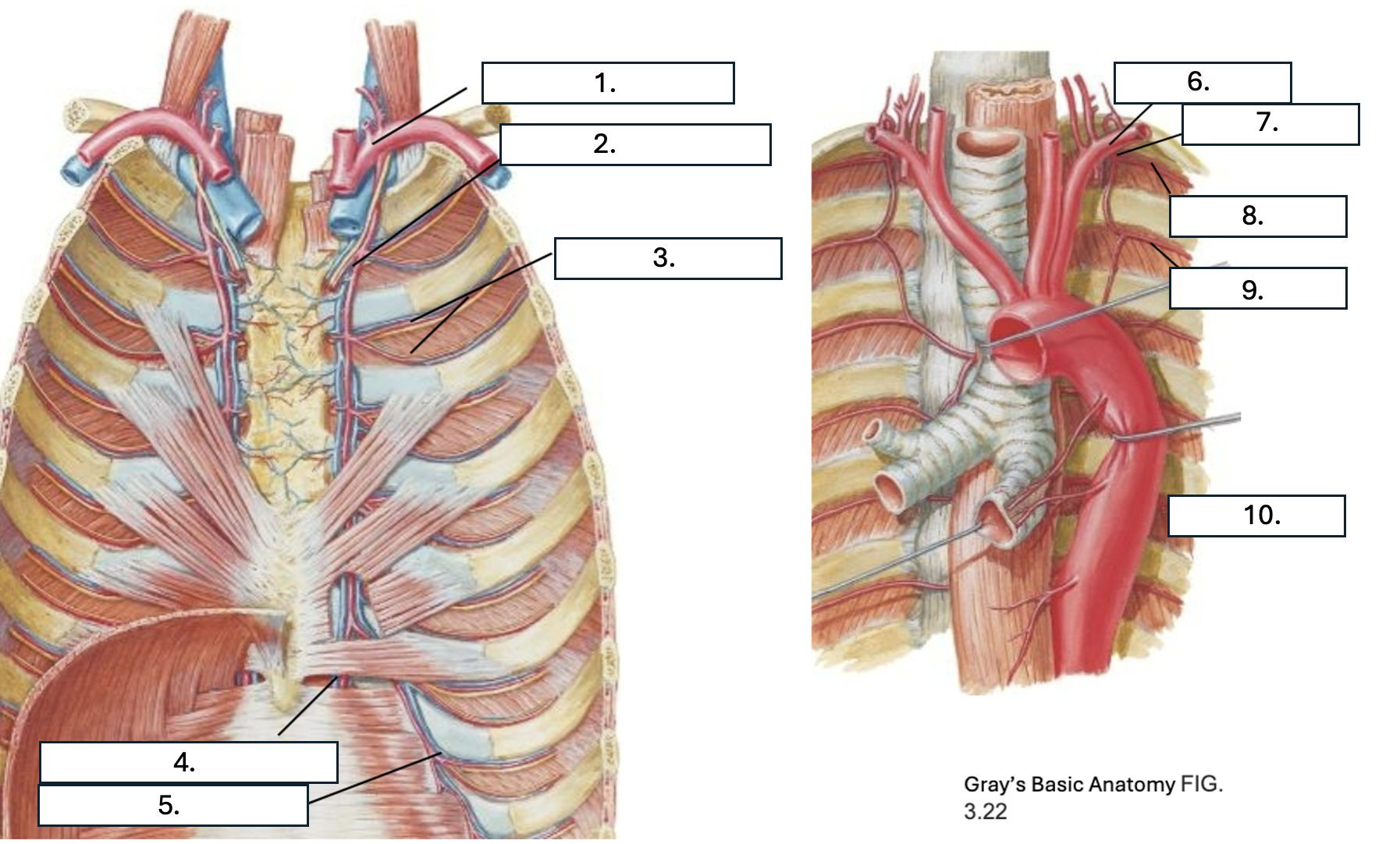
What is number 5?
Musculophrenic artery
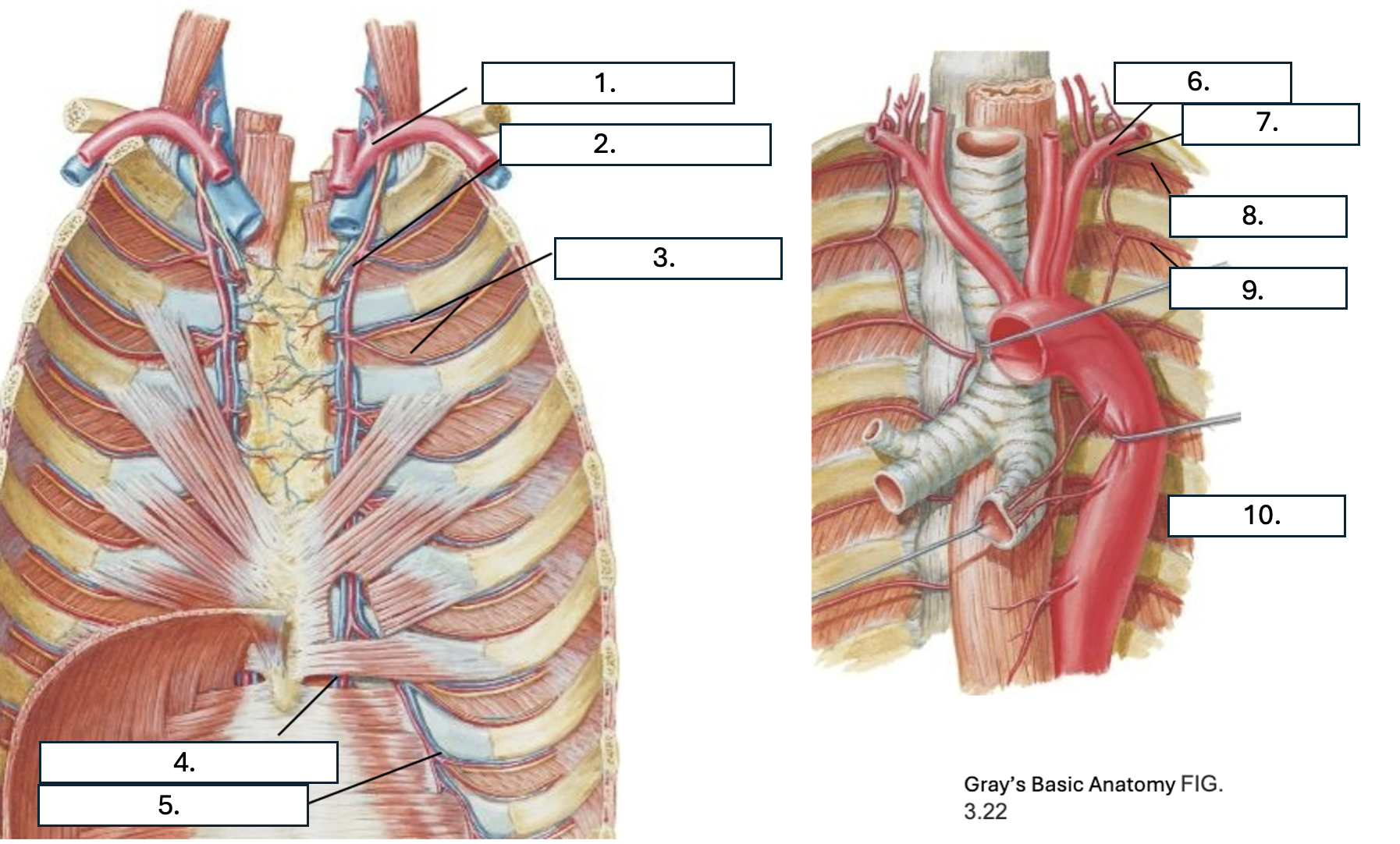
What is number 6?
Subclavian artery
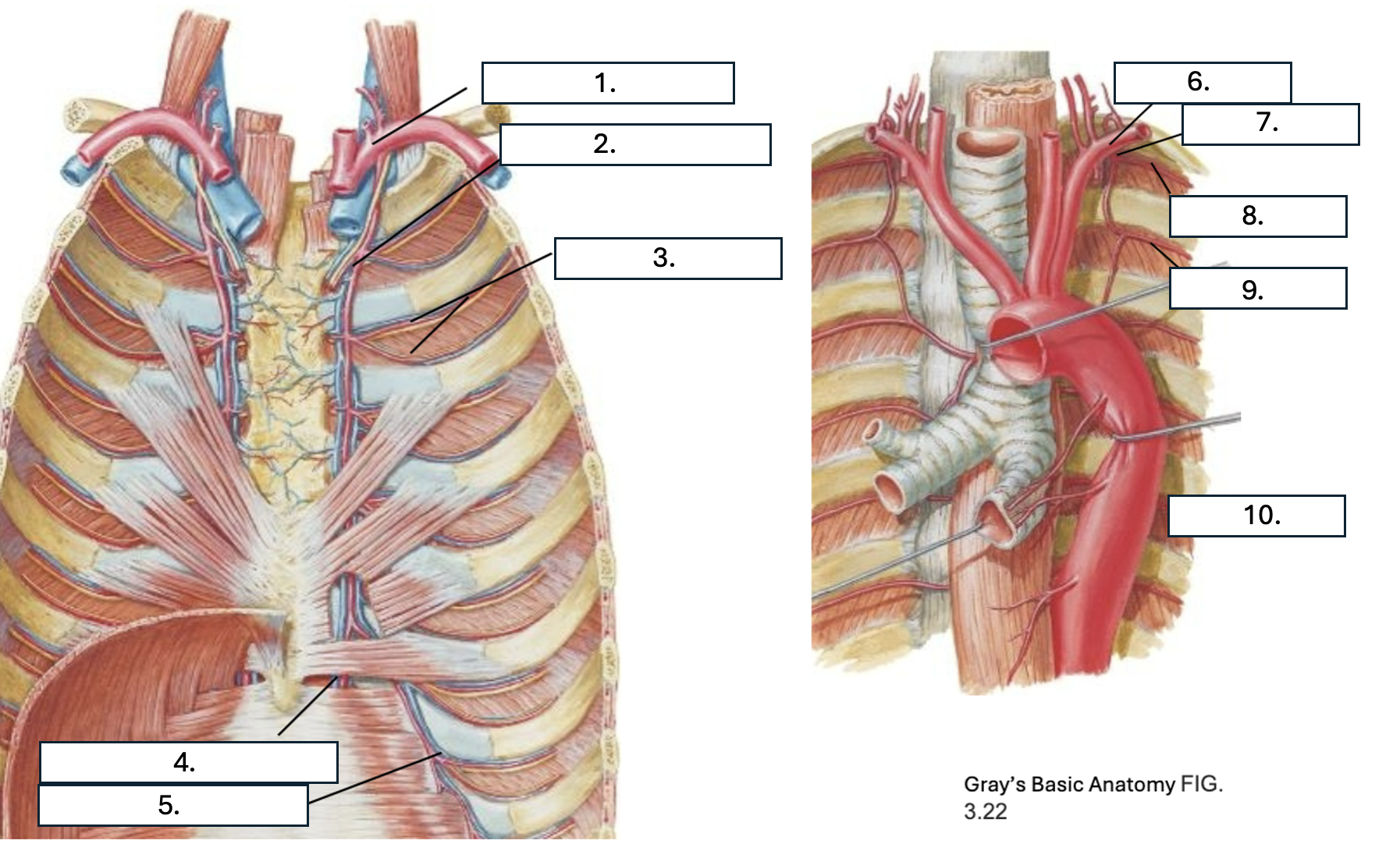
What is number 7?
