Biology photosynthesis
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
1
New cards
Autotrophs
\
An __________ is an organism that can produce its own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, using energy from the sun or chemicals in the environment.
An __________ is an organism that can produce its own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, using energy from the sun or chemicals in the environment.
2
New cards
Heterotrophs
A __________ is an organism that cannot produce its own food and relies on consuming other organisms for energy and nutrients.
3
New cards
Photoautotroph
The type of autotroph that uses light as a source of energy to make organic molecules is called a ___________.
4
New cards
What is required for photosynthesis to happen?
sunlight, carbon dioxide, water and pigments
5
New cards
Food is used to make macromolecules like
Proteins and nucleic acids
6
New cards
Electromagnetic spectrum consist of
\
\
The range of all types of electromagnetic radiation, from radio waves to gamma rays. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
7
New cards
Wave nature has
Wave length and frequency
8
New cards
Particulate nature include
photons and quanta
9
New cards
Photon
A __________ is a fundamental particle of light that carries energy and has zero mass.
10
New cards
Visible Light
_____________ is a type of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye and has a wavelength range of approximately 400 to 700 nanometers.
11
New cards
Chlorophyl
_________ is a green pigment found in plants and algae that is essential for photosynthesis, as it absorbs light energy from the sun and converts it into chemical energy.
12
New cards
Chlorophyll A and chlorophyll B
are green pigments found in plants that absorb light energy for photosynthesis.
13
New cards
Carotenoids
a group of pigments that are responsible for the orange color of many fruits and vegetables. They also play an important role in photosynthesis and photoprotection in plants.
14
New cards
Chlorophyll absorbs only what pigments?
Red blue and violet
15
New cards
Thylakoids contain
Photosynthetic pigments
16
New cards
Pigments
Molecules that can absorb light energy
17
New cards
When light strikes pigment
it is either absorbed or reflected by the pigment molecules. The color we perceive is the result of the wavelengths of light that are reflected back to our eyes.
18
New cards
The leaf section
This part of a plant is responsible for photosynthesis and gas exchange. It is usually flat and thin, with a network of veins that transport water and nutrients.
19
New cards
Mesophyll
_________ is the tissue in the interior of a leaf that contains the palisade layer and spongy layer, where most chloroplasts are located.
20
New cards
stroma
is the fluid-filled space surrounding the thylakoid membranes in a chloroplast,
21
New cards
Grana
are the stacks of thylakoids where the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur.
22
New cards
Stromata
Pores for gasesous exchange
23
New cards
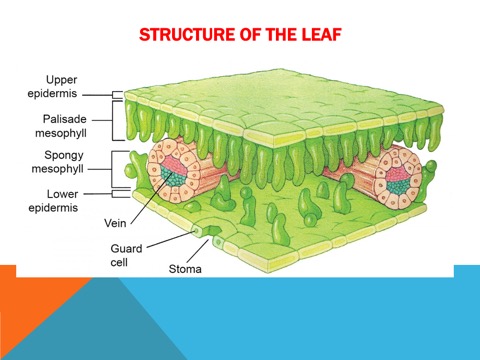
Structures of the leaf
24
New cards
Absorption spectra of the leaf
The ___________ of the leaf refers to the wavelengths of light that are absorbed by the pigments in the leaf, which can be used to identify the types of pigments present and their concentrations.
25
New cards
Summary equation of photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O + sunlight energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2.
26
New cards
Output of photosynthesis are
The __________ of photosynthesis are oxygen and glucose.
27
New cards
The input for photosynthesis is
Carbon dioxide, water, light energy
28
New cards
Light dependent reactions
Light dependent reactions are the first stage of photosynthesis that occur in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts.
During this process, light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH, which are used in the lightINDEPENDENT stage of photosynthesis.
\
\
During this process, light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH, which are used in the lightINDEPENDENT stage of photosynthesis.
\
\
29
New cards
Steps of light dependent reaction
Process that occurs in the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts.
involves the absorption of light by pigments such as chlorophyll, which excites electrons and passes them down an electron transport chain.
This generates ATP and NADPH, which are used in the light-independent reactions to produce glucose.
involves the absorption of light by pigments such as chlorophyll, which excites electrons and passes them down an electron transport chain.
