Electrophile addition reactions
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
H-x what adds
H X
H-x regiochemistry
mark
H-X sterochemtrisy
forms carbocation
H-X reaction
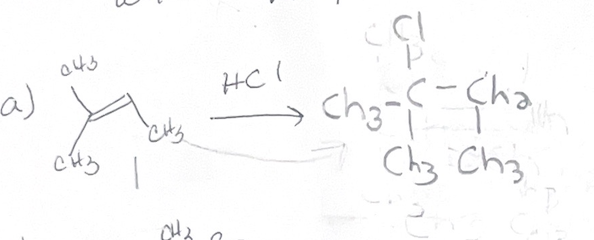
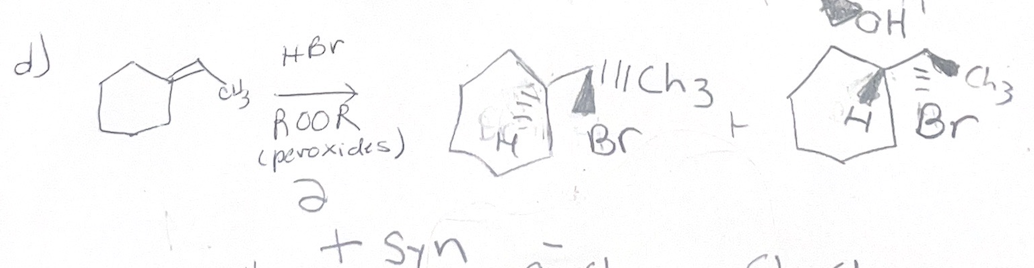
H- Br/ peroxide what adds
H Br
H- Br/ peroxide regiochemistry
anti mark
H- Br/ peroxide sterochemistry
does not matter
H- Br/ peroxide reaction
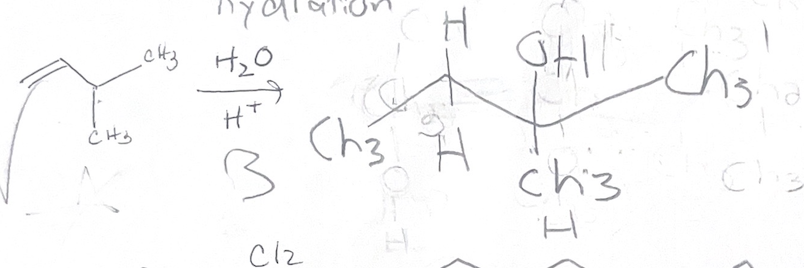
H2O, H+ what adds
H OH
H2O, H+ regiochemistry
mark
H2O, H+ stereochemistry
forms carbocation
H2O, H+ reaction
Hg(OH2)2/ NaBH4 what adds
H OH
Hg(OH2)2/ NaBH4 regiochemistry
mark
Hg(OH2)2/ NaBH4 steriochemistry
anti addition
Hg(OH2)2/ NaBH4 reaction
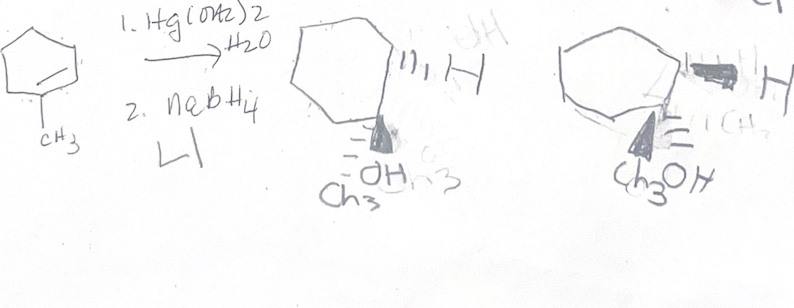
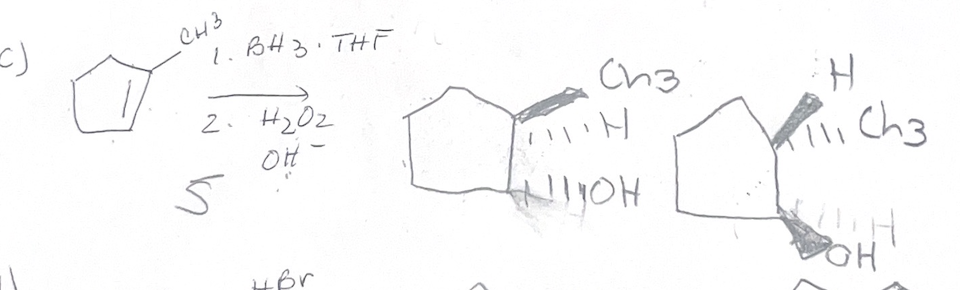
BH3/H2O2,OH- what adds
H OH
BH3/H2O2,OH- regiochemistry
antimark
BH3/H2O2,OH- stereochemistry
synaddition
BH3/H2O2,OH- reaction
