Lab Final
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:37 PM on 4/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
1
New cards
What does the trachea slide look like?
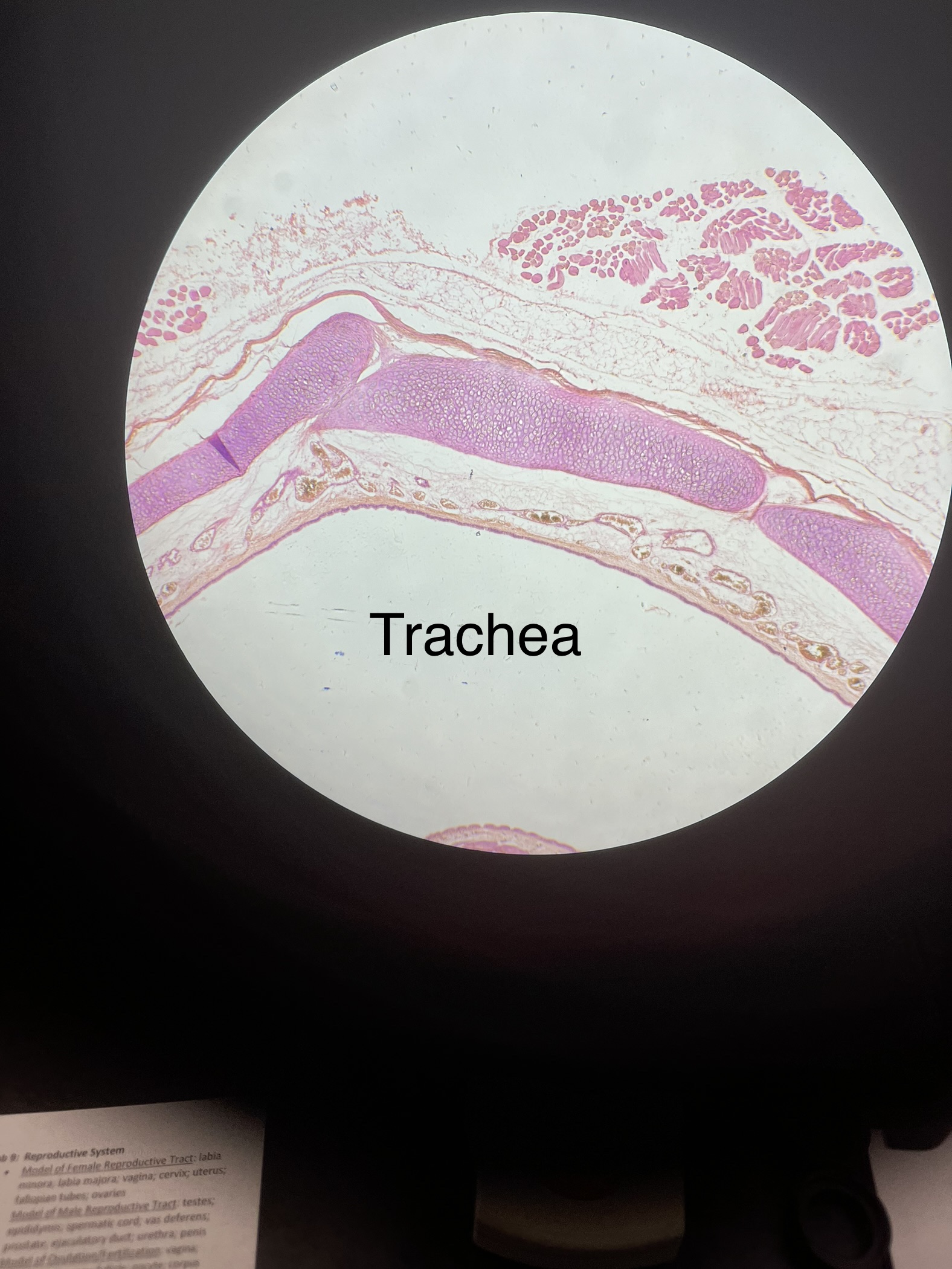
2
New cards
What does the human lung slide look like?
