Genetics Chapter 1 Test
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
What is Genetics?
Genetics is the branch of biology that studies genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms
What are some reasons that genetics is important?
-Genes affect our susceptibility to many diseases and disorders
-Genes are important in agriculture, biotechnology, and medicine
-There is a tremendous amount of DNA in the biosphere (EDNA) and scientists can use it to quantify the diversity of the biosphere.
What is cell theory? Who created it?
Cell theory tells us that all organisms are composed of basic structural units called cells. It was presented by Schleiden and Schwann
What is spontaneous generation? Who disproved it?
Spontaneous generation is the creation of living organisms from nonliving components. Louis Pasteur disproved it
Who published a book regarding the theory of evolution? What was it called
Charles Darwin. It was called The Origin of Species
In The Origin of Species, what two things did Darwin highlight that are important?
Decent with modification and Natural Selection
What tells us that existing species arose from an already existent species?
Decent with modification
What is the mechanism for evolutionary change?
Natural Selection
What was Mendel’s work the foundation for?
(Transmission) genetics which is the branch of biology that is concerned with the study of heredity and variation
What are the three divisions of genetics?
-Molecular Genetics
-Transmission Genetics
-Population Genetics
(Mikitaka took poppers)
What division of genetics is concerned with the molecular structure and function of genes and genomes? Concerns the cellular details of heredity
Molecular genetics
What division of genetics concerns how genetic traits are passed from one individual to another?
Transmission genetics
What division of genetics concerns understanding gene transmission in a group of individuals (a population)
population genetics
What is a genome?
A complete set of genetic instructions for any organisms (either RNA or DNA)
All prokaryotes and eukaryotes exclusively pass traits to the next generation using ____. Viruses, however, pass traits to the next generation using ____
DNA, RNA
Genomes are copied during the process of ______
replication
____ are the fundamental unit of heredity
genes
Genes come in multiple forms called ____
alleles
Genes confer _________
phenotypes
phenotypes are made up of _____
proteins that are made up of genes
Where is genetic information carried
DNA and RNA
Genes are located in ________
chromosomes
What are alleles?
Mutations of a gene. They are the source of genetic variation.
2 alleles exist for each gene as most organisms are diploid
What is a genotype?
The set of alleles for a given trait
What is a Phenotype?
Expression of the genotype. Produces an observable trait
What area of genetics studies the structure, function, and evolution of genes and genomes?
Genomics
What area of genetics identifies a set of proteins present in cells under a given set of conditions? Studies their function and interactions
Proteomics
What area of genetics uses hardware and software for processing nucleotide and protein data
Bioinformatics
What are organisms with characteristics that make them useful for genetic analysis?
Model genetic organisms
What are the 6 common model genetic organisms
-Fruit fly
-E. Coli
-C. Elegans
-A. thaliana
-Mice
-S. Cerevisiae
Feverishly, everyone callled anne, my sister
What are the aspects of the six model organisms that make them useful to study?
-short generation time
-number of offspring
-ability to carry out controlled genetic crosses
-ability to be reared in a lab setting
-availability of numerous genetic variants
-accumulated knowledge abt their genetic systems
What is the difference between gene, allele, and genotype?
A gene is a section of DNA that directly translates to a physical trait, like a gene that influences eye color.
An allele is a different variation of a gene. For example, some people may get the brown eye allele, or the blue eye allele, for the eye color gene. A genotype is all of the alleles that an individual has for a certain gene (Aa, AA, Bb, BB, etc.).
The genome is all of the DNA that is inside of an organism. This contains every single gene, including even the non-coding DNA
genetic material must exhibit what four characteristics?
-genetic material must contain complex information
-genetic material must replicate faithfully
-genetic material must encode the phenotype
-genetic material must have the capacity to vary(evolve)
What does DNA stand for
Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid
What is DNA/RNA made up of?
DNA?RNA is made up of nucleotides based on 3 molecules: sugar (pentose), phosphate, base
Star Platinum Bitches
What is the difference between the job of DNA vs RNA?
DNA’s role is to store genetic material. RNA’s role is to carry the genetic material into the cytoplasm and then to covert genetic material into proteins and into phenotype
What is Deoxyribose?
Deoxyribose is a sugar derived from ribose by replacing an hydroxyl (OH) group with hydrogen
What is phosphate?
phosphorus bonded to 4 atoms of oxygen
What are the five different bases of DNA and RNA?
-Adenine
-Thymine
-Cytosine
-Guanine
-Uracil
A _____ has two rings
Purine
A _____ has one ring
Pyrimidine
What bases are purines?
