Diagnostic Imaging Exam 1 Prep
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Do xray machines contain radioactive material?
No, they produce ionizing radiation without radioactive material
Which of the following are xray modalities?
a. radiographs
b. DEXA
c. fluoroscopy
d. computer tomography (CT)
computer tomography (CT)
Xrays can be detected by human senses T/F
False
When, where, and who did xrays come from?
1895, Germany, Wilhelm Roentgen
Explain xrays and inverse square law
xrays obey inverse square law in relation to intensity over distance (if you double distance from xray source, intensity will be 1/4)
How are xrays created
electron interactions with atoms
What is the proportion of heat and xrays created from the electron interactions with atoms?
99% heat, less than 1% xrays
What is AP vs PA relating to xrays?
direction of xray beam as it goes through patient
Explain AP and PA
anterior to posterior, ideal for spine imaging
posterior to anterior, ideal for sternum imaging
Know the 5 basic radiographic densities. Order them from darkest to lightest
air, fat, water, bone, metal
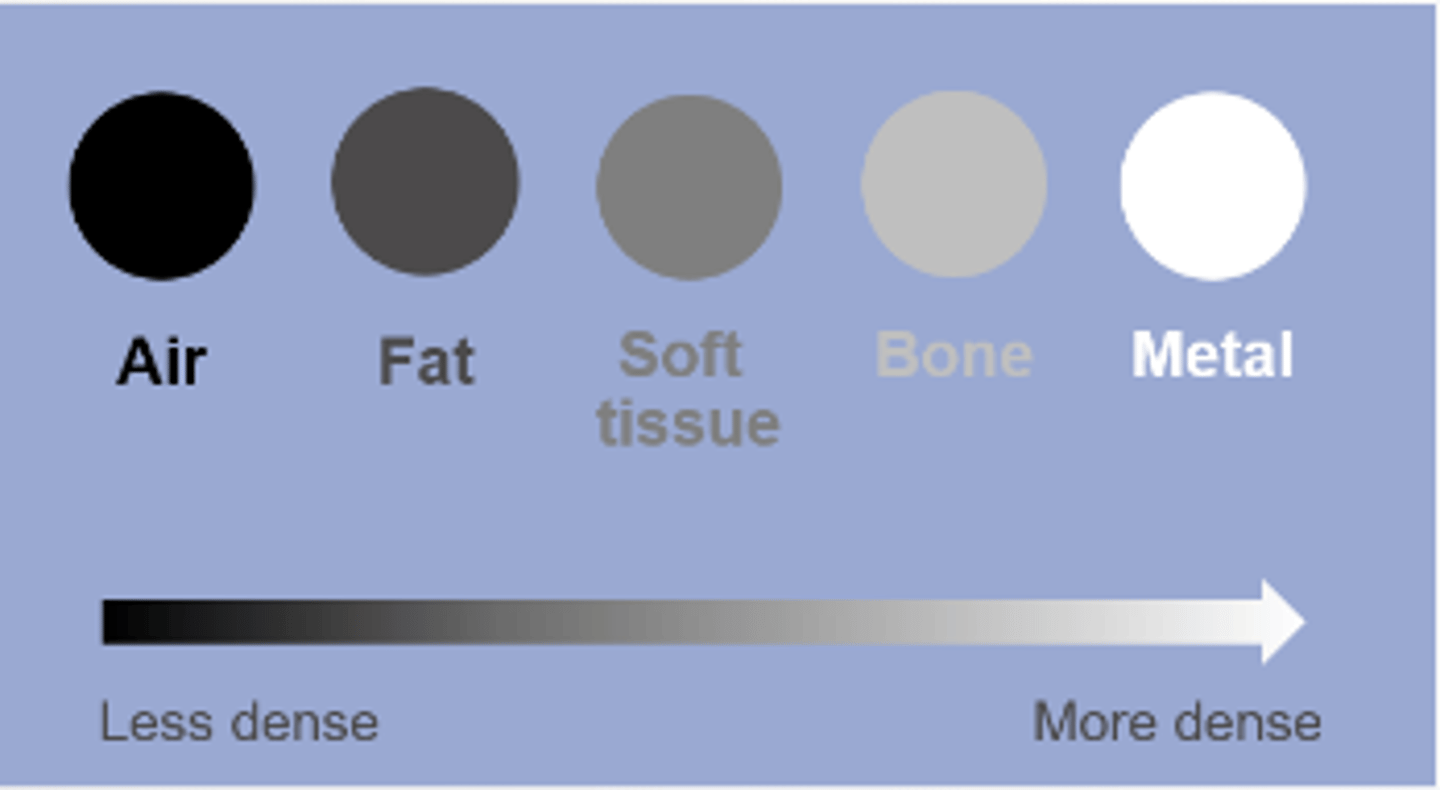
What is radiopaque? What does it look like on exposed film?
not penetrable by xrays, appears white on exposed film, reletively dense
What is radiolucent? What does it look like on exposed film?
freely penetrable by xrays, appears black on exposed film, relatively not dense
What does high contrast look like in radiography?
black and white
What does low contrast look like in radiography?
lots of shades of gray
What is the purpose of collimation?
restricts xray beams to area of interest, improves contrast resolution, reduces radiation dose to patient
What are CTs used for?
soft tissues, more accurate
What is the gold standard for measuring bone mineral density?