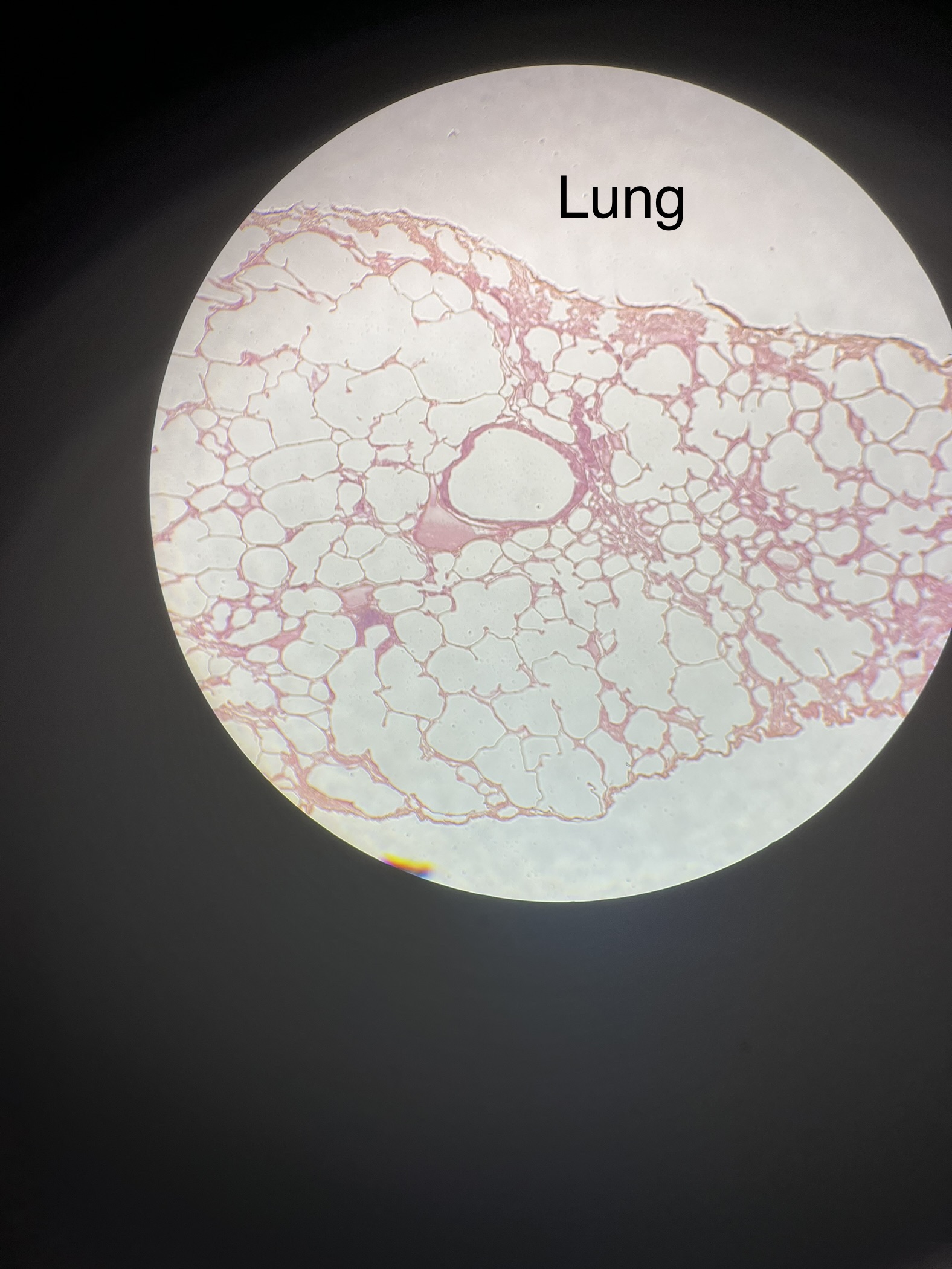
3
New cards
What does the smokers lung slide look like?
