insects midterm 2
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Nutritional
(+,+)
Food
Digestions
Nutritional metabolism
Reproductive
(+,-)
Sex ratio determination
Cytoplasmic incompatibility
Speciation
Pathogenic
(+,-)
Fitness benefits
Protection from heat, parasitism, pathogens
why isn’t eusociality seen in more species of insects?
limited resources
inbreeding
conflict over reproduction
age polyethism
worker division of labor based on age
caste polyethism
social control of developmental rate
environmental influences
nutritional differences- can lead to size or developmental differences
peer-reviewed scientific research paper structure
title
abstract (summary)
introduction (background)
methods (study procedures)
results (data)
discussion (analysis)
conclusion (contribution + future questions)
references (list of resources)
When will you have to read a scientific research paper?
term paper assignments for other classes
conducting own research
verify scientific claims with primary literature
personal interest
false
symbiotic relationships are always mutualistic
vertical transmission
symbiont is inherited from the parent (usually mother)
symbiont and host co-evolve and may not survive without each other
very effective association
pressure to maintain association (coevolution)
can sometimes result in bottleneck (genetic)
horizontal transmission
symbiont is acquired from the environment or other individuals (not inherited)
4 things different Wolbachia strains can do to their hosts
kills male embryos of hosts
Parthenogenesis (makes offspring of host always female)
cytoplasmic incompatibility
increases or decreases fecundity
provides host with nutrients like vitamin B
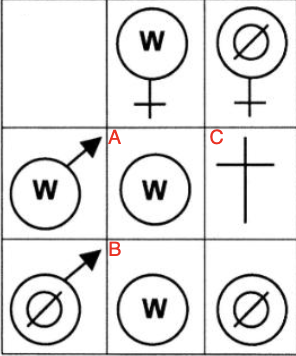
what is happening at A?
infected offspring
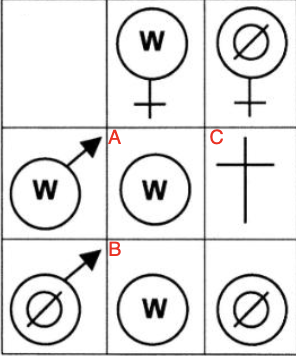
What is happening at C?
embryonic mortality
What is an advantage of biological control?
cost-effective
self-sustaining in the case of classical biological control
no chemical environmental hazards
integrates well with other methods of control except insecticides
reasons why pests aren’t naturally regulated in farms
enemy release: introduced pests are not control by natural predators, pathogens, or parasites
plant domestication makes crops more susceptible to pests
monocultures have fewer alternative resources and microclimates, thus reduces natural enemy diversity and abundance
Pesticides harm natural enemies of pest (if present)
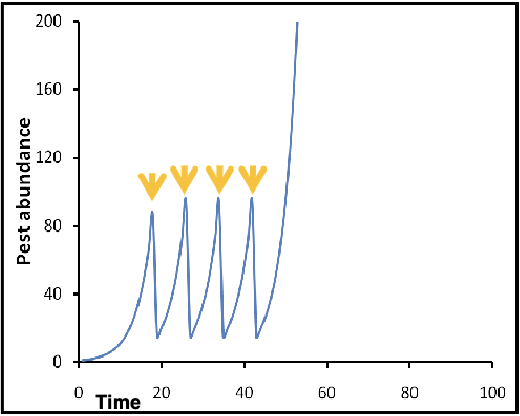
What type of population control measure is this graph an example of?
chemical
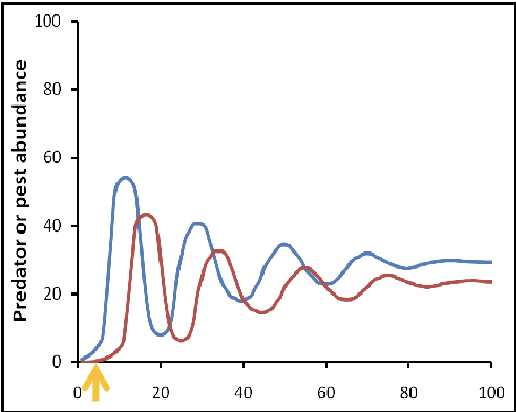
What type of population control measure is this graph an example of?
