EnvSci 4th CQA Study Set
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

33 Terms
Heat
The key ingredient to generate electricity from coal
Coal
The fuel most commonly used in the US to generate electricity
Fracking
This is not a necessary step for converting coal into electricity
CO2, Mercurry, & Sulfur are released into the atmosphere, respiratory disease is a health problem due to
Using coal to generate electricity
Benefits of using coal as an energy source
low cost electricity, easy to distribute, easy to mine, easy to process
Hydrogen gas
Not an example of a fossil fuel
Oil, Natural Gas, Coal
Examples of fossil fuels
Crude oil, petroleum, and petrochemicals
Materials used to produce pesticides, plastics, soaps, medicines
Fracking or
Hydraulic Fracturing
A method of oil and gas extraction that uses high-pressure fluids to force open cracks in rocks beep underground.
Biofuels
Solid, liquid or gas that produces energy from biological materials. Fuels, such as ethanol or methanol, that are created from the fermentation of plants or plant products.
Nuclear power and Coal
Both of these produce heat which is used to boil water and generate steam used to generate electricity.
Energy which is sustainable or renewable
Energy which is replenished over a short time scale or is available in amounts which cannot be used up.
sustainable energy
Is renewable, has small environmental footprint, and is affordable to the customer
Biomass is reusable but not sustainable because
It creates pollution when burned, reduces the amount of habitat available when it is grown and harvested, will be harvested at greater amounts as world population grows.
Wind energy is imperfect
Wind is not constant, wind turbines can be expensive, wind turbines are noisy and not nice to look at, wind turbines can kill burds
Photovoltaic
Solar energy cells, usually made from silicon, that collect solar rays to generate electricity.
geothermal energy
Energy from steam or hot water produced from hot or molten underground rocks.
water pollution
the addition of any substance that has a negative effect on water or the living things that depend on the water
Bioplastics
plant-based plastics
nuclear energy
Energy released when an atom is split (fission) or combines with another to form a new atom (fusion)

Nuclear Fission
a nuclear reaction that occurs when a neutron strikes the nucleus of an atom and breaks it into two or more parts
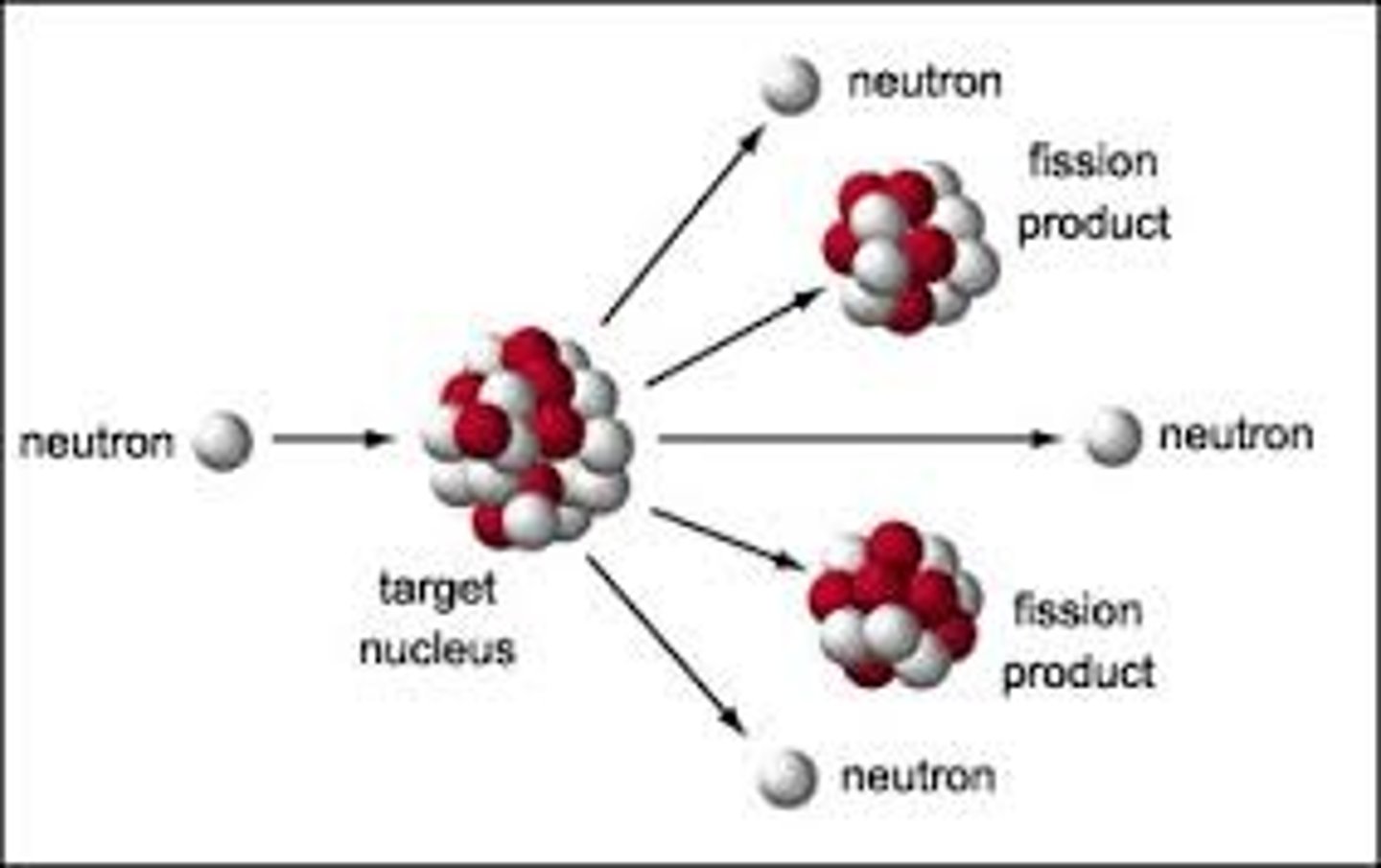
Radioactive
atoms that spontaneously emit subatomic particles and/or energy

radioactive half-life
the time it takes for half of the radioactive isotopes in a sample to decay to a new form