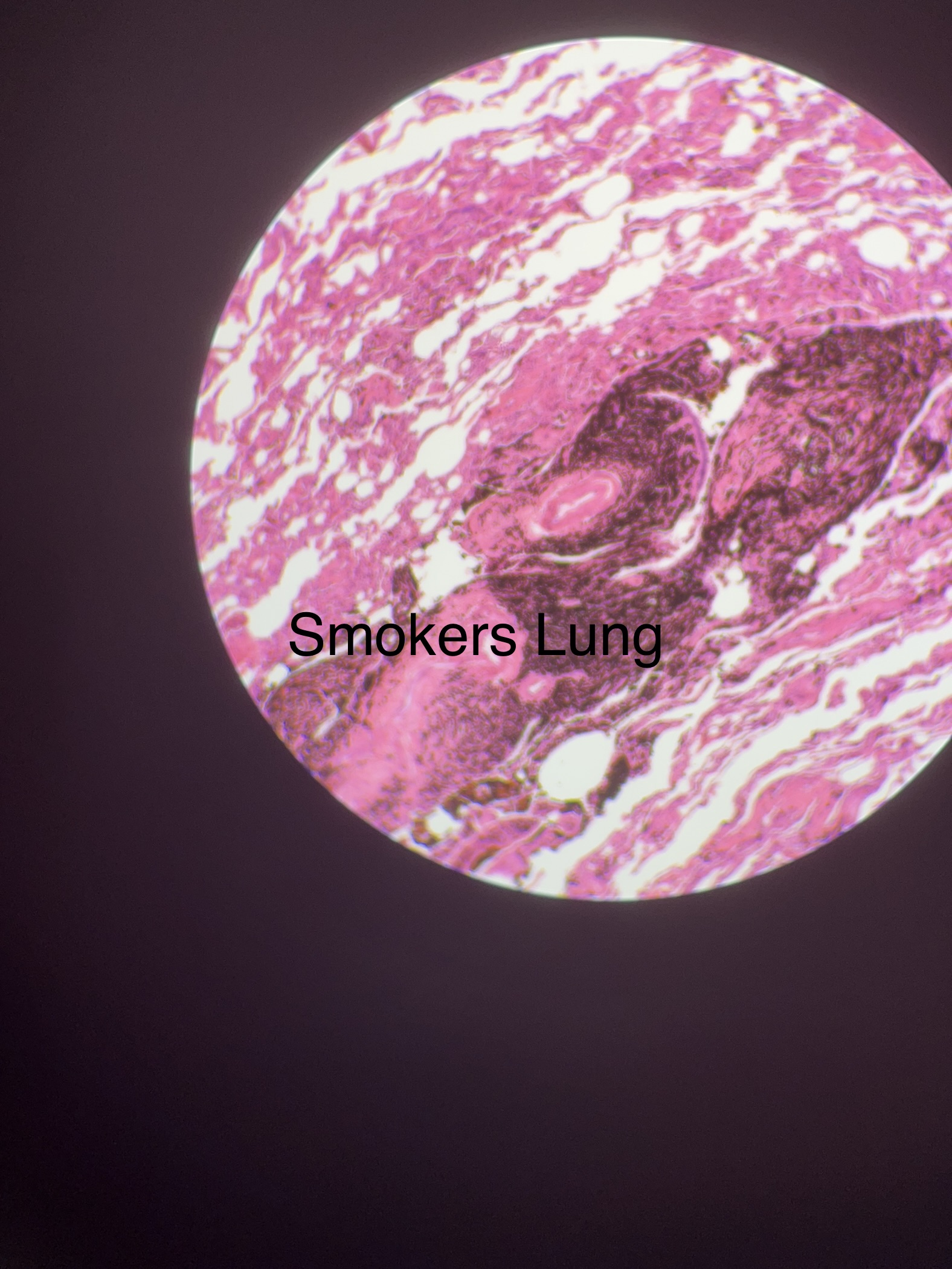
4
New cards
What structure makes an Adams apple and why are men more likely to have one?
Adams apple is thyroid cartilage and the laryngeal prominence. During puberty, testosterone makes males vocal cords grow thicker and longer. Cartilage grows and tilts slightly forward. Testosterone stimulates growth.
5
New cards
What role does the arytenoid cartilages have in sound production?
They help move the vocal folds, allowing tension, relaxation, or approximation of these. This is because the vocal move along with them
6
New cards
What is the purpose of the “C” shape to the cartilage? Why not go all the way around?
They support the trachea but also allow it to move and flex when breathing. Also allows for flexibility and keeping it from collapsing.
7
New cards
What is inside alveolar sacs?
Air
8
New cards
What does the human kidney slide look like?