Supreme IC artery
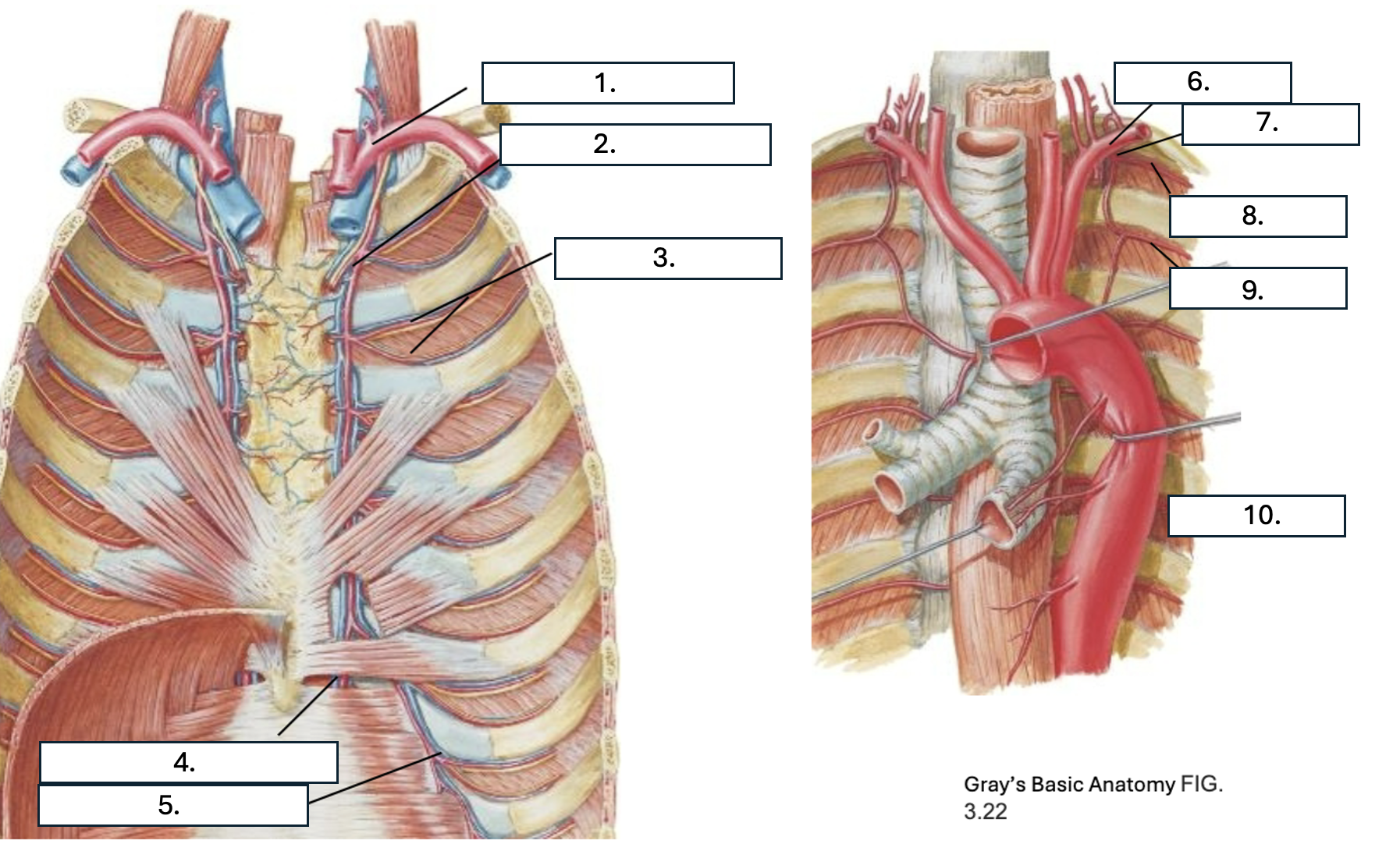
What is number 8?
1st posterior IC artery
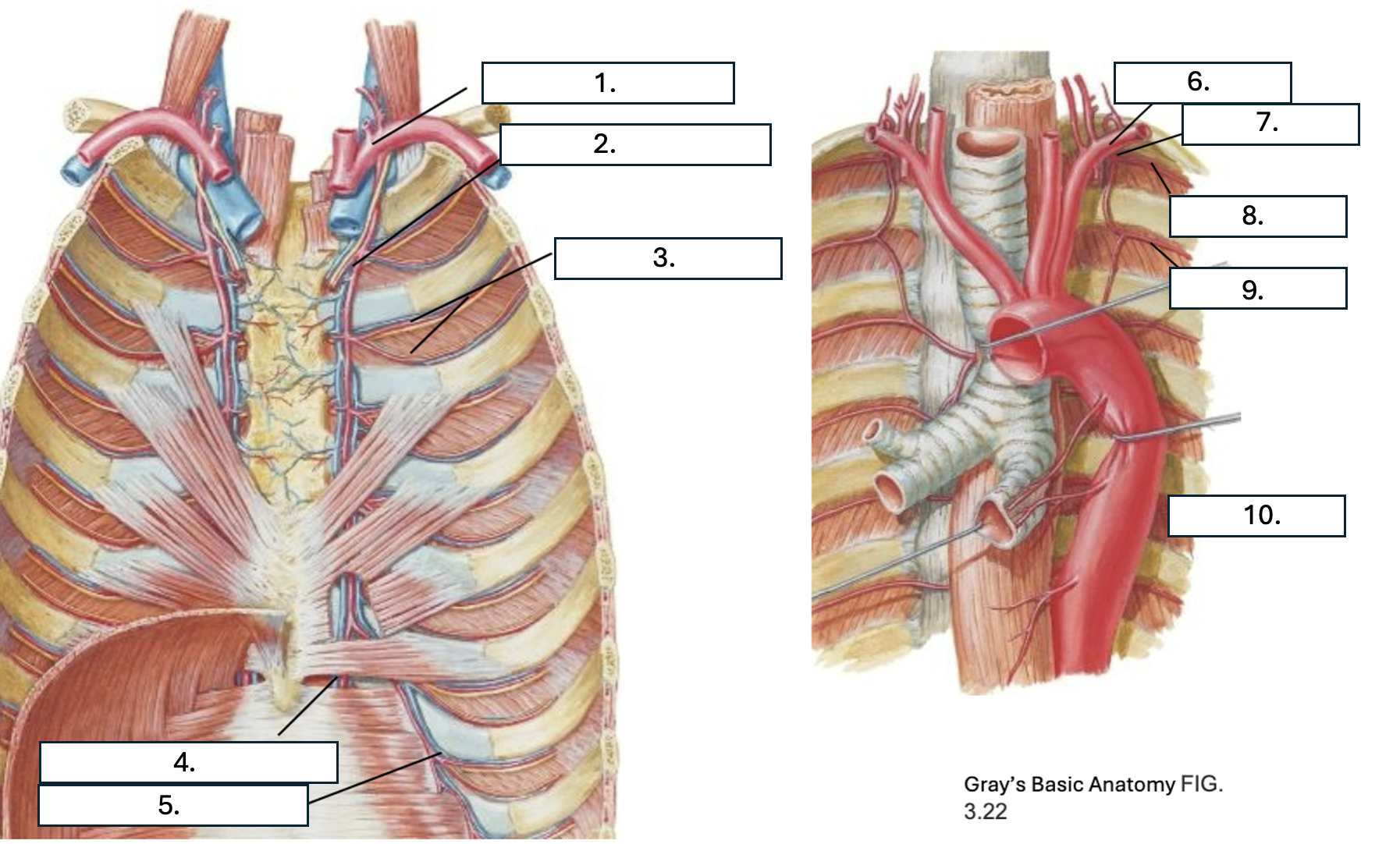
What is number 9?
2nd posterior IC artery
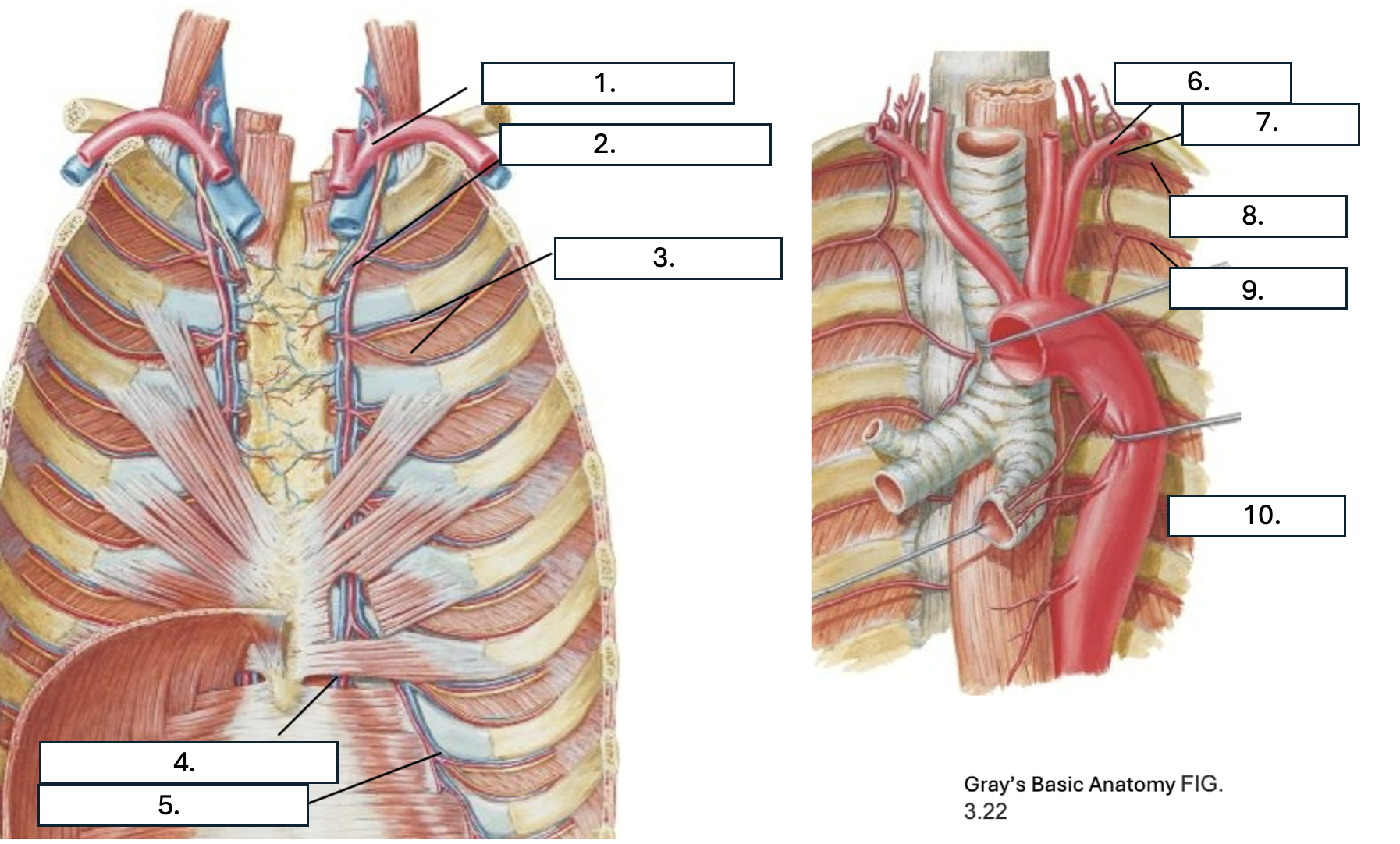
What is number 10?
