Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
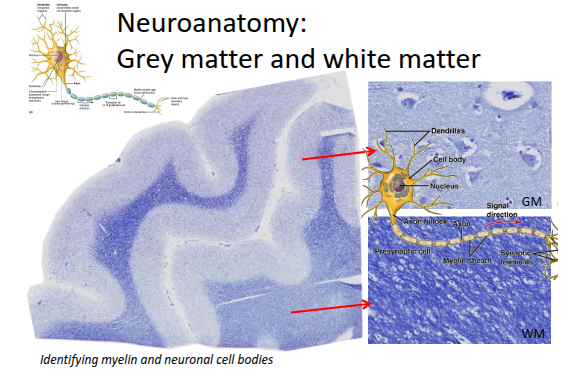
What are the two main types of tissue that make up the central nervous system (CNS)?
Grey matter and white matter.
What does grey matter primarily consist of?
Neuron cell bodies, dendrites, and axon terminals.
What is the main function of grey matter in the CNS?
Signal processing and integration; it’s where information is processed and activity is initiated
What structures in grey matter are responsible for receiving signals from other neurons?
Dendrites.
Which part of the neuron in grey matter is responsible for sending signals to other neurons?
Axon terminals
What does white matter mainly consist of?
Myelinated axons.
What is the primary function of white matter in the CNS?
Transmission of information through the formation of tracts (ascending or descending).
What are the three types of white matter pathways?
Commissural, association, and projection pathways
What is the function of commissural pathways?
They connect the left and right hemispheres of the brain (e.g., corpus callosum).
What is the function of association pathways?
They connect different regions within the same hemisphere.
What is the function of projection pathways?
They connect the cerebral cortex with lower brain regions and the spinal cord
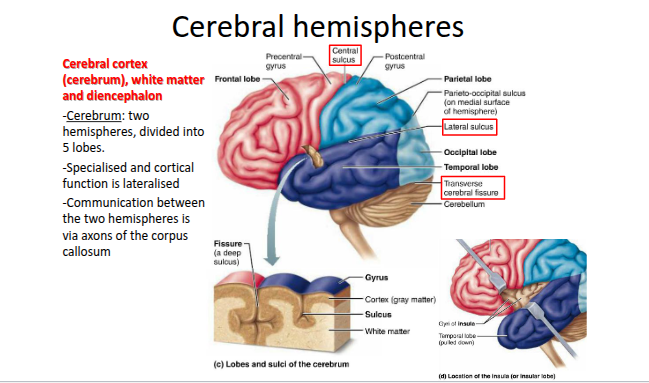
What is the main function of white matter in the cerebral hemispheres?
Communication between the cerebrum and lower CNS structures.
What is white matter composed of?
Myelinated axons bundled into large tracts.
How are white matter tracts classified?
According to the direction in which they run.
What are the three main types of white matter fibres in the cerebral hemispheres?
Association fibres, commissural fibres, and projection fibres.
What is the function of association fibres?
They connect different parts of the same cortical hemisphere
What is the function of commissural fibres?
They connect the two cortical hemispheres, allowing them to function as a coordinated whole.
What is the function of projection fibres?
They project to, or from, other CNS centres (connecting the cerebrum with lower brain and spinal structures)
Projection fibers are crucial nerve pathways connecting the cerebral cortex to lower brain structures (brainstem, spinal cord, diencephalon) and subcortical areas, transmitting sensory and motor information up and down the CNS, forming dense bundles like the internal capsule, and including major tracts like the corticospinal and optic radiations.