DEXA
Where are DEXAs typically measured at in the body?
lumbar spine or proximal femur
How do DEXAs work?
it is two xray beams of different energy levels pasing through the area of interest
What is the significance of a whole body DEXA scan?
gives information on body composition along with bone density
Does mammography use radiation?
yes, much lower energy xray beam than conventional radiography
What anode material is used in a mammography?
molybdenum
What anode material is used in an xray?
tungsten
What is the purpose of fluoroscopy?
demonstrates motion of internal structures while the xray tube is energized (swallow study video)
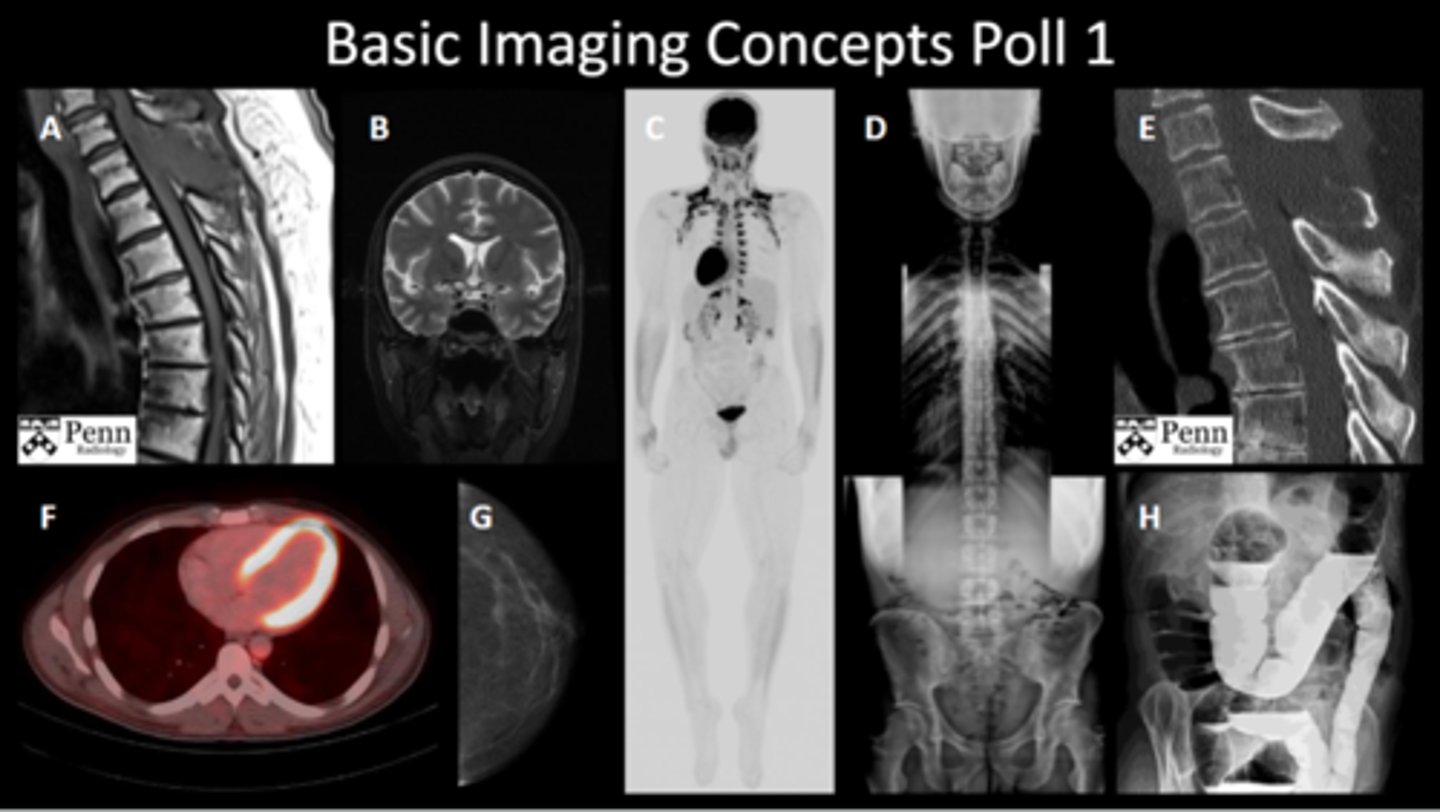
