Neuro and Skull
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
What is the signalment for atlanto-axial subluxation?
Toy breed dogs less than 1 year old
What is the pathogenesis of atlanto-axial subluxation?
Dens agenesis/hypoplasia
Ligament agenesis
Dens fracture
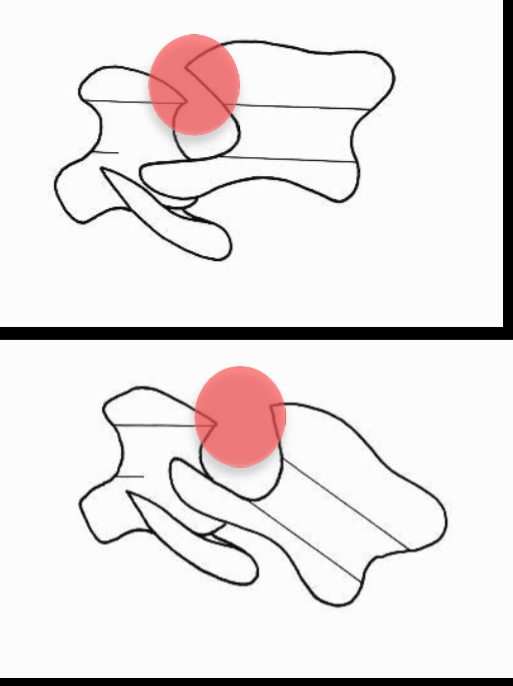
Atlanto-axial subluxation
What are the radiographic findings of an atlanto-axial subluxation?
Caudodorsal angulation of C2
Increased interarcuate space
Small or absent dens
What can help you identify a small or absent dens in a atlanto-axial subluxation case?
Oblique lateral view or MILD flexed lateral view
When taking a radiograph for a atlanto-axial subluxation what do you need to be cautious with?
Neck flexion
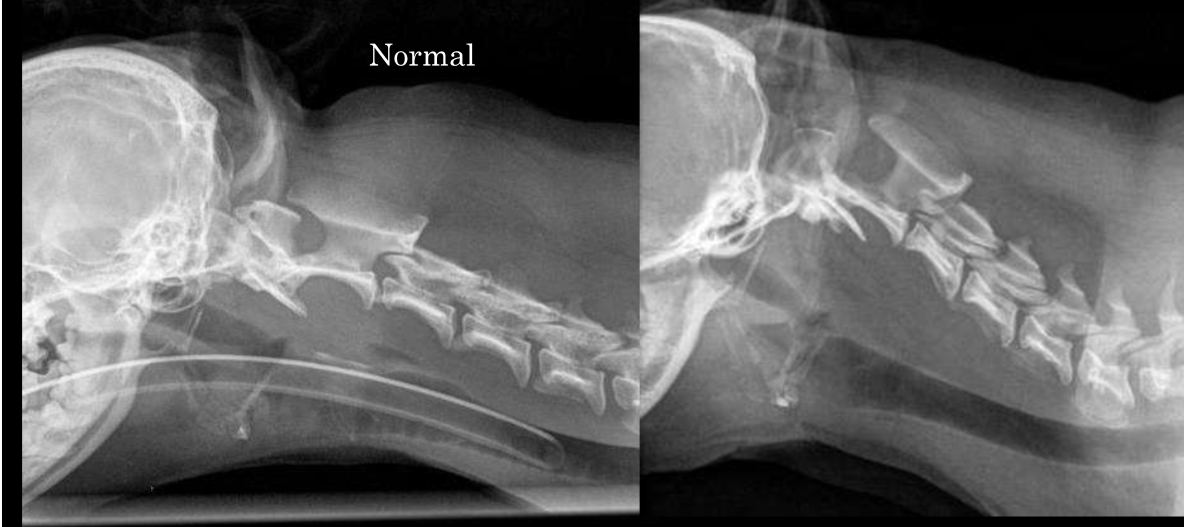
Atanto-axial instability
Atlanto-axial instability due to no dens being present
How do you treat atlanto-axial instability?
Surgically to add pins and plates to stabilize
What are the degenerative spinal conditions?
Spondylosis
Spondyloarthrosis
Disc degeneration
What is spondylosis?
