CPPS 306 Drug and Substance Abuse
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What is drug abuse
Any use of a drug that does more than harm than good for the individual or for society
Define:
Inappropriate use
Inappropriate non-use
Recreational or non-medical use of drugs
Inappropriate use = using a drug when you should
Inappropriate non-use = not using a drug when you hsoul d
Recreational / non medical use = using drugs without medical intent
What are the club drug classes and the drugs names
Depressants: GHB, Flunitrazepam
Dissociative: Ketamine, PCP
Stimulant/hallucinogens MDMA
Adictive potential of a dug
Addictive drugs have pleasant direct effects and short half-lives
What are the natural stimulant recreational drugs
Nicotine
Caffeine
Cocaine
Ephedrine (in stimulant lecture)
What are the synthetic stimulant recreational drugs
Amphetamine and its relatives (methylphenidate)
What are the natural depressant recreational drugs
Marijuana
Opium
Ethanol
What the the synthetic depressant recreational drugs
Barbiturates
Opioids (heroin)
Benzodiazepines
What is the mechanism of THC
THC receptors linked to Gi protein → decrease cAMP which reduces activity in NE, DA, Glu, and other pathways
Whare the the two ENDOGENOUS endocannabinoids
Arachidonylethanolamide
2-arachidonylglycerol (2-AG)
How does the combinaiton of a stimulant with a depressent affect the “high”
Combination of a stimulant and a depressant MAKES THE HIGH BETTER
Potentiates the high
What are hallucinogens
Hallucinogens alter or distort perception
What are the natural hallucinogens
Ergotamines = fungus growing on rye grain
Mescaline = peyote cactus
Psilocin = shrooms
Atropine and scopolamine
What ae the synthetic hallucinogens
LSD
PCP
Benztropine (ANTI CHOLINERGIC THERAPY)
Amphetamine
TMA
MDA
MDMA
How do opioids affect the reward pathway
Opioids activate the mu receptors on GABA interneurons in the VTA and decreases the activity of GABA inhibition which act on dopamine neurons
Less inhibition in dopamine neurons leads to more release of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens and enhances the reward pathway.
What are the mechanisms of action of hallucinogens
increase neural activity in NE, DA, and 5-HT
Reduce Ach pathway activity
How does cross tolerance develop with hallucinogens
Cross tolerance develops to drugs sharing the same mechanism of action, but not across mechanisms
What drugs are used to treat opioid abuse
Methadone (narcotic analgesic)
Naloxone / naltrexone = opioid ataganoist
Specifically, which drug is used for opioid dependency
Methadone
Good oral absorption, less euphoria
Long half life
What drugs are used to treat nicotine abuse
Nicotine replacement therapy
Varenicline
Buproprion (atypical antidepressant)
Is alcohol a depressant or a stimulant
Depressant
Explain the metabolism of ethanol
Ethanol —ADH→Acetaldehyde —ALDH→ Acetic Acid
What receptors do ethanol act on
GABA
NMDA
5HT
What are mechanism of action of ethanool
Reinforcing action through reward pathway
Supresses neuronal excitability in a concentration dependent manner
Limbic nerons are more sensitive than neurons in other parts of the brain
What drigs are used to treat alcohol dependence
Disulfiram = inhibits ALDH
Acamprosate = Glutamte receptor antagonist
Naltrexone = opioid receptor anatagonist with good oral absorption
Naloxone = opioid receptor antagonist with poor oral absorption
Explain the metabolism of methanol
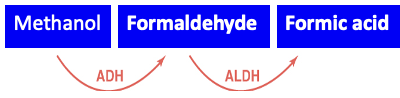
Formaldehyde and Formic Acid = toxic
What is the treatment for methanol toxicity
Mix ADH with ethanol
Give bicarbonate to reduce acidosis
initiate hemodialysis
Formepizole
What is Fomepizole
An ADH inhibitor used for treating methanol poisoning
Explain the metabolism of ethylene glycol
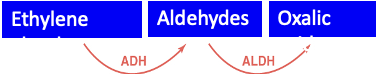
These metabolites are very toxic!!!!!
What happens with ethylene glycol metabolites
They are toxic and severe metabolic acidosis develops 4-12 hours in
What are the treatmenrts of ethylene glycol
Ethanol
Fomepizole
Bicarbonate
Dialysis
Then add fluids and calcium