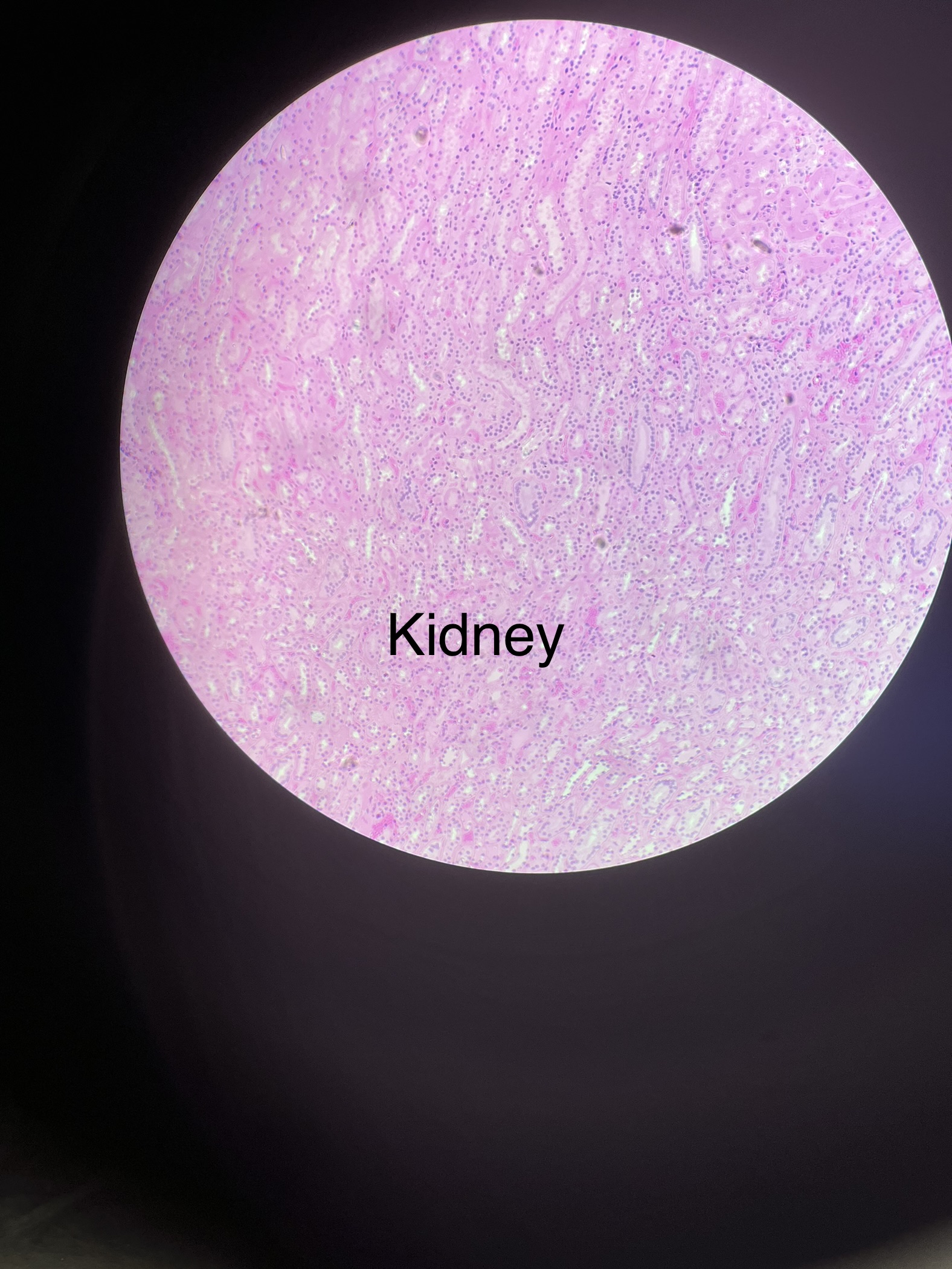
9
New cards
What are peristaltic contractions?
A series of normal coordinated, rhythmic muscle contractions, that occurs automatically to move food through the digestive tract.
10
New cards
What is the anatomy and physiology behind being able to hold pee?
The bladder expands as it fills up and only when the nerves in the bladder wall detect expansion, are signals sent to the brain indicating the bladder is full.
\
Internal sphincter → smooth/involuntary
External sphincter → skeletal/controlled + voluntary
\
Internal sphincter → smooth/involuntary
External sphincter → skeletal/controlled + voluntary
11
New cards
Nephron filtrate ultimately comes from the?
Blood
12
New cards
Where are the kidneys located in the body?
Just below the ribcage, one on each side of the spine. They are retroperitoneal.
13
New cards
What is the pathway of fluid from the point of glomerular filtrate formation to leaving the body as urine?
* Glomerular capsule
* proximal convoluted tubule
* nephron loop
* distal convoluted tubule
* collecting duct
* papillary duct
* minor calyx
* major calyx
* renal pelvis
* ureter
* urinary bladder
* urethra
* proximal convoluted tubule
* nephron loop
* distal convoluted tubule
* collecting duct
* papillary duct
* minor calyx
* major calyx
* renal pelvis
* ureter
* urinary bladder
* urethra
14
New cards
What does the human stomach (stomach fundus) slide look like?

15
New cards
What does the small intestine slide look like?
