maddison sims study guide
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
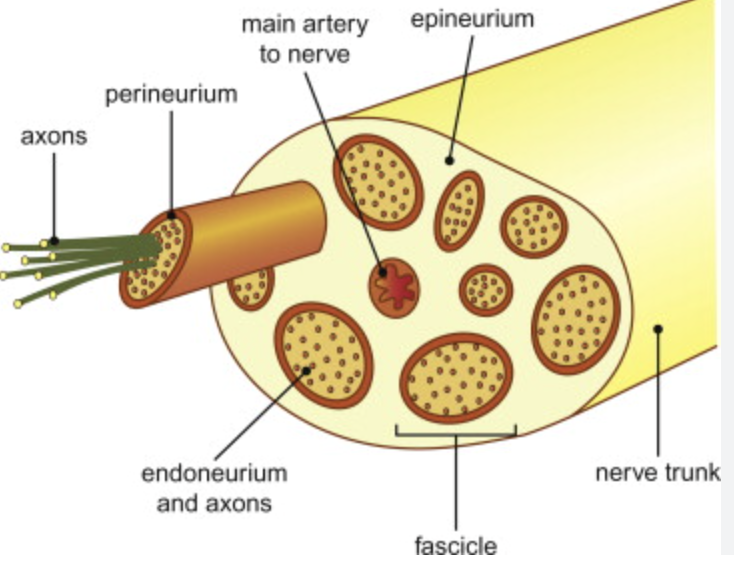
what do these cover
epineurium
perineurium
endoneurium
covers entire nerve
covers the fascicles
covers individual axons

ok
what does it mean when nerves are mixed
mixed nerves carry sensory and motor neurons
a nerve in the peripheral nervous system that carries both sensory (afferent) signals to the central nervous system (CNS) and motor (efferent) signals from the CNS
CRANIAL NERVES!!!!
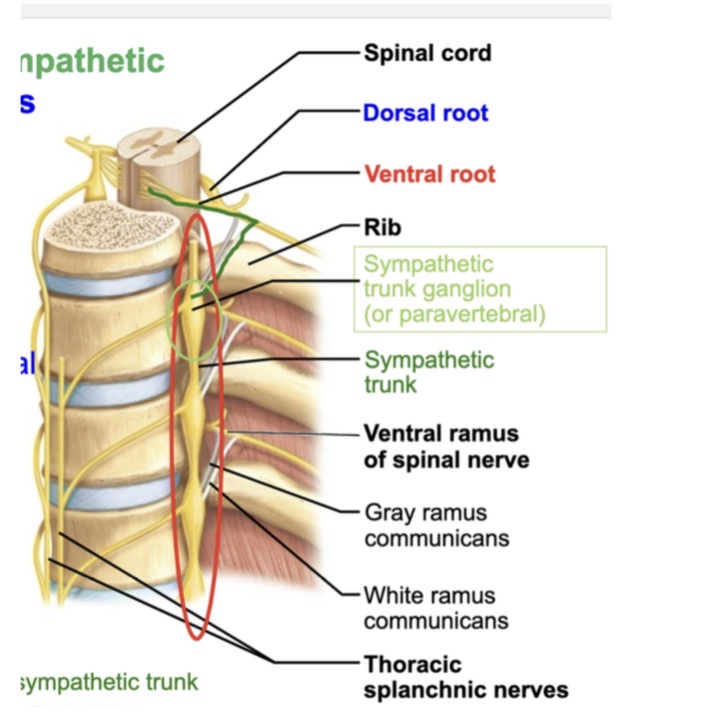
For spinal nerves, which parts are mixed?
1. Dorsal roots 2. Dorsal rami
3. Ventral roots 4. Ventral rami
A. 1, 2 and 3
B. 1 and 3
C. 2 and 4
D. 4 only
E. 1, 2, 3 and 4
C. dorsal rami and ventral rami are mixed
ok
study the descriptions of the cranial nerves
ok
what is wrist drop and what nerve is affected
wrist drop is the inability to EXTEND your hand at the wrist. radial nerve is damaged
what is the epineurium made out of and what does it cover
Made of tough fibrous CT that surrounds the nerve
Know where dendrites, axon terminals and axons are located in ascending and descending tracks.
ASCENDING: sensory tracts ascending to carry sensory input to the PRIMARY SOMATOSENSORY CORTEX
dendrites and cell bodies located in periphery or spinal cord ig where they receive stimulus
Axon terminals located in gray matter (Cerebral cortex), postcentral gyrus, primary somatosensory cortex
Know where dendrites, axon terminals and axons are located in ascending and descending tracks.