This generates ATP and NADPH, which are used in the light-independent reactions to produce glucose.
30
New cards
Steps of light independent reaction
Step 1: Carbon fixation - CO2 combines with RuBP to form PGA.
Step 2: Reduction - ATP and NADPH are used to convert PGA to G3P.
Step 3: Regeneration - G3P is used to regenerate RuBP.
Step 4: Release - One G3P is released as a product while the other five continue in the cycle.
Step 2: Reduction - ATP and NADPH are used to convert PGA to G3P.
Step 3: Regeneration - G3P is used to regenerate RuBP.
Step 4: Release - One G3P is released as a product while the other five continue in the cycle.
31
New cards
Which of the following occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast?
Calvin cycle, where CO2 is fixed into sugars using ATP and NADPH produced in the thylakoid membrane during photosynthesis.
32
New cards
The oxygen produced in photosynthesis comes from what molecule?
Water.
33
New cards
The photosynthetic process used by some plants to survive in a hot dry climate, like the desert?
\
C4 photosynthesis
C4 photosynthesis
34
New cards
C4 photosynthesis
allows plants to conserve water by keeping their stomata closed during the day and only opening them at night. Carbon dioxide is stored as a 4-carbon molecule before being converted to sugar, which increases efficiency.
35
New cards
C3 photosynthesis
The process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of glucose and oxygen.
36
New cards
Where does C3 photosynthesis happen ?
This process occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells and involves two stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions.
37
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a produce of the light dependent reaction?
Glucose is NOT a product of the light dependent reaction.
The products of the light dependent reaction are ATP, NADPH, and oxygen.
The products of the light dependent reaction are ATP, NADPH, and oxygen.
38
New cards
Which of the following is the source of the carbon in sugar produced during photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide
39
New cards
What is the main difference between cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation
Cyclic photophosphorylation produces ATP only,
while noncyclic photophosphorylation produces both ATP and NADPH.
while noncyclic photophosphorylation produces both ATP and NADPH.
40
New cards
Carbon fixation is catalyzed by what enzyme
Rubisco
Protein enzyme found in plants and other photosynthetic organisms that catalyzes the first step in the carbon fixation process, converting atmospheric CO2 into organic molecules.
Protein enzyme found in plants and other photosynthetic organisms that catalyzes the first step in the carbon fixation process, converting atmospheric CO2 into organic molecules.
41
New cards
The calvin cycle requires
The Calvin cycle requires carbon dioxide, ATP, and NADPH as inputs, but does not require oxygen.
42
New cards
In the light dependent reactions, when light strikes the pigments (P700 or P680) what is the immediate result?
Excitation of electrons and their transfer to an electron acceptor.
43
New cards
In the calvin cycle, more ATP than NADPH is used, how is this difference made up?
\
The cyclic pathway creates more ATP through the oxidation of water
The cyclic pathway creates more ATP through the oxidation of water
44
New cards
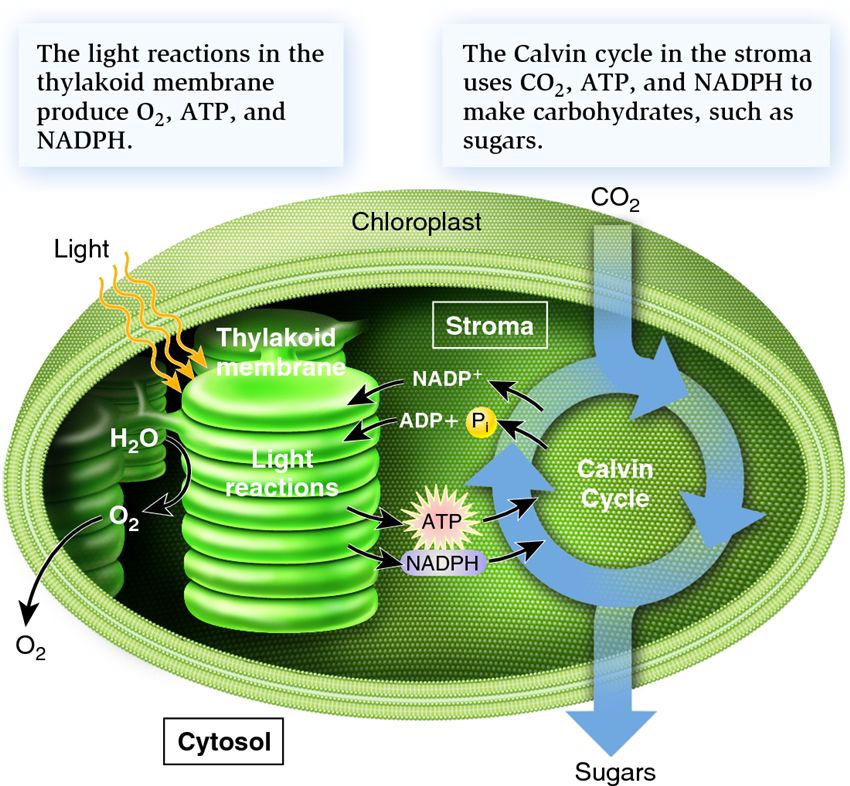
The two stages of photosynthesis
45
New cards
The Photosystems:
Photosystems are protein complexes in the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts.
