Art 101 Midterm (CSUF David Plouffe)
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
143 Terms
Role Of The Artist #1
Help see the world in new and inovative ways
Role Of The Artist #2
Record the world
Role Of The Artist #3
Give form to the immaterial
Role Of The Artist #4
Make things beautiful
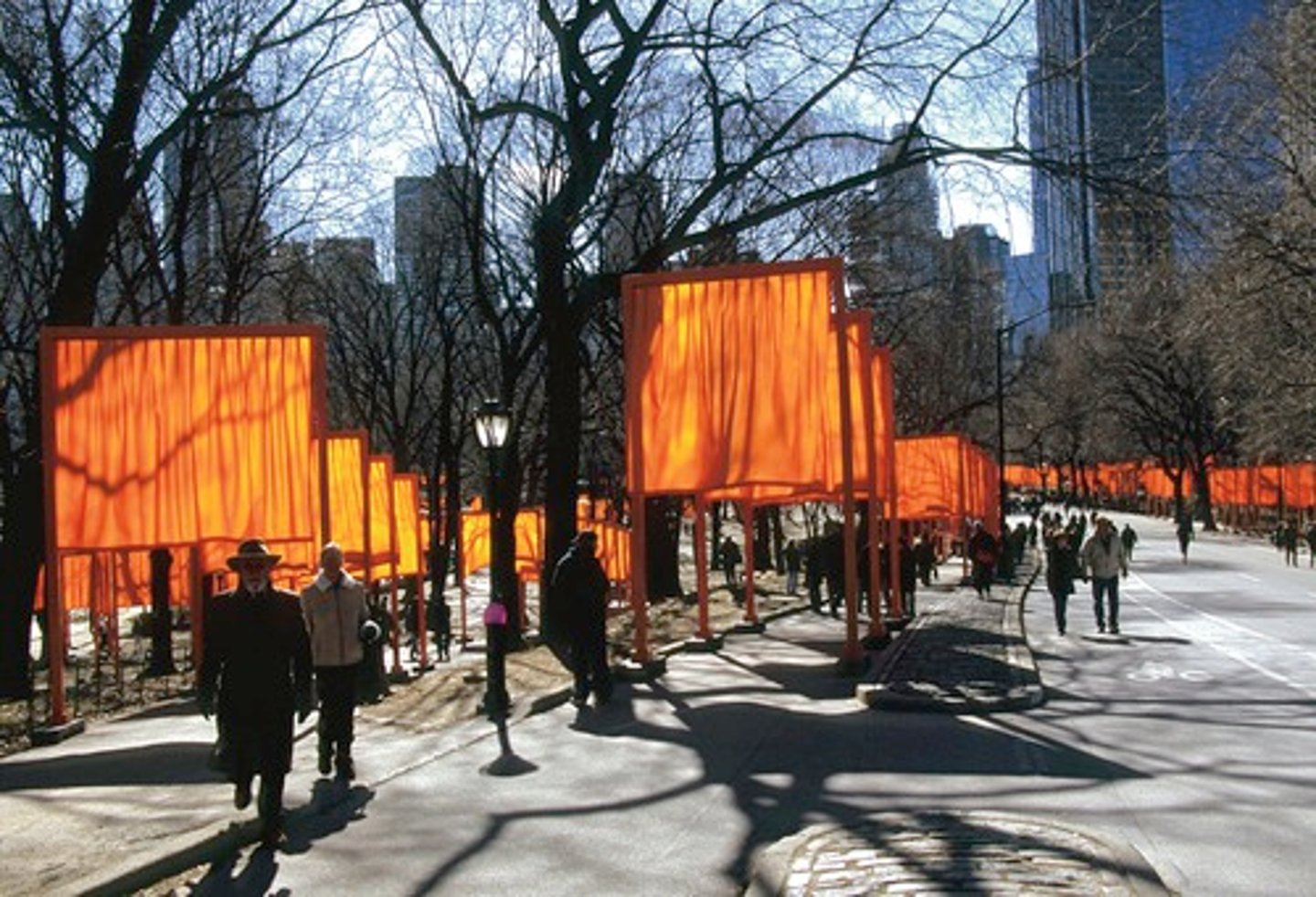
Example Of Role #1 Of The Artist
The Gates By Christo and Jeanne-Claude

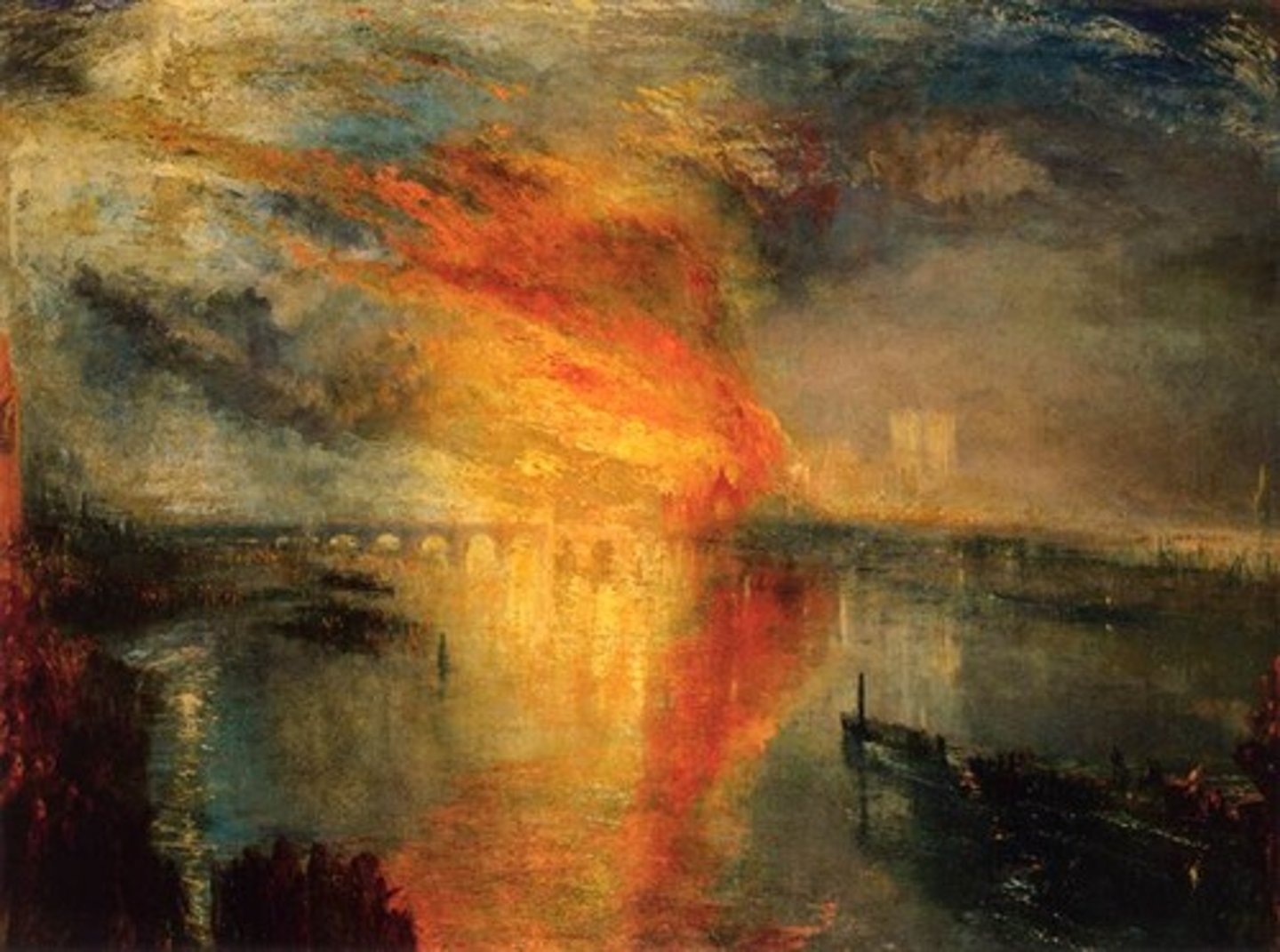
Example Of Role #2 Of The Artist
The Burning Of The Houses Of Parliament