Thoracic aorta
What artery do the 1st and 2nd posterior IC artery originate from?
Supreme IC artery from subclavian artery
What artery do all but the 1st and 2nd posterior IC arteries originate from?
thoracic aorta
T/F: there are two anterior IC arteries per IC space
True
Which IC spaces have anterior IC arteries?
1st through 9th
Which artery do the 1st through 6th anterior IC arteries originate from?
internal thoracic artery
Which artery do the 7th through 9th anterior IC arteries originate from?
musculophrenic artery
What three arteries anastomose in the IC space?
2 anterior IC arteries and Posterior IC artery & collateral arteries
Where does blood brain from the right 1st intercostal space?
right brachiocephalic vein
Where does blood drain from the right 2nd through 4th intercostal space?
arch of azygos vein
Where does blood drain from the right 5th through 11th intercostal space?
azygos vein
Where does blood drain from the left 1st through 4th intercostal space?
left brachiocephalic vein
Where does blood drain from the left 5th through 7th intercostal space?
accessory hemiazygos vein
Where does blood drain from the left 8th through 11th intercostal space?
hemiazygos vein
What are some causes of thoracic outlet syndrome?
Cervical rib, tight neck muscle, trauma, tumor
What are some findings of thoracic outlet syndrome?
Vascular & neurological symptoms in the upper limb (pain, numbness, tingling, etc.) that worsen with overhead activity
What is flail chest?
fracture of multiple ribs that detaches a segment from the rib cage
how does a flail segment move?
paradoxically during respiration
Why is the angle of ribs the preferred injection site for a nerve block?
that site has the most far reaching effects
What are some symptoms of Costochondritis/ Tietz Syndrome?
Severe chest pain and local tenderness
What are some causes of Costochondritis/ Tietz Syndrome?
Injury, arthritis
What is Costochondritis/ Tietz Syndrome?
Inflammation of the costochondral joint
Where is the costodiaphragmatic recess?
Lowermost part of pleural cavity, Angle between costal & diaphragmatic pleura
Where is the costomediastinal recess?
Along the anterior margin of pleura, Between costal & mediastinal pleura
is parietal pleura under somatic or autonomic innervation?
Somatic
is visceral pleura under somatic or autonomic innervation?
Autonomic
what part of the embryo gives rise to the parietal pleura?
Somatopleuric mesoderm
what part of the embryo gives rise to the visceral pleura?
Splanchnopleuric mesoderm
what part of the embryo gives rise to the pleural cavity?
Intraembryonic coelom
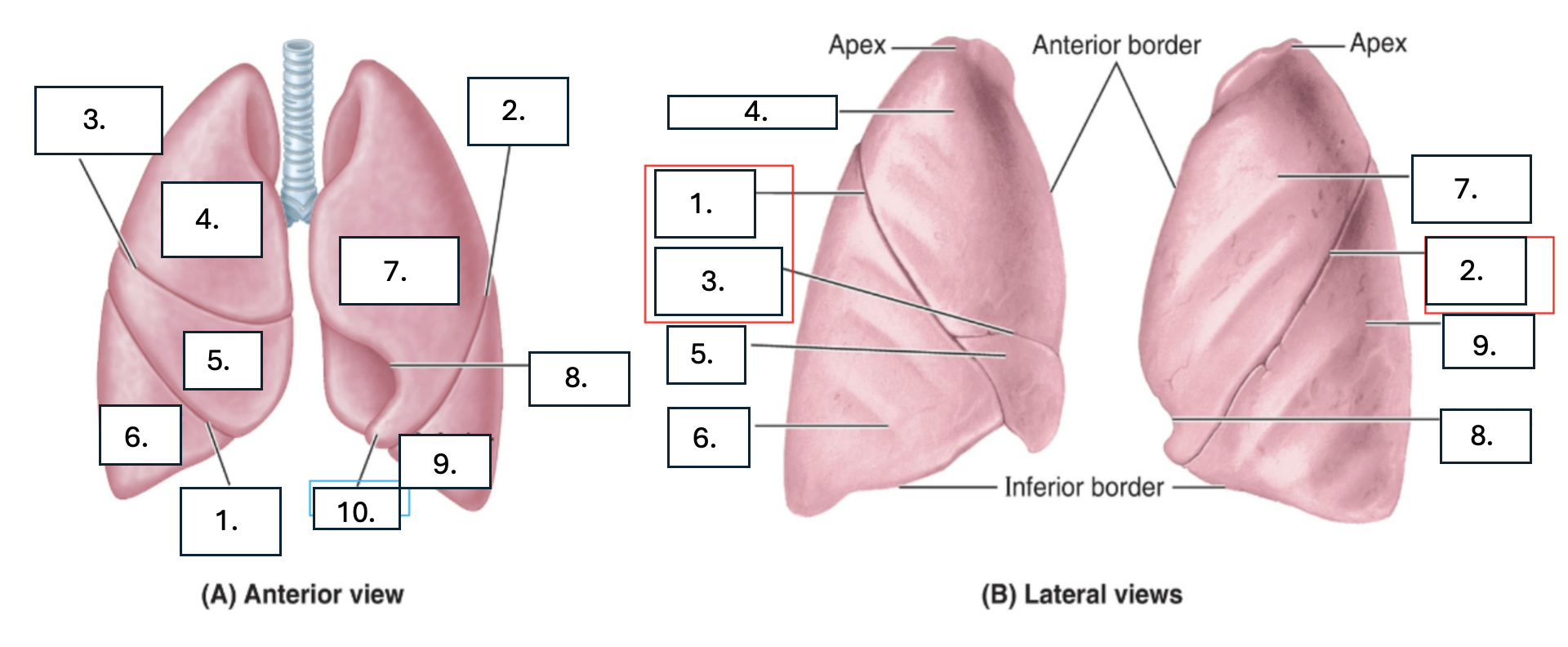
What is number 1?
oblique fissure of right lung
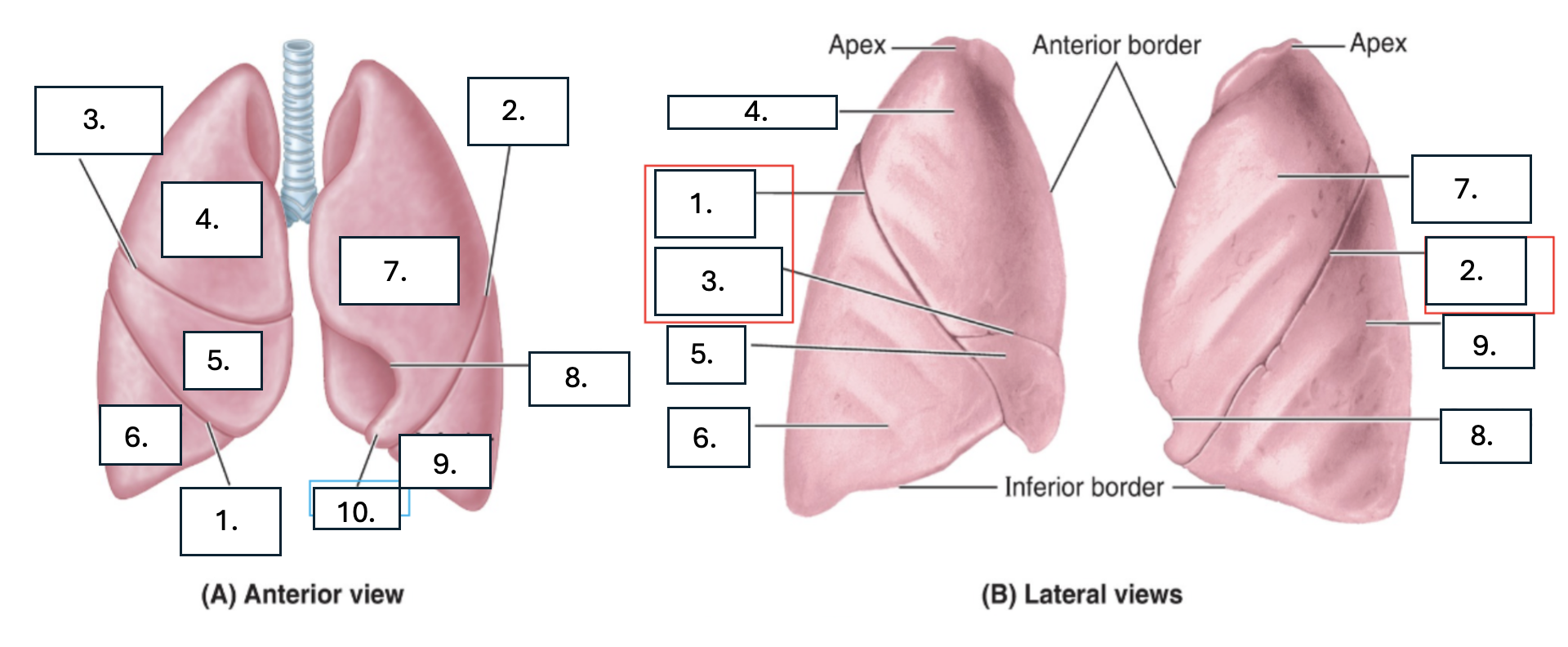
What is number 2?
