GEOG 1350 Mass Wasting and flooding
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
What are the endogenic and exogenic processes that influence mass wasting
landform building and transforming processes creating relief
Modify landforms gradually by carving, shaping, and reducing the earth’s surface
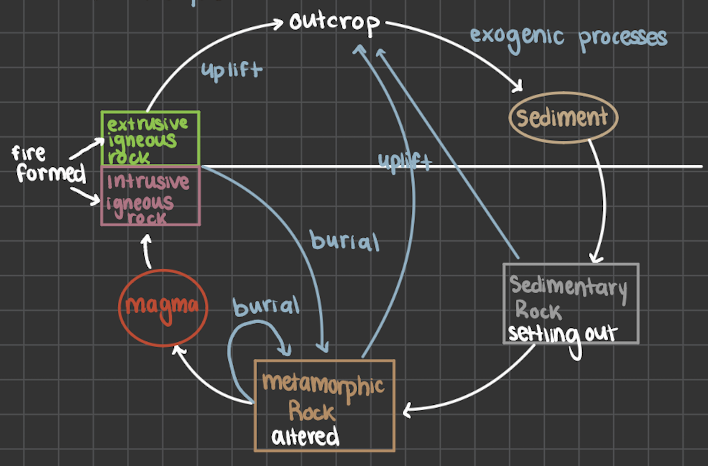
The rock cycle
What are the two main classifications of mass wasting
1) physical/mechanical (breakdown of rock into smaller pieces by heat, water, ice, and pressure)
2) Chemical (decomposition of rock due to chemical reactions altering chemical structures (involved water)
What is mass wasting
is the slow to rapid downslope movement of rock and earth under the sole influence of gravity
What is the driving force behind mass wasting
shear stress (acts as a downslope “pull”)
What are the factors of driving force
gravity
weight of sediment and structure
slope angle
shape of surface material
What is the Resisting force behind mass wasting
Shear strength (resists the pull)
What are examples of resisting force
friction
cohesion
vegetation
What are stable vs unstable slopes
what are stable slopes, when the strength exceeds the weathering and erosion processes
What are unstable slopes, the slope materials are weaker than the weathering and erosion processes
What is the equation of slope stability
balance of shear strength vs shear stress ratio
F = (resisting force)/(driving force)
What is the angle of repose
maximum angle loose material can remain in place without sliding represents a balance between driving and resisting forces
Why might the angle of repose change
moisture conditions and sediment shapes
How does the angle of repose influence mast wasting
The larger the slope angle, the higher the chance of the mass wasting
What is the angle of repose normally around
33-37
What are the triggers of mass wasting
Vibrations (earthquakes, volcanoes, blasting, fracking, construction, sound vibrations)
Over steepened slope (road cutes and coastlines)
Increased weight on slope (buildings, change in drainage patters, precipitation)
Removal of vegetation (roots hold ground together, removing trees, roots pull water)
How does water impact mass wasting
water shifts the balance of the forces
weight of water: sedimentary rocks and soil have pores that fill with water, adding to their mass
clay, water can make clay layers swell and become slippery
Absorption
Positive pore-water pressure
What is positive pore-water pressure
increase of water concentration that pushes particles in soil apart causing slope instability
Dry vs Damp vs Saturated Sand
Dry sand- angle related to friction between grains
Damp sand- surface tension of water helps to keep sand grains together
Saturated Sand- water between particles keeps them apart
Lost all cohesion
Creates mass wasting events
What are rock falls
detachment of rock or block of sediment (due to weathering)
falls straight down or bounce and hits things
What are the broken up rocks at the bottom of the slopes from rock falls
Talus slopes or cones (shattered rock)
Do Rock falls have water involved
some, but doesn’t require any to cause this movement
How fast or Rock falls
very fast with no warning
What are rock avalanches
starts as one block => breaks up as moving down slop
Forms when a massive rock falls and explodes apart on contact with a slope
It kind of acts like a fluid (fluidization) which means it moves faster because of less fricition
what is an example of rock avalanches
Banff, Bow Glacier Falls 2025
What are the two types of landslides
Transitional slides
Rotations slides/slumps
What are landslides
a mass of sediment/rock traveling downslope as a coherent block along a tilted plane or surface of weakness
What are translation landslides
slides downslope as a coherent block along a straight failure slop or slip face
What is the difference between translational and rotational slides
translational is along a linear plane whereas rotational has a slight bent in the path, almost a semi circle (curved) that causes a small amount of rotation
Why do Japan get landslides
road cuts increase the steepness of slope along with building along these slopes adding to the weight