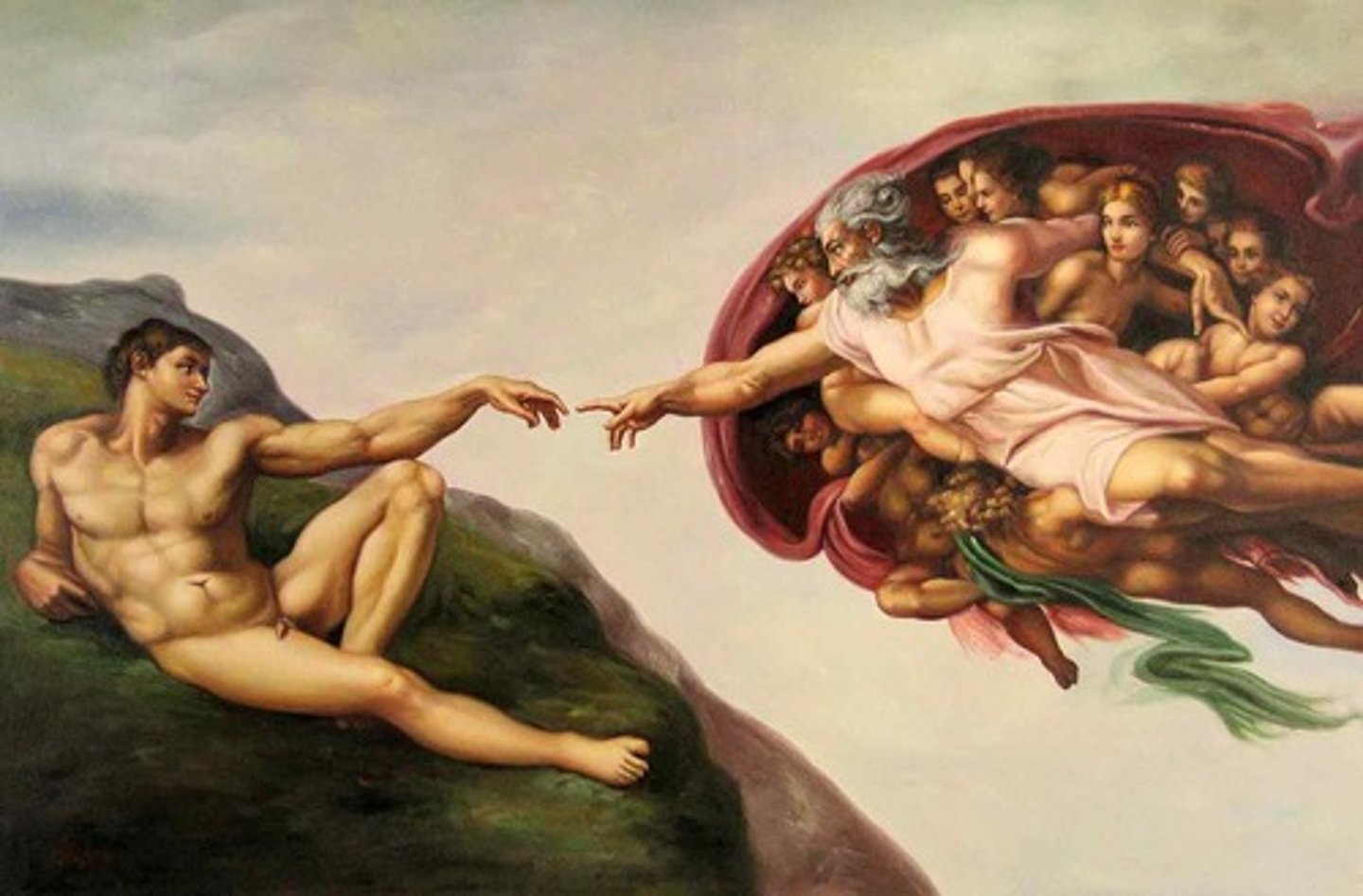
Example Of Role #3 Of The Artist
Creation Of Adam By Michelangelo

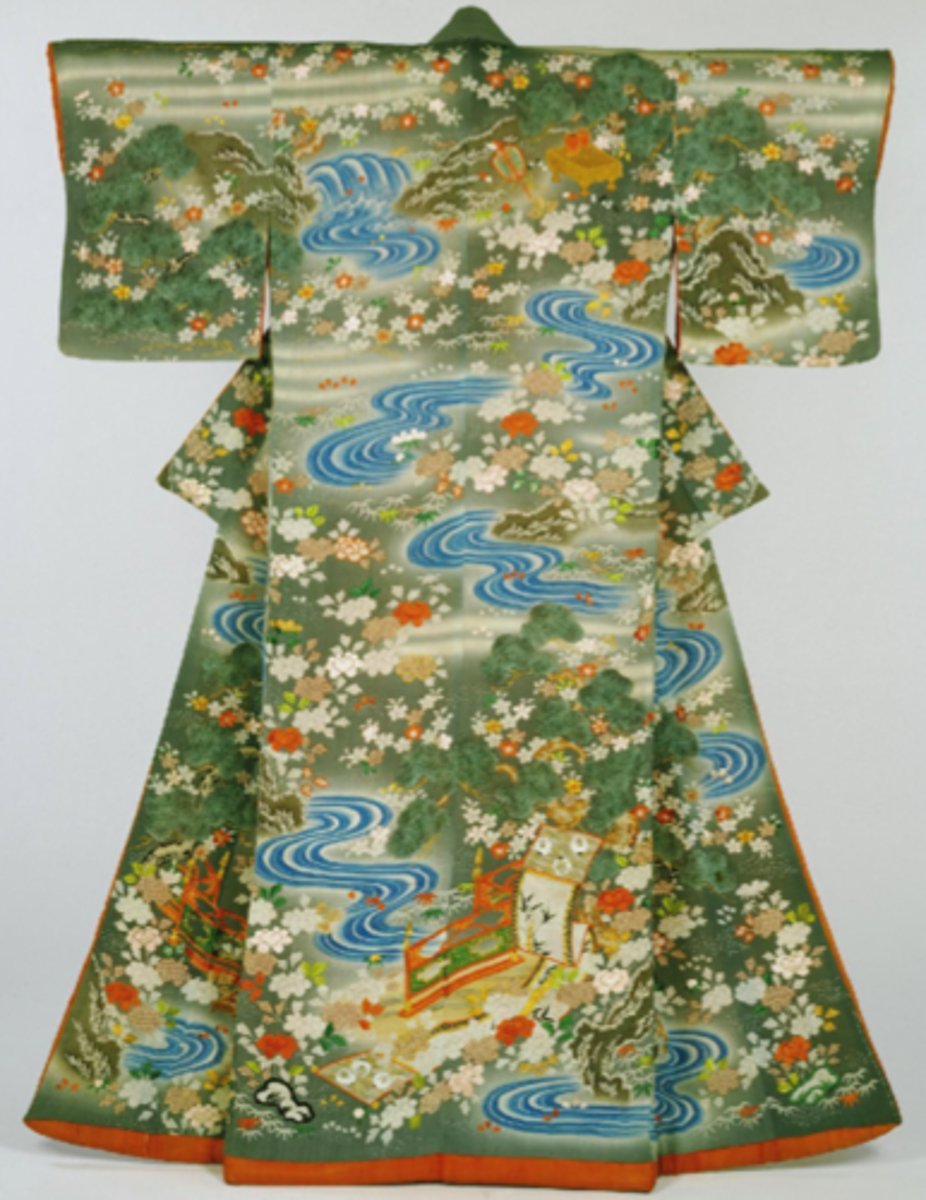
Example Of Role #4 Of The Artist
Kimono, Japan, Edo Period, c. 1700