oblique fissure of left lung
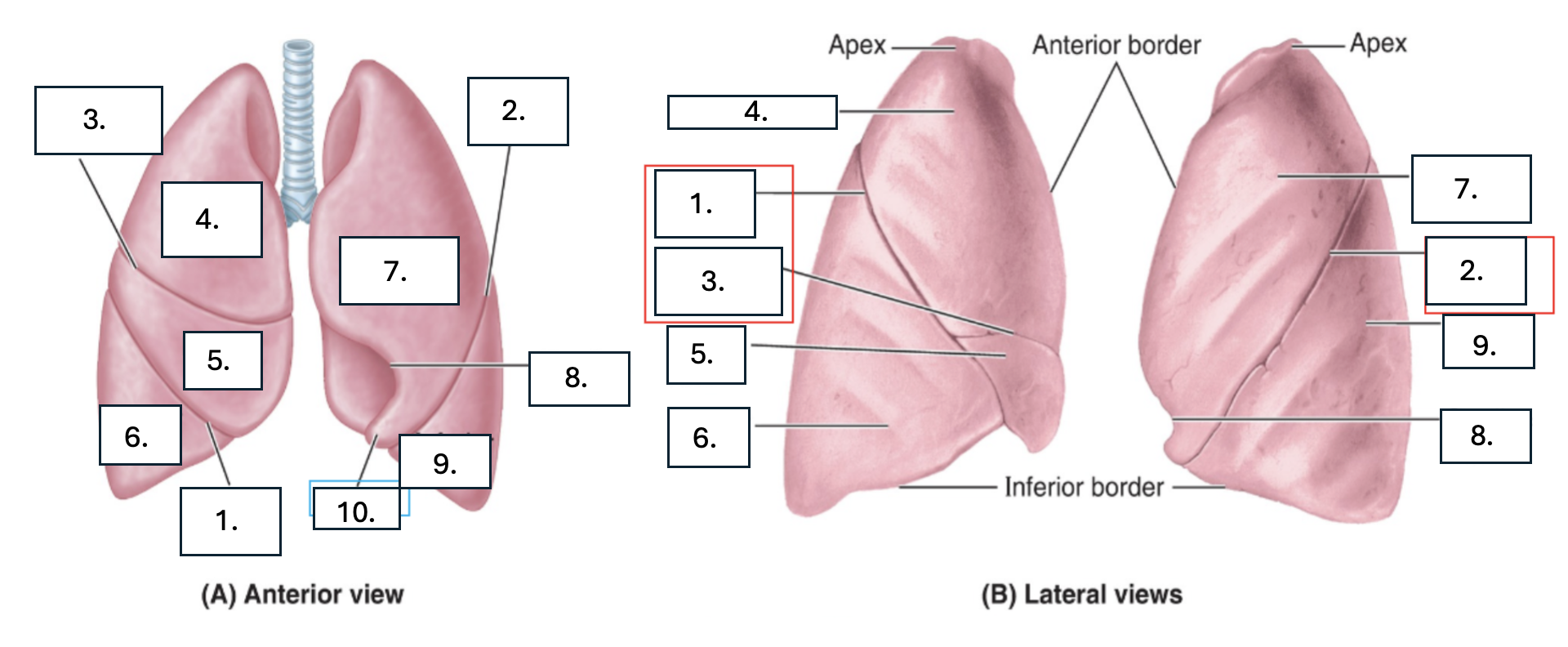
What is number 3?
horizontal fissure of right lung
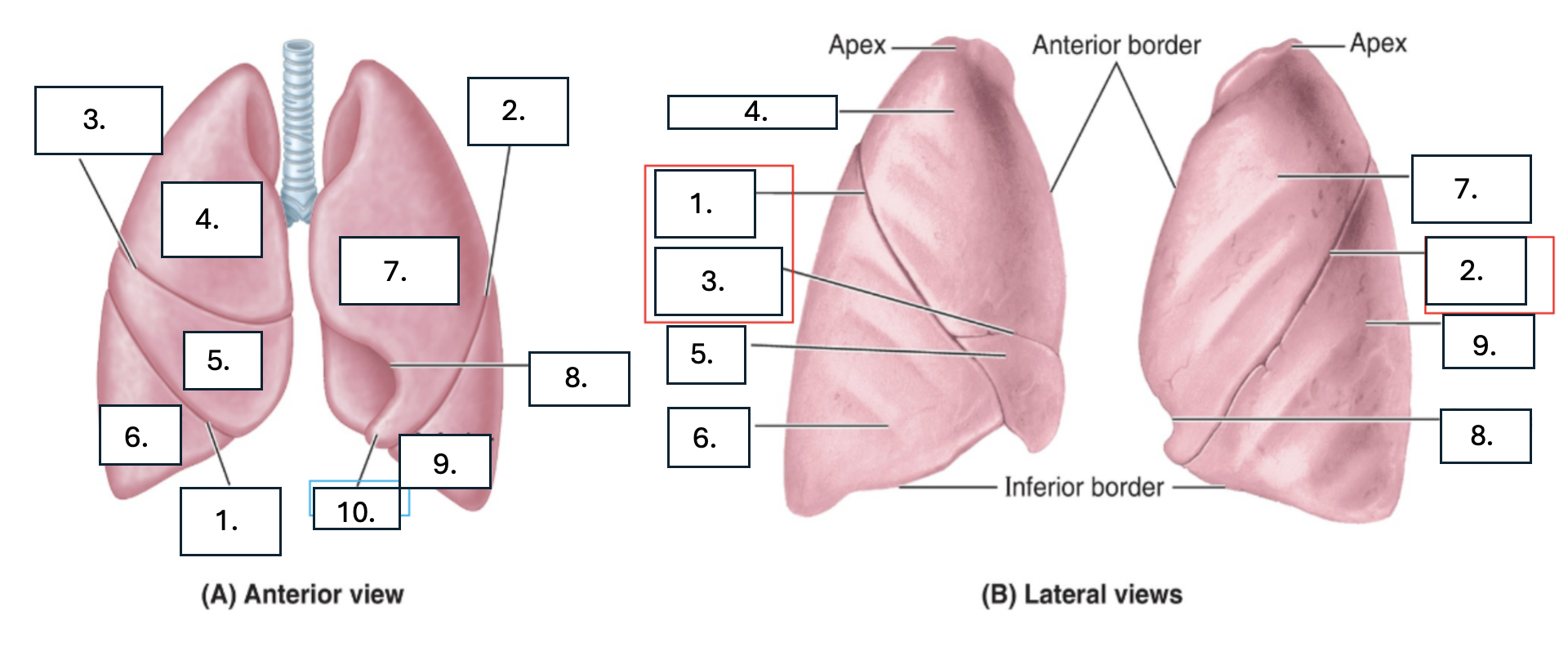
What is number 4?
Superior lobe of right lung
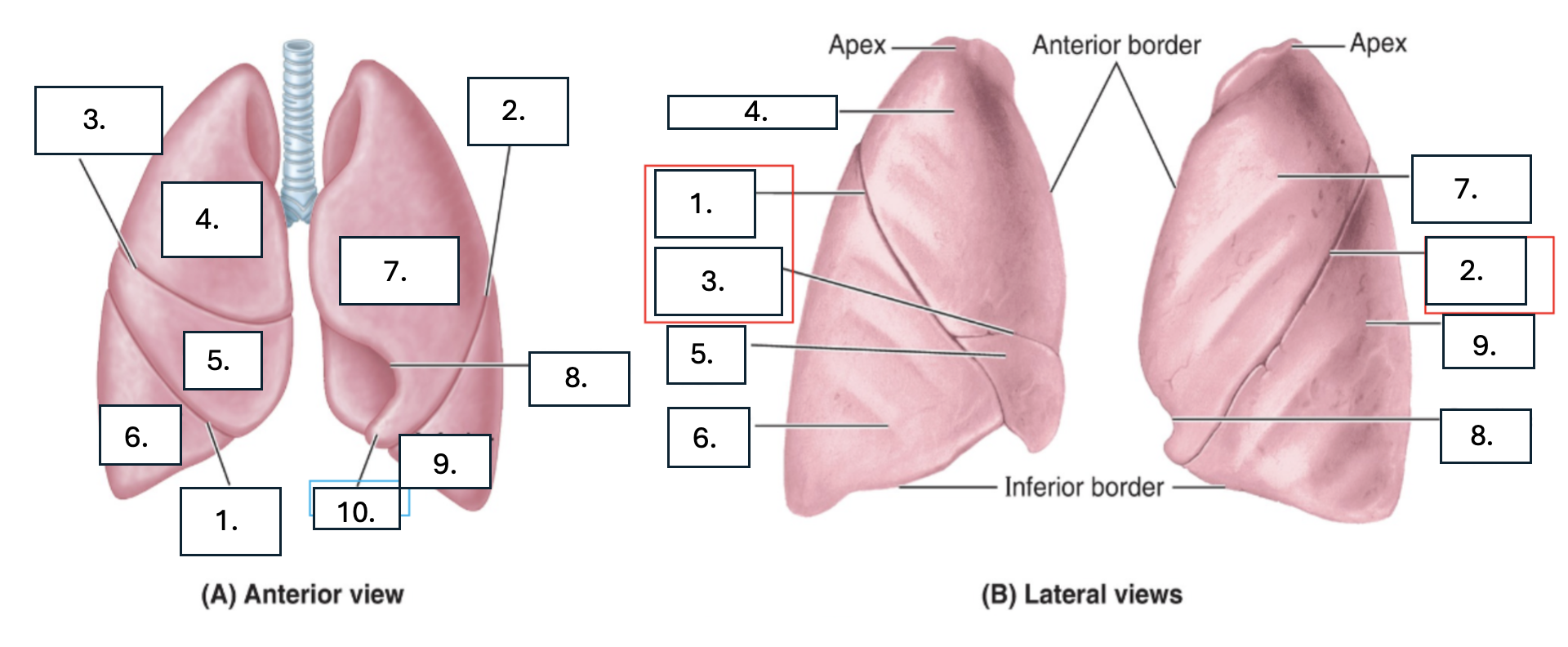
What is number 5?
middle lobe of right lung
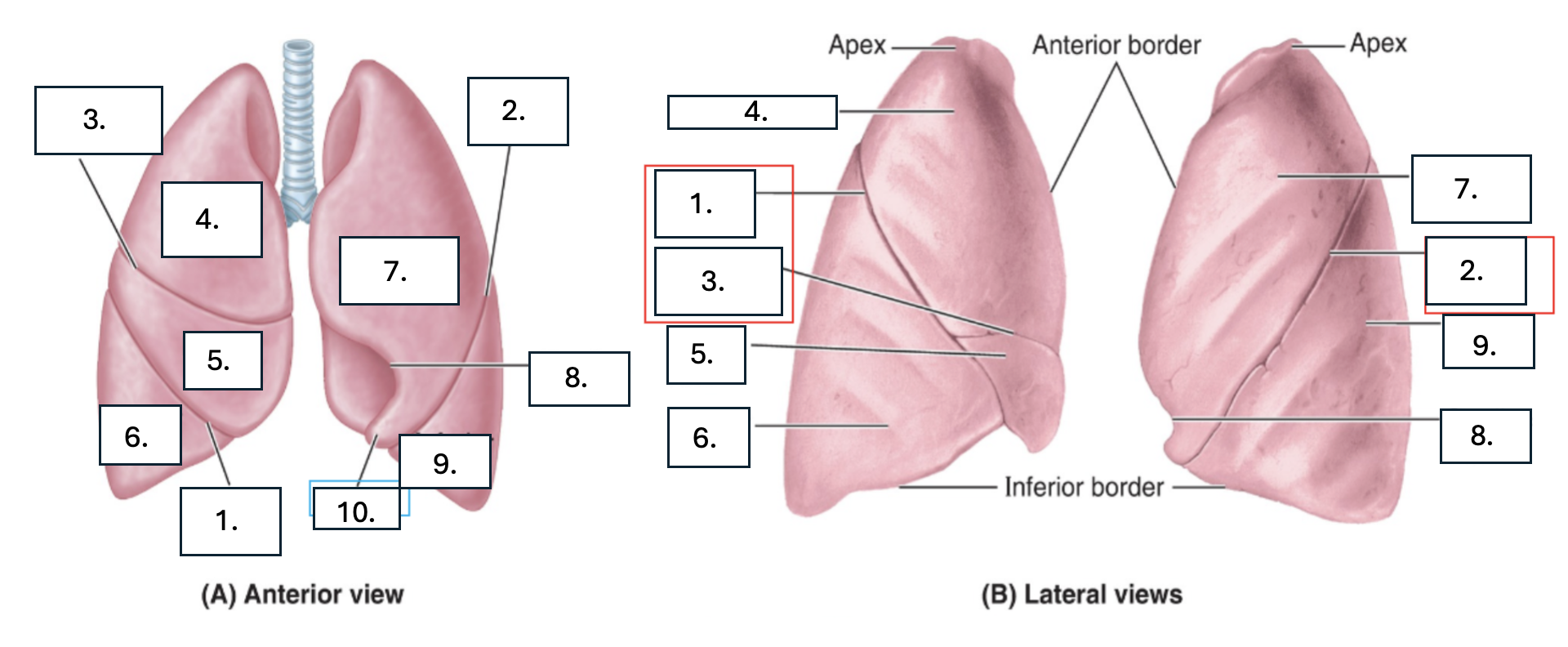
What is number 6?
