APES Unit 5 Review Part 2
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Semester 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Soil Erosion
Result of Clear-cutting
-Caused by loss of stabilizing root structure
Removes soil organic matter & nutrients from forest
Deposits sediments in local streams
Warms water & makes it more turbid (cloudy)
-decrease H2O holding
Increased Soil and Stream Tempatures
Result of Clear-cutting
Loss of tree shade increases soil temperature
Soil has lower albedo than leaves of trees
Loss of tree shade along rivers & streams warms them
Erosion of sediments into rivers also warms them
-decrease H2O holding
Flooding and Landslides
Result of Clear-cutting
Logging machinery compacts soil
Increased sunlight dries out soil
Loss of root structure = erosion of topsoil & O horizon
-decrease H2O holding
Tree Plantations
Areas where the same tree species are repeatedly planted, grown, and harvested
-lowers biodiversity
-all trees planted at the same time
What happens when there is a lower species diversity?
lower resilence
Examples of soil benefits
Filtering of Air pollutants
Removal & storage of CO2 from atm
Habitats for organisms
Slash and Burn
method of clearing land for agriculture by cutting trees & burning them releases CO2, N2O and water vapor into the atmosphere (all GHGs)
Deforestation Consequences
Reduces air filtering and carbon storing services
Cutting trees down releases CO2 from decomposition of leftover organic material
Slash & burn method of clearing land for agriculture by cutting trees & burning them releases CO2, N2O and water vapor into the atmosphere (all GHGs)
Ecologically Sustainable Forestry
a holistic management approach that balances timber harvesting with preserving forest health, biodiversity, and ecosystem functions for current and future generations
-Using human & pack animal labor to minimize soil compaction from machinery
-Maximizes long-term productivity of land & preserves forest for future generations
Sustainable Forestry Practices
methods for managing forests to provide timber, wildlife habitat, clean water, and recreational opportunities today, without compromising their health, biodiversity, or ability to provide those benefits for future generations
-Using recycled wood, or simply reusing without recycling (furniture, decoration)
-Wood can be chipped and used as mulch for gardens or agricultural fields
Fire Suppression
Stopping Natural Fires
Problem-Leads to more biomass buildup
Solution- Monitoring instead
(an automatic or manual setup designed to detect and extinguish fires using agents like gas, foam, or chemicals (instead of just water) to cool, smother, or interrupt the chemical reaction of flames)
Prescribed Buring
an automatic or manual setup designed to detect and extinguish fires using agents like gas, foam, or chemicals (instead of just water) to cool, smother, or interrupt the chemical reaction of flames
problem-dead biomass builds up
solution- small, controlled fires burn lots of dead biomass
solution-promotes nutrients recycling
Urbanization
Removing of vegetation to convert natural landscape to CITY (urban)
soil, vegetation, wetlands»»»»» concrete,cement, asphalt
-prevents groundwater recharge
Urban Heat Islands
occur when cities replace natural land cover with dense concentrations of pavement, buildings, and other surfaces that absorb and retain heat.
Urbanization in Coastal Cities
Population growth in coastal cities can lead to saltwater intrusion due to:
-seal level rise
-excessive groundwater withdrawal
Why do sea levels rise?
due to warming of ocean (thermal expansion) and melting of ice caps (increasing ocean volume) can contaminate fresh groundwater with salt
What can excessive groundwater with drawl do?
the water table to drop, leading to dried-up wells, streamflow depletion, land subsidence (sinking ground), sinkhole formation, and saltwater intrusion (near coasts)
Where do people tend to move from?
People move from rural → urban areas for jobs, entertainment, cultural attractions
Urban Sprawl
Pop. movement out of dense, urban centers to less dense suburban areas surrounding the city (Atlanta → Metro ATL)
Urban Sprawl Causes
Expanded highway system makes travel easier and increases driving
Increase in driving increases fuel tax revenue, which is used to build more highways
Highway expansion makes it easier and easier to commute from suburbs into urban areas
Urban Sprawl Solutions
Urban growth boundaries: zoning laws set by cities preventing development beyond a certain boundary
Public transport & walkable city design that attract residents to stay
Mixed land use: residential, business, and entertainment buildings all located in the same area of a city
Enables walkability & sense of place
Urban Footprint
the total land area and resources (food, water, energy) required to support a city's population and activities
What are some consequences to Urban Footprint?
-decreased infiltration (groundwater recharge)
-rain washed pollutants into storm drains
What are some solutions that can help reduce urban runoff?
Permeable Pavement
Rain Gardens
Public Trait
Building up, Not out
Permeable Pavement
SOLUTION TO URBAN RUNOFF
a specialized surface that allows rainwater to filter through its structure easily to the ground below.
+Decreases runoff, decreasing pollutants carried into storm drains & into local surface water
+Decreases likelihood of flooding during heavy rainfall
-More costly than traditional pavement
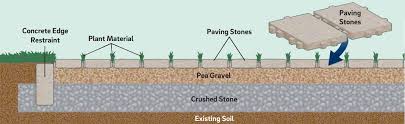
Rain Gardens
SOLUTION TO URBAN RUNOFF
Gardens planted in urban areas, especially surrounding a storm drain
+Decreases runoff by allowing it to soak into garden soil surrounding storm drain
+Decreases likelihood of flooding during heavy rainfall
+Redirected water to recharge groundwater.