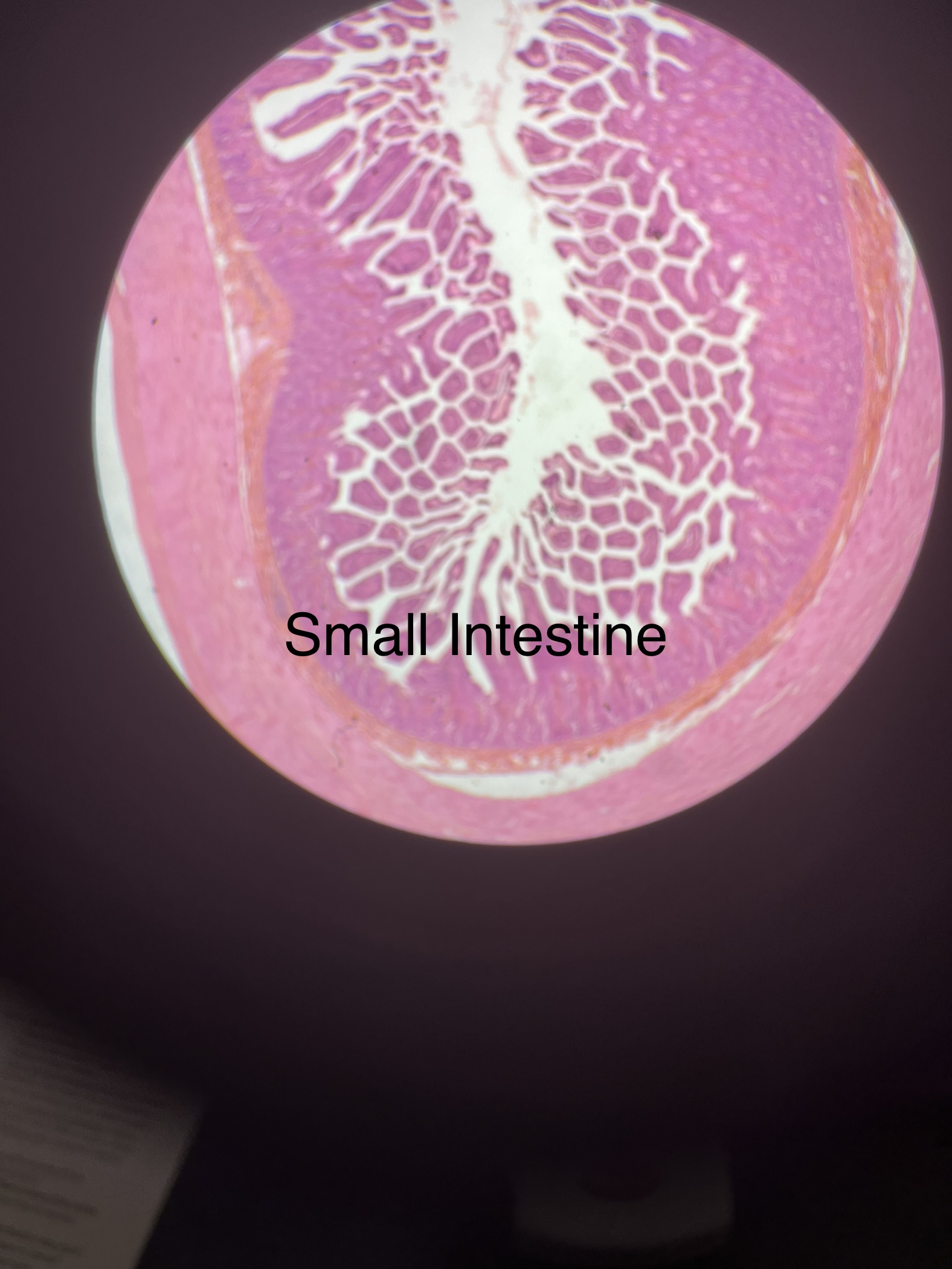
16
New cards
What does the large intestine (human colon) slide look like?