inferior lobe of right lung
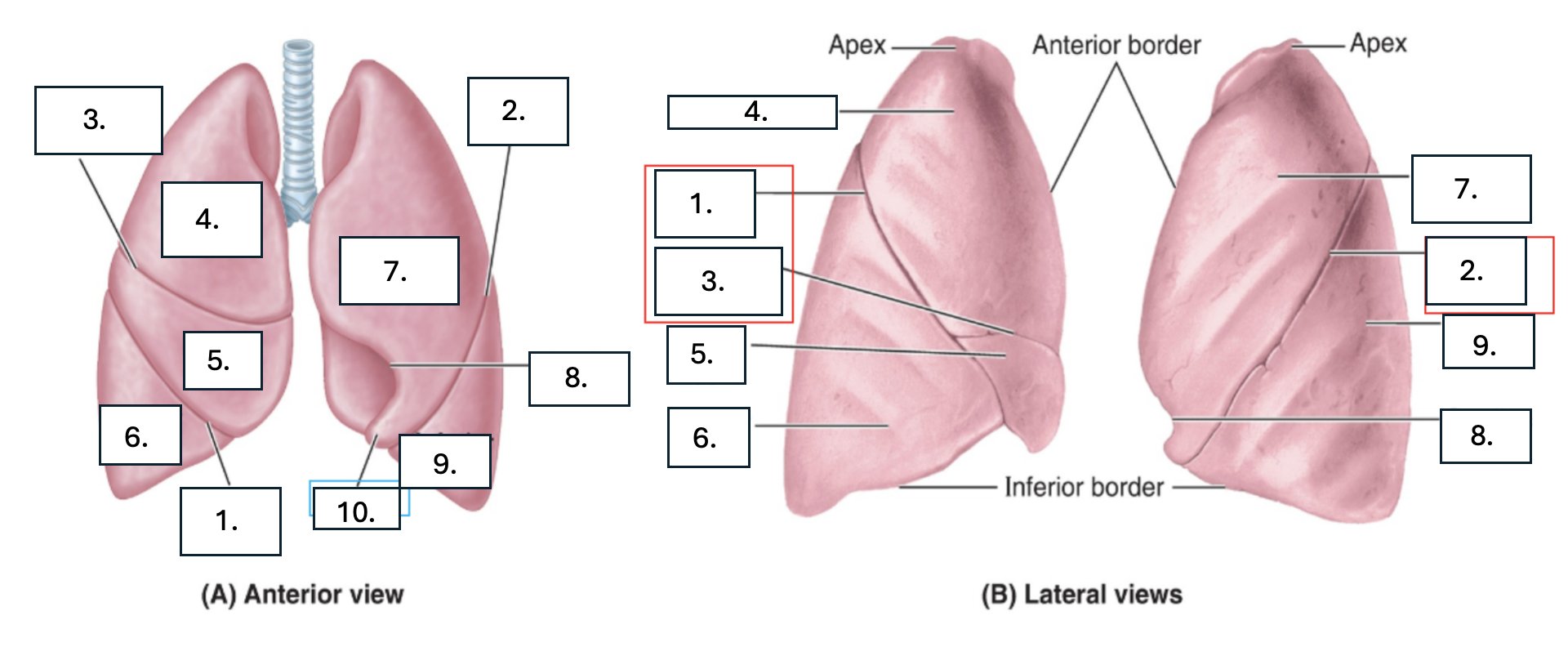
What is number 7?
superior lobe of left lung
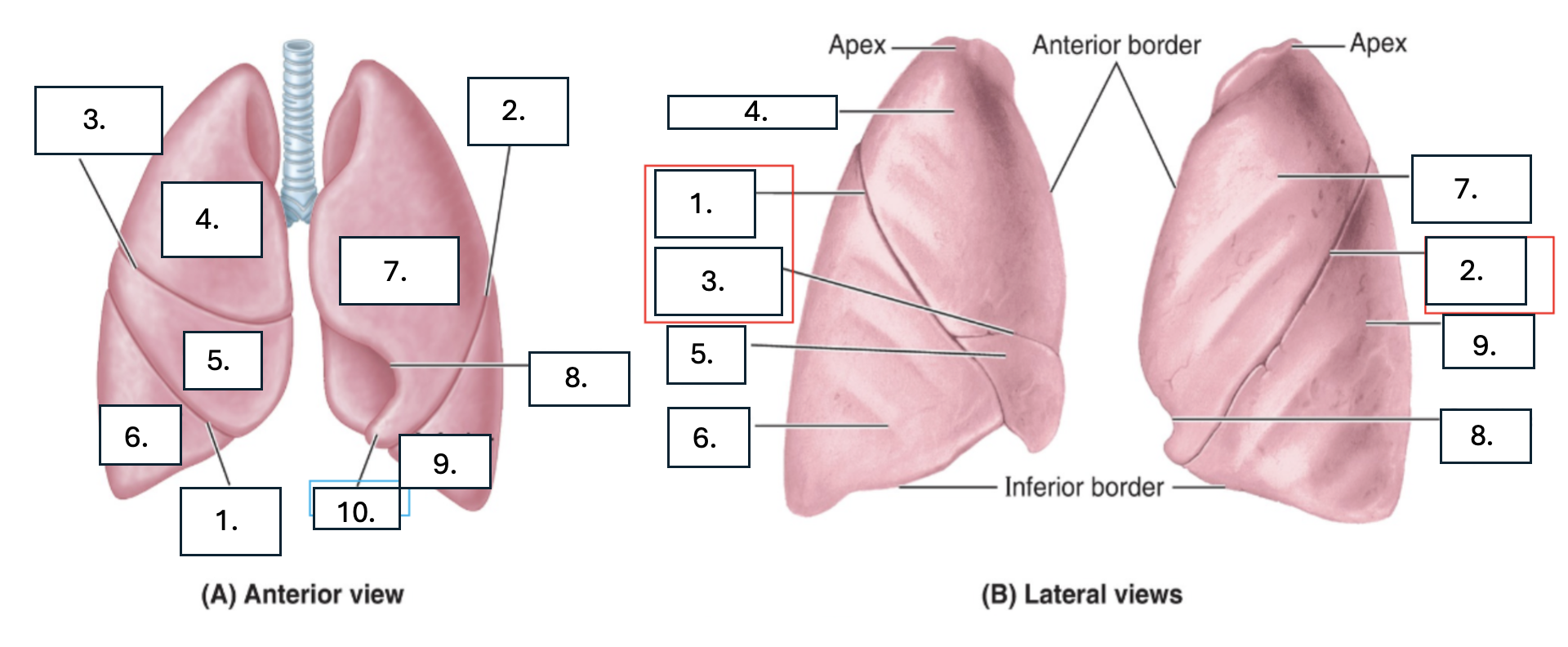
What is number 8?
cardiac notch of left lung
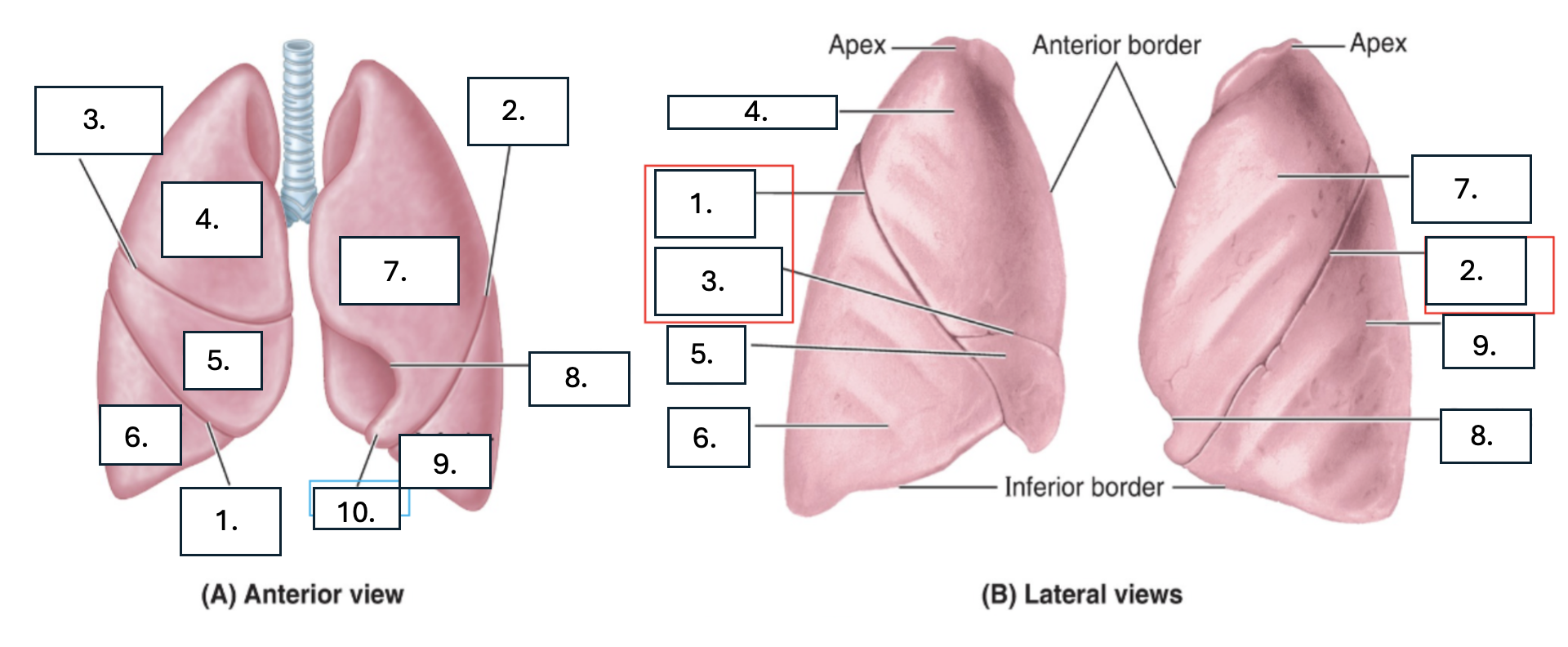
What is number 9?