Degenerative disease of the spine
What happens during spondylosis?
Periarticular new bone ventral/lateral aspect of adjacent vertebral bodies
I/V foramina can be impinged
What is the degree of spondylosis?
Varies and can progress to fusion/bridging spondylosis
What is essentially degenerative joint disease around the vertebral joints?
Spondylosis
Describe primary spondylosis?
Not clinically significant unless it progresses to nerve root involvement
What does primary spondylosis at lumbosacral region indicate?
Cauda equina
What can spondylosis be secondary to?
Cervical vertebral instability (Wobblers)
IVDD
Discospondylitis
Trauma
Spondylosis
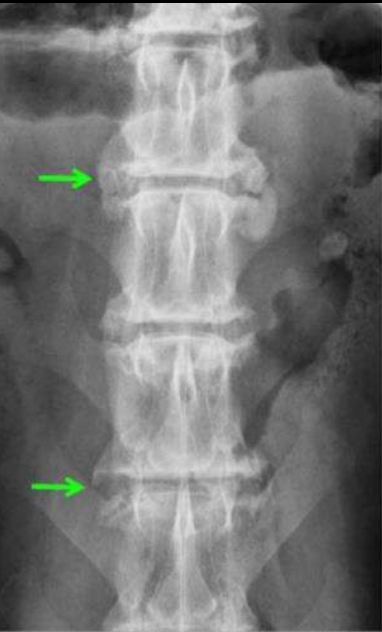
Spondylosis
What is spondylarthrosis?
DJD of articulation facets
What is the signalment for spondylarthrosis?
Older dogs
What can spondylarthrosis progress to?
Extend to involve the IVF or impinge on spinal cord
What can IVDD be?
Traumatic or degenerative
What animals get degenerative IVDD?
Young chondrodysplasia breeds and older other breeds
Why should you do for an IVDD neurological exam?
To neurolocalize
What is Hansen Type 1?
Extrusion
What is Hansen Type II?
Protrusion
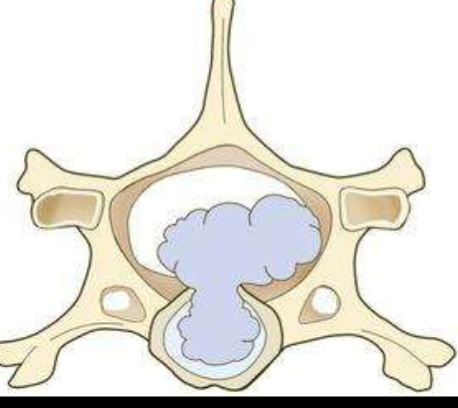
Hansen Type 1 IVDD
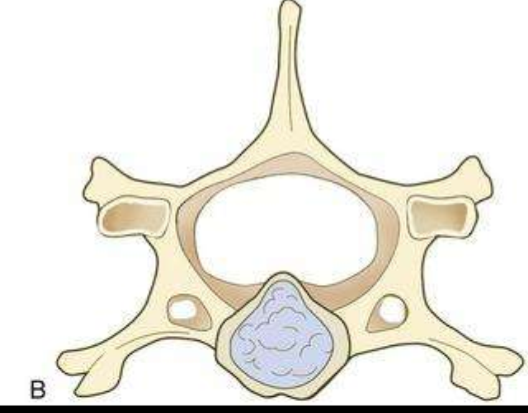
Hansen Type II IVDD
What are the radiographic findings of IVDD?
Narrowing of the IV disc space
Narrowing of articular facet joint space
Small IV foramen
Increased opacity in intervertebral foramen or spinal cord
What is disc mineralization indiciative?
Degeneration
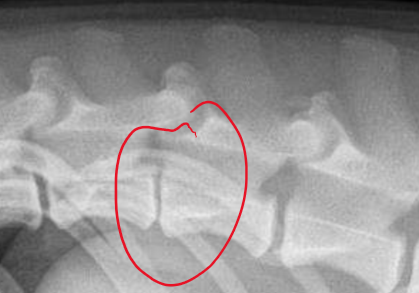
IVDD
What does a mineralized disc not indicate?