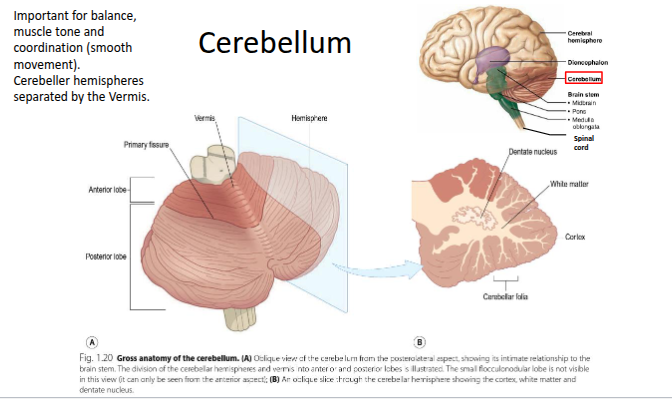
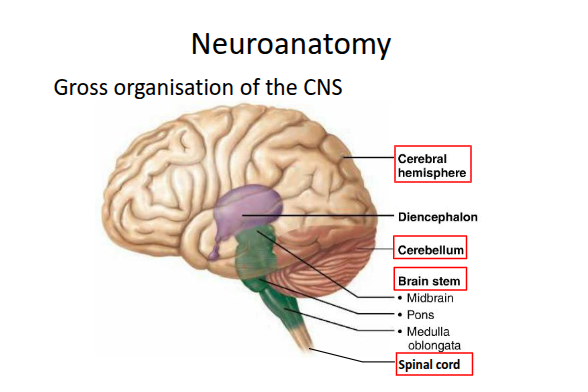
What are the three main parts of the brain stem?
The midbrain, pons, and medulla.
How is the cerebellum connected to the brain stem?
It is connected via the cerebellar peduncles (attached to the pons).
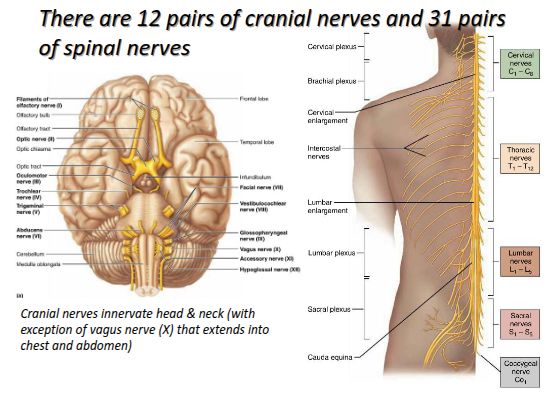
How many cranial nerves arise from the brain stem?
Twelve (12) cranial nerves.
Into what two main regions can the brain stem be subdivided?
The base (basilar region) and the tegmentum.
What is contained in the base (basilar region) of the brain stem?
Motor tracts
What structures are found in the tegmentum of the brain stem?
The reticular formation and nuclei of the cranial nerves
What is the reticular formation?
A network of neurons within the brain stem involved in autonomic and reflex functions.
What vital centres are located in the reticular formation?
Respiratory and cardiovascular centres
What reflexes are controlled by the reticular formation?
Coughing, sneezing, and gagging reflexes.
What is the spinal cord a continuation of?
The brain stem.
Where is the spinal cord located?
Within the bony spinal canal
What is the main function of the spinal cord?
To transmit nerve impulses to and from the brain and the body
At which regions is the spinal cord enlarged, and why?
At the cervical and lumbar regions, to sense and supply the upper and lower limbs.
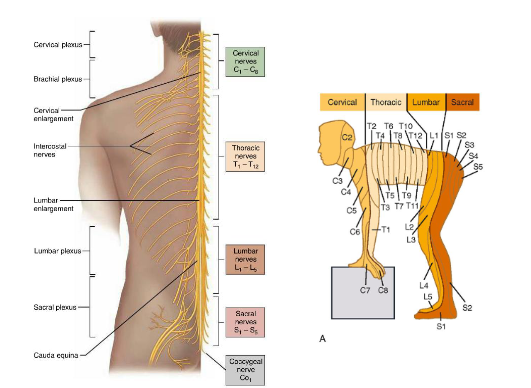
How many pairs of spinal nerves connect to the spinal cord?
