SOCY 210 - Experiments
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Experiment
A systematic attempt to test a causal hypothesis about the effect of one variable on another variable
Key Components of a Classical Experiment
IV and DV
Pre-testing and post-testing
Experimental and control groups
The experimenter’s control (ability to manipulate) of the IV
Pre-Test
Initial measurements of the dependent variable prior to introduction of the independent variable (experimental stimulus)
Post-Test
Follow-up measurements of the dependent variable after introduction of the independent variable
Experimental Group
Exposed to the treatment, policy or initiative being manipulated
Control Group
Group not exposed to the experimental manipulation
Artificial Experiment
Experiment conducted under highly controlled, artificial conditions (e.g., online, a psychology laboratory)
Field Experiment
An experiment conducted in real world conditions
True Experiment
Experiment in which the experimenter manipulates the IV and assigns cases to treatment or control conditions randomly
Quasi Experiment
Experiment in which the experimenter manipulates the IV but cases are not assigned to conditions randomly
Do not use random assignment of cases to attributes of the IV
Natural Experiment
Experimental approximation in which an event, policy, or circumstance created comparison conditions in which the experimenter does not manipulate the IV or randomly assign cases, but simply observes the resulting differences
Double-Blind Experiment
Experiment in which both subjects and experimenters do not know which subjects are in the experimental group or the control group, group assignment is tracked to compare group differences, but in a way that reduces the impact of researcher subjectivity
Experimenters can pre-judge results when they are anticipating a certain effect
Dichotomous Variable
A variable that has only two attributes; also called a binomial variable
Hawthorne Effect
Researchers discovered that their presence affected the behaviour of the individuals being studied, any impact of researcher on the subject of study
Random Assignment
The procedure of randomly assigning experimental subjects to experimental and control groups, such that each subject has an equal probability of being in either group
Ensures that the subjects exposed to the test are as comparable as possible to those exposed to the control factor
Matching
Procedure whereby pairs of subjects are matched on the basis of their similarities on one or more variables; then one member of the pair is assigned to the experimental group and the other to the control group
Is a way to achieve comparability between experimental and control groups
Internal Invalidity
Refers to the possibility that the conclusions drawn from experimental results may not accurately reflect what went on in the experiment itself
Threat is present whenever anything other than the experimental stimulus can affect the dependent variable
Sources of Internal Invalidity
History, Maturation, Testing, Instrumentation, Statistical Regression, Selection Biases, Experimental Mortality, Causal Time Order, Diffusion or Imitation of Treatments, Compensation, Compensatory Rivalry, Demoralization
Sources of Internal Invalidity - History
During the course of the experiment, historical events may occur that will confound the experimental results
Sources of Internal Invalidity - Maturation
In a long-term experiment, the fact that subjects grow older may have an effect
In a short-term experiment, they may grow tired, sleepy, bored or hungry, or change in other ways that may affect their behaviour in the experiment
Sources of Internal Invalidity - Testing
Process of testing + retesting will influence people’s behaviour, thereby confounding the experimental results
Sources of Internal Invalidity - Instrumentation
If experimenters are making the measurements, their standards or abilities may change over the course of the experiment
Sources of Internal Invalidity - Statistical Regression
Danger that changes occurring by virtue of subjects starting out in extreme positions will be attributed erroneously to the effects of the experimental stimulus
Sources of Internal Invalidity - Selection Biases
Comparisons don’t have any meaning unless the groups are comparable
Sources of Internal Invalidity - Experimental Mortality
Experimental subjects may drop out of the experiment before it’s completed, which can affect statistical comparisons and conclusions
Sources of Internal Invalidity - Causal Time Order
Ambiguity about the time order of the experimental stimulus and the dependent variable can arise
Whenever this occurs, the research conclusion that the stimulus causes the dependent variable can be challenged with the explanation that the “dependent” variable actually caused changes in the stimulus
Sources of Internal Invalidity - Diffusion or Imitation of Treatments
When experimental and control-group subjects can communicate with each other, experimental subjects could pass on some elements of the experimental stimulus to the control group
Sources of Internal Invalidity - Compensation
In experiments in real-life situations, subjects in the control group are often deprived of something considered to be of value - in such cases, there may be pressures to offer some form of compensation; in such a situation, control group is no longer a genuine control group
Sources of Internal Invalidity - Compensatory Rivalry
In real-life experiments, the subjects deprived of the experimental stimulus may try to compensate for the missing stimulus by working harder
Sources of Internal Invalidity - Demoralization
Feelings of deprivation within the control group may result in their giving up
In educational experiments, demoralized control-group subjects may stop studying, act up, or get angry
External Invalidity
Refers to the possibility that conclusions drawn from experimental results may not be generalizable to the “real” world
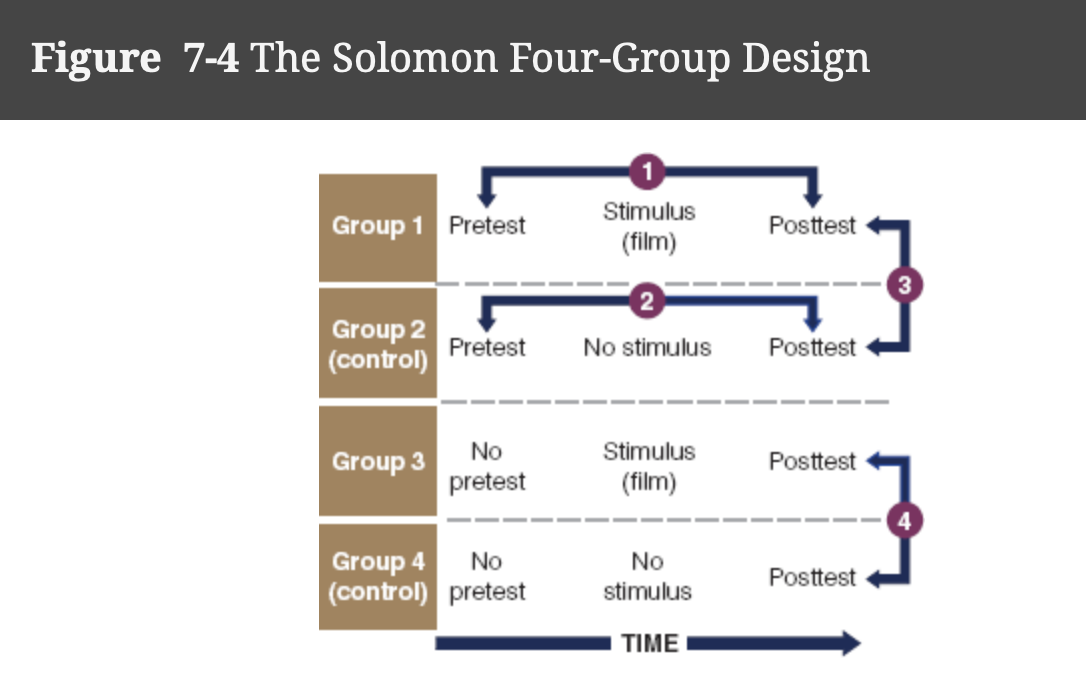
Solomon Four-Group Design
Design that addresses the problem of testing interaction with the stimulus, involves four groups of subjects assigned randomly from a pool
Labelling Theory
Addresses the phenomenon of people acting in accord with the ways they are perceived and labelled by others
Pygmalion Effect
Differences in study outcomes attributable to the researcher’s expectations of participants
When researchers believe in an individual's potential, that individual often works harder and achieves more to meet those positive expectations