Disc herniation
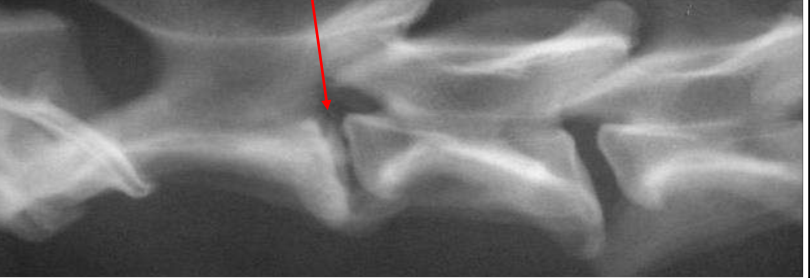
IVDD
T/F anesthesia is necessary to critically evaluate disc spaces?
True
What dogs typically get lumbosacral disease?
Large breeds
What are the C/S of lumbosacral disease?
Pain on HQ extension/manipulation
Struggling to get up
Cadua equina
Fecal/urinary incontinence
How do you take a radiograph to diagnose lumbosacral disease?
Flexed, hyperextended, and neutral lateral radiographs
What are the radiographic findings of lumbosacral disease?
Narrowed LS space
End plate sclerosis
T/F LS spondylosis is often seen without C/S?
True
What are the two inflammatory conditions in the spine?
Discospondylitis
Spondylitis
What is discospondylitis?
Infection of the intervertebral discs and end plates
What are the common causes of discospondylitis?
Bacteria dn fungus
How do you diagnose discospondylitis?
Radiograph whole vertebral column and repeat every 2-3 weeks to monitor healing
Why can discospondylitis present at multiple sites?
The bacteria or fungus spreads hematogenously
What is the earliest sign of discospondylitis?
Decreased width of i/v disk space (will increase in width shortly after)
What happens during the early stage of discopsondylitis?