Representational Art
Art the resembles the real world (Easily Identifiable Objects)
Abstract Art
Art where we can identify the objects but don't appear natural (Abstraction Must Be Derived From Something)
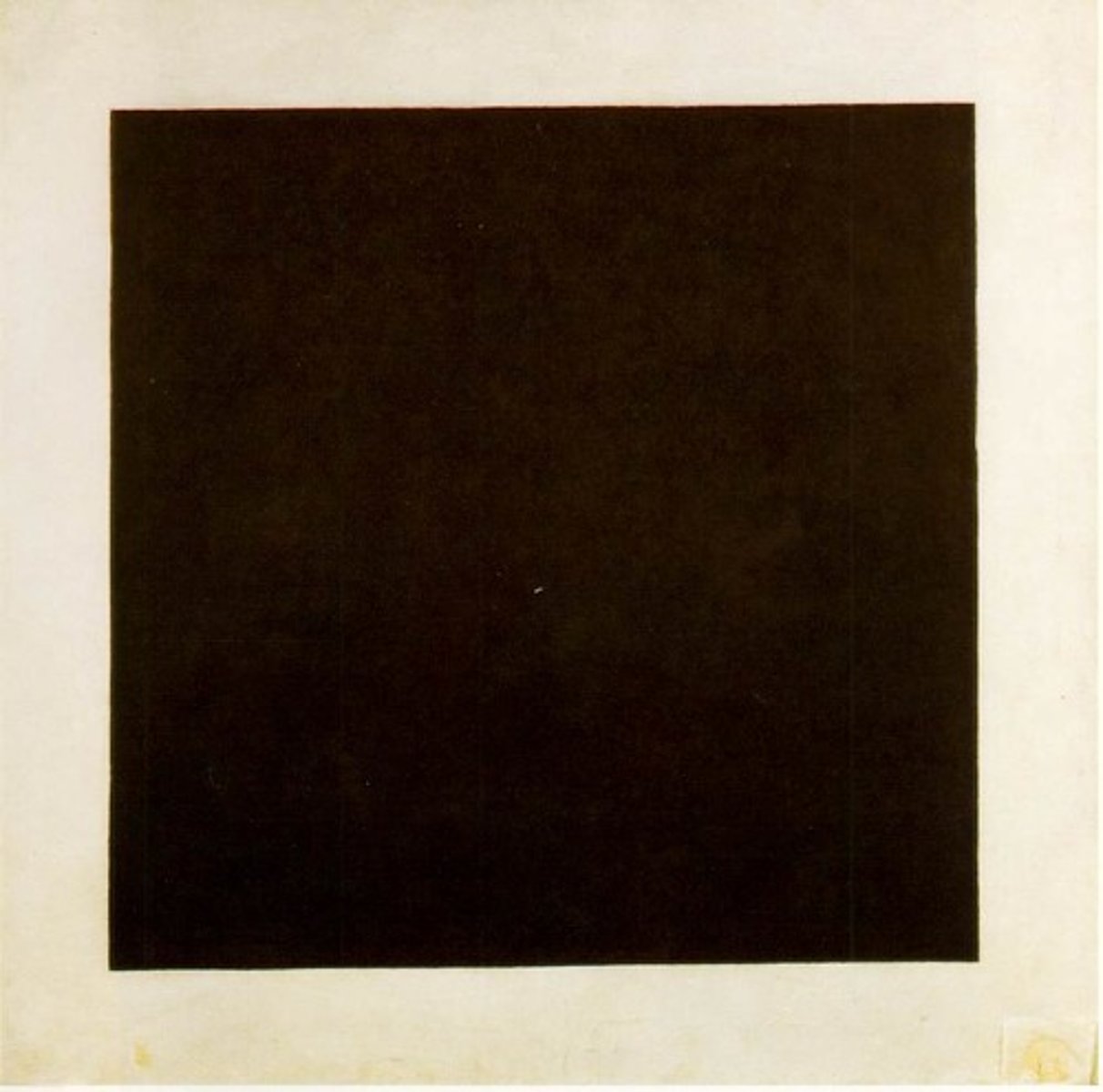
Non-Objective Art
Art that makes no reference to the natural world (Ex. Jackson Pollock)
Black Square By Kasimir Malevich
Form
Deals with visual aspects of the work (Line, Shape, Color)
Manipulation of the formal elements and principles of design
*All Artworks Have Form
Content
Subject matter has a story
Implies subject matter has story, narrative, information
Idea that the artwork is seeking to communicate
*Not All Artwork Have Content
Iconography
Study the meaning of images (art historians look at an artwork and decide what is going on)
Positive Space
Anything that can be seen, felt, or touched in 3D works
Negative Space
Space between objects in 3D works (Empty Space)
Figure
The objects in a 2D work
Ground
The background in a 2D work
Pictorial Plane
Surface of the 2D work (Ex. Canvas & Paper)
Scale
Objects closer to us look larger than those far away
Overlapping
Objects closer to us cover/hide objects far away
Vertical Location/Placement
The higher the object is placed the farther away it is from us
Atmospheric Perspective
As forms move further back into the background their figures become less clear and start to take the color of the background
Amplified Perspective
Artist purposely reduces/distorts parts of an object but still convey what they are trying to (Foreshortening
Linear Perspective
The most convincing way of representing a 3D space on a 2D surface (Formulaic math equation invented by Filippo Brunelleschi)
Horizon Line
Where the sky and the land meet (Wall and floor meet)
Vanishing Point
A point that lives on the Horizon Line (In a linear perspective artwork it's where all the lines connect)
Frontal Recession
Straight in-front Vanishing Point