31 pairs
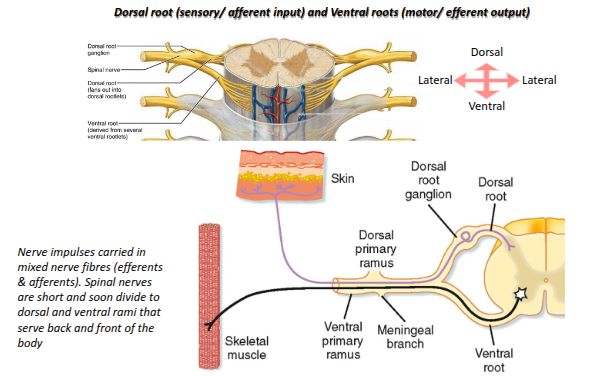
What are the two types of roots through which spinal nerves contact the spinal cord?
Dorsal (sensory) roots and ventral (motor) roots
What is the function of the dorsal roots?
They carry sensory information into the spinal cord
What is the function of the ventral roots?
They carry motor information out from the spinal cord to the body
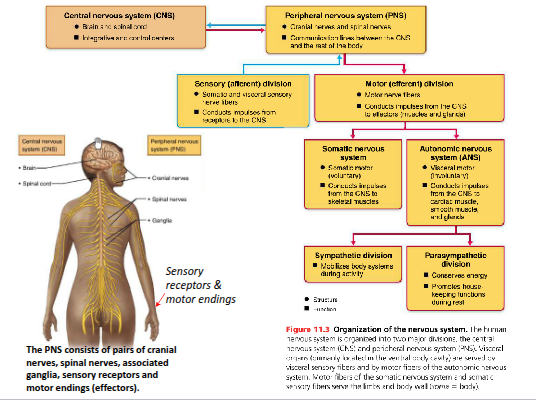
What structures make up the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)?
Cranial and spinal nerves that innervate the head, neck, and body
What is the function of sensory receptors and sensory fibres in the PNS?
They send information to the CNS along afferent pathways
What is the function of motor pathways in the PNS?
They elicit motor (muscle) activity in the body and arise from the CNS along efferent pathways.
What are the two main divisions of the motor (efferent) division of the PNS?
The somatic (voluntary control) and autonomic (involuntary control) divisions
What does the somatic nervous system control?
Voluntary movements of skeletal muscles
What does the autonomic nervous system control?
Involuntary activities of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands.
What are the two subdivisions of the autonomic nervous system?
The sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions.
What is the mnemonic to remember the direction of nerve signals in the PNS?
Efferent = Exit the CNS, Afferent = Arrive at the CNS.
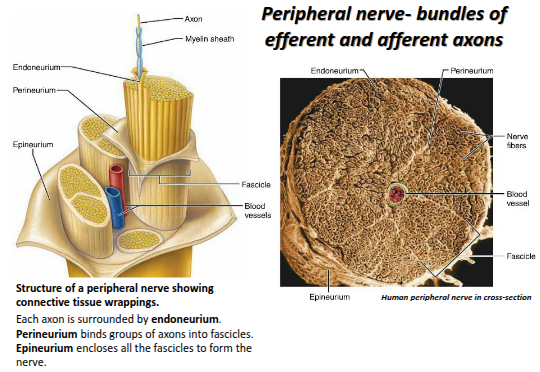
What surrounds each individual axon in a nerve?
The endoneurium.
What does the perineurium do?
It binds groups of axons together into fascicles.
What does the epineurium do?
It encloses all the fascicles to form the whole nerve
List the three connective tissue layers of a peripheral nerve from deep to superficial.
Endoneurium → Perineurium → Epineurium
Demyelinating diseases
Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS) is a
devastating, paralysing and life-
threatening disease of the PNS.
Caused by antibodies mistaking
proteins of the bacterium/ virus for
those of the node of Ranvier
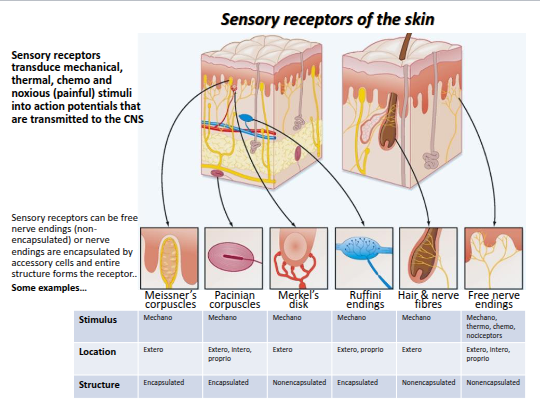
What is the sensory (afferent) division of the nervous system responsible for, and how are sensory receptors classified?