What happened during the Frank Slide in Alberta
1903, largest mass wasting event in Canada
Peak of turtle mountain collapsed
1km wide block
70 people died
In 100 seconds 30 million m³ of rock fell
What are theories of why the debris traveled so far in the Frank Slide Alberta
Air cushion → pocket of air beneath is → removed friction
Fluidization
What were some of the triggers of the Frank slide
mountains unstable structure due to mining and antisycline structure. The weather the preceding day was warm and then very cold during the night
What are rotational slides/slumps
downward at top and outward rotation at the bottom
involve movement along one or more curved slip/failure surfaces
Often due to clay layers
What are flows
movement of individual particles within the flow itself
Steep slope
Lots of water
Fast and chaotic
What are the two types of flows
Debris and mudflows (also includes Lahars)
What is the difference between debris and mudflows
Mudflows are dominated by small grain sizes
Slurry of mud (high water content and high velocity)
Debris flows start as mudflows but pick up debris as it flows, variety of grain sizes
Higher water content and high velocity
Where do debris flows evolve from
denuded slopes due to heavy rainfall evolves from large rock avalanches and fast moving slumps (mudflows)
What happened in Japan 2021 with mass wasting
mudflow => debris flow
Fast moving and very destructive
27 people died
131 courses destroyed
Massive loss in power
What triggers lahars
eruptions
post eruption rainfall
What are the traits of lahars
low-viscosity flows moves very rapidly down slope
What is creep
Slow movement down slope (cm/yr)
upper level soil movement
long term damage
What triggers creep
freeze-thaw cycle
wet-dry cycle
What is solifluction
the down slope movement of soil over a permanently frozen subsurface
Very slow movement of saturated particles
What does solifluction create
Forms lobes or terraces
How does solifluction occur
the active layer of permafrost melts, land become saturated and moves
What happened in Racho Palos Verdes, California 2024 with landslides (creep)
underground creep because of increased rainfall
loss of power
Damaged sewage system
No insurance => unable to move
How to minimize risks of mass wasting
sites of previous mass movement with fail again
identify hazardous slopes and vulnerable areas
What are soft solutions of mass wasting
rezone as parks
prohibit building
education
prediction
monitoring
What are ways to monitor mass wasting
rain gauges
pore pressure
slope movement sensor
geophones
what are hard solutions towards mass wasting
Drainage => drainage tiles, pipes that are perforated
Plastic covering of slopes of short Crete => slopes water from saturating surfaces
Reducing the slope angel
Benching (stair step pattern)
'Rock bolts
Blasting
Channeling and containment
dams and rock fall barriers (nets)
What are compound hazard associated with mass wasting
earthquakes
volcanoes
wildfires
atmospheric rivers
What is infiltration
water that enters the surface soil
What is subsurface and groundwater flow
underground water flows towards streams or the ocean
What is runoff
Water flowing across land surface to lower elevation, occurs when the amount of water at the ground’s surface is greater than the infiltration rate.
What increases runoff
urban areas
low vegetation
What decreases runoff
vegetation
What are drainage basins and streamflow
where water drained from the surface and subsurface flow into river channels and eventually into the ocean.
What is the discharge of rivers
when a stream cannot accommodate increased discharge, it overflows its banks and flooding occurs
Discharge = velocity x depth x width
What are braided channels
steep slopes
multiple unstable channels with short-lived bars and islands (constant erosion and deposition)
Variable discharge and excess sediment supply
Coarse sand, gravel, and boulders
What are Meandering Streams
Gradual Slopes
Single sinuous channel
Weaves back and forth across landscapes (carries small rocks, sand, and gravel)
Asymmetrical channels form
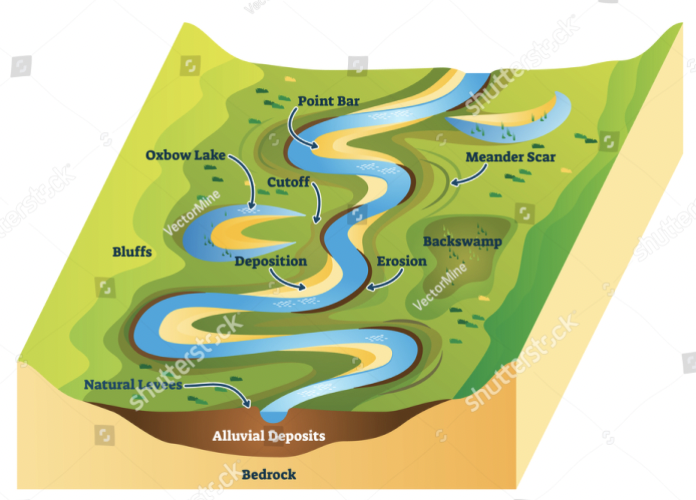
What is a floodplain
The flat, low-lying area adjacent to a channel of water and subjected to recurrent flooding.