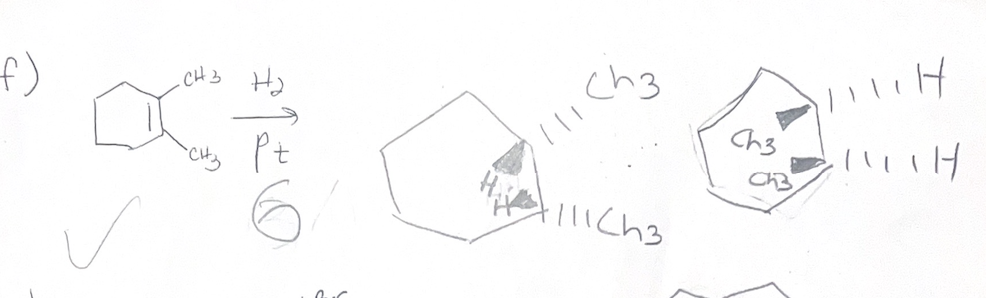
H2/PT what adds
H H
H2/PT regiochemistry
does not matter
H2/PT stereochemistry
syn addition
H2/PT reactions
X2/CCl4 what adds
X X
X2/CCl4 Regiochemistry
does not matter
X2/CCl4 stereochemistry
antiaddition
X2/CCl4 reaction
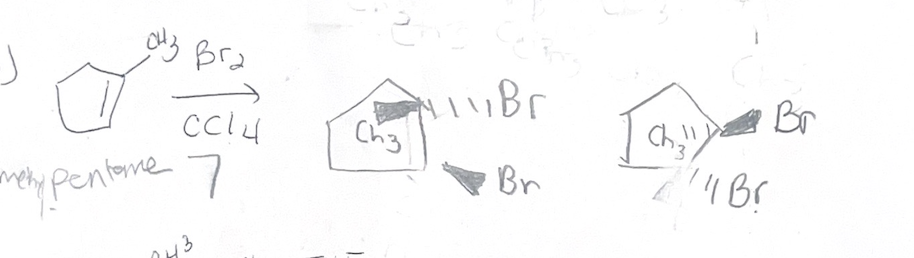
X2/H2O X=Cl, Br, or I what adds
X OH
X2/H2O X=Cl, Br, or I regiochemisty
mark
X2/H2O X=Cl, Br, or I stereochemistry
anti addition
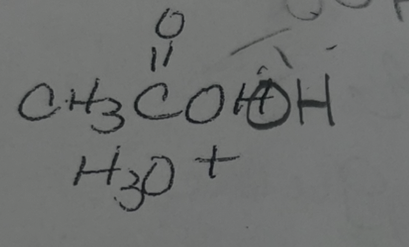
what adds
OH OH
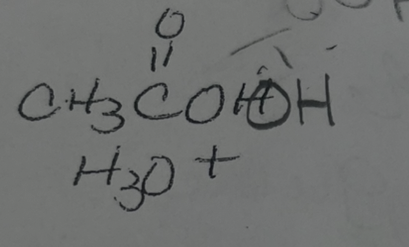
regiochemmistry
does not matter

stereochemistry
anti addition
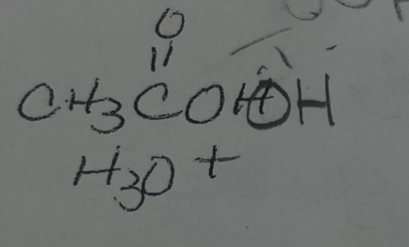
reactions

O5O4/ H2O2 what adds
oh oh
O5O4/ H2O2 regiochemistry
does not matter
O5O4/ H2O2 stereochemistry
syn addition
O5O4/ H2O2 reaction

cold dil KmNNO4/ H20 what adds
OH OH
cold dil KmNNO4/ H20 regiochemistry
does not matter
cold dil KmNNO4/ H20 stereochemistry
syn addition