Public Transit
SOLUTION TO URBAN RUNOFF
shared transportation like buses, trains, and subways
+Public transit decreases urban runoff, pollutants on road, CO2 emissions & even traffic!
-More cars = more lanes & parking lots (impervious surfaces) & more stormwater runoff
-More cars on the road = more pollutants on streets to runoff into storm drains & local waters


Building Up, Not Out
SOLUTION TO URBAN RUNOFF
Building vertically decreases impervious surfaces (decreasing urban runoff)
Can be combined with “green roof” or rooftop gardens to further decrease runoff
Green roof also sequesters CO2 and filters air pollutants out
Clearcutting
a logging method where nearly all trees in a specific area are harvested at once, maximizing short-term timber yield but causing significant environmental damage like erosion, habitat loss, increased water temperature, and reduced biodiversity
Bottom Trawling
Especially harmful fishing method that involves dragging a large net along ocean floor
-Bycatch: unintended species like dolphins, whales, turtles caught in nets
-Stirs up ocean sediment (turbidity) & destroys coral reef structure
-decreases biodiversty
Bycatch
Unintended species like dolphins, whales, turtles caught in nets
What happens when we fish down the tropic Cascade/ Food web?
As we deplete large, predatory fisheries, we move down to smaller fish species
Depletion of smaller fish pop. limits fishery recovery and decreases food supply of marine mammals & seabirds
Over-fishing-example of TOC
Overharvesting of a species or several species from a body of water at such a rate that they cannot replace themselves.
-Leads to instability in aquatic ecosystems
Maximum Sustainable Yield
the highest possible annual catch that can be sustained over time, by keeping the stock at the level producing maximum growth
Fisheries
Populations of fish used for commercial fishing
Fishery collapse
When overfishing causes 90% population decline in a fishery
ITQs (Individual transferable quotas)
fishing limits calculated using maximum sustainable yield. If they can’t catch enough to remain economically viable, quotas can be sold to another fisher.
Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act
annual catch limits and accountability measures (ie fishing equipment) in federal fisheries.
Aquaculture
Raising fish, or other aquatic species in cages/enclosures underwater
Tragedy of the Commons
Individuals will use shared/public resources* in their own self interest, degrading** them
Ore
commercially valuable deposits of concentrated minerals that can be harvested and used as raw materials
Metals
elements that conduct electricity, heat, and have structural properties for building (found within ores)
Reserve
The known amount of a resource left that can be mined.
Usually measured in years left of extraction.
Overburden
Soil, vegetation, & rocks that are removed to get to an ore deposit below
TailingsZ&Slag
leftover waste material separated from the valuable metal or mineral within ore (often stored in ponds @ mine site)
Surface Mining:
Removal of overburden to access ore near surface
Open Pit Mining
Digging of large pits in the ground to extract valuable minerals
Mountaintop Removal
Explosives blast off mountain summits to access coal seams
Strip Mining
Removal of long strips of overlying soil and rock to expose mineral deposits
Subsurface Mining
underground mining, extracts minerals and ores located deep below the Earth's surface by digging tunnels or shafts to reach the deposits
Acid mine drainage
rainwater leaks into abandoned mine tunnels & mixes with pyrite, forming sulfuric acid
Methane Release
coal mining releases methane gas (CH4) from rock around coal
Vented out of mine to prevent explosion & continues seeping out after mine closes
Environmental impact of mining
PM Release
coal mining especially, releases lots of soot and other particulates that can irritate human & animal lungs
-environmental impact of mining
Smelting
roasting ore to release metals
-major source of air pollution
Heap-Leach Extraction
crushed ore piled in large heaps and sprayed with a dilute alkaline cyanide solution which percolates through the pile to dissolve the impurities.
Mine Reclamation
Process of restoring land to original state after mining has finished
-Includes:
Riling of empty mine shafts
Restoring original contours of land
returning topsoil, with acids, metals, and tailing removed
replanting of NATIVE plants to restore community to as close to originals state as possible
Surface Mining Control & Reclamation Act of 1977
Federal law that regulates the environmental effects of strip mining in the U.S.
Ecological Footprint
Measured in land (gha - global hectare) which is a biologically productive hectare (2.47 acres)
Carbon Footprint
Measured in tonnes of CO2 produced per year
Sustainability
Consuming a resource or using a space in a way that does not deplete or degrade it for future generations
-EX: sing compost (renewable) over synthetic fertilizer (fossil fuel dependent)
Maximum Sustainable Yield
The maximum amount of a renewable resource that can be harvested without reducing or depleting the resource for future use
ENV. indications of sustainability
Factors that help us determine the health of the environment and guide us towards sustainable use of earth’s resources
Human POP & Resource Depletion
As human population grows, resource depletion grows