Know which modalities are used for each study (poll 1):
a. thoracic spine MRI
b. brain MRI
c. whole body PET scan
d. full spine XRAY
e. sagittal CT scan
f. PET CT fusion
g. mammography
h. barium enema contrast XRAY
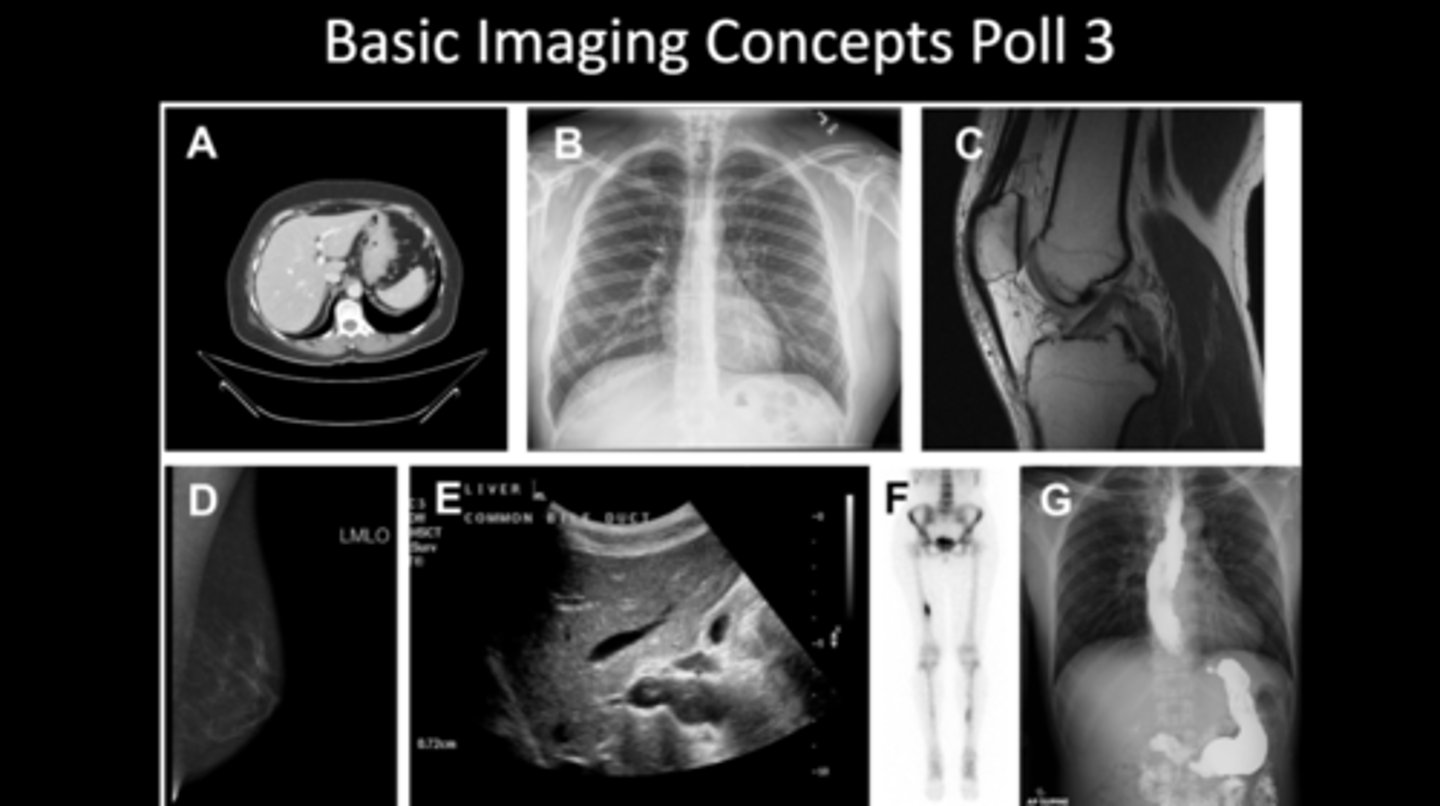
Know which modalities are used for each study (poll 3):
a. MRI
b. XRAY
c. MRI
d. MAMMO
e. ULTRASOUND
f. DEXA
g. CT contrast study
What rotates in a CT?
xray tube rotates around patient, can be reformatted into other planes or 3d images
How does a CT differ from an MRI visually?
cortical bone appears white in a CT
Know the Hounsfield units for air, lung, fat, distilled water, blood, skeletal muscle, medullary bone, and cortical bone