inferior lobe of left lung
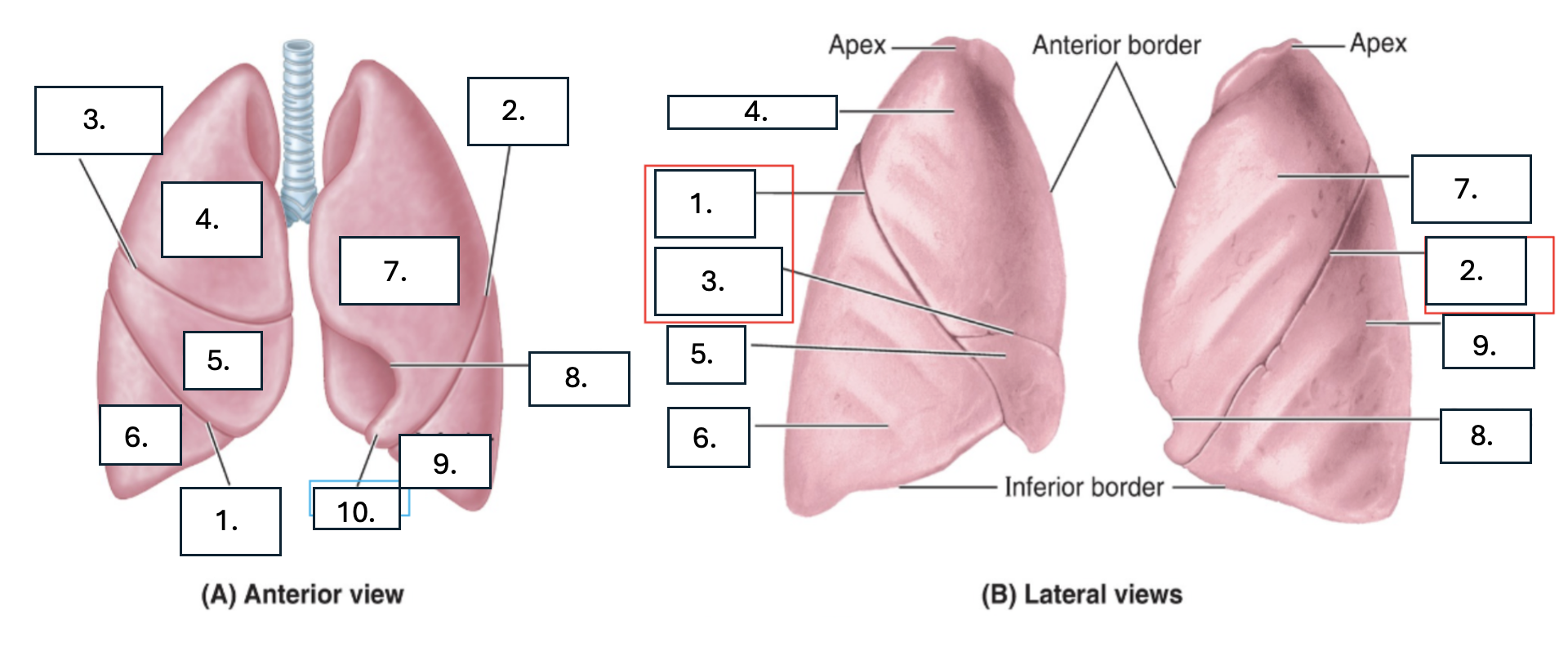
What is number 10?
lingula
where is the phrenic nerve in relation to the vagus nerve?
ventral
Does the pulmonary artery carry oxygenated or deoxygenated blood?
deoxygenated
Does the pulmonary vein carry oxygenated or deoxygenated blood?
oxygenated
What does the phrenic nerve innervate?
diaphragm and parietal pleura
Where is the tracheal bifurcation?
about T4
What is the path of the right main bronchus?
shorter, broader and straight
What is the path of the left main bronchus?
Long and angulated
What is a segmentectomy?
removal of a lung segment
What borders each lung segment?
pulmonary veins
What is at the center of each lung segment?
Tertiary/ segmental bronchus & pulmonary artery
What innervates the parietal pleura?
phrenic nerve and intercostal nerve
What sympathetic nerves innervate the visceral pleura and lungs?
T4 to T6
What parasympathetic nerves innervate the visceral pleura and lungs?
vagus nerve
The diaphragm is relaxed or contracted during inspiration?
contracted
The diaphragm is relaxed or contracted during exspiration?
relaxed
Where is pain in pleuritis of the costal pleura referred to?
Chest wall
Where is pain in pleuritis of the Diaphragmatic pleura or diaphragm referred to?
Shoulder
What is a pleural effusion?
Excess fluid in the costodiaphragmatic angle
What is pneumothorax?
Presence of air in the pleural cavity
Which two bronchopulmonary segments are most vulnerable for aspiration in pneumonia?
Superior segment of right lower lobe and posterior segment of right upper lobe
A 50-year-old male was admitted with breathlessness. He was diagnosed with right heart failure due to cirrhosis of the liver. Imaging showed massive bilateral pleural effusion. The ER physician prepared to perform thoracocentesis. Which of the following would be the safest locations to insert a needle for thoracocentesis of the pleural cavity?
immediately superior to the 10th rib at the midaxillary line
During internal medicine rotations, an OMS-3 student examined a patient with complaints of chronic cough. On auscultation, he found diminished breath sounds on the left side over the left auscultation triangle. A chest x-ray showed a mass in the lung that corresponded with the student’s auscultation finding. Which lobe is likely affected?
Left lower lobe
A penetrating injury of the medial surface of the tagged organ led to severe bleeding. The source of hemorrhage was most likely which of the following? (tag: left lung)
Arch of aorta
What are the contents of the middle mediastinum?
pericardium, heart, great vessel roots
What is the fibrous pericardium a continuation of?
pretracheal fascia of neck
How is the fibrous pericardium attached to the sternum?
sternopericardial ligament
What is the function of the fibrous skeleton of the heart?
Support valves & maintain patentcy, Electrical insulator between atrial & ventricular conduction systems
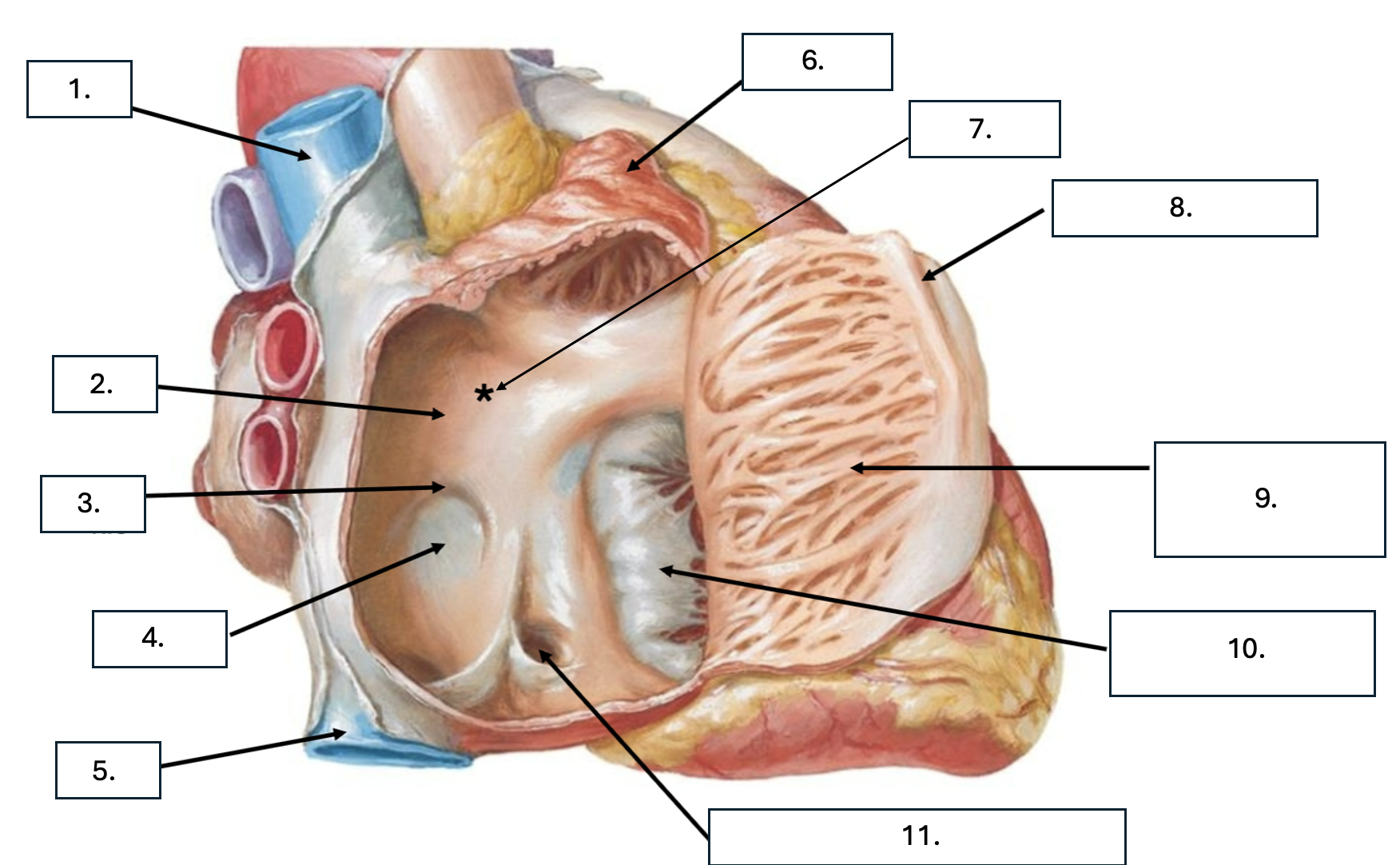
What is number 1?
