Heat Transfer - Thermodynamics L4
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Conduction
Form of heat transfer where heat energy is directly transferred between particles through particle collisions or direct contact.
Convection
The transfer of heat by the movement of a fluid
Fluid
any substance that can flow and take the shape of the container that holds it
q
The variable used for Thermal Energy
Δ (Delta)
The greek letter used to indicate change
Latent Heat of Fusion (Lf)
The amount of thermal energy absorbed per gram as solid melts (fuses) at its melting point. The same amount of heat per gram must be released to freeze the substance.
Latent Heat of Vaporization (Lv)
The amount of thermal energy absorbed per gram as a liquid boils (vaporize) at its boiling point. The same amount of heat per gram must be released to condense the substance.
c
Heat capacity is the number of joules of energy needed to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree. In physics, it is Cp; in chemistry it is c
Density
Mass per unit volume of a substance
Radiation
Energy that is radiated or transmitted in the form of rays or waves or particles.
Solid
A state of matter that has a definite shape and a definite volume
Liquid
A state of matter that has no definite shape but has a definite volume.
Gas
A state of matter with no definite shape or volume
Boiling Point
The temperature at which a liquid changes to a gas
Melting Point
the temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid
Phase change
a change from one state (solid or liquid or gas) to another without a change in chemical composition
Melt
change from a solid to a liquid
Freeze
Change from liquid to solid
Boil/Vaporize
the change from a liquid to a gas
Condense
The change from a gas to a liquid
Sublimate
change directly solid to gas, without becoming liquid
Deposition
change directly from a gas to a solid
Celcius
Metric temperature scale on which water freezes at 0 degrees and boils at 100 degrees at sea level
Fahrenheit
A temperature scale with the freezing point of water 32 degrees and the boiling point of 212 degrees at sea level
Kelvin
the SI unit for temperature, abbreviated K; a temperature change of 1 Kelvin is the same as a temperature change of 1°C. Not based on the properties of water
absolute zero
The coldest temperature, 0 Kelvin, that can be reached. It is the hypothetical temperature at which all molecular motion stops.
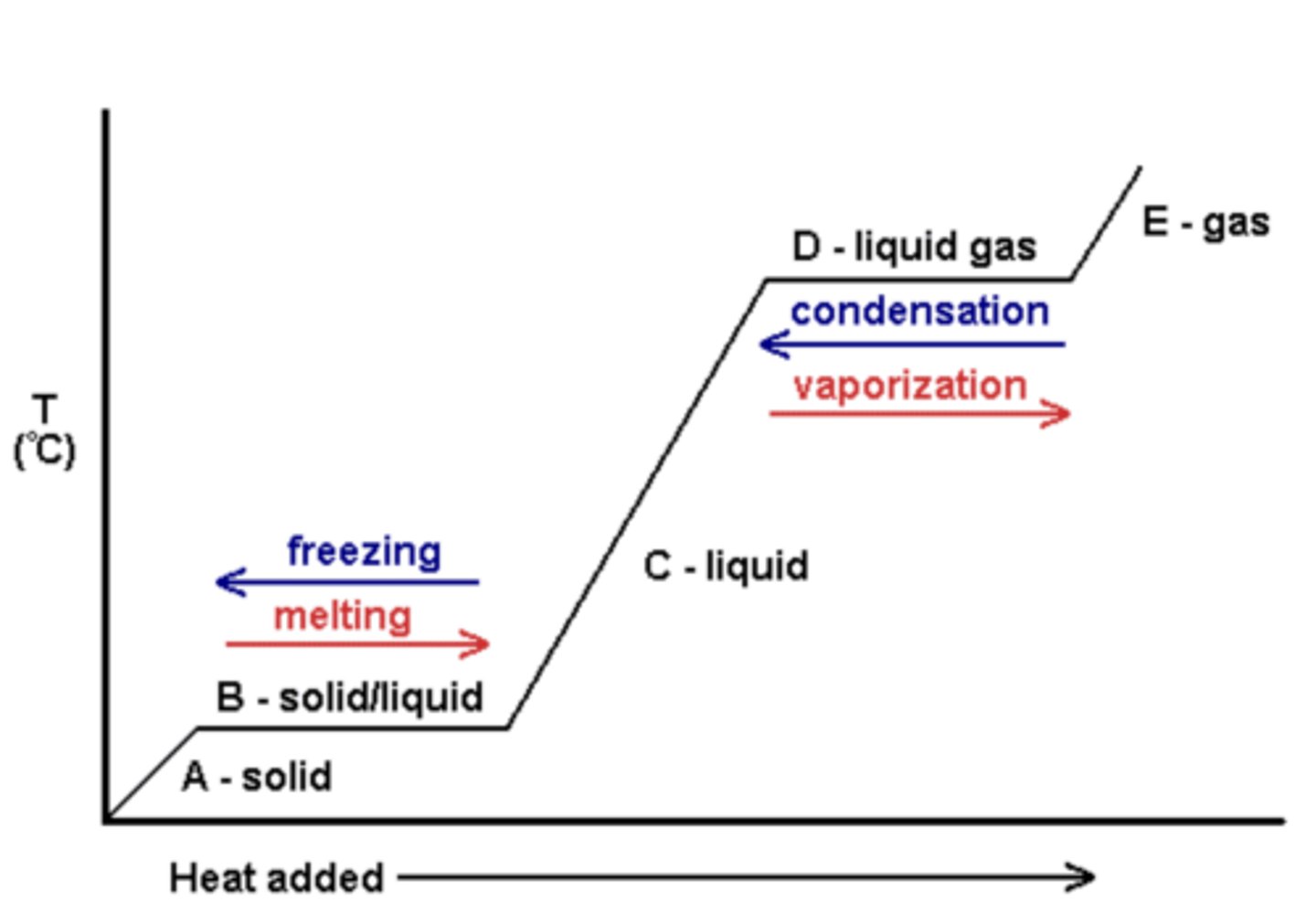
heating curve of water
shows the temperature of water in its three states as heat is added to the system
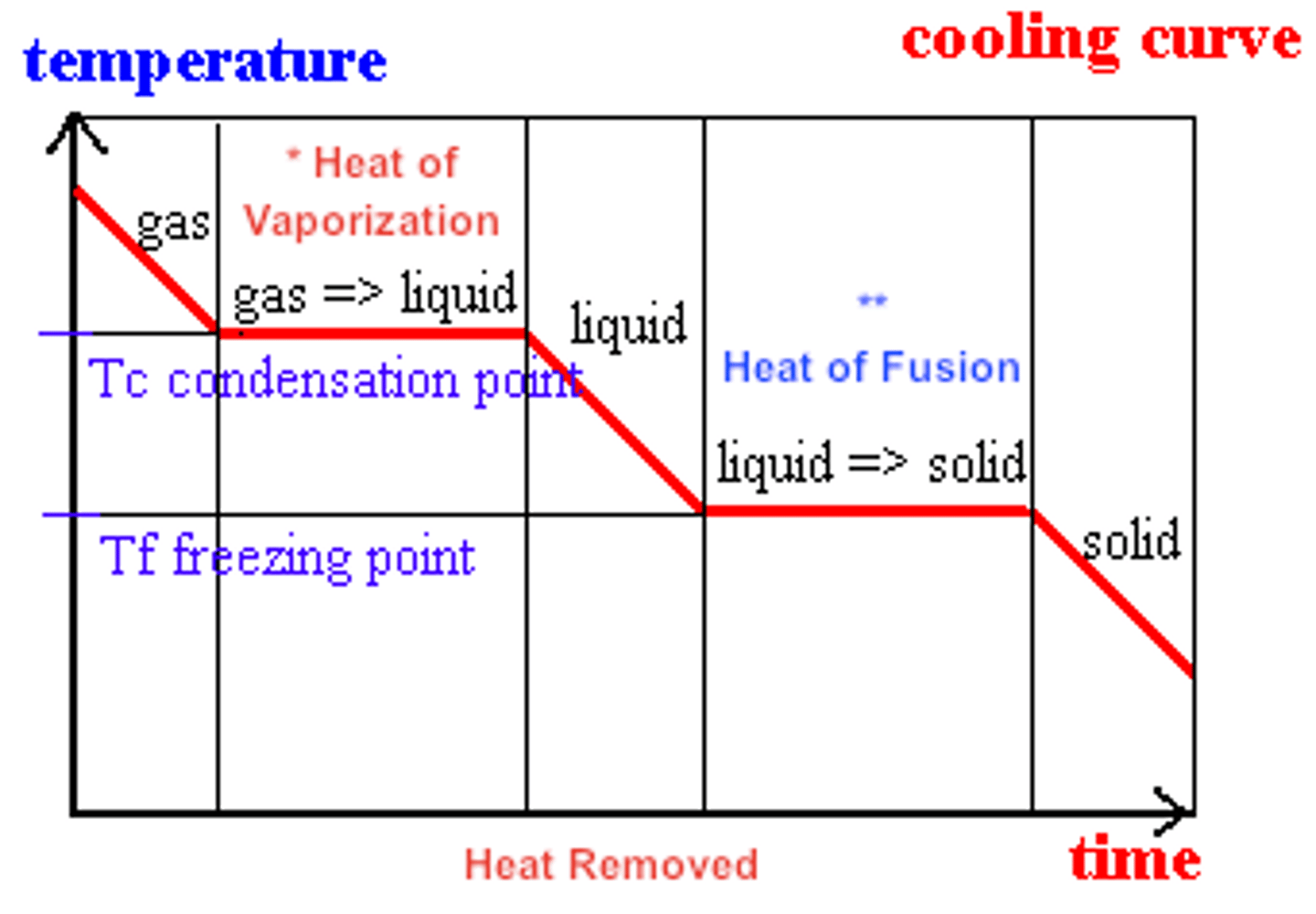
cooling curve of water
shows the temperature of water in its three states as heat is removed to the system