air: -1000 HU
lung: -400 to -600 HU
fat: -100 to -50 HU
distilled water: 0 HU
blood: +25 HU
skeletal muscle: +10 to +40 HU
medullary bone: +700 HU
cortical bone: +3000
What is window width (WW)?
describes the range of Hounsfield units displayed
What is the maximum range possible for CT window width?
2000
What is window level (WL)?
represents the Hounsfield unit in the center of the window width
Know the anatomic planes
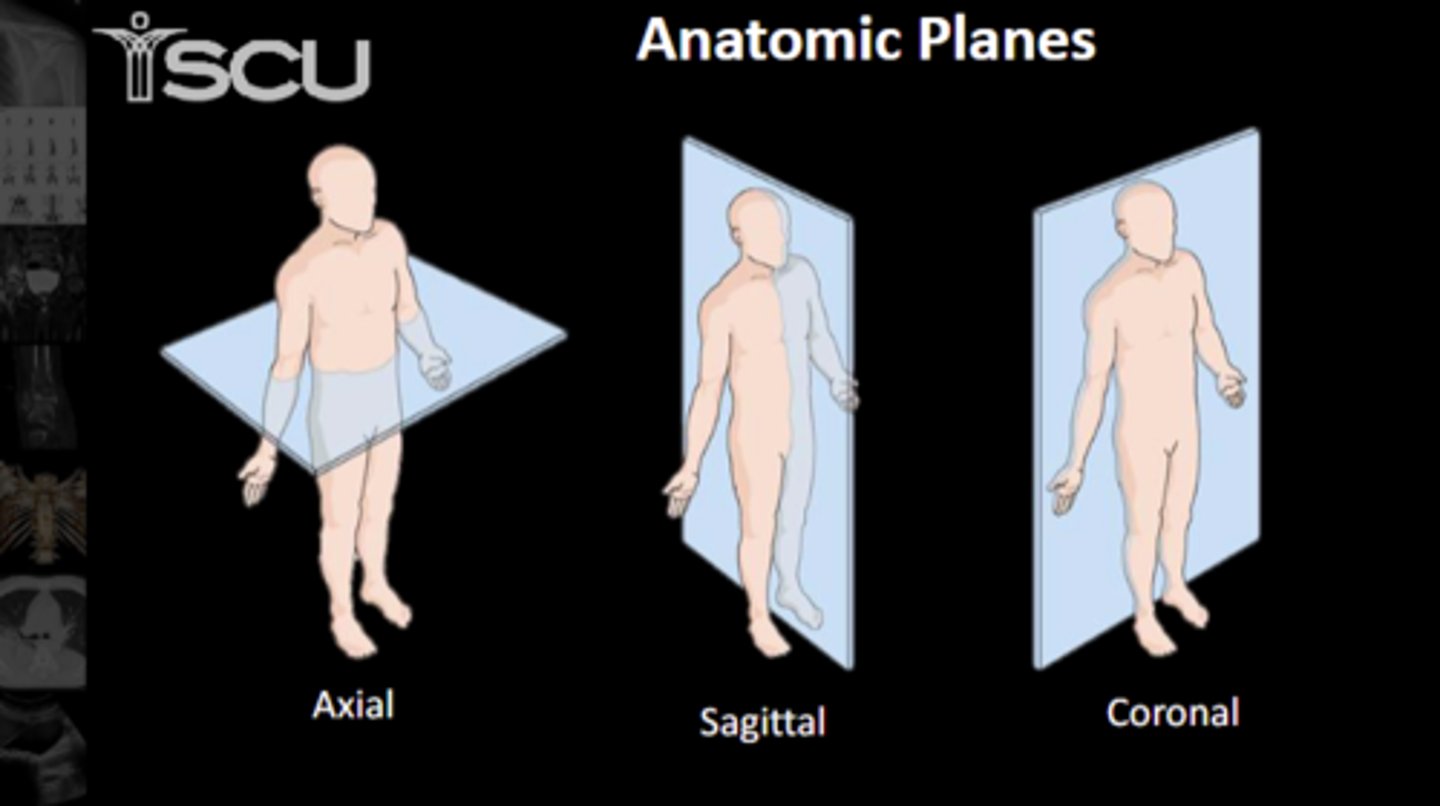
Know which view is which
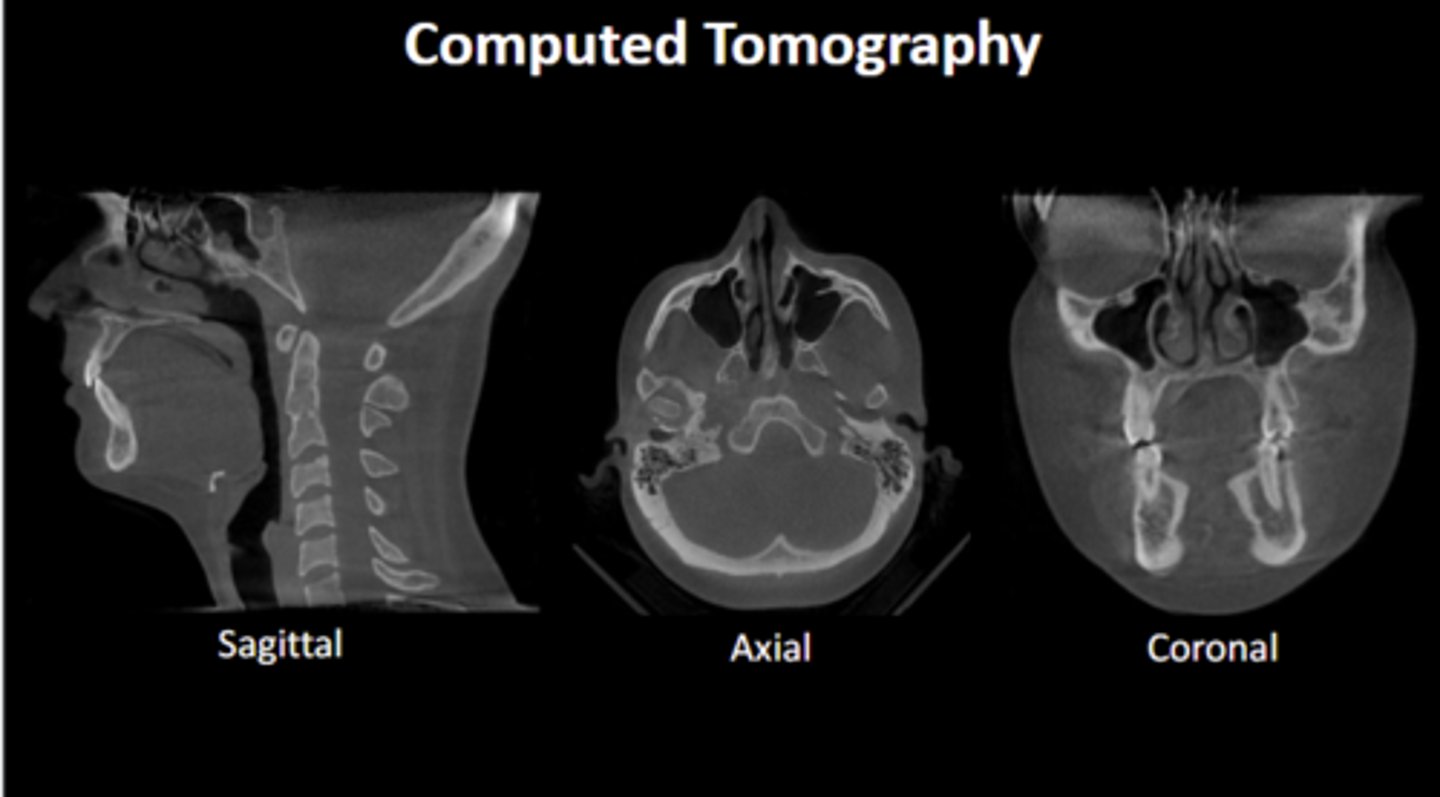
What form of imaging typically has bright white outlines for bones?
CT scans
When was the first MRI of human body performed?
