Biology Terms T2
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Movement
They can move and change their position
Reproduction
They make more of the same kind of organism as themselves
Sensitivity
They can detect or sense stimuli and respond to them
Growth
They can permanently increase their size or dry mass by increasing the number or size of their cells.
Respiration
They can create chemical reactions that break down nutrient molecules in living cells to release energy
Excretion
They can excrete toxic materials, waste products of metabolism, and excess substances
Nutrition
They can take in and absorb nutrients such as organic substances and mineral ions. These nutrients contain the raw materials or energy needed for growth and tissue repair
Cytoplasm
The site of chemical reaction
Nucleus
Where the genetic material is stored
Cell membrane
Controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of aerobic respiration
Ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis
Chloroplasts
Site of photosynthesis
Cell wall
Protects the cell from bursting or shrivelling/ keeps it in shape
Permanent vacuole
Filled with cell sap to help keep the cell turgid
What is the order of organisms (smallest to largest)
Cells
tissues
organs
organ systems
organism
Name 3 organs
Heart
lung
stomach
Name 3 organ systems
Circulatory system
digestive system
respiratory system
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Osmosis
the movement of water molecules from a high concentration of water molecules to a lower concentration of water molecules through a partially permeable membrane
Active transport
the movement of molecules across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, requiring the cell to expend energy
Respiration chemical equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
Photosynthesis chemical equation
6CO2 + 6H2O ------> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Arteries
Carry blood from heart to other organs
Veins
Carry blood from organs to heart
Capillaries
delicate blood vessels that deliver nutrients and oxygen to cells throughout your body
Right ventricle
pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs
Left ventricle
pumps oxygenated blood to the body
Pulmonary artery
Carries deoxygentated blood from the heart to the lungs
Pulmonary vein
carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart
Right atrium
Receives deoxygenated blood from the body
Left atrium
receives oxygenated blood from the lungs
Valve
structure in veins or in the heart that temporarily closes an opening so that blood flows in only one direction
Trachea
Allows air to pass to and from lungs
Rib
Protects the lungs
Rib muscle
Moves the rib up and down for breathing.
Bronchus
one of the two tubes that connect the lungs with the trachea
Bronchiole
Airways in the lungs that lead from the bronchi to the alveoli.
Alveoli
tiny sacs of lung tissue specialized for the movement of gases between air and blood
Diaphragm
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathing by contracting and relaxing
Larynx
The voice box
What order does the blood circulate?
Heart -> arteries -> capillary network -> vein -> heart
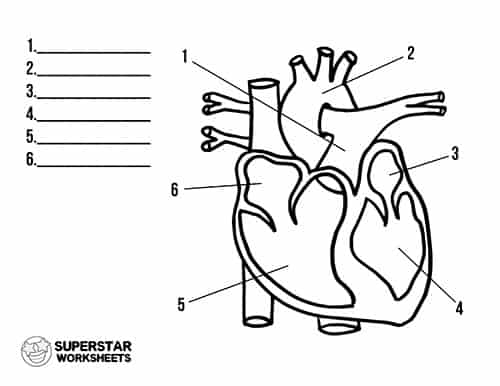
What is 1
pulmonary artery
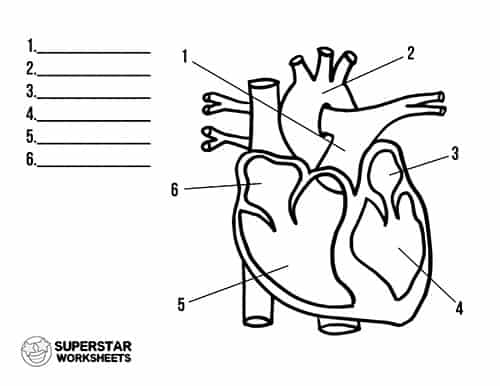
what is 2
aorta
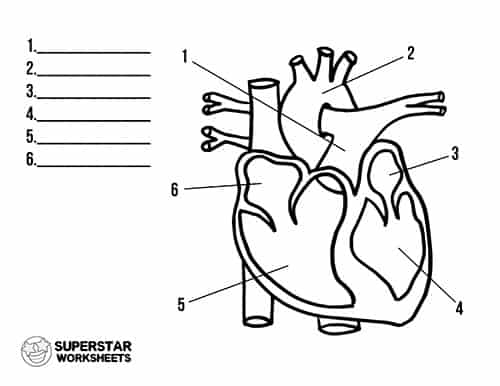
what is 3
left atrium
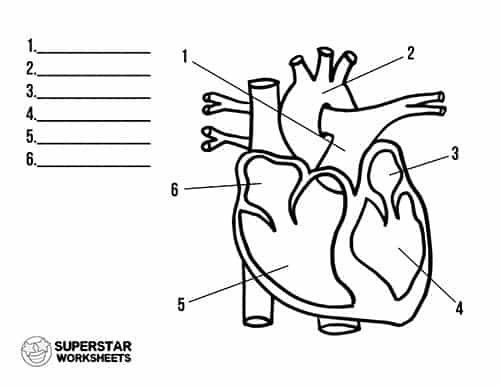
what is 4
left ventricle
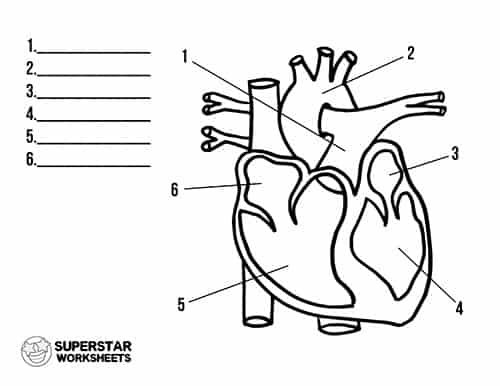
what is 5
right ventricle
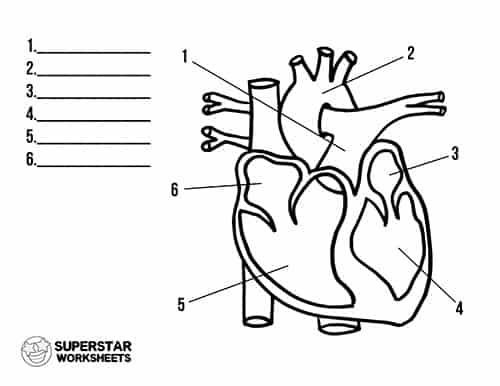
what is 6
Right atrium