cold dil KmNNO4/ H20 reaction
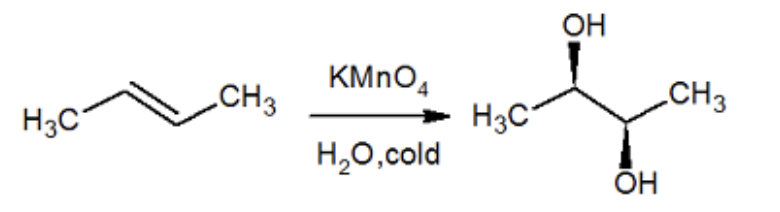
warm concentrate KmNO4 cuts the
double bond
warm concentrate KmNO4 gives
ketone and carboxylic acids
warm concentrate KmNO4 gives grop
c=o
warm concentrate KmNO4 reaction
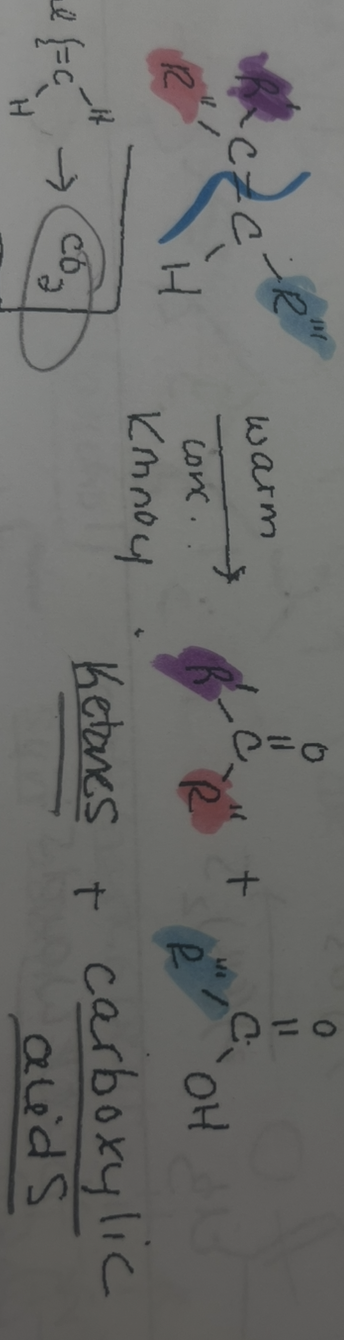
O3(CH3)2S cuts the
double bond
O3(CH3)2S gives
aldehydes and ketones
O3(CH3)2S gives group
c=c c=o o=c
syn addition
two new substituents are added to the same side
anti addition
two new substituents are added to the different sides
markovnikov
adds to the carbon atom of the double bond that has the greater number of hydrogen atoms
anti markovnikov
adds to the carbon atom of the double bond that has the least number of hydrogen atoms
hoffmans rule
elimination reaction (E2), the less substituted alkene is formed as the major product.
saytzeff rule
elimination reaction (E1 or E2), the more substituted alkene is usually the major product.