biological
4 types of plants to disrupt pest establishment/activity
companion crops: releases chemical cues that masks main crop
repellant plants: releases chemical cues that actively repel pests
barrier plants: physically block pest establishment
trap crops: more attractive plant to pull pest away from crop
downsides of using plants to disrupt pest establishment/activity
takes away area for planting main cash crops
additional plantings may require significant additional resources like water and fertilizer
plantings may compete with main cash crop for resources
plantings complicate crop care and harvesting
What are the steps of classical biological control?
determine geographic region of origin of pest
search for pest and its natural enemies
test natural enemies for efficacy against pest
rear prospective natural enemies
test for safety against useful native insects
quarantine to avoid pathogens or parasites
release
direct pest vs indirect pest
direct: pest damage results directly from pest activity such as feeding or oviposition
indirect: insects that create conditions for another pest to cause damage
example of cultural method ot control pests
Cultural control: adopting farming practices to reduce pests
crop rotation
pathogen management
host switching
sanitation
solarization (create condition where heat from sunlight kills pest)
treatment of machinery
nutrient, water management: avoiding over-fertilization/overwatering
plant resistant crops
economic injury level (EIL)
pest density that causes more damage than the cost of control
Economic threshold
level of pest population at which control should be begun to avoid reaching EIL
advantage of breeding plants to have pest resistance
safe since no chemicals are used
cost-effective
compatible with other pest control methods
disadvantage of breeding plants to have pest resistance
can require a long time (some plants take years for each generation)
not always achievable
not as well developed for ornamentals compared to crops
categories of pest control methods
Biological control
cultural control
genetic engineering
pesticides
pheromones to attract or repel pest
plant resistance
sterilizing insects
Altruism
behaviors that increase the fitness of another individual at a cost to the actor
The sperm of the fruitfly Drosophila bifurca is longer than any other species, uncoiled it is nearly 2 inches long. What benefit does this serve?
Sperm competition: long sperm acts as a physical barrier to block the uptake of sperm from other males
Male bruchid beetles have penis covered in spines that can damage the reproductive tract of the female after mating. How does this benefit the male?
the damage reduces the likelihood of other males being successful with mating with the female
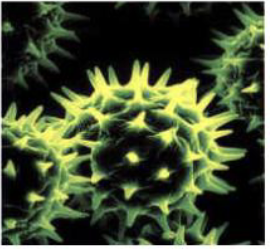
What is the category of pollination
biotic and spread by animals
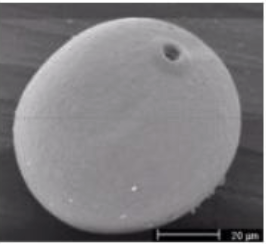
What is the category of pollination
abiotic and spread by wind
Animals that pollinate flowers other than insects
birds: hummingbirds, honey creepers
mammals: bats, mice, monkeys
order of socialities
quasisocial
subsocial
eusocial
communal
5 threats to honeybees
limited/monotonous floral resources
fungicides
pesticides
parasites
pathogens
polydnaviruses
endogenous
exist in wasp genome
means vertically transmitted
replicated inside of wasp, released with egg into host (eg caterpillar)
virus subdues immune response allowing wasp egg and larva to “fly under radar”
sexual dimorphism
observable differences between sexes
mutlimodal
describes a courtship display that uses multiple sensory cues
sexual arms race
reduce likelihood of another male mating
hooked/spined genitalia
scoop out sperm or destroy female genitalia
sperm competition
chemical blocking in sperm proteins
physical blocking: plugs or long sperm
nuptial gift
nutritional supplement given by male to female before mating. it can influence pre- and post-mating selection
nuptial gift cost + benefit
cost: males invest more in mating-higher risk if female doesn’t produce offspring with male sperm; sometimes males “cheat” and there aren’t many nutrients in the “gift”
benefits: nutritional value to female may benefit offspring
three types of symbiotic relationships
parasitism: one party benefits, one incurs costs
commensalism: one party benefits, one neutral
mutualism: both parties benefit
insecticide resistance
enzymatic
enzyme binds to insecticide
breakdown
mutation/existing genetic variation in existing insecticide target site
adaptations that insects that live underwater have
aerial respiration “tubes”
physical gills
closed tracheal system
“suckers” to help stick to surface due to high water flow
challenges to living underwater
respiration + water flow + surface tension