DESCENDING:MOTOR TRACKS DESCEND TO CARRY MOTOR OUTPUT FROM THE PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX
dendrites and cell bodies located in gray matter (cerebral cortex), precentral gyrus. and primary motor cortex
Axon terminals are located in the spinal cord
WHITE MATTER
what is white matter specifically in the CNS
why is it called white matter
what would be found there
White matter is the region of the central nervous system (brain + spinal cord) that contains:
Myelinated axons (the main component)
Some unmyelinated axons
Glial cells (especially oligodendrocytes)
called white matter because it consists mainly myelinated axons, myelination has a white appearance
Myelinated axons (the main component)
Some unmyelinated axons
Glial cells (especially oligodendrocytes)
what nerve causes carpal tunnel syndrome
median nerve is affected with carpal tunnle syndrome
VENTRAL RAMI
what are they
where are they from (branching out from)
where are they branching to
ventral rami are the front branches of spinal nerves
Originate from spinal nerves and branch to innervate muscles, skin, plexuses
Muscles, skin, plexuses. Innervate lateral and anterior neck, and innervate upper and lower limbs.
what are the ranges of these plexuses
cervical
brachial
lumbar
sacral
coccygeal
cervical: C1-C4
brachial: C5-C8 and T1
Lumbar: L1-L4
Sacral: 4-S4
Coccygeal: coccygeal nerve
where is the primary somatosensory cortex
found in postcentral gyrus of parietal lobes
what does it mean when cells are excitable
able to respond to a stimulus by generating AP
cells can generate and conduct electrical activity
PLEXUSES
Why are they way they are in terms of damage, and how will this affect paralyzation
Can plexus lose complete innervation
why are they located where they are
damage to a single spinal nerve or root would only cause PARTIAL loss of function(limb wont be completely paralyzed)
NO, each plexus branch has fibers to form multipal spinal nerves so it will never lose complete innervation
Located in specific regions to provide innervation to specific muscles in the body
What is the starting course for the optic nerve, starting with light entering the eye
retina
optic nerve
optic chiasm
thalamus
primary visual cortex
occipital lobe
what do rami carry, sensory, motor, both?
dorsal rami
ventral rami
dorsal rami: carries sensory and motor neurons
ventral rami: carries both sensory and motor neurons
know the cranial nerves
ok functionsthis
this nerve…
passes anteriorly down arm and forearm
pases through carpal tunnle
innervates flexor muscles in forearm, palm and fingers 1-3 and part of finger 4
median nerve
this nerve…
passes anteriorly along arm and parallel to ulna. innervates forearm flexors and fingers 4-5
ulnar nerve
this nerve…
longest and thickest nerve in the body. innervates hamstring muscles in posterior thigh for thigh extension and leg flexion, composed of two nerves
sciatic nerve
this nerve…
innervates skin and muscles of neck, ear, and back of head and shoulders. causes hiccups when irritated
phrenic
this nerve…
found in the thoracic cavity. Carries motor and sensory neurons. Run between the ribs
intercostals
ok
what 3 nerves are specific to the brachial plexus
1. median
ulnar
radial
KNOW THE RANGES OF PLEXUSES
OK
The sciatic nerve is a combination of two nerves, what are the names of the two nerves that come together
tibial and common fibular nerves (peroneal)
Bells palsy
what is it
what causes it
what is the treatment
inflammation of the facial nerve
causes paralysis of facial muscles usually on one side
corticosteroids for treatment
********PRE MEDICAL STUDENTS CAN GET BALLS PALSY DUE TO THEIR STRESS FROM FINALS
Olfactory nerve
