Imaging of the canine and feline reproductive tract
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
what are the principles of ultrasound waves (physics)?
Wavelength, frequency, velocity
What is wavelength?
distance travelled by a sound wave in 1 cycle (millimeters)
what is frequency?
rate per second of a vibration constituting a wave (Hz/MHz/GHz)
adjust to select for depth and axial/lateral resolution
What is the relationship between frequency and resolution? frequency and attenuation?
higher frequency = lower penetration
resolve superficial lesions better
higher frequency = higher attenuation in tissues
What is velocity?
the rate at which sound travels through an acoustic medium
what are the types of transducers

what are some uses for 10-17 MHz frequency?

what are some uses for 6-10 MHz frequency?
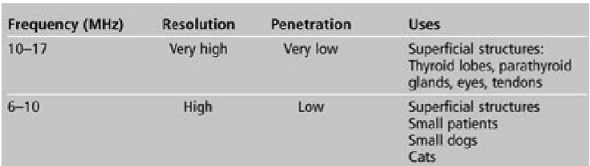
what are some uses for 5 MHz frequency?
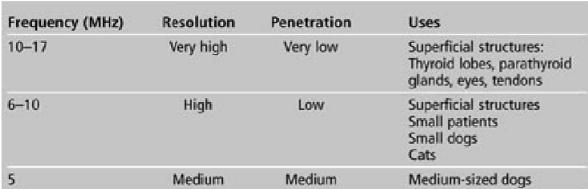
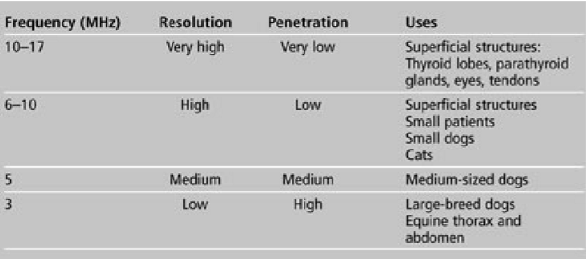
what are some uses for 3 MHz frequency?
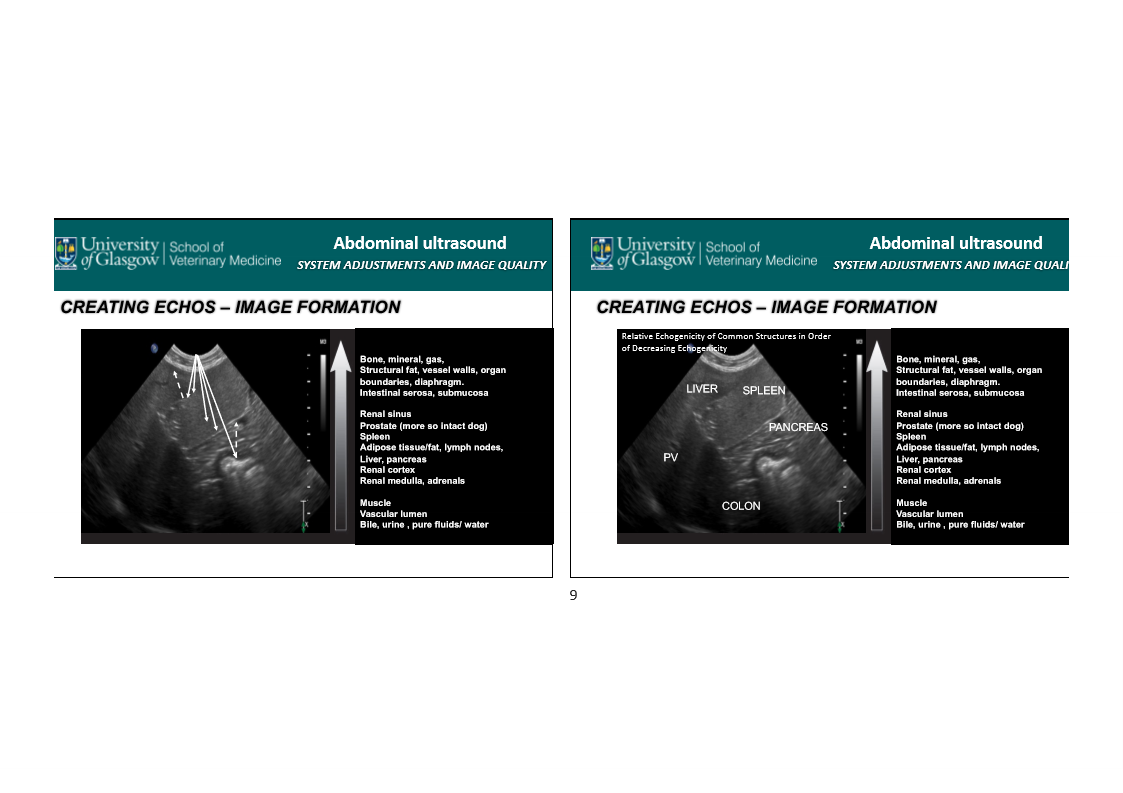
Reminder for shades of tissues in ultrasound
Where is resolution highest in proximity to the probe?
The near field (fresnel zone)
What is the far field referred to as?
frauhofer zone
what is the transition point of a beam?
point where near field ends, divergence begins becoming far field
What does depth control?
the length of the long axis (cm tissue imaged)
What does gain control?
determines amplification level of echoes to compensate for attenuation of tissues
increases brightness
What does time gain compensation (TGC) control?
reduces superficial amplification or increases depth amplification
varies from animal to animal and even from region to region on animal
what does adjusting the focus control?
beam electronically focalized to reduce diameter at specific depth, increasing capacty of the system to depic small structures along the y (lateral) and z (slice thickness) planes
How do you position for an abdominal radiograph?
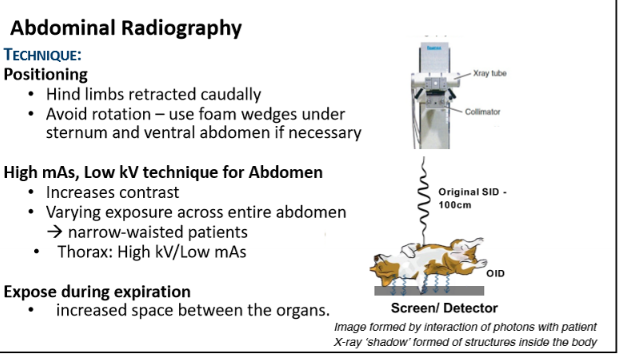
helpful radiograph graphic