Superior vena cava (SVC)
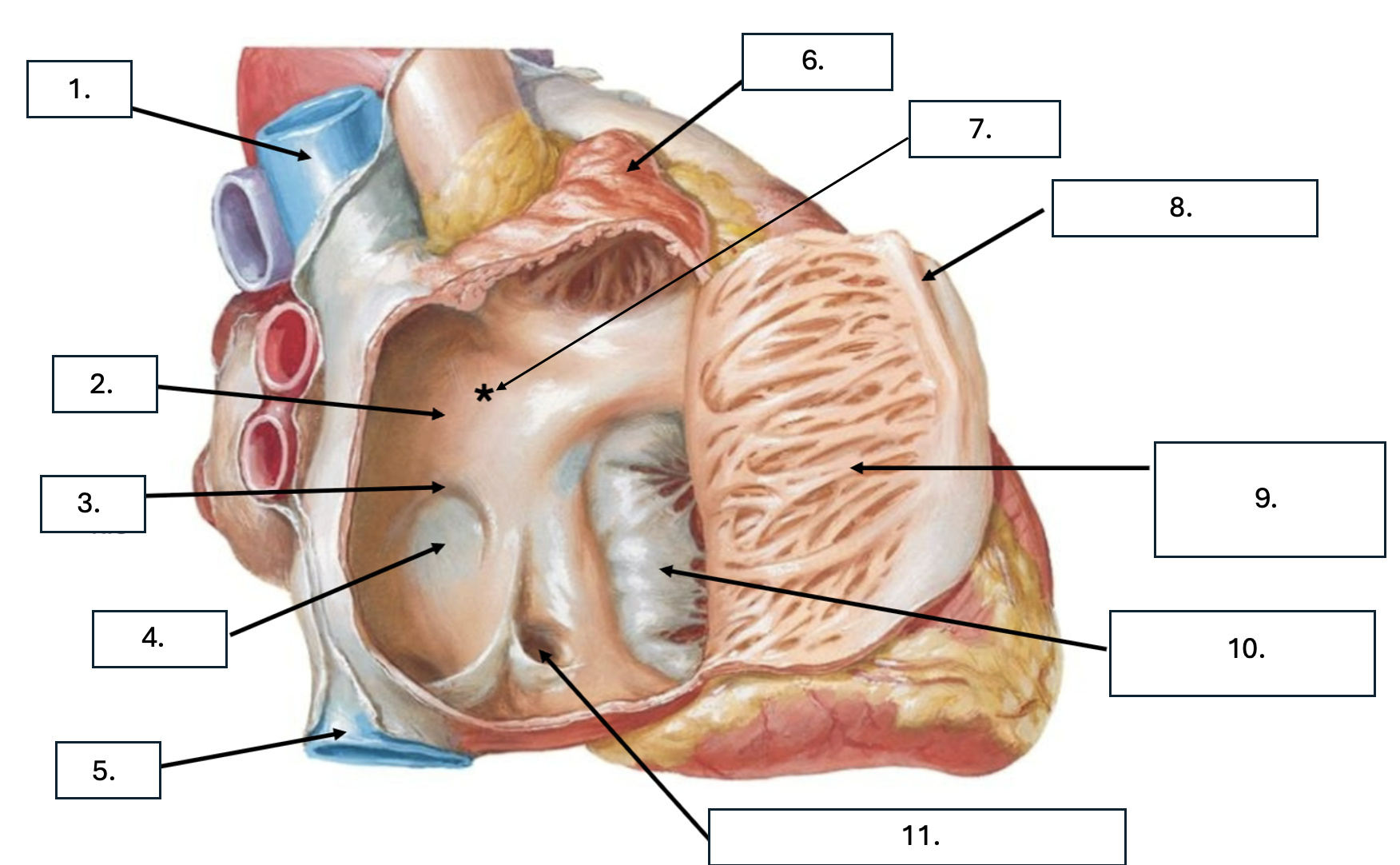
What is number 2?
Interatrial septum
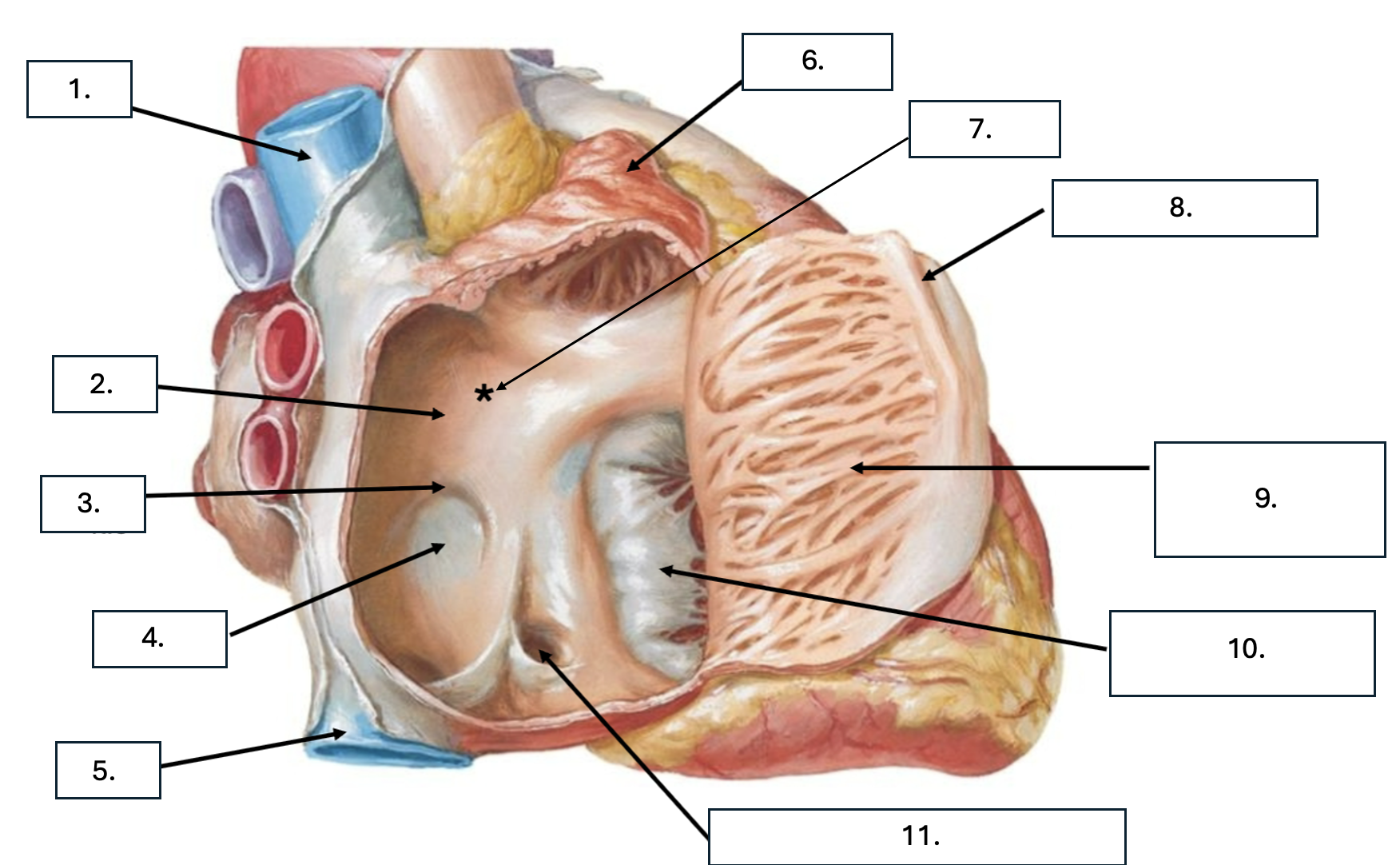
What is number 3?
Limbus of fossa ovalis
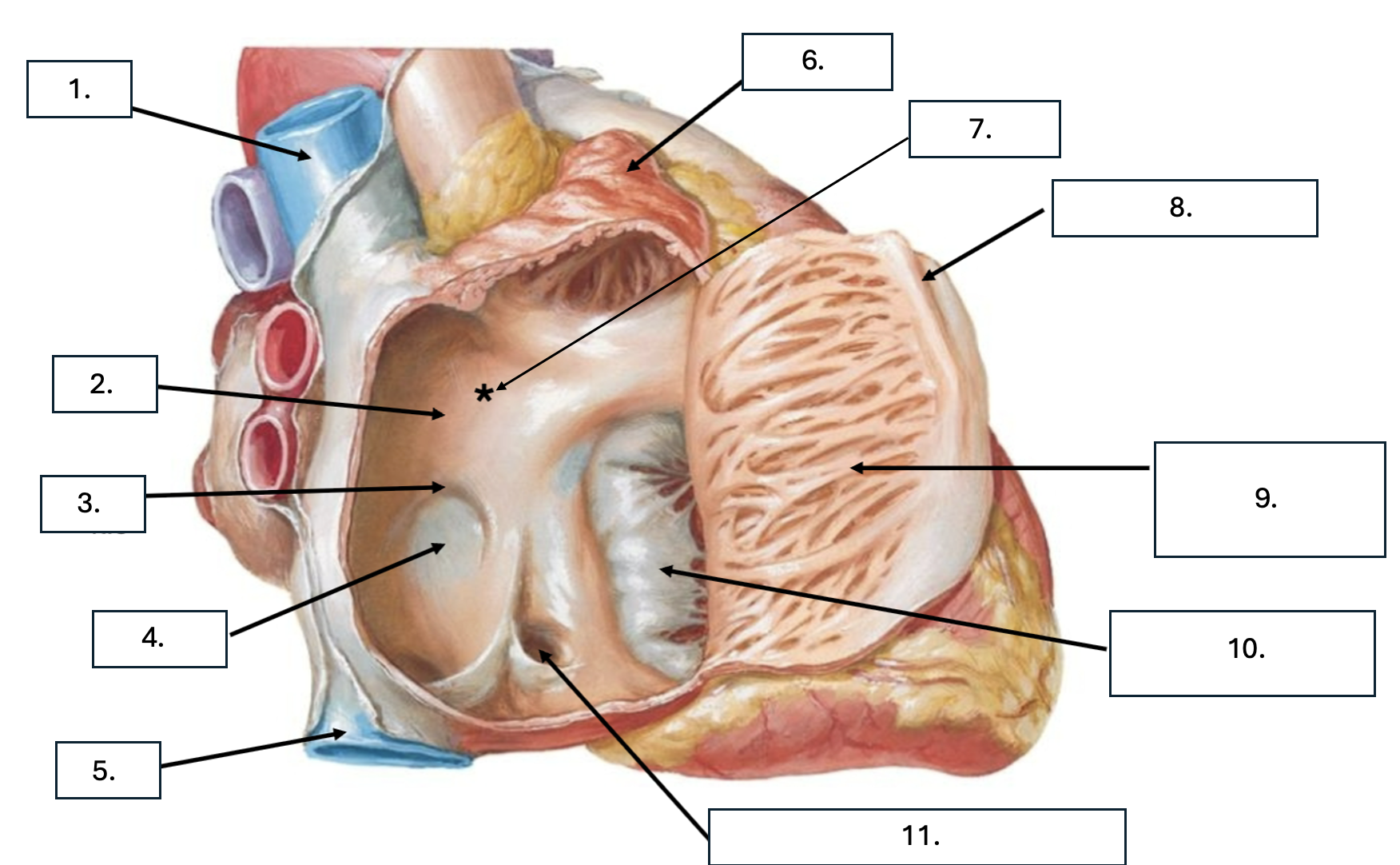
What is number 4?