Diagonal Recession
Off to the side Vanishing Point

One Point Linear Perspective
One Vanishing Point
Two Point Linear Perspective
Two Vanishing Points
Multi Point Linear Perspective
Three or more Vanishing Points
Line
A point set in motion
Horizontal Lines
Can make us slow down/At rest
Vertical Lines
Have potential of movement/Can become movement
Diagonal Lines
Have action/ Show movement
Rectilinear Line
Straight lines and Man-made (Rarely found in nature)
Curvilinear Line
Curved, natural, flowing and organic lines (Commonly seen in nature)
Outline
Indicates the edges of a figure or object, stencil-like, and deals with 2D artworks tend to be bold and obvious
Contour Line
Indicates the edges of a figure or object concerned with establishing volume, and deals with 3D artworks
Implied (Psychic) Lines
No physical lines exist (invisible) "Understood" extremely powerful (line of sight, eye contact/gaze, pointing)
Expressive Line
Conveys the mood and feeling of the artist (Jackson Pollock)
Analytical Lines
Precise, controlled, based on mathematical principles, easily recreated
Classical Lines
Refers back to Greek and Roman art (Simple, Well Proportioned, Balanced, Symmetrical, Involves Ratios)
*Based On Beauty And Aesthetic)
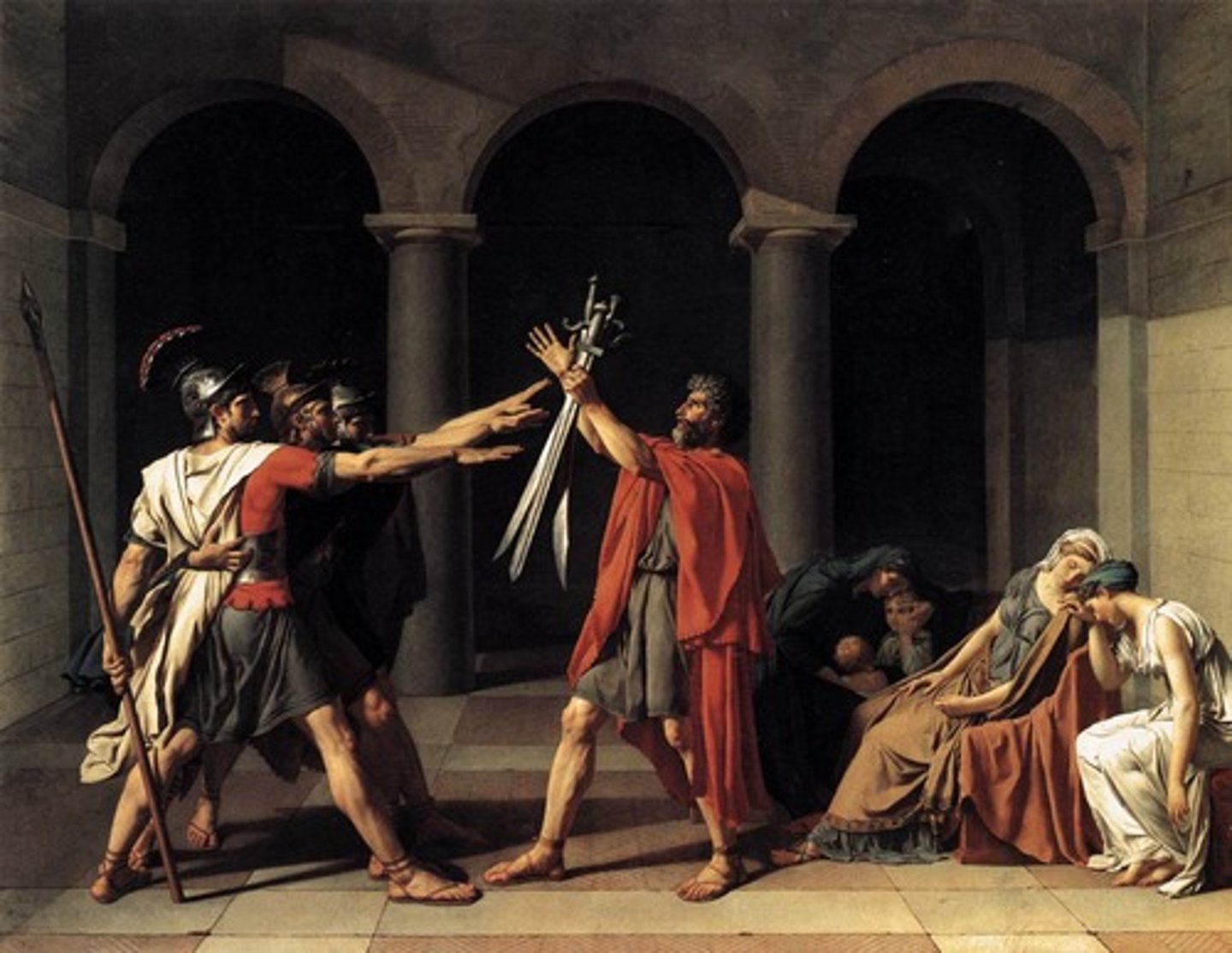
Oath Of The Horatii
Helped spark the French Revolution (War of two cities resolved through a fight, The Horatii brothers vs other brothers from the other city, one of the Horatii sisters was married to one of the other brothers, only one person survived and that was one of the Horatii brothers, he ends up killing his sister because she was sad over her husband, whom was an enemy of the state, so in turn she betrayed the state which is why she was killed)

Color
The first thing we notice when we look at an artwork
Hue
When light is refracted through a prism it is broken down into a spectrum of colors
The Hues
Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Violet
Tint
Hue + White
Shade
Hue + Black
Additive Process
Deals with light
Subbtractive Process
Deals with paint/pigment
Primary Colors
Red, Yellow, Blue
Secondary Colors
Violet, Green, Orange
Intermediate/Tertiary Colors
Colors that are hyphenated, usually paired with a primary color (Ex. Blue-Violet)
Analogous Colors
Colors next to each other on the color wheel
Complimentary Color
Opposite colors on the color wheel
Triadic Colors
Colors on the color wheel that make a triangle and make us feel comfortable (Ex. Red, Yellow, Blue or Green, Orange, Violet)
Local Color
Color objects are associated with and are (Ex. Firetruck = Red)
Perceptual Color
The color an object is at a particular time, light is what makes color so color changes with light change (Did Painting En Plein - Air to achieve)
En Plein - Air
Translation: In the open air
Painting outside the studio
Invented in the late 1800's (Revolutionary then, common practice now)
Arbritrary Color
Artist decides what color to paint an object (Ex. Firetruck = Brown)
Pointillism (Divisionsm)
Painting with dots, not mixing colors but instead putting colors close to each other to "mix them"
Sunday On The Island Of La Grande Jatte By George Seurat
Example Of Pointillism
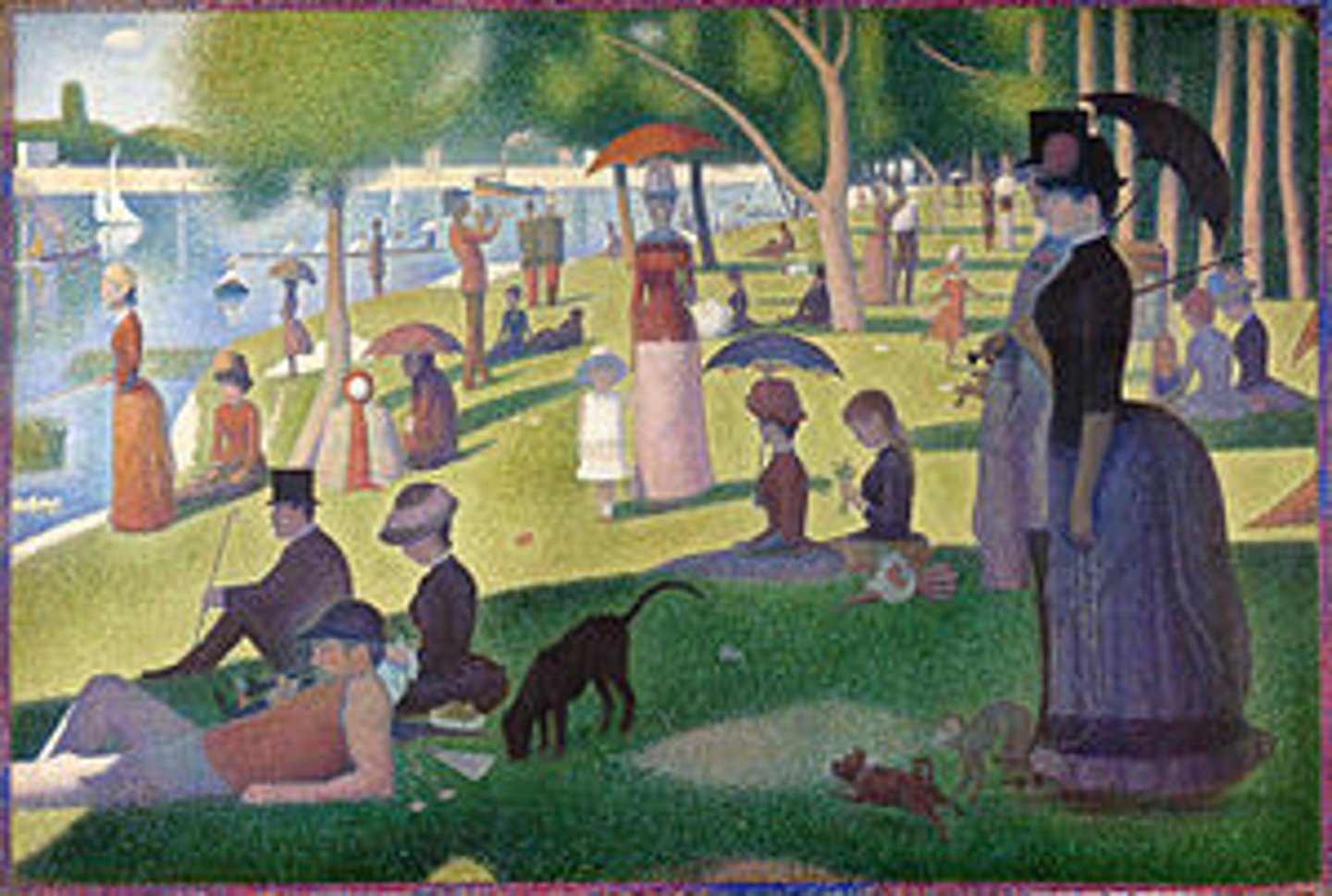
Value
The measurement of light and darkness
(Through changes of it we are able to perceive form)
Extremes: Black and White
Value Contrast
Helps create illusions in space
Tenebrism
Extreme contrast in value (Mainly in artworks with a single light source like a candle)
Chiaroscuro
Slow change is value
Pattern
Repeated design
Texture
The surface quality of an artwork
Actual Texture/Tactile
Texture that is felt
Impasto
Thickly applied paint (Ex. Vincent Van Gogh)

