Cellular Structure and Function pt. 2
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
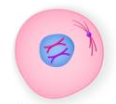
Prophase
Chromatin condenses into 2 chromosomes
Mitotic spindle begins to form
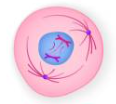
Metaphase
Nuclear membrane disintegrates
Sister chromatids align along metaphase plate with aid of spindle fibers attached to the kinetochore of the centromeric region

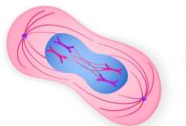
Anaphase
Spindle fibers pull sister chromatids in opposite directions towards the poles of the cell
Centromere regions separate
Telophase
Two nuclear envelopes form around separated chromosomes at opposite ends
Complete division of genetic material
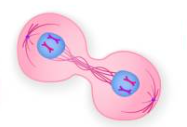
Cytokinesis
Division of all other organelles of the cell to complete mitosis

Interphase
Composed of G1, S, and G2
G1 (First gap)
Cell growth
Protein synthesis
S (synthesis)
Cell stops growing
Synthesizes and replicates DNA
G2 (Second gap)
Cell growth
Protein synthesis
Organelle development
Multicellular organisms
Cell division allows organism to grow and develop
When growth is complete, cell division is necessary for repair and renewal
Unicellular organisms
Can reproduce/clone offspring through cell division
G1/S checkpoint
Cell cycle stops and cell won’t divide anymore
G2/M checkpoint
Cell cycle stops to repair damaged DNA
G0 (senescence)
Cell stops dividing and ‘retires’ until apoptosis
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death brought by formation of ‘suicide’ proteins
Chromatin
The DNA-protein complex packed into the nucleus during interphase
Chromosomes
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes when cell enters mitotic phase
Chromatids
Each chromosome formed from chromatin during prophase has two sister chromatids
Cancer
Abnormal cells dividing without control of normal cellular checks and balances
Cancerous cells have the ability to invade other tissues (metastasis) and consume their resources
When mitosis and apoptosis are not in homeostasis…
Tumors can form