Increased width if i/v disc spaces a.r.o lysis of end plates
Sclerosis of adjacent vertebral bodies
What happens in the late stage of disconspondylitis?
Spondylosis
Lytic area fills up with bone causing fusion
What are some complications with discospondylitis?
Spinal cord compression
Empyema
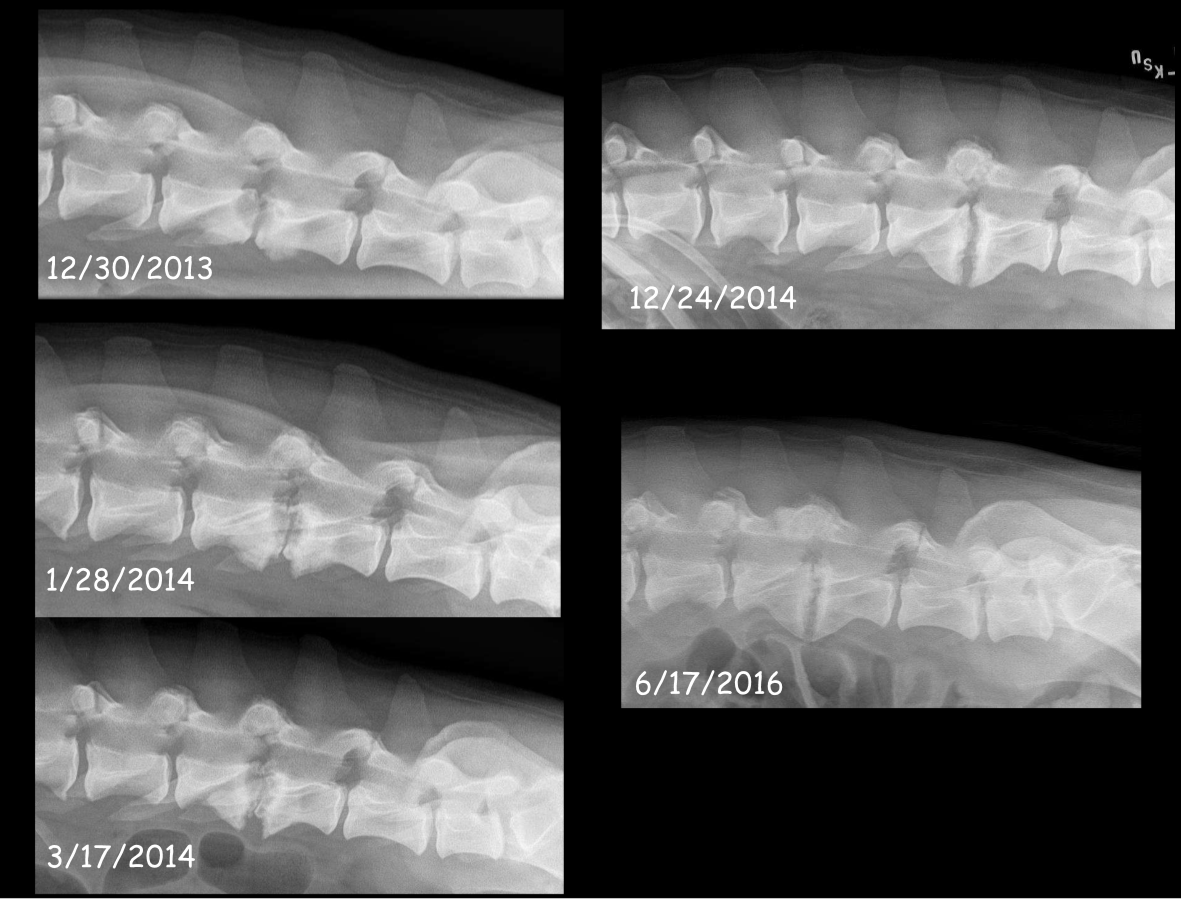
Progression of diskospondylitis
What is spondylitis?
Inflammation/infection of the vertebral body
T/F spondylitis involves the vertebral disk
False
What are the causes of spondylitis?
Bacteria
Parasite
Foreign bodies (grass awn)
Metastatic neoplasia
What neoplasm usually causes spondylitis?
Prostate concer
What does spondylitis look like usually?
Ventral periosteal reaction
Brushlike/spiculated
Lamellar
Solid
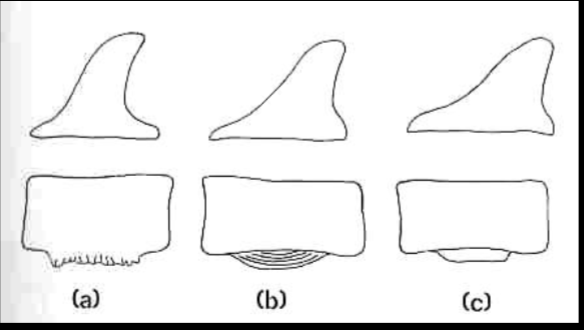
Spondylitis
What are the common indications for a skull radiograph?
Dentals, aural, nasal and frontal sinuses, TMJ, Trauma to skull, neoplastic condition
What doe skull radiology have limited value in?
Intracranial dz
What is the trick to taking skull radiographs?
Be perfectly symmetrical
What is the problem with acute aural injury on a radiograph?
There are no changes
What chronic changes in the ears can be seen w/ a radiogrpah?
