micro exam 1 LC
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Select the characteristics of a microbe. Choose all that apply.
Too small to be seen with the unaided eye
Composed of cells
Primary role is to cause illness
Found almost everywhere
1 and 4
Did Pasteur’s work support the theory of biogenesis or the theory of spontaneous generation?
Biogenesis
Spontaneous generation
Both
Neither
1
You discovered a unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus. The cell wall of this organism was found to contain peptidoglycan. To which domain does this organism belong?
Domain Eukarya
Domain Bacteria
Domain Archaea
2
Why are viruses not included in the three domain system of classification?
Viruses do not have plasma membranes
Viruses are not alive
Viruses do not have cells
Viruses do not have nuclei
2 and 3
A bacterial cell is measured to be 4000 nm in length. Express this measurement in micrometers.
4
What is the total magnification with a 10X ocular lens when using the high-dry objective (40X)?
10X
40X
50X
100X
400X
4000X
400X
Why is immersion oil necessary when using the 100X objective (1000X total magnification), but not when using the lower power objectives?
The 100X objective lens is larger than the lower power objective lenses
The 100X objective lens is smaller than the lower power objective lenses
The 100X objective lens uses a shorter wavelength of light
The 100X objective uses a longer wavelength of light
2
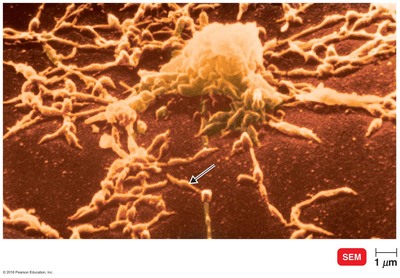
What type of microscopy would you use if you wanted a high resolution view of structures on the surface of a paramecium (a unicellular protozoan)?
Brightfield
Darkfield
Phase-contrast
Confocal
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
Atomic force
6
What type of microscopy would you use if you wanted to study the structure of a bacterial biofilm on a glass slide?
Brightfield
Darkfield
Phase-contrast
Confocal
Scanning acoustic microscopy
Atomic force
5
Select the major features of a prokaryotic cell.
Lack membrane bound organelles
DNA found in the nucleus
DNA associated with histones
Chemically simple cell walls
Divide by binary fission
Divide by mitosis
DNA is typically a single, circular chromosome
1, 5 and 7
This is a Gram stain from a sputum (mucus) sample of a patient with a respiratory infection.
Are the bacterial cells in this image Gram positive or Gram negative?
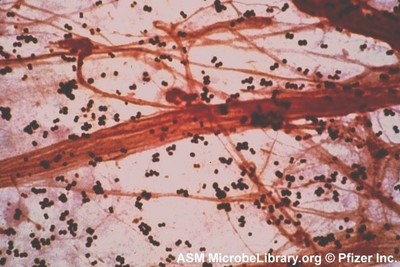
Gram positive
This is a Gram stain from a sputum (mucus) sample of a patient with a respiratory infection.
What is the cell shape and arrangement of the bacterial cells in this image?
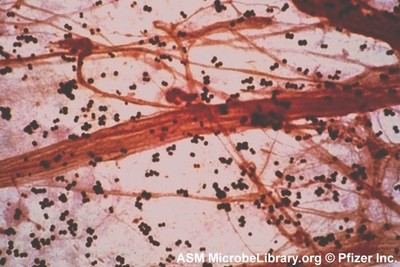
Diplobacilli
Streptobacilli
Staphylococci
Cocci in tetrads
Streptococci
Individual spirochetes
C
Which two structures are used to identify the serovar of Escherichia coli O157:H7?
(Hint: E. coli is a Gram negative bacillus)
Peptidoglycan
Lipopolysaccharide
Teichoic acid
Flagella
Pili
Axial filament
Plasma membrane
2 and 4
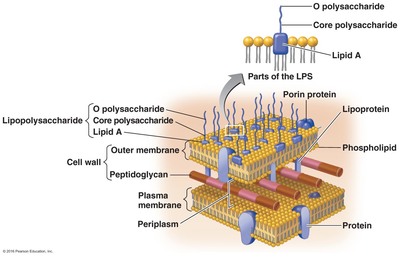
What type of bacterial cell wall is depicted in this image?
Gram positive
Gram negative
Acid-fast
Encapsulated
2
Why should bacterial cells not be placed in a solution of pure water?
The cells will lose water, causing plasmolysis
The cells will lose water, causing them to burst
The cells will take on water, causing them to burst
The cells will take on water, causing plasmolysis
3
Which of the following statements about bacterial endospores is TRUE?
Endospores are used for reproduction.
A single vegetative cell can produce many endospores.
Endospores allow a cell to survive environmental changes.
A vegetative cell produces one endospore and keeps growing.
Endospores are easily stained using a Gram stain.
3
Select the major features of a eukaryotic cell.
Lack membrane bound organelles
DNA found in the nucleus
DNA associated with histones
Cell walls usually contain peptidoglycan
Chemically simple cell walls
Divide by binary fission
Divide by mitosis
DNA is typically a single, circular chromosome
2, 3, 5 and 7
Which of the following may be found in eukaryotic cells, but not in prokaryotic cells?
(Select all that apply.)
Cell wall
Cytoplasm
Cytoplasmic membrane
DNA
Endoplasmic reticulum
Flagella
Golgi body
Mitochondria
Nucleoid
Nucleus
Peptidoglycan
Ribosomes
Fimbriae
5, 7, 8,10
What is unusual about the ribosomes found in the chloroplasts and mitochondria?
They are larger than eukaryotic ribosomes
They are smaller than eukaryotic ribosomes
They are similar to prokaryotic ribosomes
Nothing. They are the same as other ribosomes in the eukarytotic cell.
2 and 3
True or false?
Fungal spores and bacterial endospores have the same structure and function.
False
Are viruses living or non-living?
Living
Non-living
2
Why can viruses not be cultivated in plain culture media like bacteria?
Normal culture media does not contain enough protein for viruses to replicate.
Normal culture media does not contain enough ATP for viruses to replicate.
Viruses require host cells to be able to replicate.
Viruses are too small to be isolated in the laboratory.
3
Which of the following is NOT part of a bacteriophage replication cycle?
Virion binds to a host cell surface protein that provides an important host function
The virion injects its genome into the host cell
The capsid of the virion enters the host cytoplasm
The viral genome directs the host ribosomes to synthesize viral components
3
This is Epulopiscium fishelsoni, an organsism found in the gut of the Red Sea surgeon fish. It is 80 µm x 600 µm. Based only on this information, how would you classify this organism?
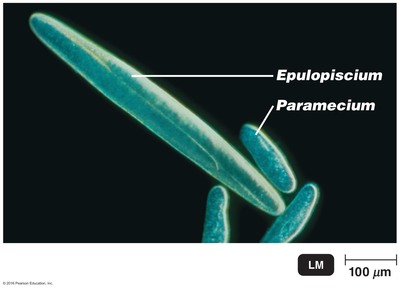
Eukaryote
This is Mycoplasma pneumoniae. It is 0.1-0.25 µm. How would you classify it?
Prokaryote