Visual Texture
Impression or suggestion of texture where none exist
Frottage
Rubbing from a textured surface to form the basis of an art (Ex. Max Ernst)
Tromp L'oeil
Visual deception (Illusions) objects rendered in incredible detail
Subversive Texture
Undermines our ideas about the object itself (Can attract and repel at the same time)
Kinetic Art
Art that moves (Begins in 1819)
Illusionary
Before Kinetic Art artist used illusionistic techniques to show movement
Abstract, Uses Illusionistic Techniques, In Armory Show, First Abstract Art Brought To America, Criticized Harshly By Americas, Part Of The Dada Movement
Descending A Staircase By Marcel Duchamp
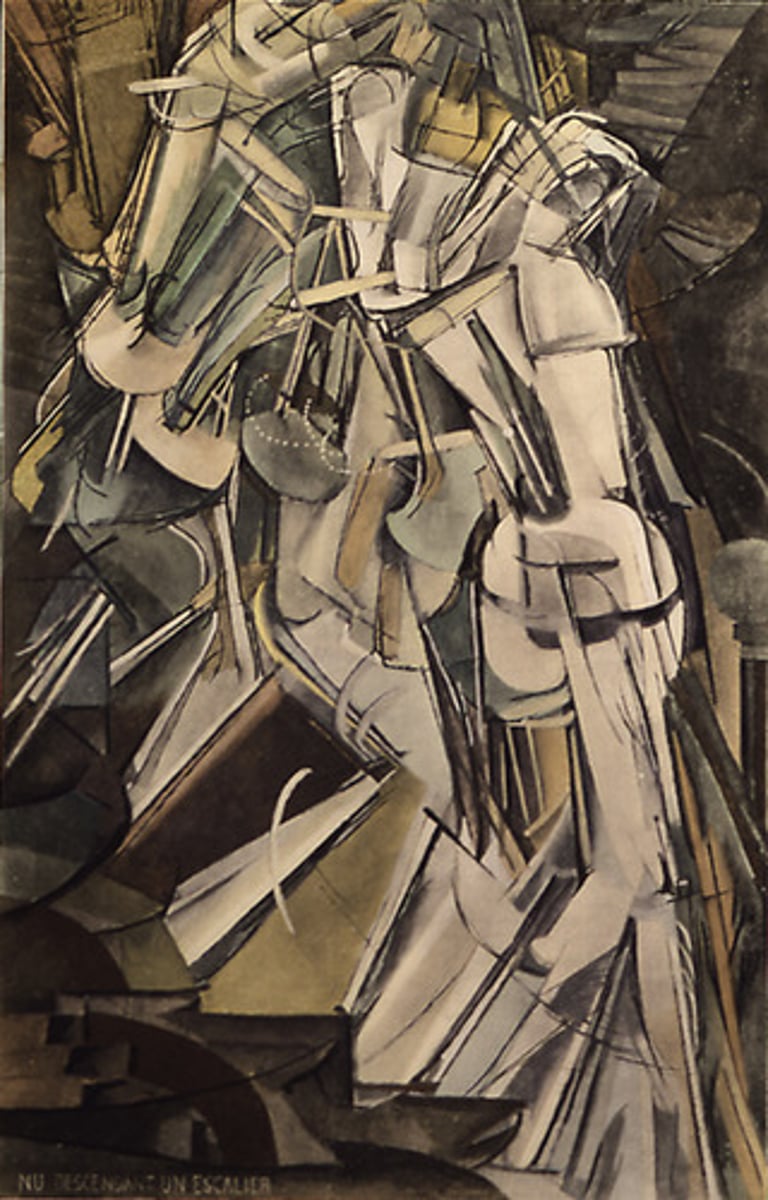