Built up by erosion and deposits
Can be used as a prediction source, if a flood has occurred here before it there is a high change it will occur again.
When does flooding occur in rivers
when the stream’s normal capacity is exceeded and water overflows onto land
What are causes of flooding in rivers
extreme precipitation, storm surge, snow melt, frozen ground, damns, or levee failure, and ice jams
What happened in Spain 2025 related to flooding
excessive rainfall that cannot be absorbed, runoff into rivers; the rivers then rise with no warning flooding occurred, 50 mm of rain/hour
What is the most common disaster in Canada
Flooding
What is the main causes of flooding in Canada
too much water volume for the capacity of streams
Coastal areas
Outburst floods (glacier-dammed lakes)
Dam Failure (triggered by natural events)
What factors increase flooding in Canada
amount and type of precipitation
Characteristics of the drainage basin
Characteristics of floodplain
urban stormwater runoff
Climate
Why are flood trends increasing in Canada by year
more records/better records
climate change
urbanization
loss of wetlands
development on flood plains
What months are floods in Canada most common
Apr/May - snow melt
Jan - ice jams
What is a hydrograph
a graph of a specific stream discharge over time for a specific place
What do hydrography show
the relationship between precipitation and water flow in stream channels
How long it takes to rise from base flow to maximum and back
What are the different aspects of the hydrographic
rising limb (surface runoff, ground and soil water reach the river)
Crest (peak discharge)
Lag time (time between peak precipitation and peak discharge)
Falling limb (water is still reaching the river, but in decreasing amounts)
Baseflow (stream discharge before a rainfall event)
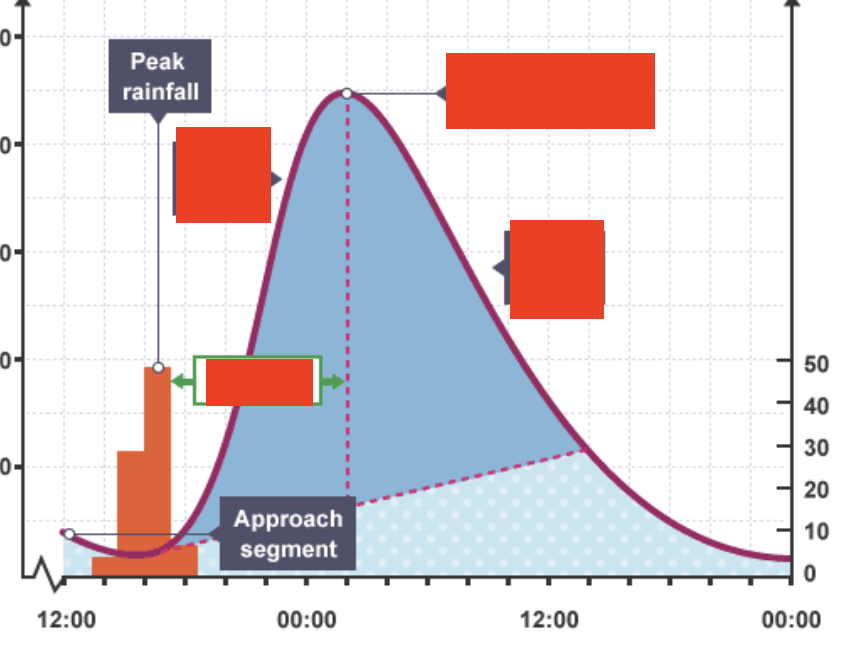
What is each box pointing too that is covered
bottom left (lag time)
Top Left (rising limb)
Top right (peak discharge)
Bottom right (falling limb)
What controls the drainage basins
size, shape, and relief
Steep slope = faster water runoff = higher peak flow
How does urbanization change the shape of the hydrograph
less infiltration = higher runoff (because of paved over ground)
Storm sewers
Urban floods only last 20% as long, but are four times higher
What is the frequency of floods
larger floods = longer recurrence intervals
Flood frequency curves differ for different streams
can be used to estimate return time of given flood size
What are the different flood types
Local thunderstorms (flash flooding)
extreme rainfall over days (atmospheric river, regional floods)
Extreme rainfall over hours (regional or local floods)
hurricane storm surges (coastal areas)
broken ice on rivers, ice jams
short lived natural dams
Failure of human-built levees or dams
What are flash floods
thunderstorms can release heavy rainfall, creating flash floods, that have steep topography which causes rapid run off
What are majority of flash flood deaths from
50% of deaths are vehicle related (trapped in cars)
What are regional floods
inundation of an area with floods for weeks
Low sustained rainfall leads to saturated soils which then leads to runoff
Slower water rise - therefore evacuations can be applied
few deaths
extensive damage
large river valleys with low topography
widespread system → prolonged heavy rains
What causes regional floods
atmospheric river
La Niña
What is the red river attributions
a) unusual northward flow (spring flows)
as winter snow melts in the south the water moves northwards, where the ground is still frozen therefore no infiltration = flooding.