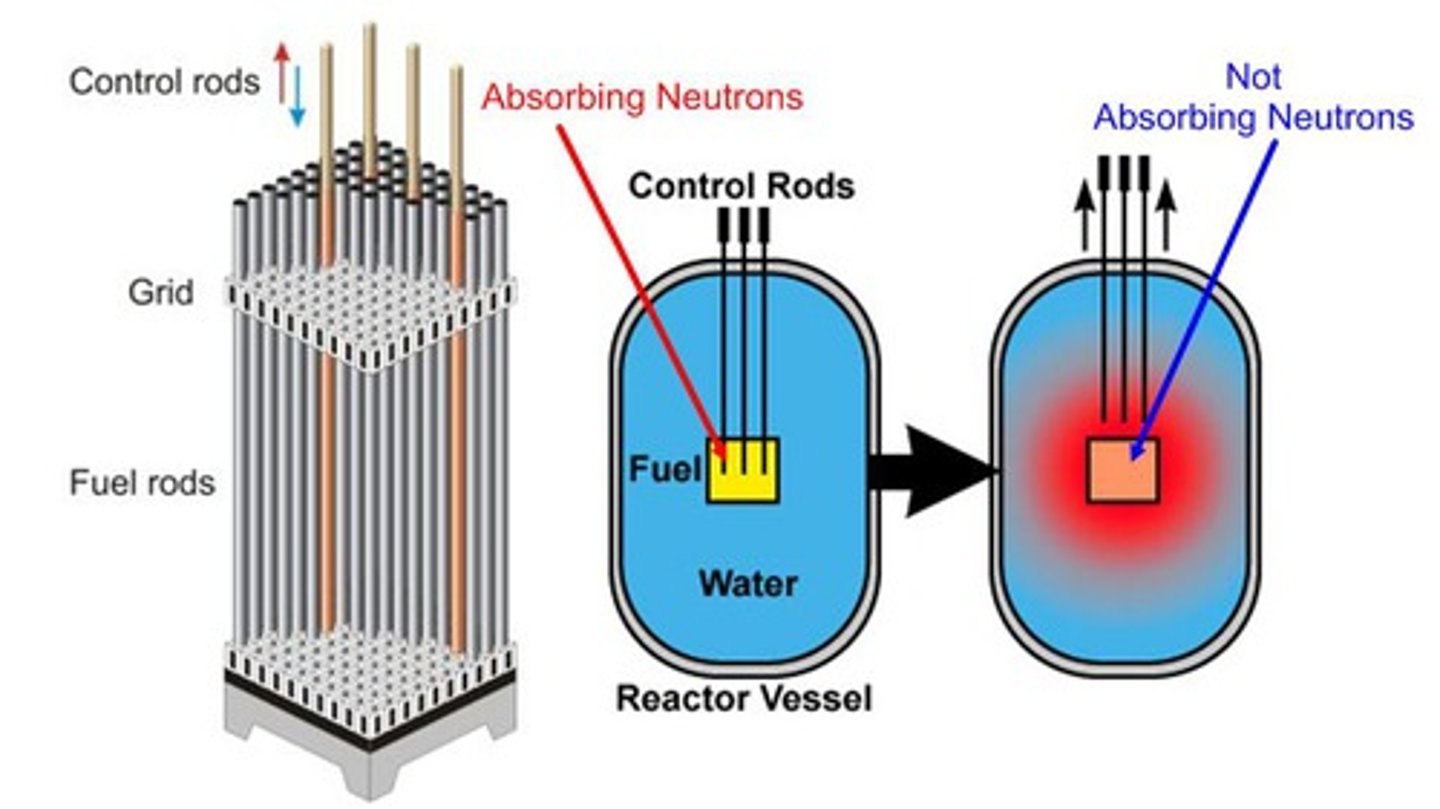
fuel rods
hollow metal cylinders filled with uranium fuel pellets for use in fission reactors

control rods
rods that absorb neutrons and slow the fission chain reaction
Nuclear Fusion
Process of joining atoms resulting in the release of energy
Nuclear waste
radioactive waste material produced by nuclear power plants
nuclear chain reaction
the continued process of atoms splitting and releasing neutrons that trigger more atoms to split
Nuclear Reactor
consists of a core, control rods, moderator, steam generator, turbine, containment building.
Chernobyl
nuclear power plant that had an explosion in 1986 & released radioactive materials into the air
Heat
Nuclear power plants use this to boil water and produce steam to generate electricity
"Three E's" of sustainability
Environment (conservation efforts)
Economy (profits)
Equity (fair distribution of resources)
The greatest amount of electricity in the United States is generated using ____________________.
Coal