Futurism (Technique)
Images overlapping to make movement
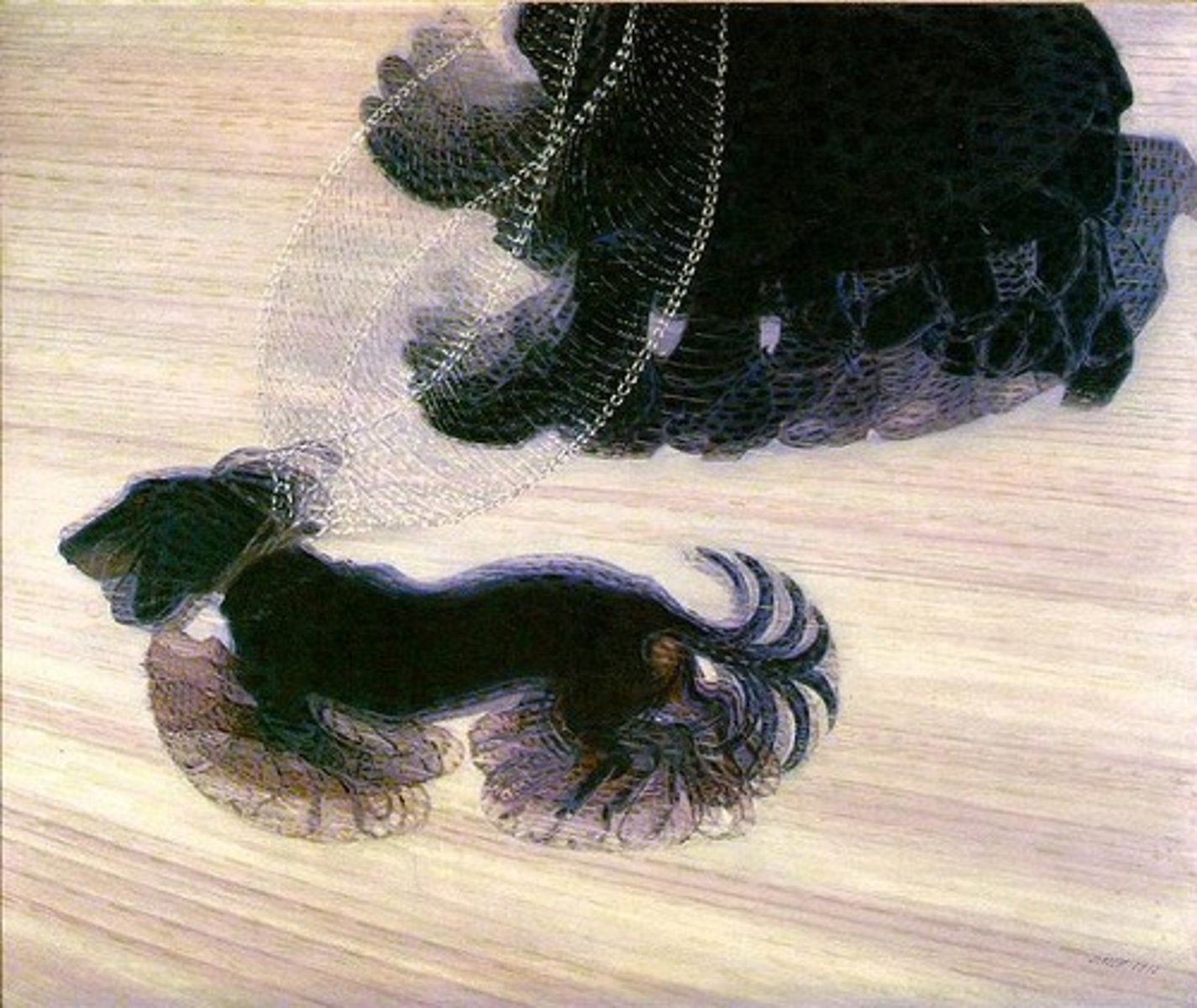

Chrono-Photograph
Photographs of movement over time
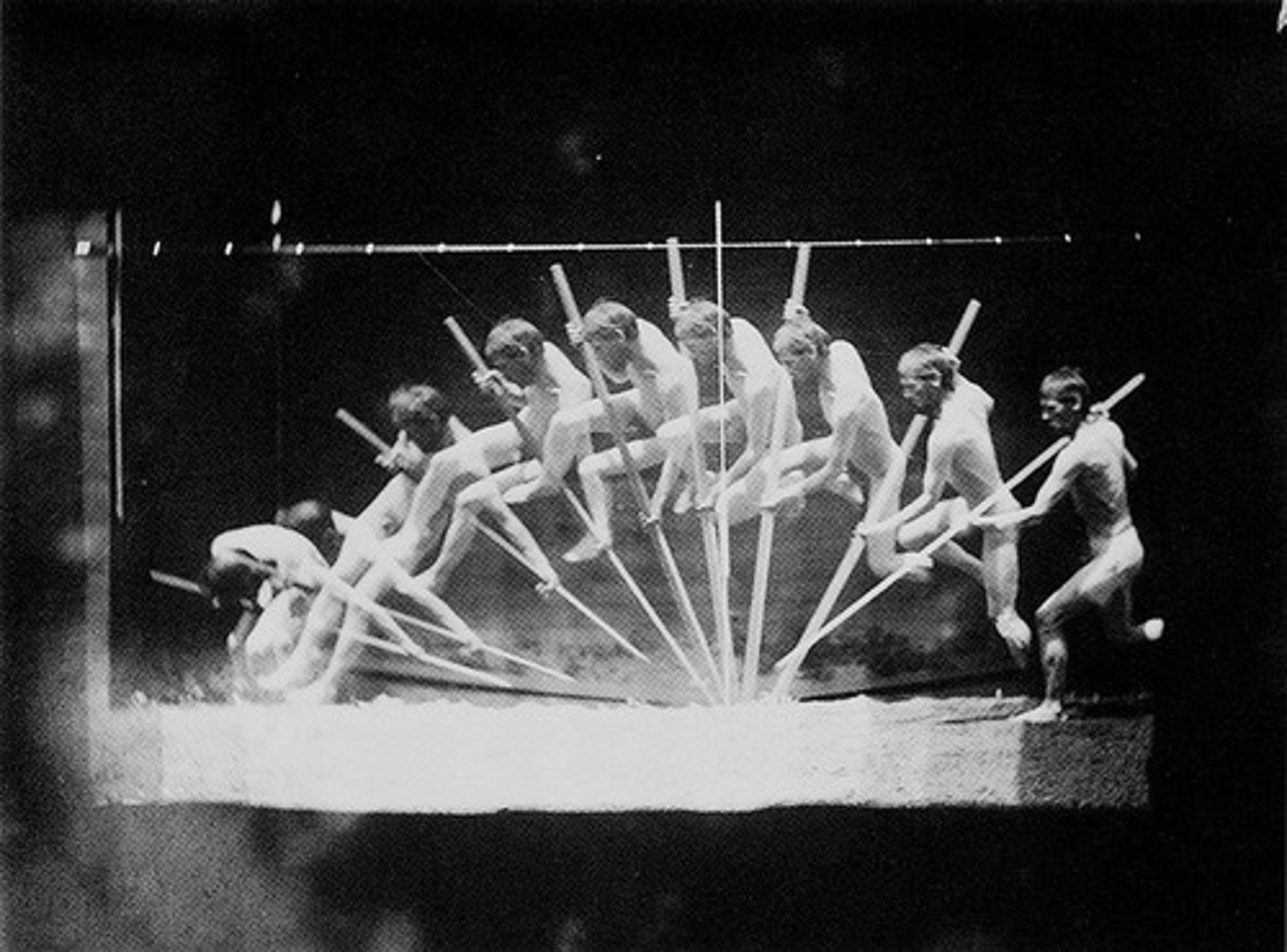
Blurred Figure
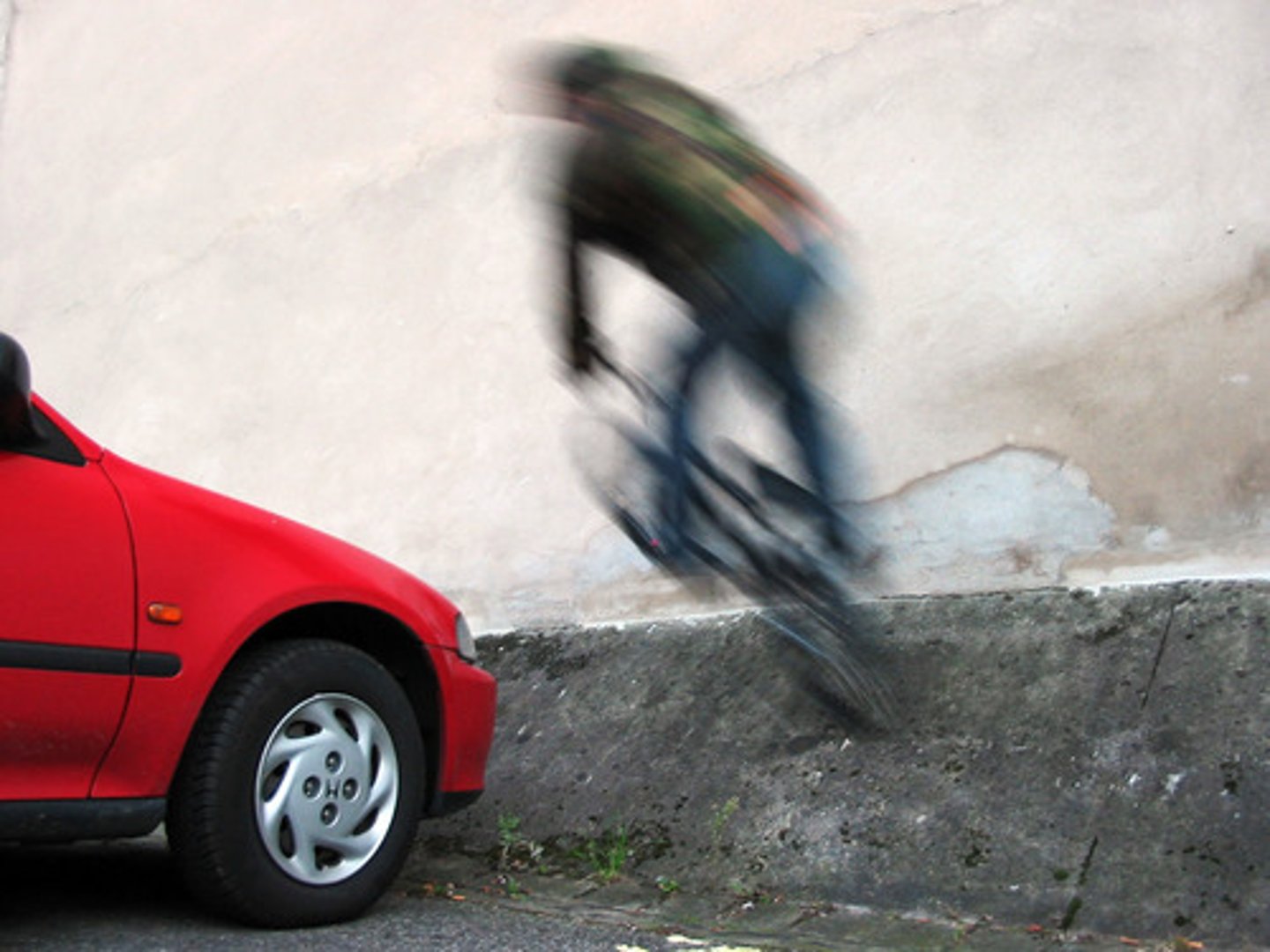