1977
What are the basic physics for MRIs?
hydrogen protons all over the human body are randomly spinning, then aligned by large magnet. radiofrequency wave is then pulsed to misalign the protons, when frequency is removed the protons align back with magnetic field and give off energy. MRI is listening for radiofrequency pulses given off by the body
Different body tissues have:
a. the same concentration of protons
b. different concentrations of protons
different concentrations of protons
MRIs give off ionizing radiation T/F
false
High signal in MRIs refer to ___?
areas of white on MRI
Low signal in MRIs refer to ___?
areas of black on MRI
Intermediate signal in MRIs refer to ___?
areas of grey on MRI
What does hyperintense mean in MRIs?
used to describe region that is whiter in appearance that what it is being compared to
What does hypointense mean in MRIs?
used to describe region that is more black in appearance than what it is being compared to
What does isointense mean in MRIs?
used to describe two different areas sharing a similar appearance
Bright signal in tissues after administration of contrast are described as ___
enhancing
What will have high intensity in a T1 MRI?
fat is high signal intensity, along with subacute hemorrhage and Gadolinium
What will have high intensity in a T2 MRI?
water demonstrates high signal intensity, fat is also high signal
What are typically the only substances that are high signal in both T1 and T2?
fat and subacute hemorrhage
Know how to differentiate between T1 and T2 imaging
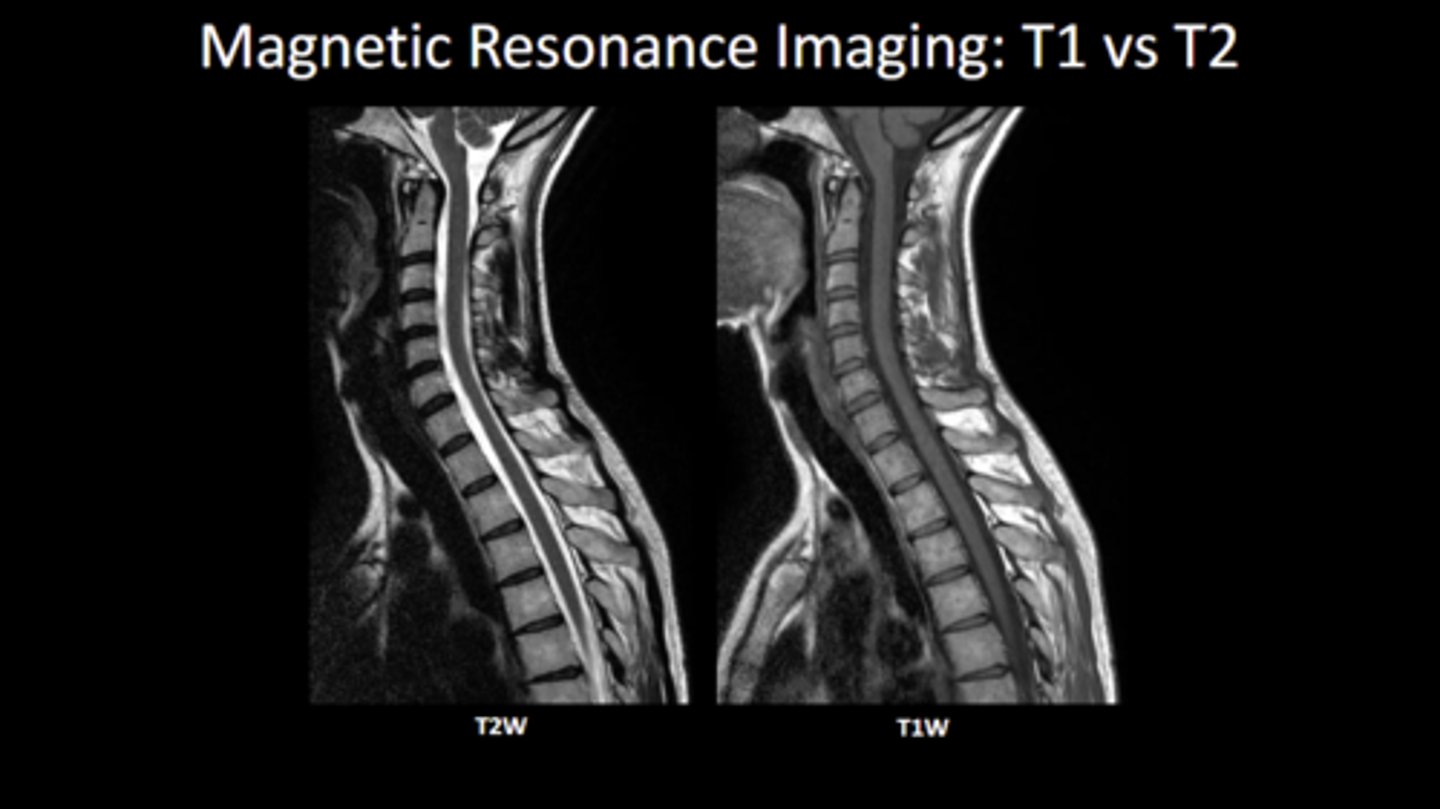
What is high intensity in STIR MRIs?
water is primarily high intensity, fat is low signal
What is T1 CE?
contrast enhanced T1 MRI.
