FOR Exam III - Serology and DNA
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is forensic serology?
The applicaiton of the study of blood, semen, saliva, and other bodily fluids to the law.
What do forensic scientists mainly do?
Detect enzymes and antigens, like the identification of seminal stains or blood typing and DNA typing.
What’s actually in blood?
55% plasma, 40-45% red blood cells, 1% platelets and white blood cells
What do antigens do?
They’re responsible for blood-type characteristics and are on the surface of red blood cells
What does plasma contain?
Antibodies! For every antigen, there is a specific antibody
How much of the population falls into each blood type?
43% type O, 42% type A, 12% type B, and 3% type AB
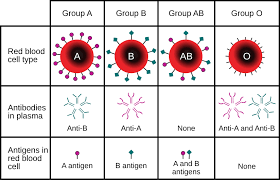
What questions do you need to answer when examining dried blood?
Is it blood?
Is it human? If not, what is it?
If it’s human, how closely can it be matched to a particular individual?
What are the blood color tests?
Kastle-Meyer: very indicitave of blood, and Luminol and Bluestar tests which are used to search for trace stains at scenes
What test determines if a blood sample is human or not?
The precipitin test. It identifies proteins that are only found in human blood
How is a precipitin test performed?
An animal is injected with human blood, the animals blood forms antibodies, those antibodies are harvested, a sample of the unknown blood is added to those antibodies, and if a precipitate forms, it’s human.
What are presumptive tests for seminal stains?
UV light (it glows) and Acid Phosphotase, which is an enzyme secreted into semen (on filter paper). The turns purple if semen is detected. The reagents are Alpha-Naphthyl Phosphate and Fast Blue B
What are the confirmatory tests for seminal stains?
Microscopic visualization of the sperm and a Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) test (the semen of adult men has higher PSA levels than anywhere else)
Why are PSA tests helpful?
Its useful in identifying semen from individuals who have had vasectomies and azoospermic individuals.
What are chromosomes, and what are they made of?
Physical carriers of genes; consists of DNA and other proteins
What is a nuclear DNA strand?
A large molecule made by linking nucleotides
What are nucleotides made of?
A sugar, a phosphorous-containing group, and a nitrogen base (Adenine, Cytosine, Thymine, Guanine)
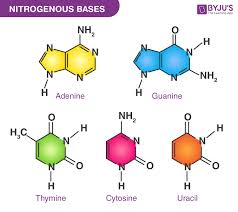
How are the bases connected in DNA?
Complementary-base pairing. Adenine to thymine, and cytosine to guanine.
How does DNA replication start?
Duplicates before cell division, unwinds the strands of the double helix, and joins a new strand.
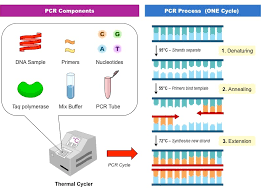
What is Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) testing?
Since polymerases are used to replicate DNA, this testing can replicate small pieces of DNA at scenes.
How does Polymerase Chain Reaction testing work?
-DNA is heated
-Primers (small DNA strands to target DNA sections for replication) are added to hybridize with the strands
-DNA polymerase and free bases (ACTG) are added to rebuild the strands
-Cycle repeated 25-30 times (hour can replicate billions)
What is a DNA tandem repeat?
Portions of the DNA where the bases repeat multiple times. They act as spacers between the coding regions of DNA.
How are DNA tandem repeats helpful to forensic scientists?
They offer a means to identify an individual from another via DNA typing. For every tandem, everyone has a difference in the amount of times that tandem repeats.
What were tandem repeats known as up until the mid 90s?
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLP). They’re length differences in relatively long repeating DNA strands. A typical core sequence is 15-35 bases and repeats up to 1000 times.
Whats the difference between PCR and RFLP?
PCR can’t be used in RFLP typing because the RFLP strands are too long (thousands of bases). PCR should only be used on strands no longer than a couple hundred bases.
What is the latest, most successful, and most widely used DNA profiling system?
Short Tandem Repeats (STR). STRs are locations on the chromosome that contain short tandem repeats that repeat themselves within the molecule.
How long are STRs?
3-7 bases long which repeat, and the entire STR strand is less than 450 bases long.
What are the STR advantages?
Less susceptible to degradation because they’re so small and can be recovered from severely decomposed bodies, and they can be multiplied via PCR, making them into a bigger sample size.
What is the basis of STR profiling?
Short DNA strands are categorized by a repeat unit. Repeats are present in variable numbers in individuals. Number of repeats distinguishes one person from another. DNA analysis is designed to isolate, count, and compare STRs of individuals.
Are genomes individual?
Yes, excluding identical twins, and they’re passed down from parents. DNA tests do NOT look at genes (little to no info about race, disease, or phenotypical info)
How many STR core loci are there?
Initially 13, but as of 2017, we have 20 in CODIS. Only 125 picograms of DNA is needed for analysis which is roughly 18 DNA-containing cells.
How is sex determined in STR testing?
The amelogenin gene. It’s shorter by 6 bases in the X chromosome than the Y chromosome.
What is a Y-STR?
STRs on the Y chromosome, which is male specific. There are more than 400 Y-STR markers.
What is mitochondrial DNA?
Short string of DNA from the mitochondria, inherited by the mother. All individuals of the same maternal lineage will be indistinguishable via mtDNA analysis. mtDNA typing doesn’t approach STR analysis.
Why use mtDNA typing over nuclear DNA?
When nuclear DNA is degraded, or when nuclear DNA is only present in small quantities. mtDNA is more rigorous, time-consuming, and costs more than nuclear DNA analysis.
When is human identity testing used? (involves generation of DNA profiles with the same core STR markers)
Forensic cases (match suspect w evidence), mass disasters, historical investigations, missing persons investigations, and paternity testing.
What are the rules of evidence?
Human error:
-Don’t compromise chain of custody of samples
-Collection of evidence must be recorded and access to evidence must be controlled
-Follow standards and procedures to prevent DNA damage during analysis
DNA and Juries:
-Must make sense to the jury
-Statistics can be confusing
What are sources of biological evidence?
Blood, semen, saliva, urine, hair, teeth, bone, and tissue
What are items that can be used for DNA testing?
Cig butts, clothing, condoms, stains, makeup and hair products, paper
Do you need a bigger blood sample for RFLP or PCR?
RFLP.
How is DNA evidence typically collected?
Standard/reference samples are taken via buccal (mouth and cheek) swab.