Mineralization of ear canals
Narrowing of ear canals
Thickening of tympanic bulla
Lysis of tympanic bulla
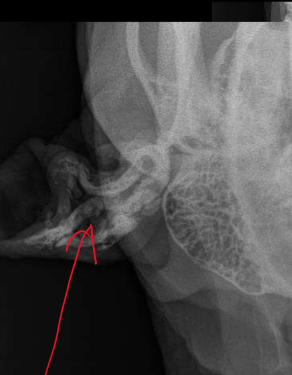
What is happening and important
Mineralization of ear canals indicated chronic otitis externa
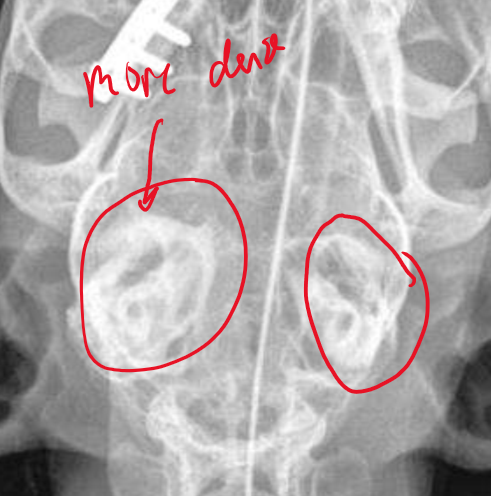
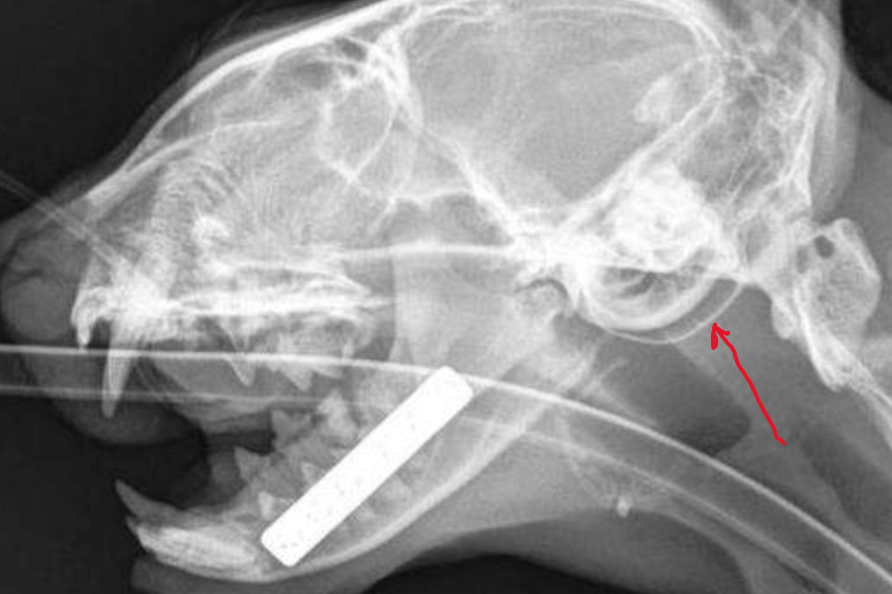
What is happening and importance?
Chronic otitis media with thickened bulla
What is happening and importance?
Chronic otitis media with thickened bulla
What are the causes of nasal disease?
Neoplasia
Infection
Foreign body
Idiopathic
What are the C/S of nasal disease?
Stertor/stridor
Nasal discharge
Facial deformity
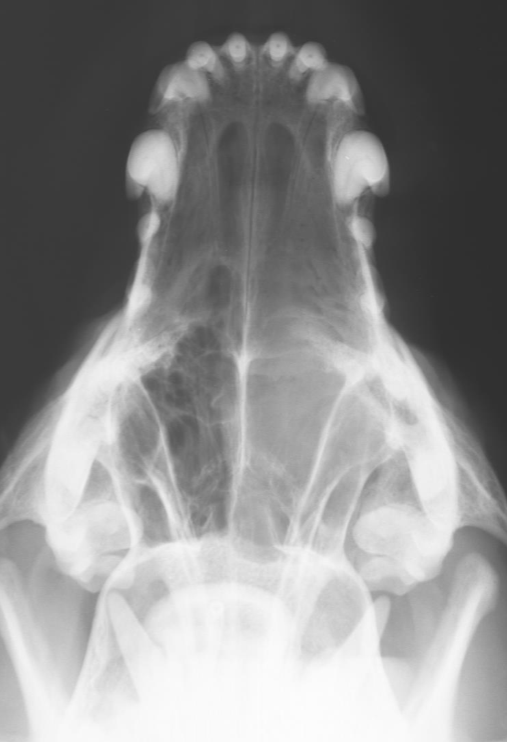
Fungal rhinitis
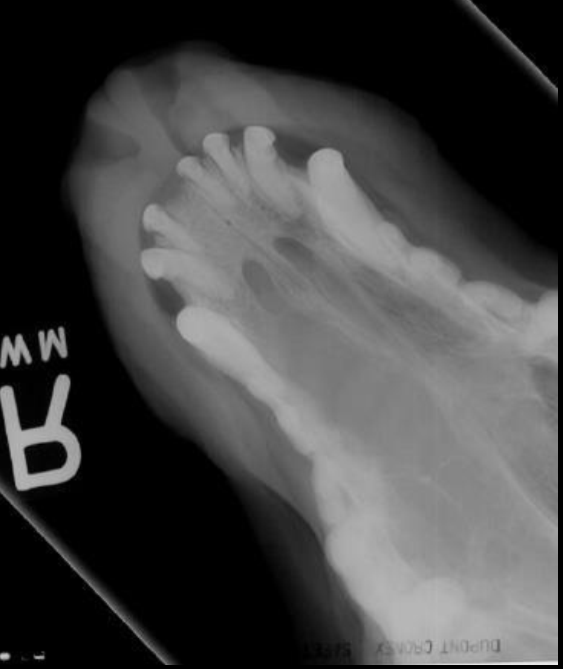
Nasal adenocarcinoma
How do you eliminate superimposition of the mandible?