What contrast agent is used for T1 CE? Where does it collect in the body?
contrast agent is typically gadolinium based. collects in areas of high blood flow like leaky vessels in pathologic situations like tumors and infections
Know the difference between T1, T2, and STIR
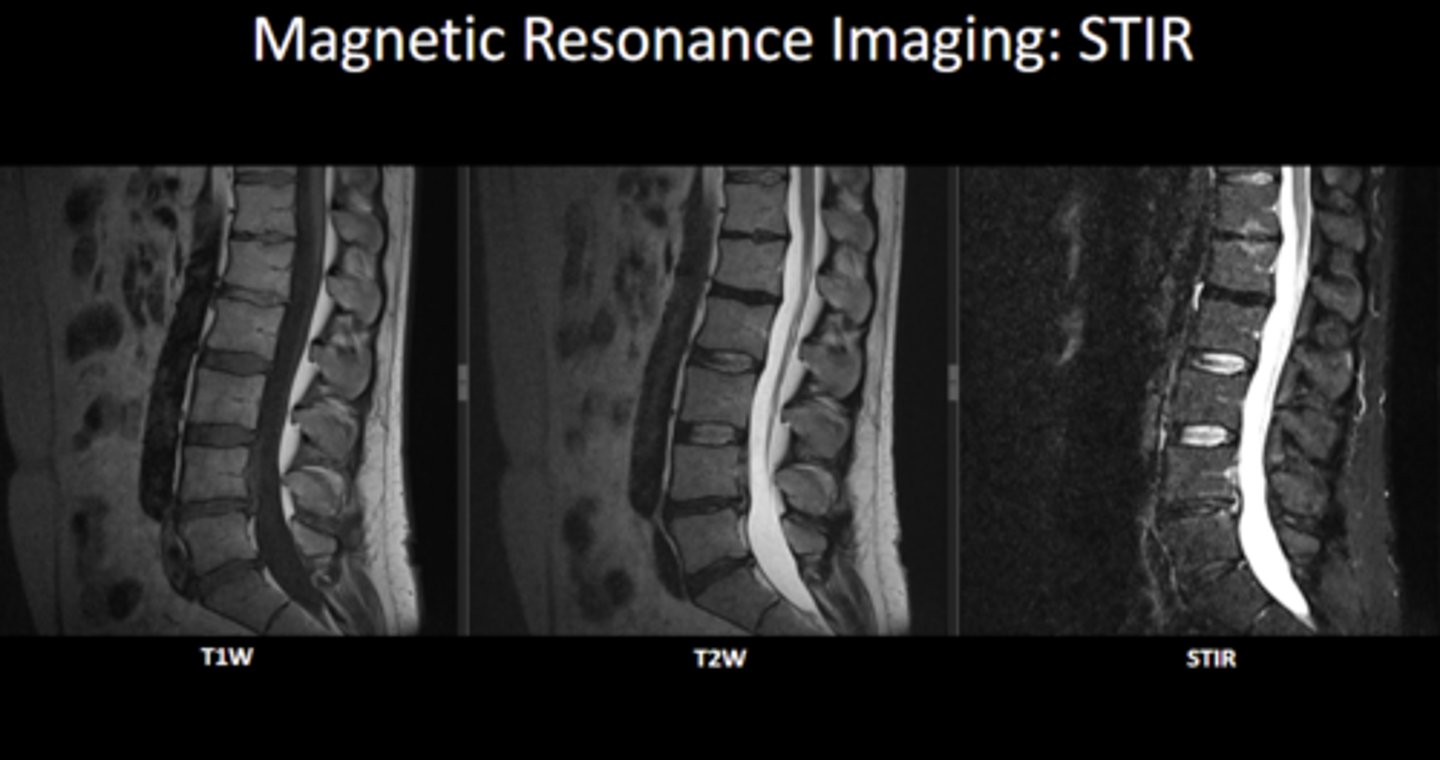
Be able to differentiate FS and CE MRIs
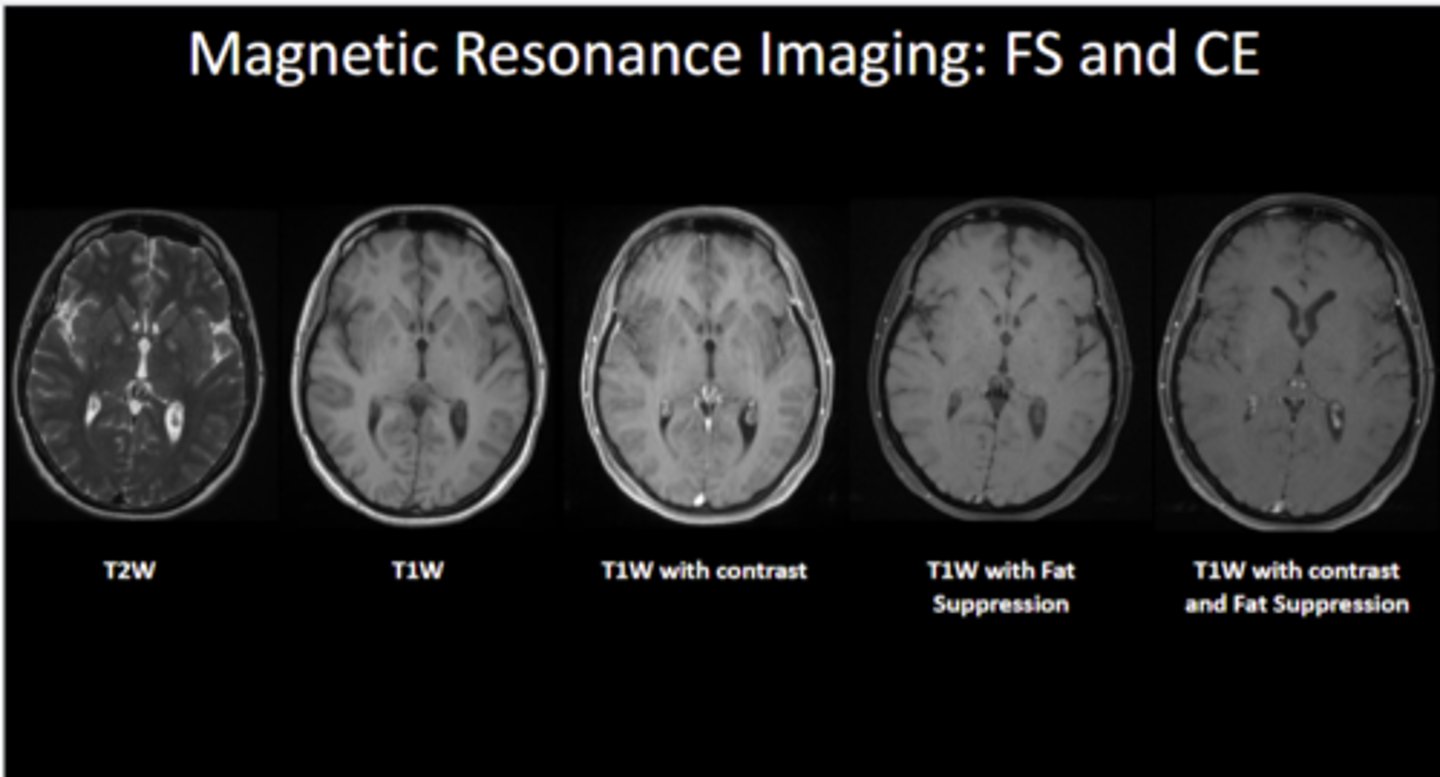
What must be screened to make sure they are absent in the patient before MRI exams?