Adenine and Guanine
What bases are pyrimidines?
Cytosine, thymine, and uracil
What is dNTP
Deoxy-nucleoside-tri-phosphate
monomeric unit of DNA
How are backbones of DNA structure formed?
They are composed by altering sugar and phosphate groups
and phosphodiestar (C-O) bonds (covalent)
Silly Piccolo
What bonds make up DNA backbones? What direction do they run in?
phosphodiester bond (C-O) Covalent bond
runs in 5’ 3’ direction and 3’ to 5’ the other way
What keeps the two back bones together?
complementary bases (ATCG)
What is true of the bonding of the complementary bases in DNA?
Purines ALWAYS bond with Pyrimidines
Bases are attached through hydrogen bonds.
What is over all true about the components of the DNA structure?
DNA is made up of a double helix where the two backbones are bonding through complimentary bases in an antiparallel direction.
How does RNA differ from DNA in structure?
It is made of only a single helix and thymine is replaced with uracil
Can sometimes make a double helix but the helixes are VERY weak. This is because uracil is not capable of making a strong bond with uracil and OH group presents additional weakening to the helix
The two DNA strands will spontaneously bond as far as they are…
complementary and antiparallel
What is Chargaff’s rule?
Ratio of pyrimidine=ratio of purine
A=T
C=G
What is true of the secondary structure of DNA?
-double helix
-backbone formed through phosphodiester bonds
-hydrogen bonds and base pairings
-antiparallel complementary DNA strands
Who identified the three dimensional structure of DNA?
ROSALIND FRANKLIN!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! and watson and crick if they even really did anything
_____ is the right handed clockwise screwing helix with approx 10 base pairs per turn
B-DNA
______ is created when there is less available water. shorter and wider DNA
A-DNA
______ is left handed DNA. Double helix bases are oriented in zig zag type orientation. Could be involved in the protection against viruses
Z-DNA
__________ is a single strand of nucleotides when sequences of nucleotides on the same strand are introverted complements. RNA molecules may contain numerous of these allowing them to fold up into complex strucutres.
Hairpin structure (loop)
What is DNA replication?
the process of making a copy of the DNA genome
When does DNA replication occur?
S phase of the cell cycle in both mitosis and meiosis
Why must replication must be extremely accurate?
One error per million base pairs leads to 6400 mistakes every time the cell divides
What are the three proposed DNA replication models?
-Conservative replication model
-Dispersive replication model
-Semi-conservative replication model
What replication model stated that parental molecules directs synthesis of an entirely new double-stranded molecule, such that after one round of replication, one molecule is conserved as two old strands? This is repeated in the second round
Conservative replication
What replication model states that material in the two parental strands is distributed more or less randomly between two daughter molecules? Old material is dist. symmetrically between two daughter molecules.
Dispersive replication model
What replication model is the intuitively appealing model because separation of the two strands provides two templates, each of which carries all the information of the original molecule? It is also the correct one as determined by Stahl and Meselson
Semiconservative Replication model
What is the unit of replication-segment of DNA that undergoes replication?
replicons
What is the place at which replication begins?
Replication origin
What type of replication involves the circular DNA of prokaryotes?
Theta replication
What type of replication involves DNA or eukaryotes?
Linear replication
At the site of replication, a helix is unwound creating the what
replication fork
If replication is bidirectional there are how many replication forks
2
how many replication origins are present per replicon
1
What is the difference between Theta replication and Linear replication?
Theta replication occurs in prokaryotes such as bacteria and archaea where as linear replication occurs in eukaryotes. Theta replication has only one ORI while linear replication has thousands. Theta replication is circular. Linear is linear. Linear DNA replication takes place in eukaryotic chromosomes.