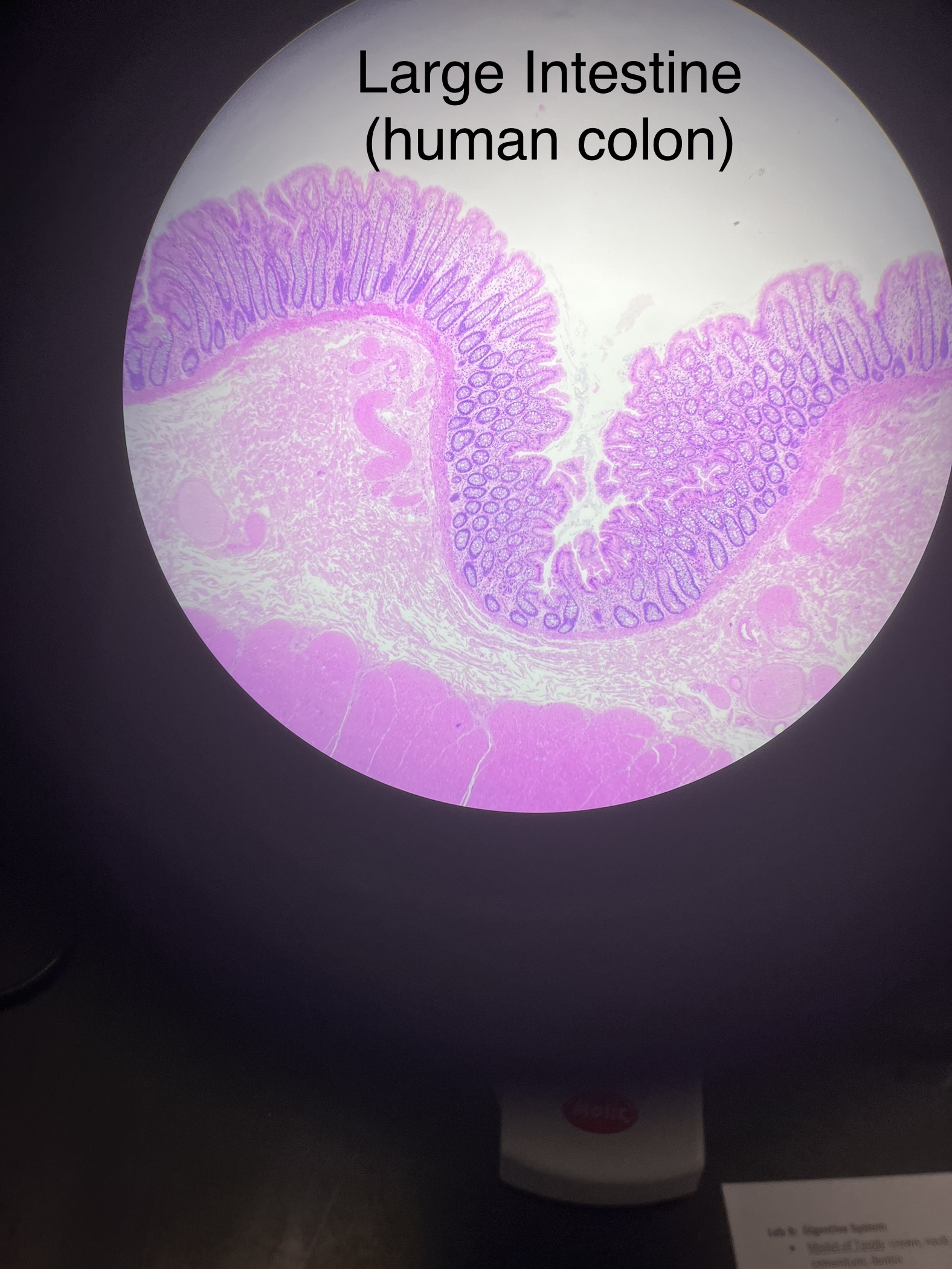
17
New cards
How many teeth are there?
20 Decidious (baby teeth) and 32 adult teeth
18
New cards
What are the two types of digestion?
Mechanical: involves physically breaking down food substances into smaller particles to more efficiently undergo chemical digestion
Chemical: further degrade the molecular structure of the ingested compounds by digestive enzymes into a form that is absorbable into the bloodstream
Chemical: further degrade the molecular structure of the ingested compounds by digestive enzymes into a form that is absorbable into the bloodstream
19
New cards
What is the path of food through the digestive tract from oral cavity to anus?
mouth → pharynx → esophagus → stomach (chime) → small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum) → large intestine ( cecum - appendix & colon - ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid)
20
New cards
What are the 4 terms for food along digestive tract?
Food/drink → bolus → chime → feces/stool
21
New cards
What is the flow of bile from the liver to the small intestine?
common hepatic duct → cystic duct → common bile duct, hepatopancreatic sphincter → duodenum
22
New cards
What is the role of bile?
Bile helps with digestion. It breaks down fats into fatty acids, which can be taken into the body by the digestive tract.
23
New cards
What is the contribution of the pancreas in digestion?
Pancreas makes juices called enzymes which break down sugar, fats, starches, and makes hormones.
\
Pancreas produces amylase, lipase, RNA, and DNA
\
Pancreas produces amylase, lipase, RNA, and DNA
24
New cards
What plays the biggest role in chemical digestion?
Small intestine
25
New cards
What are the most abundant cells in the large intestine?
Goblet cells (intestinal mucosal epithelial cells that serve as the primary site for nutrient digestion and mucosal absorption)
26
New cards
What does an ovary with maturing follicle slide look like?