Photosystem I (PSI) absorbs light at 700 nm
and photosystem II (PSII) absorbs light at 680 nm.
Both photosystems work together to carry out the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
\
PSII splits water molecules, generating oxygen gas and protons,
PSI reduces NADP+ to NADPH.
Photosystem I (PSI) absorbs light at 700 nm
and photosystem II (PSII) absorbs light at 680 nm.
Both photosystems work together to carry out the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
\
PSII splits water molecules, generating oxygen gas and protons,
PSI reduces NADP+ to NADPH.
46
New cards
What is the series of protein complexes that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions during photosynthesis? (Hint: It generates ATP and NADPH for the Calvin cycle)
Electron Transport Chain
47
New cards
The electron transport chain transfers and delivers electrons and makes ATP
The _________ transfers and delivers electrons and makes ATP.
48
New cards
Electron carrier molecules
are molecules that transport ELECTRONS during cellular respiration and photosynthesis.
49
New cards
Is NADP an electron carrier
NADP is a coenzyme that accepts and donates electrons during photosynthesis. It acts as an electron carrier, transferring electrons from one molecule to another.
50
New cards
\
**The components of a photosystem**
**The components of a photosystem**
Antennae chlorophylls
Reaction center chlorophylls
Reaction center chlorophylls
51
New cards
What are the functions of photosystems?
Absorb light
Energize electrons
Transfer electrons to electron acceptor
Energize electrons
Transfer electrons to electron acceptor
52
New cards
Light dependent reaction happens in the
thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, where light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH.
53
New cards
Steps of light-dependent reaction
Absorption of light by PS II causing excitement of electrons
Transfer of electrons to PS I
Absorption light by PS I and excitement of electrons
Transfer of electrons to NADP to make NADPH
Process of photosynthesis:
1. Absorption of light by PS II excites electrons.
2. Electrons transfer to PS I.
3. PS I absorbs light, excites electrons.
4. Electrons transfer to NADP+ to make NADPH.
Transfer of electrons to PS I
Absorption light by PS I and excitement of electrons
Transfer of electrons to NADP to make NADPH
Process of photosynthesis:
1. Absorption of light by PS II excites electrons.
2. Electrons transfer to PS I.
3. PS I absorbs light, excites electrons.
4. Electrons transfer to NADP+ to make NADPH.
54
New cards
\
ATP Synthesis
\
ATP Synthesis
\
Definition: The process of generating ATP through chemiosmosis, powered by the gradient of H+ ions across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
H+ proton gradient formed to in make ATP
H+ proton gradient formed to in make ATP
55
New cards
Input of light dependent reactions
Water ATP NADPH light
The initial energy conversion step in photosynthesis where light energy is absorbed and converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH.
The initial energy conversion step in photosynthesis where light energy is absorbed and converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH.
56
New cards
Output of light dependent reactions
\
\
\
The Product of light-dependent reactions is a molecule that stores energy in the form of ATP and NADPH, and releases oxygen.