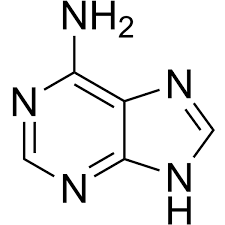
What base is this
Adenine
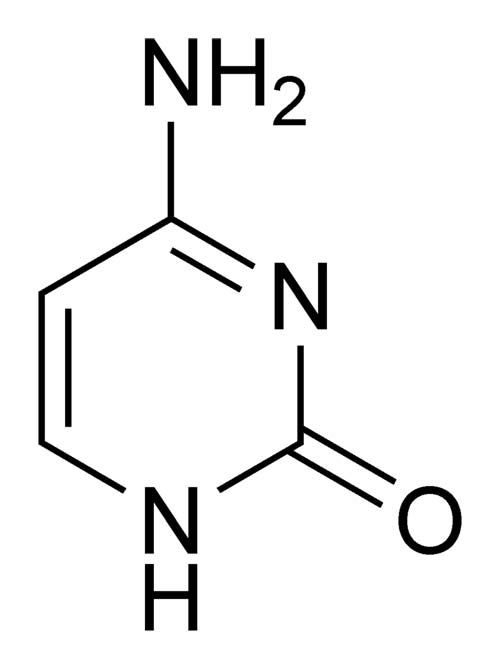
What base is this
Guanine
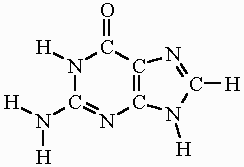
What base is this
thymine
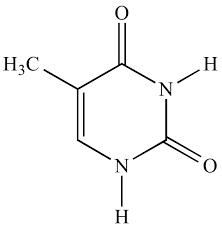
What structure is this
cytosine
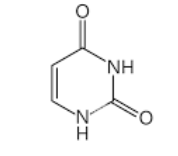
what base is this
Uracil
Which of the following clusters of terms accurately describes DNA as it is generally viewed to exist in prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
A) double-stranded, parallel, (A + T)/C + G) = variable, (A + G)/(C + T) = 1.0
B) double-stranded, antiparallel, (A + T)/C + G) = variable, (A + G)/(C + T) = variable
C) double-stranded, antiparallel, (A + T)/C + G) = variable, (A + G)/(C+ T) = 1.0
D) double-stranded, parallel, (A + T)/C + G) = 1.0, (A + G)/(C + T) = 1.0
E) single-stranded, antiparallel, (A + T)/C + G) = 1.0, (A + G)/(C + T) = 1.0
C
If DNA replication were fully conservative, how many intact parental double helices would have been detected in Meselson and Stahl's experiment after three rounds of replication?
1
Describe the three different types of DNA and their differences
A-DNA is created when there is less available water. It is shorter and wider DNA
B-DNA is right handed clockwise screwing double helix with 10 base pairs per turn
Z-DNA is left handed DNA. Double heliz bases are oriented in a zig-zag orientation. It is thought that this helps in protection against viruses
Explain the differences in the three models of dna replicaiton
-Conservative replication- parental molecules direct synthesis of an entirely new double stranded molecule such that after replication, one molecule is conserved in 2 old strands
-Dispersive replication- 2 parental strands distribute more or less randomly between two daughter moelcules
-Semi-conservative replication-
What are the requirements for DNA replication?
-A template strand of original DNA
-Raw materials: nucleotides
-Reaction Promoters: enzymes and other proteins
What are the three steps of replication
1-initiation
2- elongation
3- termination
What are the three helpers of initiation in DNA replication?
DNA helicase, Single-strand binding proteins (SSBs), and DNA Gyrase
“Hey” said Gyro
What is the enzyme that unwinds the double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between complimentary bases
DNA helicase
What protects the single-stranded DNA and avoids hairpin loops during replication?
Single-stranded binding proteins (SSB)
What reduces supercoiling during replication
Moves ahead of the replication fork, making and
resealing breaks in the double-helical DNA to release the
torque that builds up as a result of unwinding at the
replication fork
DNA Gyrase
What are the three helpers of elongation?
-Primase
-Polymerase
-Ligase
“please pray longer”
What synthesizes the beginning of a new strand (primer) during elongation?
Synthesizes a short RNA primer to provide a 3'-OH group
for the attachment of DNA nucleotides
Primase
What elongates the new strand by attaching to 3’ (OH-) during elongation?
Polymerase
What seals the breaks between Okazaki fragments during elongation?
Joins Okazaki fragments by sealing breaks in the sugar–
phosphate backbone of newly synthesized DNA
Ligase
What are the fragments that are discontinuously synthesized DNA fragments forming the lagging strand
Okazaki fragments
Which strand undergoes continuous replication
Leading strand
What strand undergoes discontinuous replication"?
Lagging strand
When does termination occur during replication?
It occurs mostly when two replication forks meet. Other times, it occurs when specific set of bases are present.
What occurs after DNA replication is complete?
Other enzymes are proofreading the DNA strands and correcting mistakes including mismatching
What does DNA synthesis in bacteria involve?
five polymerase (DNA Pol), each of which as a specific role
What are some ways in which eukaryotic dna replication is different to bacterial dna replication?
-Presence of histones (proteins)
-DNA in the nucleus
-Several origins of replication in a linear DNA
-Chromosomes have DNA more or less condensed in telomeres and centromeres
-Chromosomes are linear
In eukaryotes, due to linear chromosomes, how does replication end?
DNA Telomerase