Cropped Figure
Part of a figure cut off

Optical Art (OP Art)
Short lived movement from the mid 1960's
Action Painting
Synonym given to many Abstract Expressionist painters of the 1940's & 1950's (Jackson Pollock considered the "father" of it)
Vincent Van Gogh
1853 - 1890
Painter
Post-Impressionist
Death By Suicide(questionable but right now facts)
Was a Baptist Preacher
Oldest sibling in his family
Had many diseases
Career lasted 10 years
Only sold one painting in his lifetime
Vincent Van Gogh's Most Expensive Painting
Doctor Gachet sold to Ryoei Saito

Theo
Vincent Van Gogh's brother
Only one to continue the family line
All brothers die early on but all sisters live to about 70
Financially supported Vincent Van Gogh
Dies 6 months after Vincent today buried next to each other
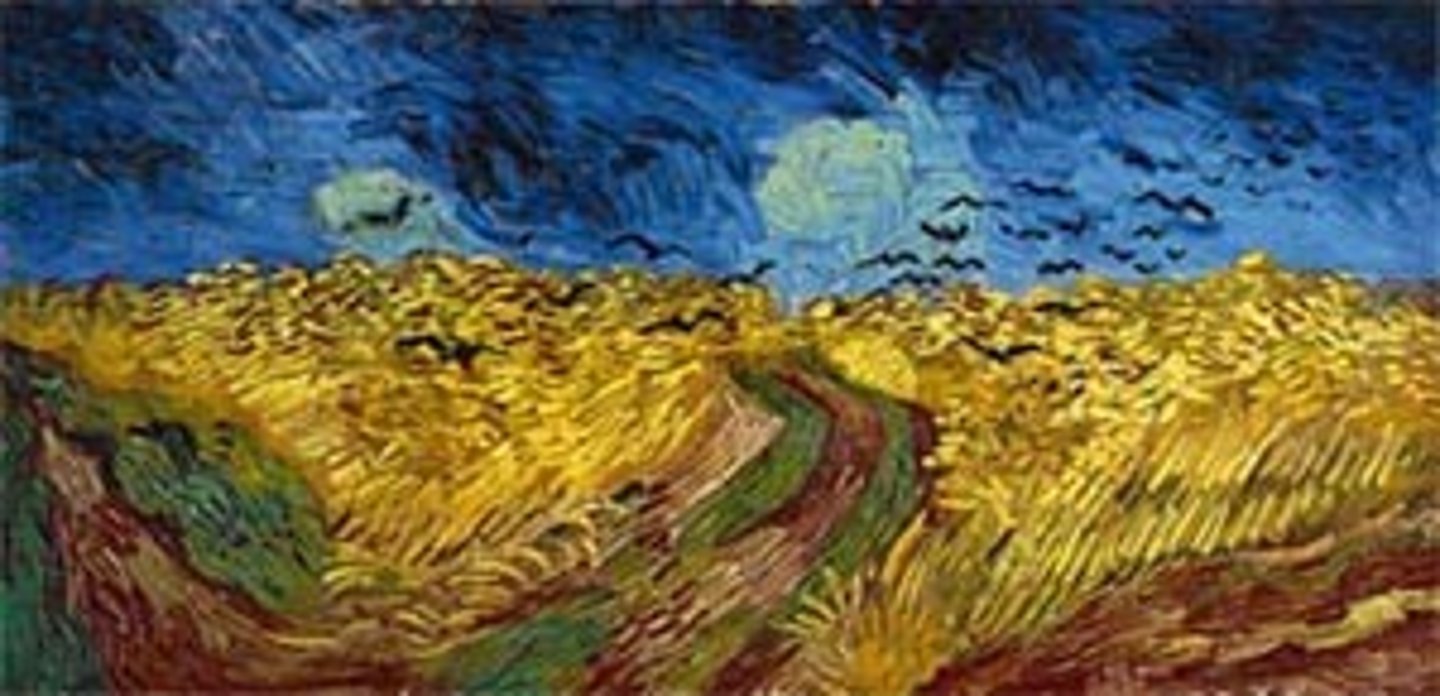
Vincent Van Gogh's Last Painting
Wheat Field With Crows
(Sent to his brother)