The Product of light-dependent reactions is a molecule that stores energy in the form of ATP and NADPH, and releases oxygen.
57
New cards
what is the important of light dependent reactions?
Importance of light dependent reactions
1) the formation of oxygen is used for respiration by aerobic organisms
2) the formation of NADPH
3) production of ATP
1) the formation of oxygen is used for respiration by aerobic organisms
2) the formation of NADPH
3) production of ATP
58
New cards
How is ATP formed by chemiosmosis in chloroplast?
ATP is formed by chemiosmosis in chloroplasts through the process of photosynthesis. During the light-dependent reactions, energy from sunlight is used to pump protons across the thylakoid membrane, creating a proton gradient. This gradient is then used by ATP synthase to produce ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. This process is known as photophosphorylation and is essential for the production of ATP in chloroplasts.
59
New cards
Where does the light-independent reaction occur?
The light-independent reaction, also known as the Calvin cycle, occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts.
60
New cards
What is the light-independent reaction?
A series of chemical reactions that occur in the stroma of chloroplasts, which were first elucidated by Melvin Calvin. These reactions convert carbon dioxide into glucose using energy from ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions.
61
New cards
What are the main phases of the light independent reaction?
Fixation of carbon by RuBP using the enzyme RUBISCO.Enzyme: RUBISCO catalyzes the process.
Chemical reorganization and formation of CHO.
Regeneration of RuBP To continue the cycle.
\
Chemical reorganization and formation of CHO.
Regeneration of RuBP To continue the cycle.
\
62
New cards
Input of light-independent reactions
CO 2
NADPH
ATP
NADPH
ATP
63
New cards
Output of light independent reaction
CHO(sugar) NADP ADP
64
New cards
What is photorespiration?
Photorespiration is a process that occurs in plants where oxygen is consumed and carbon dioxide is released, leading to a decrease in photosynthesis efficiency.
65
New cards
What are the effects of photorespiration?
1. Reduction in the efficiency of photosynthesis
2. Decrease in the production of carbohydrates
3. Wastage of energy and resources
4. Slows plant growth
5. Gains of photosynthesis are reversed is C3 plants
\
\
66
New cards
What does rubisco do in photo respiration?
Flashcard: What is the function of rubisco in photorespiration? Answer: Rubisco, or ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, is an enzyme that catalyzes the initial step of the Calvin cycle, but
also bind oxygen during photorespiration, leading to the breakdown of organic compounds and the release of CO2.
also bind oxygen during photorespiration, leading to the breakdown of organic compounds and the release of CO2.
67
New cards
Defects of rubisco
Under very bright conditions, it fixes O2 and releases CO2
68
New cards
Oxidation
Process in which an atom or molecule loses electrons, resulting in an increase in its oxidation state. Often involves the addition of oxygen or the removal of hydrogen.
69
New cards
When plant cells produce o2 from splitting water this is called ?
Photolysis
70
New cards
Chlorophyll is located in the
Found in the chloroplasts of plant cells."
71
New cards
The cyclic pathway of the light independent reactions:
Process in photosynthesis that uses carbon dioxide to produce glucose. It occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts and involves the Calvin cycle, which fixes CO2 into organic molecules using ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions. The cycle regenerates its starting material, ribulose bisphosphate, allowing it to continue.
72
New cards
What are CAM plants
Type of plants that use crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) to fix carbon dioxide during photosynthesis. They open their stomata at night to reduce water loss and store CO2 in organic acids. During the day, they use this stored CO2 to power photosynthesis. Examples include cacti and succulents.
73
New cards
The internal membrane system of a chloroplast is made up of
The internal membrane system of a chloroplast is made up of thylakoids
74
New cards
In a plant cell, where are the ATP Synthase Complexes located?
In the Thylakoid Membrane and in the Inner Mitochondrial Membrane
75
New cards
Photosynthesis uses what kind of light?
Visible light
76
New cards
What is the purpose of cyclic electron flow?
It creates only ATP, needed by the light-independent reactions
77
New cards
Light-harvesting complexes, excited by photons of light, are made of
proteins, cofactors, and pigment
78
New cards
When electrons are passed through an electron transport chain, released energy
is transformed into a hydrogen ion gradient to drive ATP synthesis
79
New cards
**Which group do most food plants, including wheat, oats, and rice, belong to? A. CAM plants B. C3 plants C. C4 plants**
Answer: B. C3 plants.