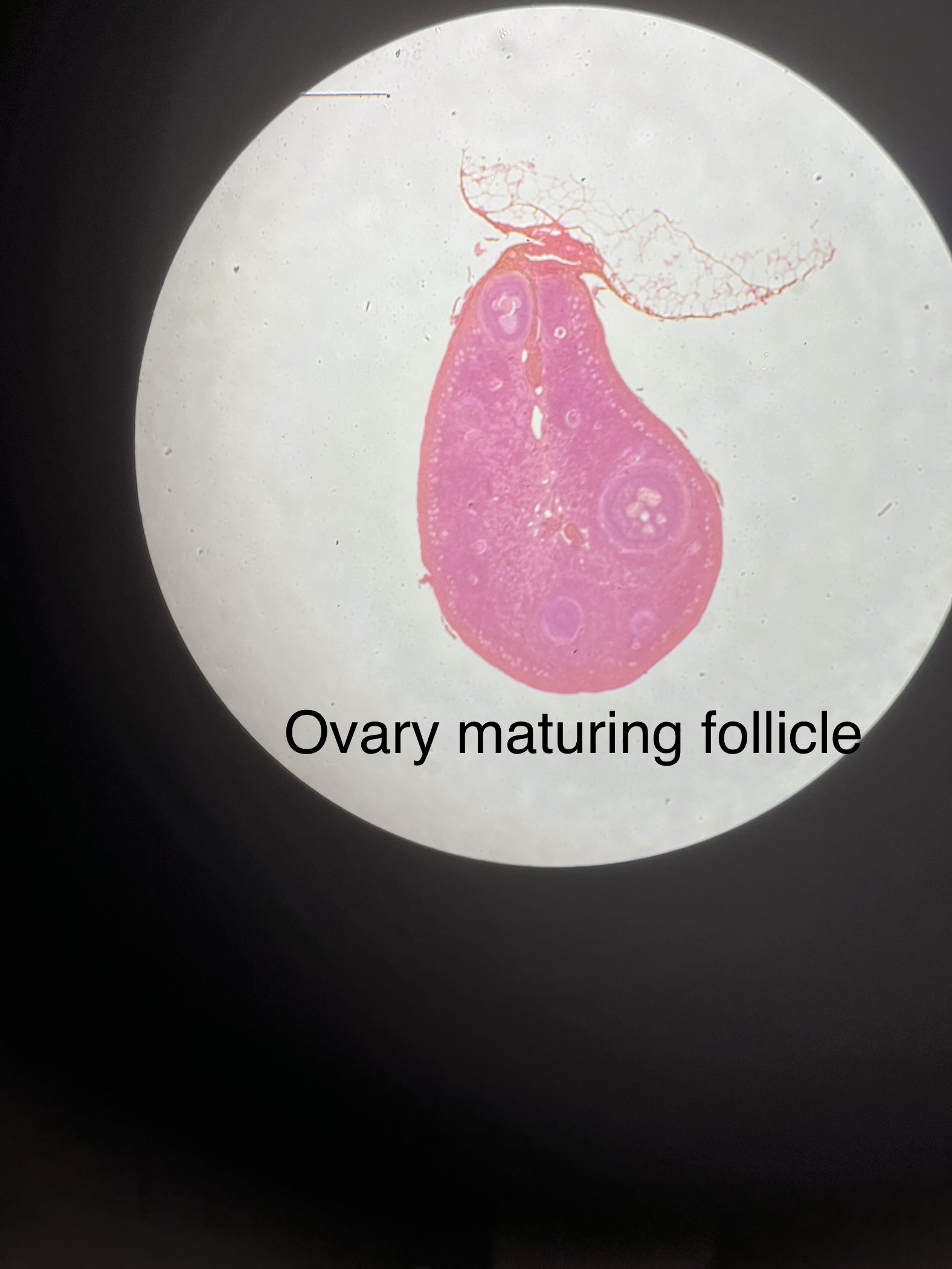
27
New cards
What does a menstrual uterus slide look like?