Put dog on its back
Shoot from above the mandible
Why are L3 and L4 more common to get migrating grass awns than other vertebra?
They are attached to the diaphragm
What happens to the ventral surface of the vertebral body with spondylitis?
It becomes flattened or convex due to periosteal reaction
What is the ventral surface of a normal vertebral body?
Concave
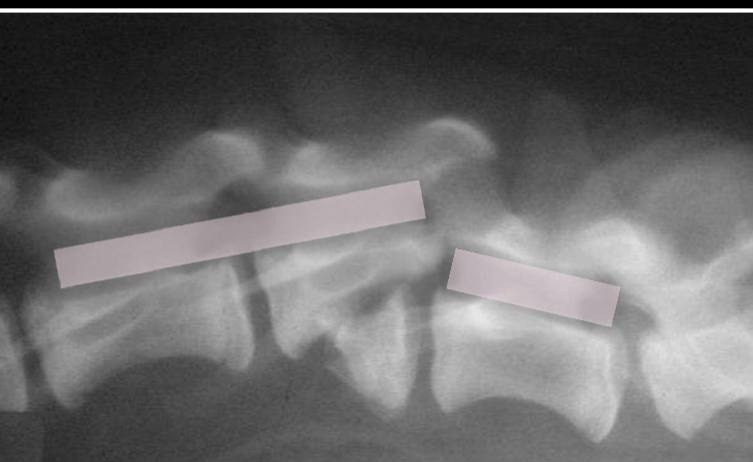
Fracture luxation
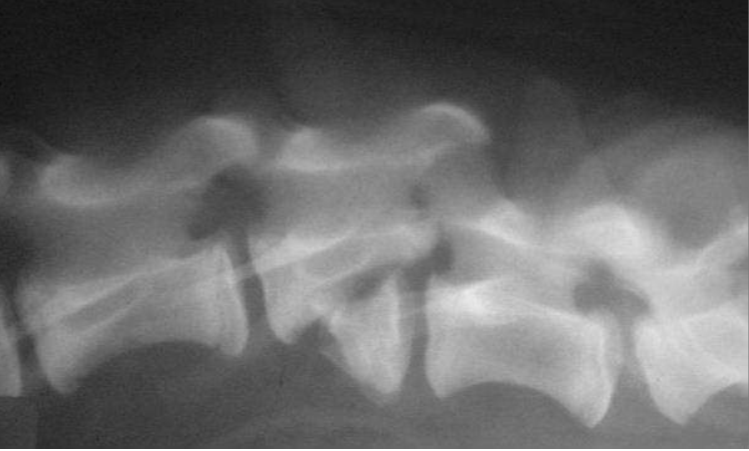
Fracture luxation
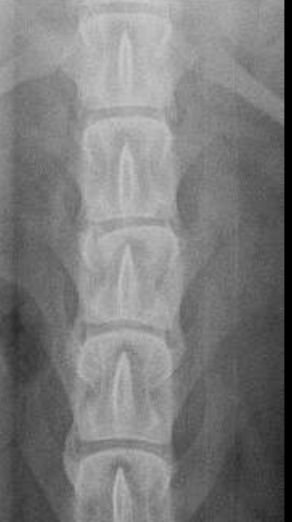
Compression fracture