Fossa ovalis
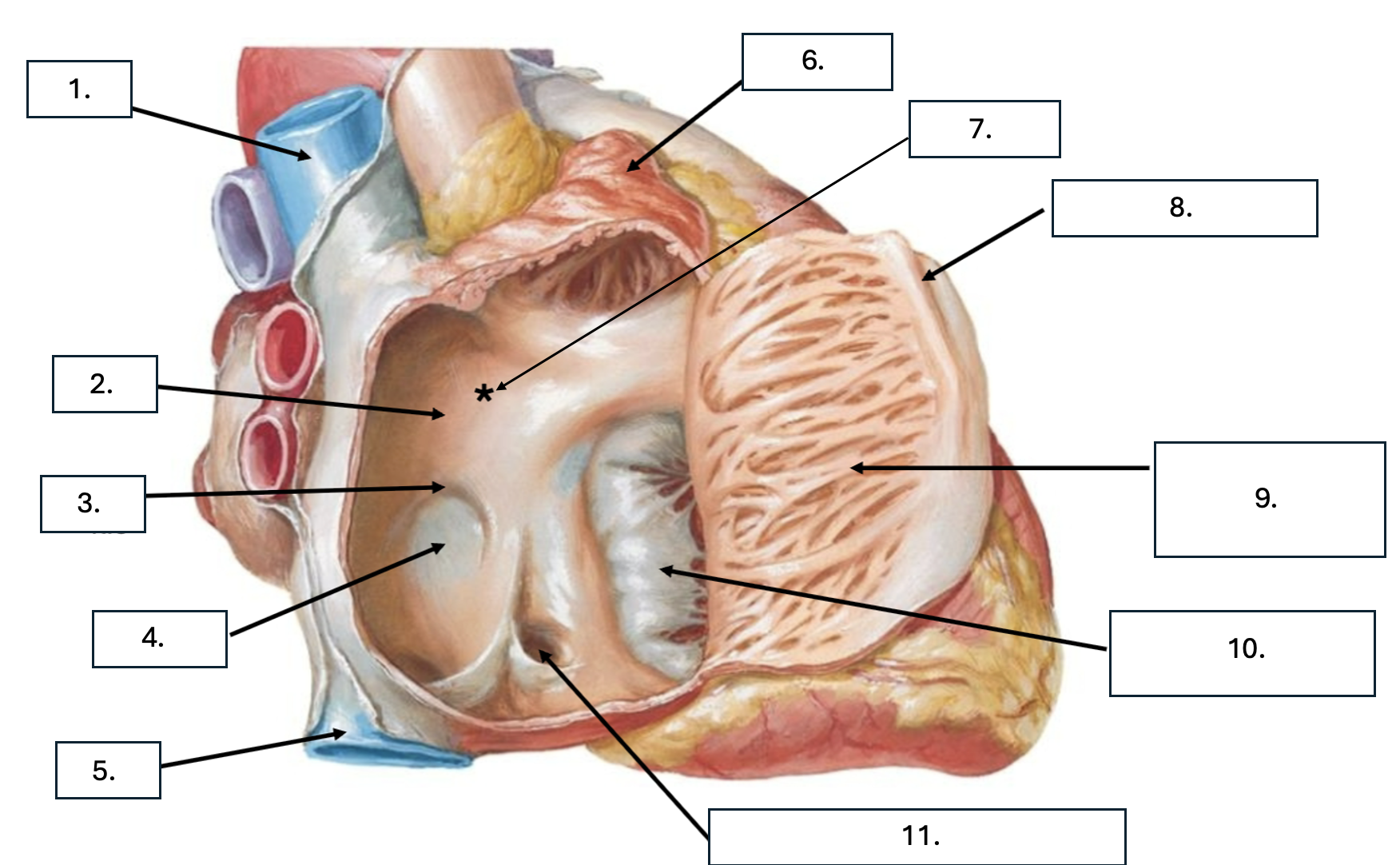
What is number 5?
Inferior vena cava (ICV)
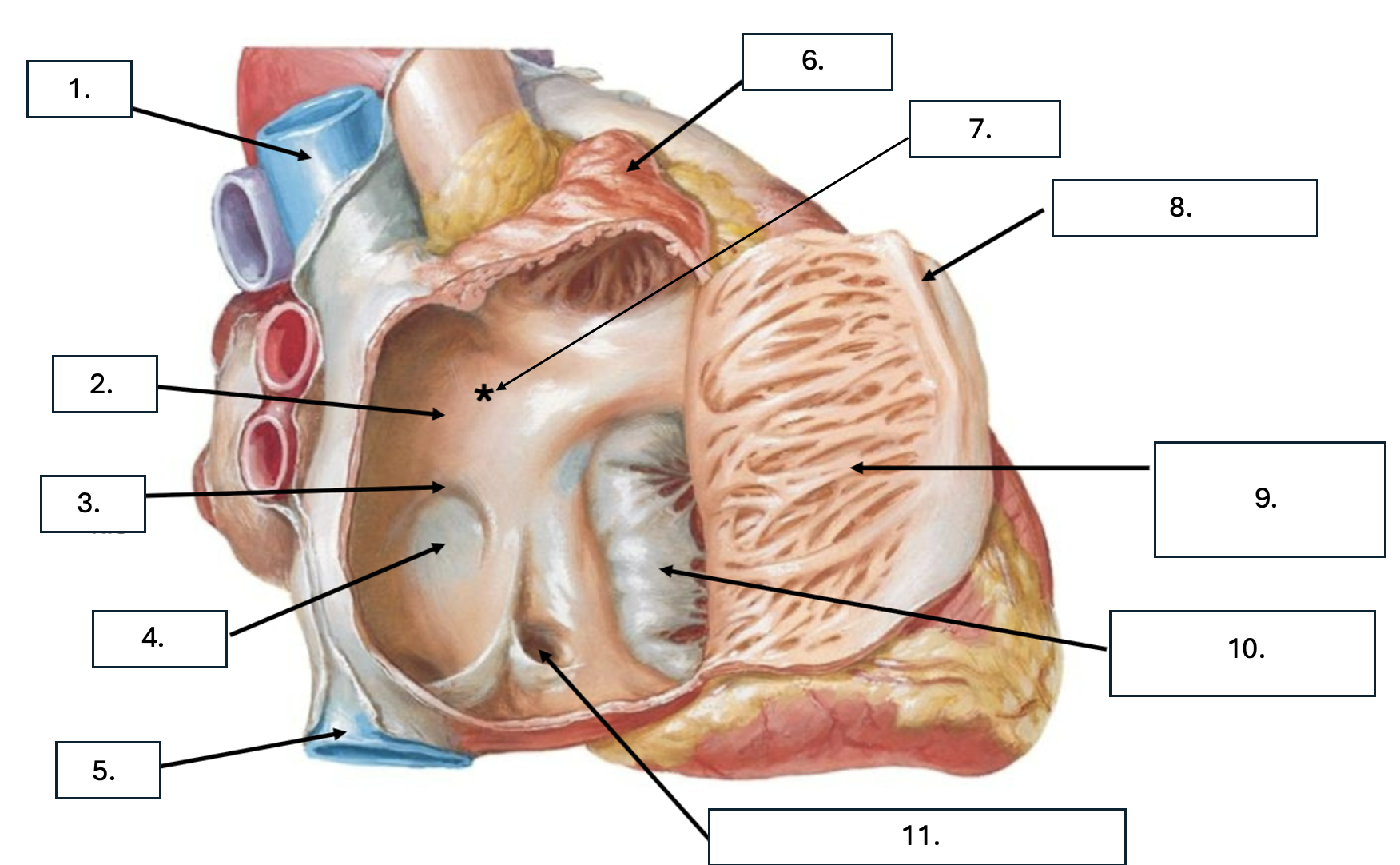
What is number 6?
Right auricle
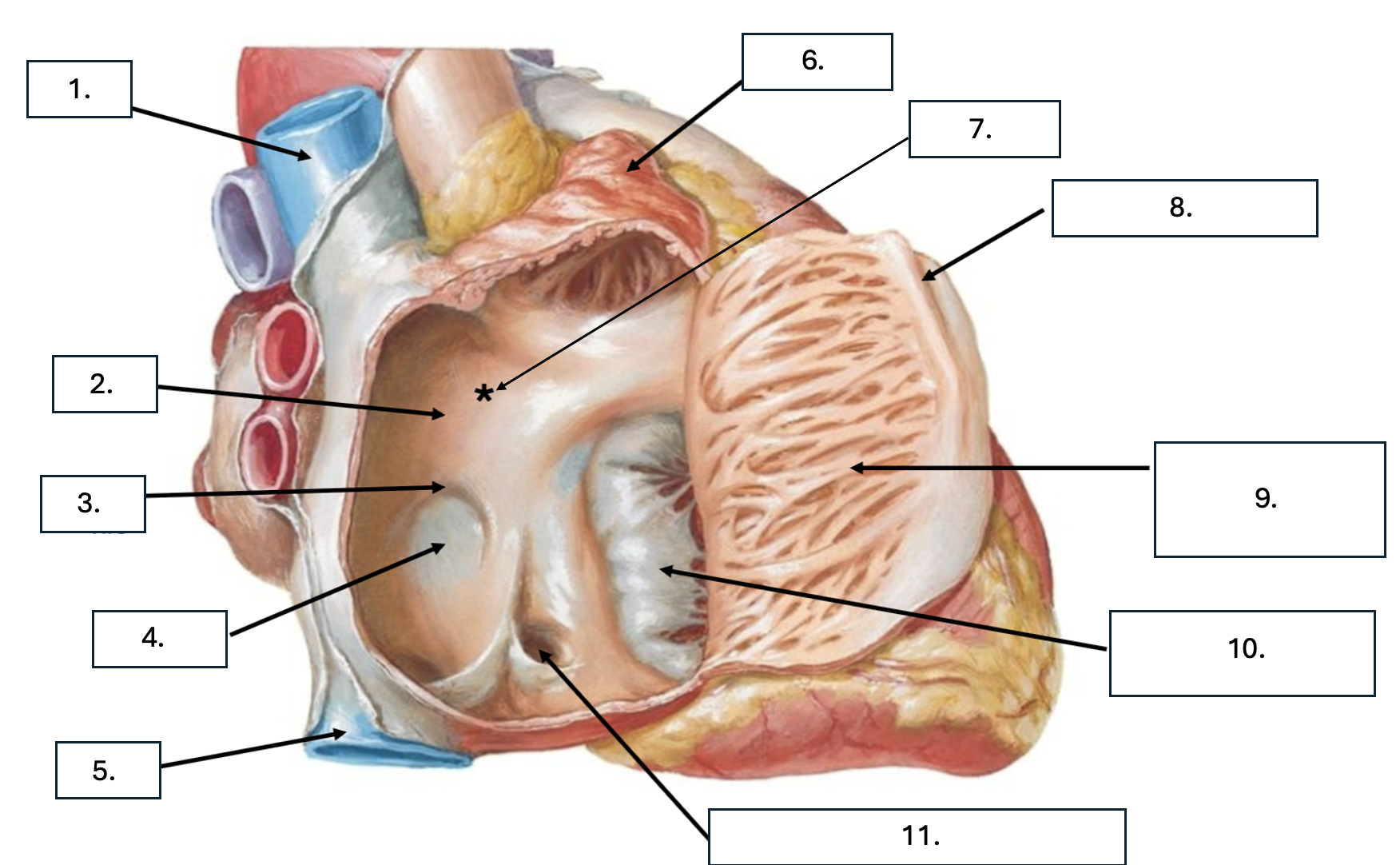
What is number 7?
Sinus venarum
What is sinus venarum?
Smooth tissue of posterior wall of right atrium
What is sinus venarum a remnant of?
sinus venosus