The sensory (afferent) division detects and transmits information about changes (stimuli) in the environment to the CNS.
Sensory receptors respond to stimuli and are classified by:
Type of stimulus:
Mechanoreceptors (touch, pressure, vibration)
Thermoreceptors (temperature)
Chemoreceptors (chemicals, taste, smell)
Nociceptors (pain)
Photoreceptors (light)
Location:
Exteroceptors (external environment)
Interoceptors (internal environment)
Proprioceptors (body position and movement)
Structure:
Encapsulated or Nonencapsulated receptors
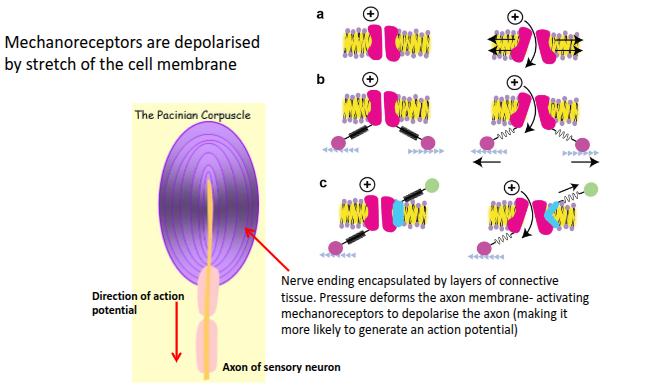
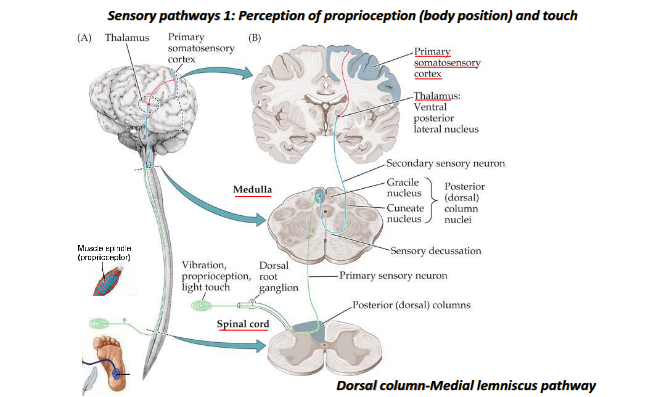
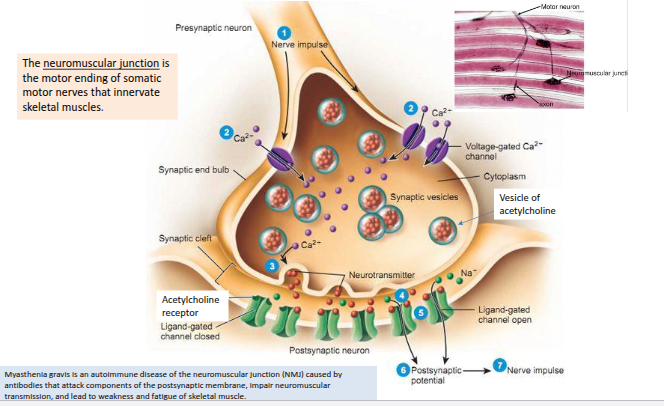
What is the motor (efferent) division of the nervous system, and how does it activate effectors?
All motor activities are initiated in the CNS.
They act on:
Skeletal muscles → somatic division (voluntary)
Visceral muscles and glands → autonomic division (involuntary)
Motor endings are the PNS structures that activate effectors (muscles) by releasing neurotransmitters.
The neuromuscular junction is the motor ending of somatic motor nerves that innervate skeletal muscles.