what are some abnormalities you can see in patients on an abdominal radiograph?
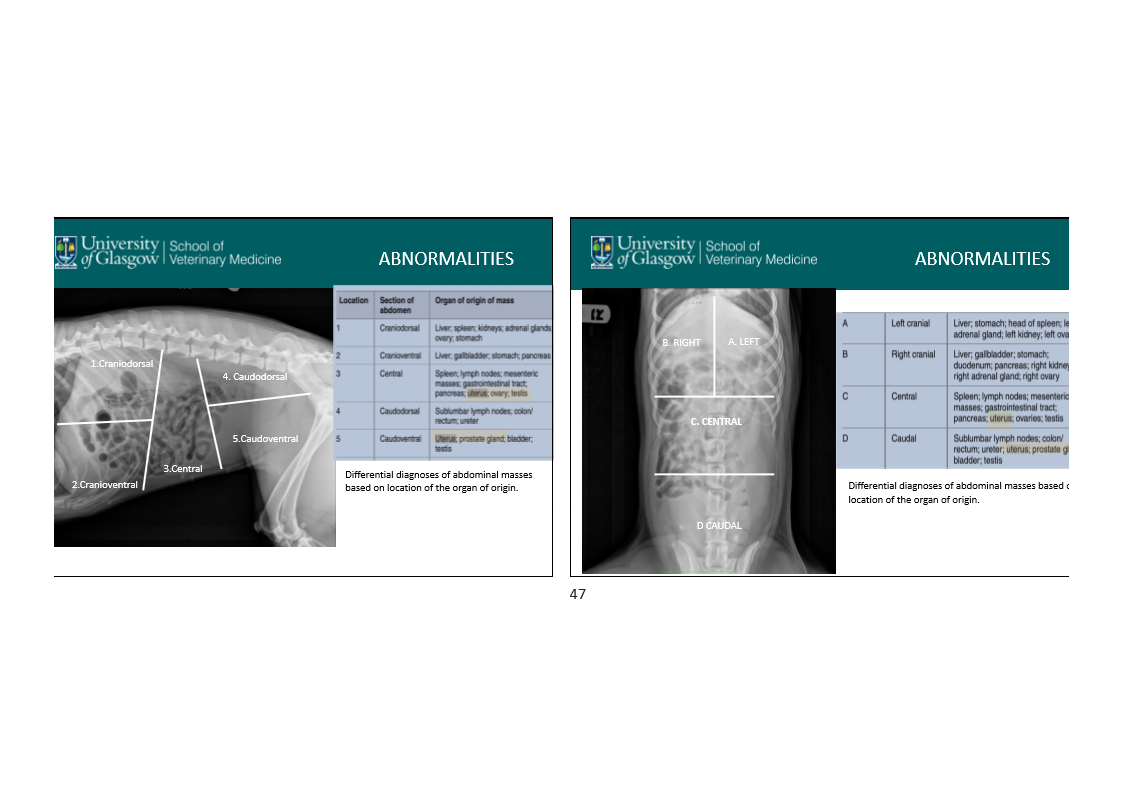
Sorry guys! not my best work. This powerpoint was kinda ass