80
New cards
\
Which statement is NOT true about C3 and C4 plants?
C3 plants are more successful in mild climates than C4 plants.
\
C4 plants contain chloroplasts only in part of their mesophyll cells.
C3 plants fix CO2 in the mesophyll cells.
C3 plants make glucose in the bundle sheath cells.
The first CO2 fixation product in a C4
Which statement is NOT true about C3 and C4 plants?
C3 plants are more successful in mild climates than C4 plants.
\
C4 plants contain chloroplasts only in part of their mesophyll cells.
C3 plants fix CO2 in the mesophyll cells.
C3 plants make glucose in the bundle sheath cells.
The first CO2 fixation product in a C4
C3 plants make glucose in the bundle sheath cells.
81
New cards
Which of the following is a TRUE statement regarding the energy-fixing reactions of photosynthesis?
* Oxygen and hydrogen are combined to create water.
* The ADP and NADP created by the energy-fixing reactions are used in the carbon-fixing reactions.
* The energized electrons from P680 are used to generate ATP.
* Oxygen and hydrogen are combined to create water.
* The ADP and NADP created by the energy-fixing reactions are used in the carbon-fixing reactions.
* The energized electrons from P680 are used to generate ATP.
Energy-fixing reactions of photosynthesis produce ADP, NADP and energized electrons from P680. Water is created by combining oxygen and hydrogen.
82
New cards
Which of the following is a TRUE statement regarding the carbon-fixing reactions of photosynthesis?
* The final product is a carbon compound called ribulose diphosphate.
* The first product of carbon fixation is phosphoglycerate.
* The reactions occur on the thylakoid membran
* The final product is a carbon compound called ribulose diphosphate.
* The first product of carbon fixation is phosphoglycerate.
* The reactions occur on the thylakoid membran
The first product of carbon fixation is phosphoglycerate
83
New cards
A mutation occurs in the chloroplasts of a lettuce plant, causing its thylakoid membranes to become more permeable to charged ions.
**How might this mutation affect the Calvin cycle?**
**How might this mutation affect the Calvin cycle?**
Fewer carbohydrates would be produced by the Calvin cycle
\
Less carbon fixation would occur in the treated chloroplast bc less ATP would-be created due to the weaker protein gradient across the thylakoid membrane
\
Less carbon fixation would occur in the treated chloroplast bc less ATP would-be created due to the weaker protein gradient across the thylakoid membrane
84
New cards
This protein triggers photorespiration when O2 is high compared to CO2. It's involved in carbon fixation and found in plants. What is it?"
Rubisco initiates photorespiration when there is a higher oxygen to carbon dioxide ratio.
85
New cards
C3 plants are best adapted to
\
\
C3 plants are best adapted to cool and wet environments, where water is abundant and sunlight is not intense. They are able to photosynthesize with less energy and water than C4 or CAM plants, but are less efficient in hot and dry environments.
86
New cards
What are examples of C3 plants?
\
\
Plants that use the C3 photosynthesis pathway are wheat, rice, soybeans, potatoes, and most trees.
87
New cards
Examples of C4 plants
Examples include maize, sugarcane, sorghum, and millet.
88
New cards
What are C4 plants?
Type of plants that have a specialized mechanism for carbon fixation in which CO2 is first fixed into a four-carbon molecule before entering the Calvin cycle. This mechanism allows them to thrive in hot and dry environments while minimizing water loss. Examples include corn, sugarcane, and sorghum.
89
New cards
What is the difference between C3 plants, C4 plants, and CAM plants?
C3 plants: Use only the Calvin cycle to fix CO2.
C4 plants: Use both the Calvin and Hatch-Slack cycles. Occurs in bundles of sheath cells
CAM plants: Open stomata at night to fix CO2 and close them during the day.
C4 plants: Use both the Calvin and Hatch-Slack cycles. Occurs in bundles of sheath cells
CAM plants: Open stomata at night to fix CO2 and close them during the day.
90
New cards
91
New cards
What is a redox reaction?
