Petrology
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Petrology
A branch of geology dealing with various aspects of rocks such as their formation, classification and occurrence
Importance to Civil Engineers
A professional civil engineer has to deal with rocks during most of his work involving design and construction of civil engineering protects such as buildings, roads, highways, tunnels damn and reservoirs.
Igneous Rocks
All rocks that formed an originally hot molten material through the process of cooling and crystallization. Very high temperature and molten state are two very important conditions for the original material
Magma
The hot molten material occurring naturally below the surface of the Earth. It is called lava when erupted through volcanoes. Igneous rocks are formed.
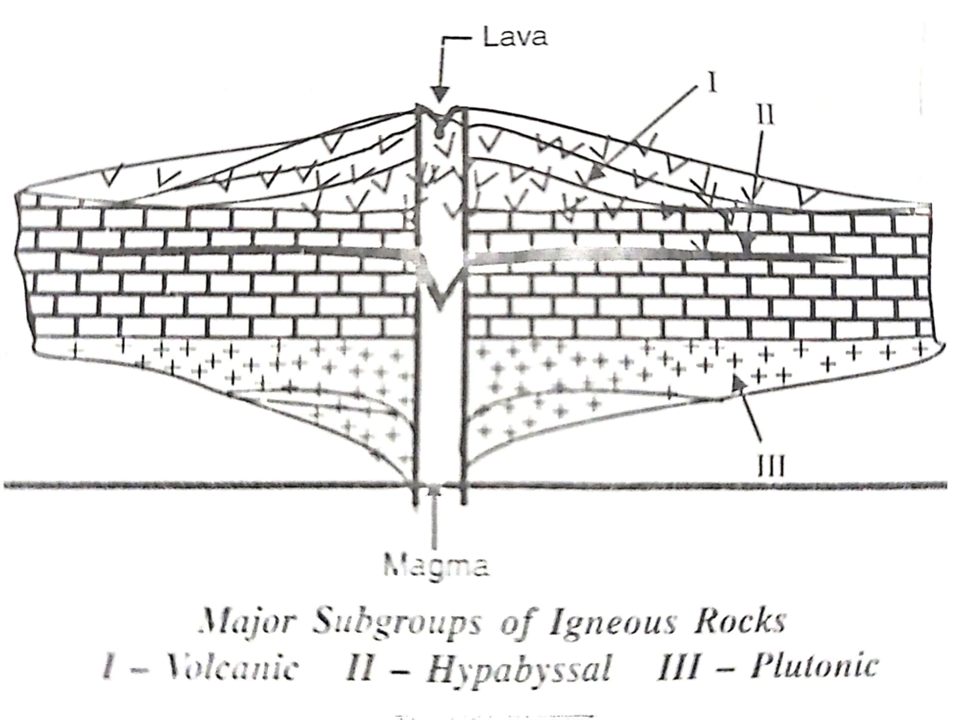
Three sub-groups of Igneous Rocks
Volcanic Rocks, Plutonic Rocks, Hypabyssal Rocks
Volcanic Rocks
these are igneous rocks formed on the surface of the Earth by cooling crystallization of lava erupted from volcanoes. Since lava cools down at a very fast rate(compared to magma), the grain size of the crystals formed in these rocks is very fine.
Plutonic Rocks
These are igneous rocks formed at considerable depths generally between 7-10 km below the surface of the Earth. Because of a very slow rate of cooling at these depths, the rocks resulting from magma are course grained.
Hypabyssal Rocks
These are igneous rocks formed at intermediate depths, generally up to 7 kms below the surface of the Earth and exhibit mixed characteristics of volcanic and plutonic rocks.
Major Subgroups of Igneous Rocks
Igneous Rocks Examples

Sedimentary Rocks
also called secondary rocks. This group includes a wide variety of accumulation, compaction and consolidation sediments.
Sediments
are fragments of rock that have been broken down as a result of weathering(wind, ice, running water, etc.)
Boulder
A rock larger than 10.08” in diameter
Cobble
A clast of rock larger than 2.52-10.08”
Gravel/Pebble
chipped or rounded rock fragments that typically range in diameter from about 0.12-2.51”
Sand
a loose granular material that results from the disintegration of rocks. Typically around 0.002-0.12”
Silt
a granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. typically around 0.00008-0.002”
Clay
a stiff fine-grained earth, typically yellow, red, or bluish-gray in color and often forming an impermeable layer in the soil. its diameter is lower than 0.002mm
Metamorphic Rocks
rocks that changed as a result of exposure to intense heat and pressure
Contact Metamorphism
Heat from magmatic source travels through the body of the surrounding rocks that undergo structural and mineralogical changes depending upon their original composition and intensity of the heating effects
Example of Contact Metamorphism
Limestone surrounding a magma chamber being turned into marble
Regional Metamorphism
this involved development of large-scale changes in the structural and chemical constitution of the pre-existing rocks and under the combined action of pressure and temperature
Example of Regional Metamorphism
Shale to Gneiss
Quartzite
Are granular metamorphic rocks composed chiefly of fine grains of quartz. Originally a sandstone just with the added heat and pressure.
Marble
is essentially a granular metamorphic rock composed chiefly of recrystalized llimestone. It is characterized by a granulose tecture but the grain size shows considerable variation in different varieties
Slate
is a product of low-grade regional metamorphism of argillaceous rocks like clays and shales
Schist
the constituent flaky and platy minerals are mostly arranged in parallel or sub parallel layers or bands
Gneiss
is a crystalline foliated metamorphic rock charaterized by segregation of minerals into layers or bands of contrasting color, texture and composition. It has alternating layers of light and dark minerals