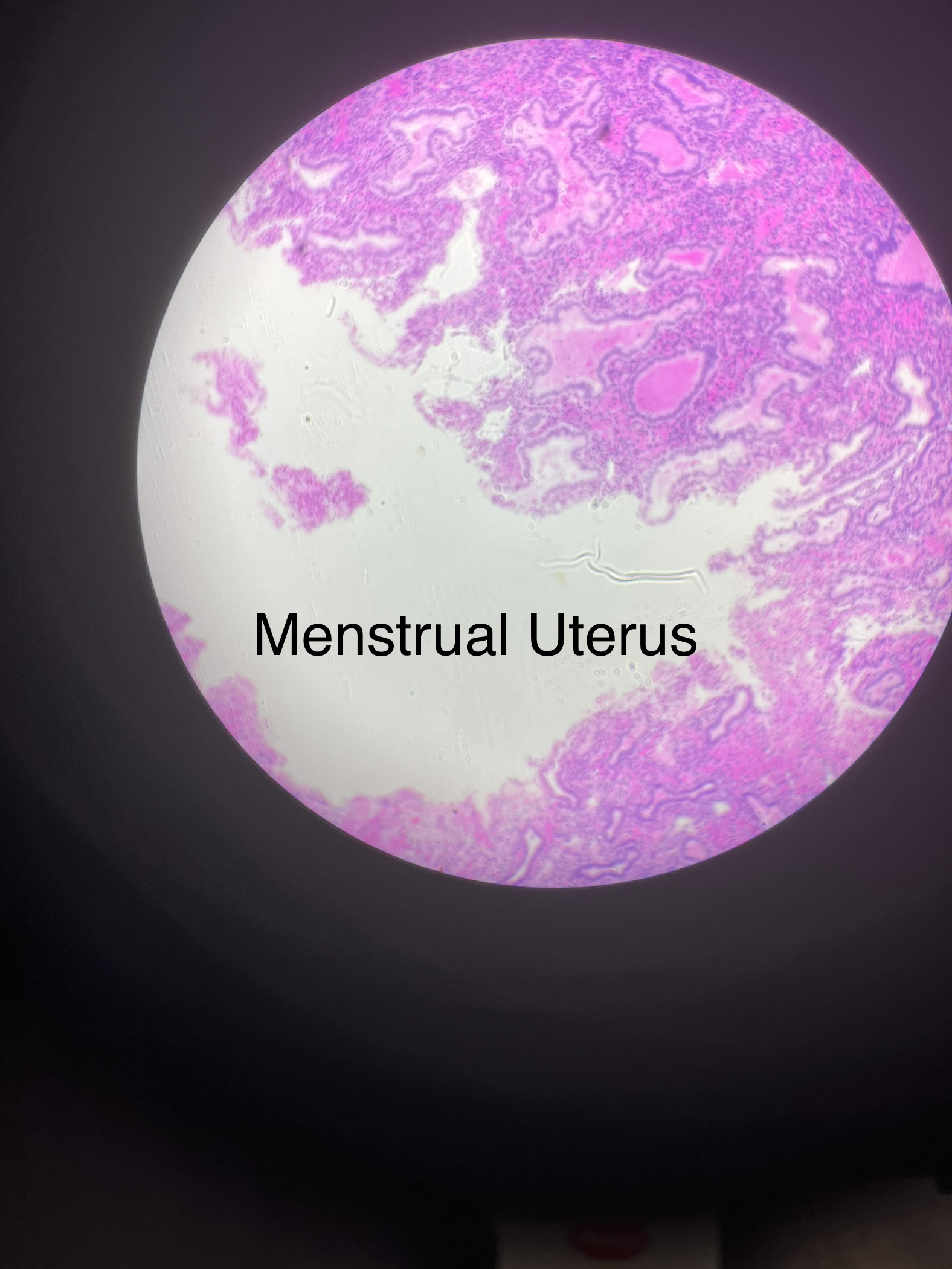
28
New cards
What is the collective term for all external genitalia?
vulva
29
New cards
What does fertilization take place?
Fallopian tubes
30
New cards
What is the name for the inner layer of the uterus?
endometrium
31
New cards
What are the phases of the menstrual cycle?
Menstrual phase (1-5): discharge of menstrual fluid from the vagina (menses)
Proliferative phase (6-14): the layer of endometrial tissue lost in menstruation rebuilt
Secretory phase (15-26): endometrium thickens, still more in response to progesterone from corpus luteum
Premenstrual phase (27-28): the period of endometrial degeneration
Proliferative phase (6-14): the layer of endometrial tissue lost in menstruation rebuilt
Secretory phase (15-26): endometrium thickens, still more in response to progesterone from corpus luteum
Premenstrual phase (27-28): the period of endometrial degeneration
32
New cards
In between which two phases does ovulation occur in the mestrual cycle?
Between proliferative and secretory
33
New cards
What is the pathway of sperm from where it is synthesized through the male body and out the penis?
Rete testis → efferent ductules → duct of the epididymis → ductus vas deferens to the terminal ampulla → ejaculatory duct → urethra
34
New cards
What are the three components of semen?
Seminal vesicles - 60%
Prostate gland - 30%
Bulbourethral (Cowper) glands - 10%
Prostate gland - 30%
Bulbourethral (Cowper) glands - 10%
35
New cards
What is cut in a vasectomy?
Vas Deferens
36
New cards
What is the secondary oocyte?
The egg
37
New cards
Anatomically, how can an egg get lost following ovulation?
It can remain trapped in follicles or get lost in the peritoneal cavity (if it falls into cavity, they would likely die)