b) geologically young
c) very low gradient of riverbed - slow flowing tends to pool
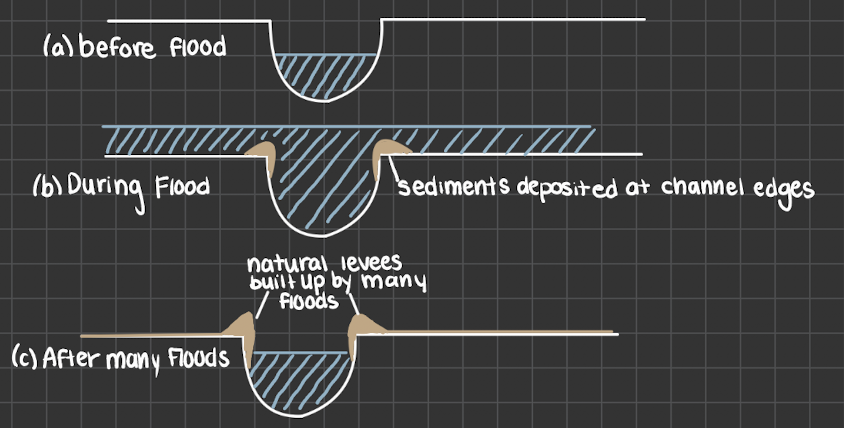
What are natural levees
deposits of past floods leads to natural levees of sand and rock at the side of a river. creates natural flood protection
What are mitigations of floods
structural
Constructions of dams, seawalls, evacuation routes
building levees
channel modification
Non structural
Flood forecasting
evacuation planning
zoning and land-use policies
managed retreat
education
insurance
What is the best flood mitigation for long term and why
managed retreat
flooding
sea level rise
Strategic relocation, moving people, buildings, and assets and infrastructure away from areas at risk of foods
Reduces risk permanently
What are levees prone to failure
cost of building may be more than value of structure intended to protect (often maintenances fall behind) sense of security.W
What are the 4 ways levees can fail
Wave attack
Overtopping water
Slumping
Sand volcanoes
Explain the New Orleans Levees and Flood walls
transformed the Mississippi into restricted ribbons of water, cutting off flood plains
Flooded channels cannot spread so they are forced to rise and the levees become overtopped
What happened with Hurricane Katrine (2005) and New Orleans
Cat 3 hurricane
Lots of rainfall lead to levee failure (50 location overtopped - 80% of the city was flooded)
125 billion in damages
Why is New Orleans sinking
built on silt, clay, and sand which comes from river deposits
without these deposits from flooding there is no fresh silt to replenish, so the material there becomes compacted + there is sea level rise
~1.8 m below sea level
What are temporary Levees
Sandbagging (easily breached, more therapeutic)
Dams (they are limited by construction material, the type, and the rate at which sediments fills reservoirs
What happened during the Saguenay flood 1996
19-21 July 279mm of rainfall
Dam overtopped
flooding
How has Winnipeg mitigated against the red river
The Floodway
Diverts the water around the city to a river
Used every 2-3 years
What is the Red River Floodway built to withstand
1 in 700 year event