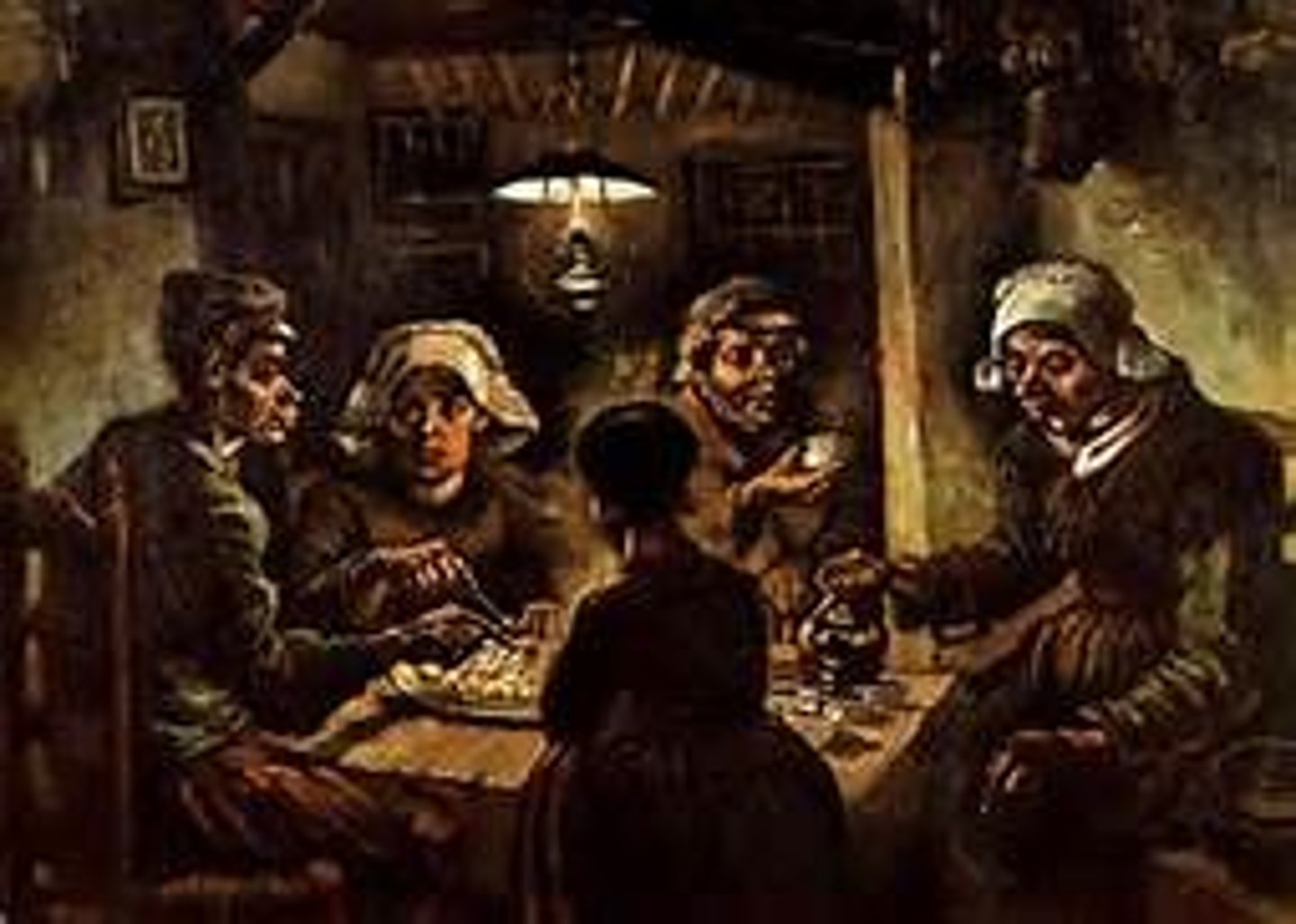
Potato Eaters By Vincent Van Gogh
Painted in 1885, one of the first paintings to depict the poor

Vincent Van Gogh Lived Before 1886
Amsterdam
Vincent Van Gogh Lived 1886 - 1890
Paris
His Life: Sleeping, Eating, Painting, Brothels
Vincent Van Gogh Lived 1888 - 1890
Arles
Where he spends the rest of his life
Paul Gauguin
Vincent Van Gogh's roommate
Died around 50 years old
Tells us about Vincent Van Gogh cutting his ear story
Post - Impressionist
Painted Tahiti
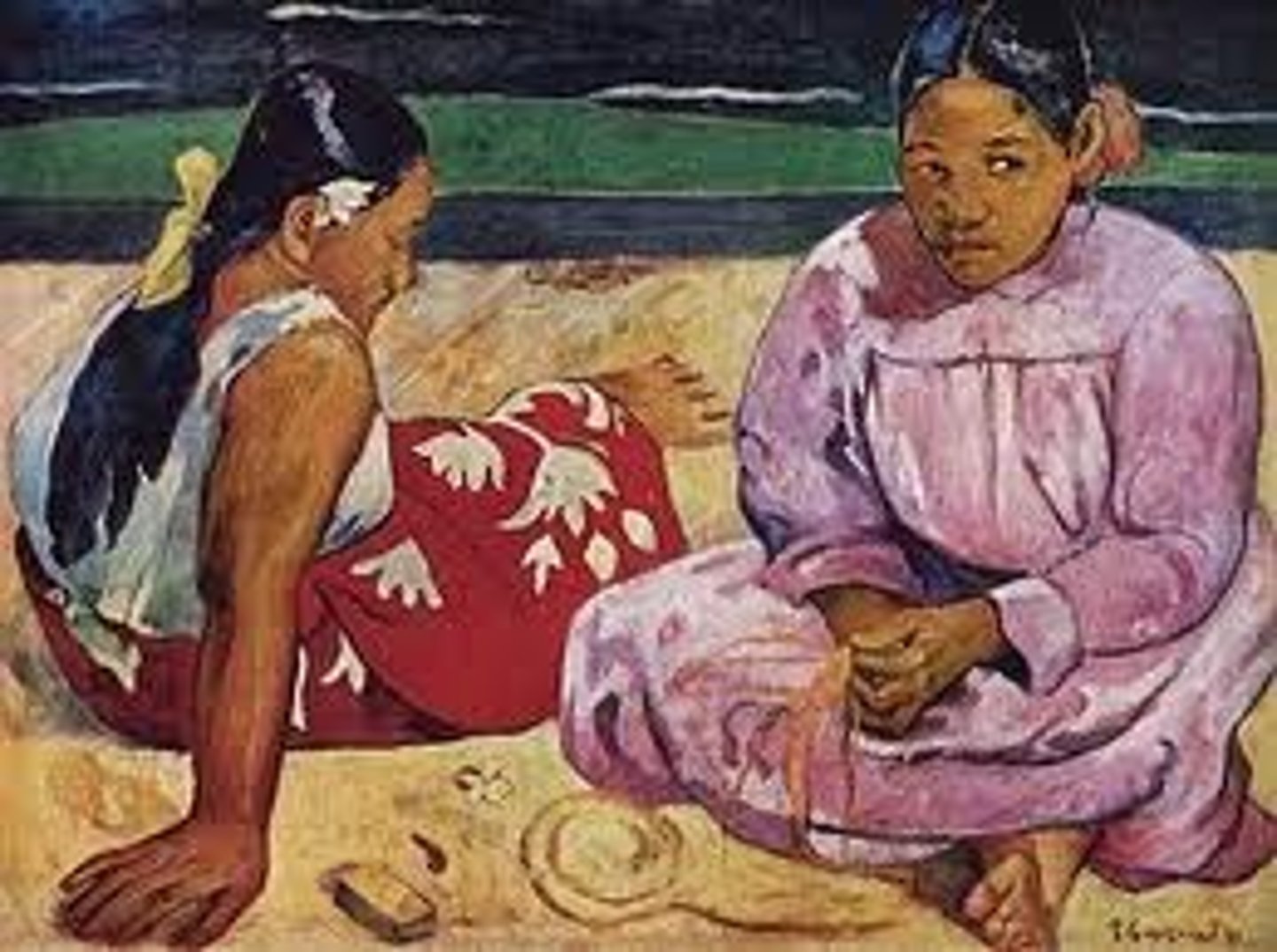

Scale & Proportion
Deal with dimensions of the art object (or the elements within the art object)
Rythm
Using the same element over and over again within the same composition
Unity With Variety
The agreement that exist between the elements in a design

Unity
Created by repeating similar aspects within the composition to create harmony
Variety
Deals with diversification without some elements of difference
(Image is lifeless & uninteresting)
Can occur throughout any of the formal elements, change in value, different textures