ferromagnetic material
How do ultrasounds create images?
uses sound wave interactions with tissues (piezoelectric effect)
What is the typical frequency for linear probes? What are they used for?
5-15 MHz, used for looking at more superficial structures like in musculoskeletal
What is the typical frequency for curvilinear probes? What are they used for?
2-5 MHz, used for looking at deeper structures like abdominal and pelvic imaging
What is the typical frequency for phased array probes? What are they used for?
1-5 MHz, coupled with small footprint allows to look at deep structures through small spaces (cardiac imaging between ribs)
What is the typical frequency for endocavity probes? What are they used for?
4-9 MHz, used for intraoral and transvaginal exams
What does hyperechoic mean in ultrasounds?
sound waves are strongly reflected back to creater bright echo on image (areas that appear whiter/brighter on image)
What does anechoic mean in ultrasounds?
area on image that appears black - no sound waves returned to transducer
What does hypoechoic mean in ultrasounds?
area on image that appears between bright and dark due to a small return of soundwaves to transducer
What is acoustic shadowing?
when ultrasound beam is reflect, absorbed, or refracted. anechoic region is created deep to this area
What is posterior acoustic enhancement?
hyperechoic area deep to a structure that transmits sound exceptionally well, commonly occurs with fluid filled structures
What is anisotropy?
when fibrillar tissue is imaged at an angle that is not 90 degree it will have hypoechoic appearance rather than normal hyperechoic appearance
What is injected into the body in nuclear medicine imaging?
radiopharmaceutical
What do scintillation cameras do?
convert radiation into electronic signals
How can scintillation cameras create 2D or 3D images?
over body in a stationary position makes 2D, 3D images are made by moving around the area of interest then manipulated into 3D
What are the two main types of 3D imaging in nuclear medicine imaging?
PET (positron emission tomography) and SPECT (single photon emission tomography)
Understand nuclear medicine 2D imaging
bladder is highlighted because that is how the body excretes the radiopharmaceutical. right shoulder is also highlighted as the injection site
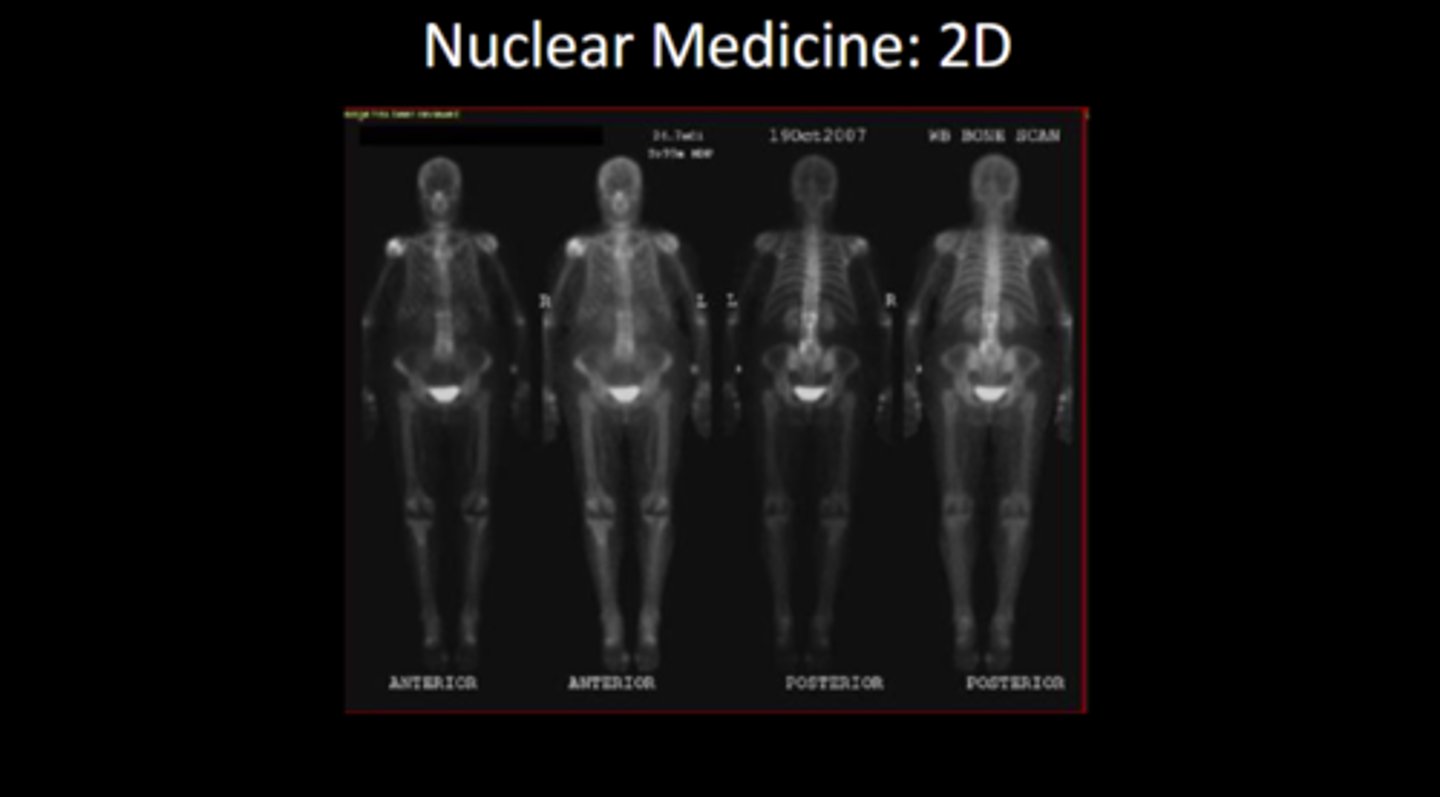
Nuclear med examinations expose patient to ionizing radiation T/F
true
What does the concentration of radiopharmaceutical in tissues mean?