A type of chemical reaction where one species loses electrons (oxidation) and another gains electrons (reduction). It involves a transfer of electrons and changes in oxidation states.
92
New cards
How is redox used in photosynthesis?
In the light dependent reaction redox involves the transfer of electrons from water to carbon dioxide. This then creates energy that is used to produce glucose and oxygen.
93
New cards
The cellular transport process by which carbon dioxide enters a leaf (and by which water vapor andoxygen exit) is _
is diffusion.
94
New cards
What's PEP carboxylase
Enzyme that catalyzes the first step of C4 photosynthesis
Only present in mesophyll cells
by fixing CO2 to phosphoenolpyruvate to form oxaloacetate.
Only present in mesophyll cells
by fixing CO2 to phosphoenolpyruvate to form oxaloacetate.
95
New cards
What is Crassulacean Acid Metabolism
A photosynthetic adaptation found in plants living in arid environments, where they open their stomata at night to reduce water loss and fix CO2 into organic acids, which are stored in vacuoles and used during the day for photosynthesis.
96
New cards
What's photophosphorlyation?
Photophosphorylation is the process of utilizing light energy from photosynthesis to convert ADP to ATP. It is the process of synthesizing energy-rich ATP molecules by transferring the phosphate group into ADP molecule in the presence of light.
97
New cards
What color light is LEAST effective when driving photosynthesis
green light is least effective
98
New cards
What are the 8 steps in linear electron flow?
1
Photon hits the light-harvesting complex in PSII and excites the electrons in chlorophyll a
2
Excited electron goes into the primary electron acceptor, Results in P680+
3
Water splits in oxygen - 2 electrons - 2 H+, H+ goes into the lumen, Electrons feed into P680+
4
Electrons go through the electron transport chain, Chain made up of Pq, Cytochrome complex and Pc
5
Exergonic fall of electrons to a lower energy level gives enough energy to make ATP, H+ creates a gradient for ATP synthase
6
PSI P700 chlorophyll electrons get excited and get picked up by the electron acceptor, P700+ can now accept the electrons from the chain
7
P700 electrons passed through a chain that does not produce ATP, Chain made of Fd
8
Electrons go from Fd to NADP+ to create NADPH, Removes H+ from stroma
Photon hits the light-harvesting complex in PSII and excites the electrons in chlorophyll a
2
Excited electron goes into the primary electron acceptor, Results in P680+
3
Water splits in oxygen - 2 electrons - 2 H+, H+ goes into the lumen, Electrons feed into P680+
4
Electrons go through the electron transport chain, Chain made up of Pq, Cytochrome complex and Pc
5
Exergonic fall of electrons to a lower energy level gives enough energy to make ATP, H+ creates a gradient for ATP synthase
6
PSI P700 chlorophyll electrons get excited and get picked up by the electron acceptor, P700+ can now accept the electrons from the chain
7
P700 electrons passed through a chain that does not produce ATP, Chain made of Fd
8
Electrons go from Fd to NADP+ to create NADPH, Removes H+ from stroma
99
New cards
1. Which of the following components is not used by both plants and cyanobacteria to carry out photosynthesis?
carbon dioxide
chlorophyll
chloroplasts
water
Carbon dioxide
100
New cards
\
**2**.
Why are chemoautotrophs not considered the same as photoautotrophs if they both extract energy and make sugars?
1. Chemoautotrophs use wavelengths of light not available to photoautotrophs.
2. Chemoautotrophs extract energy from inorganic chemical compounds.
3. Photoautotrophs prefer the blue side of the visible light spectrum.
4. Photoautotrophs make glucose, while chemoautotrophs make galactose.
**2**.
Why are chemoautotrophs not considered the same as photoautotrophs if they both extract energy and make sugars?
1. Chemoautotrophs use wavelengths of light not available to photoautotrophs.
2. Chemoautotrophs extract energy from inorganic chemical compounds.
3. Photoautotrophs prefer the blue side of the visible light spectrum.
4. Photoautotrophs make glucose, while chemoautotrophs make galactose.
Chemoautotrophs extract energy from inorganic chemical compounds, while photoautotrophs use light energy. Therefore, they are not the same type of autotrophs.