Population Genetics
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What is a gene pool?
All alleles present in a population
A population has a high degree to homozygousity or heterozygousity?
hetero
How to measure genetic variation?
Most direct way is to compare nucleotide sequences of genes carried by indv. of pop.
E.g. Drosophila → adh f and adh s allele
43 variations found in the 2721 Adh sequence base pairs.
14 variations in the coding regions but only 1 lead to a a.a replacement.
What is neutral theory?
Some genetic variation is expected simply as a result of mutation and drift.
What are the mechanisms for
What are the only source of variation?
Mutations
What shifts allele frequencies?
Natural selection (Principal) and unequal rates of survival and reproductive success.
Weak selection CANNOT cause substantial change in allele frequencies
FALSE
For rapid change in allele freq, the difference of genotype must be large
True
if Mutation rate is known, the we can calculate to what extent the allele freq change from one gen to another.
TRUE
What is genetic drift?
The number of reproducing individuals in a population is too small to ensure all alleles in a gene pool will be passed onto the next generation in existing freq.
(Some genes become fixed and some are lost)
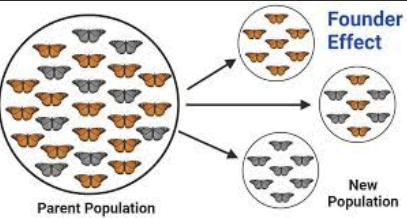
What is founder effect?
A type of genetic drift where populations originates from a smaller group of individuals whose gene pool may not reflect that of a larger population from which they(founders) were drawn from.
What is population bottleneck?
A type of genetic drift where a large population undergoes a drastic temporary reduction in numbers but can recover with genetic diversity being greatly reduced.
What is microevolution
Change in allele freq in a species population that do not result in reproductive isolation (not being able to interbreed).
What is the Hardy—Weinberg principle?
The allele and genotype frequencies in a population does not change from generation to generation when it is not influenced by evolutionary forces.
Evolutionary forces: mutations, migration, selection
What is the Hardy—Weinberg equilibrium?
When the population does not change at all genetically.
What are the assumptions of the Hardy—Weinberg model?
Random mating occurs
Large population
No selection
No mutations
No migration
For a HIV experiment to see whose genotype is resistant to HIV, how can you tell?
Determine genotypes by DNA direct analysis using PCR and RE digest analysis → Gel electrophoresis
Statement: Gene flow exists among populations that show how isolated or connected they are.
True