hot spots of increased uptake
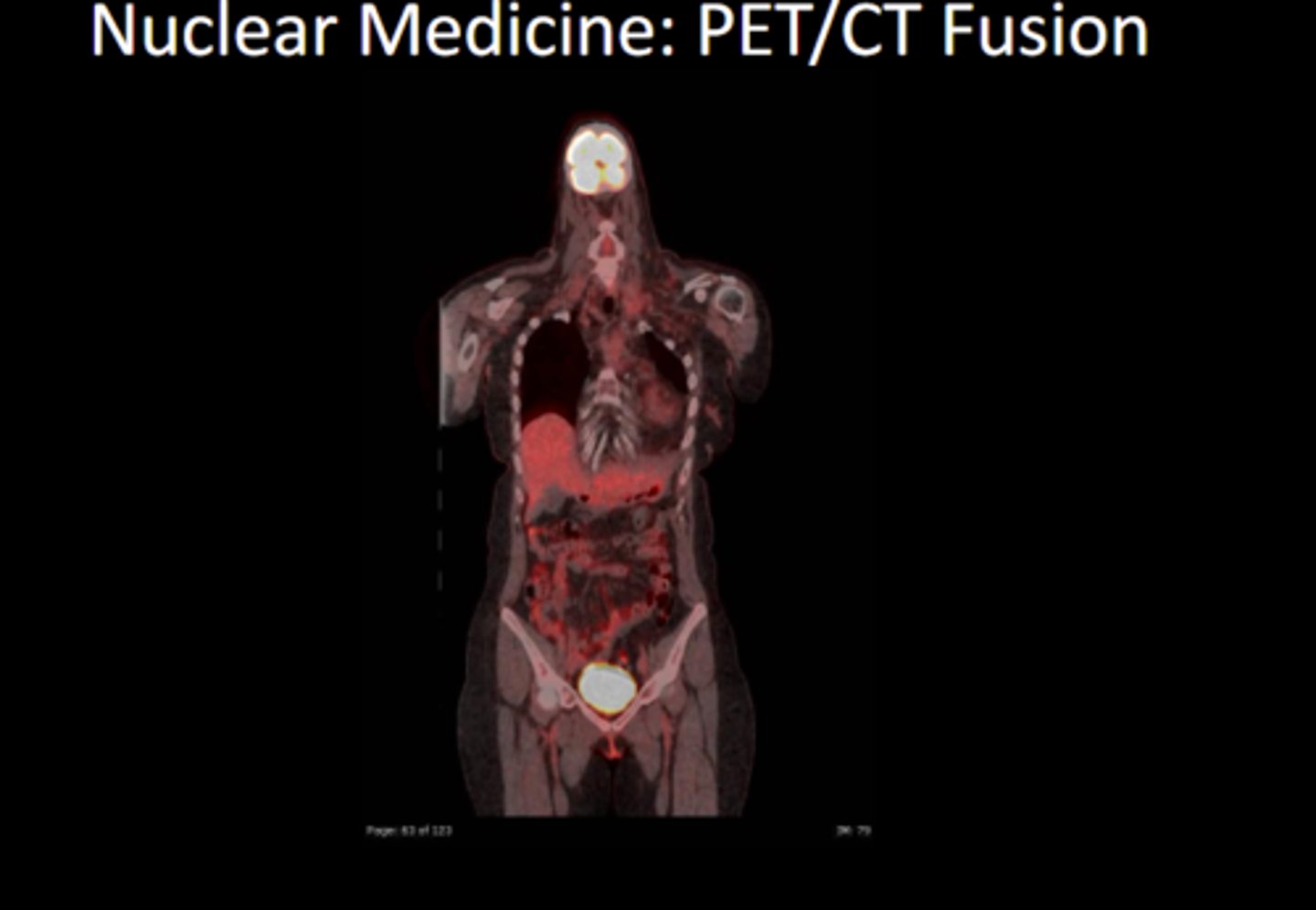
What are scintigraphy exams combined with CT or MRIs called?
fusion studies
What is different about nuc med and fusions?
fusion shows imaging for anatomy and radiopharmaceutic