what is the order that it goes throguh, the steps not the order order
begins with olfactory receptor cells that detect smell
travels through cribiform plate of ethmoid bone
fibers then synapse in olfactory bulbs
then signals are carried along a tract to the primary olfactory cortex
where are the ventral roots going towards, what do they innervate and why
ventral roots carry motor neurons out of the spinal cord toward the body
they innervate muscles involved in voluntary movement because they carry motor neurons
What are the parasympathetic and sympathetic effects for…
Eye (smooth muscle of iris)
Para: constricts pupils
Sympathetic: dilated pupils
What are the parasympathetic and sympathetic effects for…
salivary glands
PARA: increases salivation
SYMPATHETIC: decreases salivation
What are the parasympathetic and sympathetic effects for…
adrenal medulla
PARA: no effects (no innervation)
SYMP: stimulates medullary cells to secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine as hormones
What are the parasympathetic and sympathetic effects for…
Heart
PARA: decreases heart rate
SYMP: increases heart rate, increases contraction strength
What are the parasympathetic and sympathetic effects for…
digestive organs
PARA: promotes digestion
SYMP: slows/inhibits digestion
What are the parasympathetic and sympathetic effects for…
lungs
PARA: constricts bronchioles
SYMP: dilates bronchioles
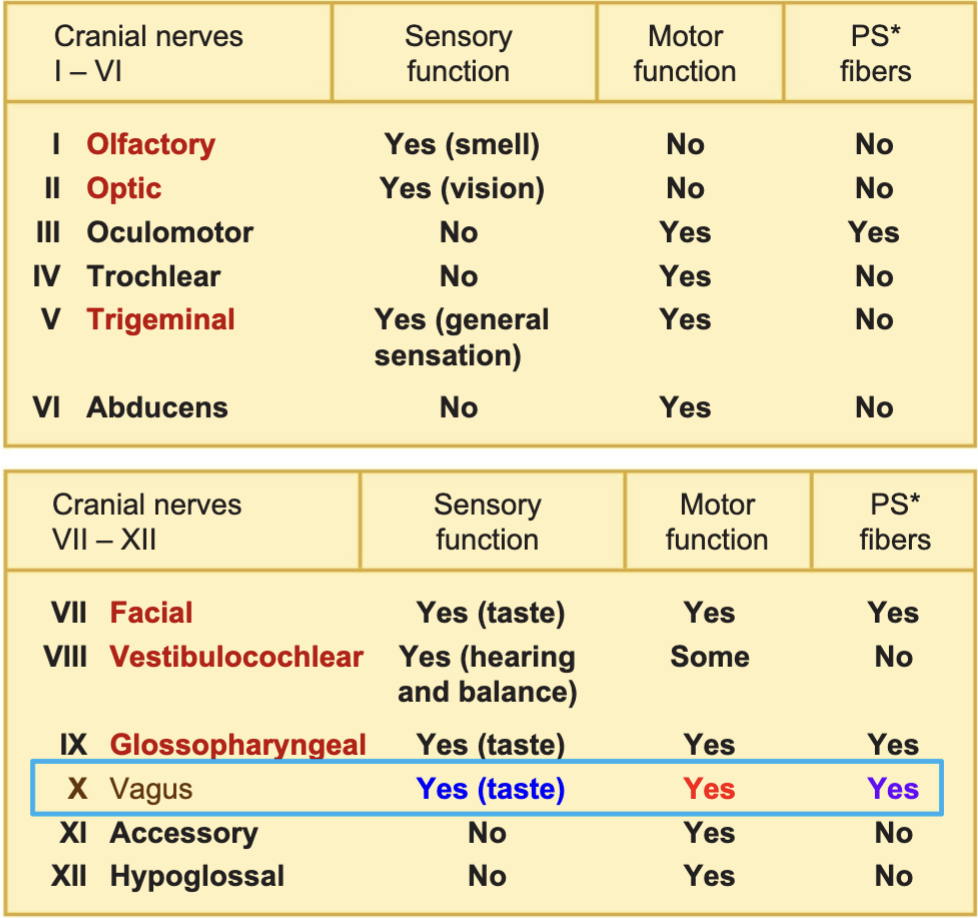
VAGUS NERVE
what is it innervating
where does it exit skull
How is it coursing
innervates organs in the thoracic and abdominal cavities
exits the skull through the jugular foramen
descend down the thorax and abdomen
RAYNAUD’S DISEASE
what is it
what causes it
what is happening in the body
painful exaggerated vasoconstriction in the fingers and toes
blood vessels in fingers and toes overreacting to cold or stress, digits turn pale
What neurotransmitters are secreted from the pre and post ganglion fibers in autonomic and parasympathetic nervous system
somatic
sympathetic PREganglionic
sympathetic POST ganglionic
parasympathetic PREganglionic
parasympathetic POSTganglionic
somatic: ACh
sympathetic PREganglionic: ACh
sympathetic POST ganglionic: norepinephrine
parasympathetic PREganglionic: ACh
parasympathetic POSTganglionic: ACh
what is the name of the bottom tip of the spinal cord
conus medullaris
know the directional terms, superior etc
ok
what are positive feedback loops and what happens in them?
positive feedback loops control processes that occur INFREQUENTLY.
temporarily increases the original stimulus and moves the variable away from the set point
returns the body to homeostasis
tight junctions
what are they
where are they found
impermeable junctions, nothing passes through
found in digestive tract in the small intestine and kidneys, BBB
What is dense irregular CT, and where is it found
bundles of collagen, think and randomly arranged. resists tension in many directions
found in dermis of skin, fibrous joint capsules, and fibrous covering in some organs
what is dense regular CT and where is it found
numerous collagen fibers arranged in parallel bundles
withstands stress with force applied in ONE SINGULAR direction
found in TENDONS and most LIGAMENTS
THIRD DEGREE BURNS
how do we classify them
what do they look like
treatment
known as a full thickness burn, destroys all layers of the skin
epidermis
dermis
nerves, hair follicles, sweat glands, blood vessels
Dry, leathery appearance, white, waxy, brown, charred
NO BLISTERING: blistering is 2nd degree
skin grafts are often used for treatment
what are the levels of organization, levels that we study at
chemical: study of atoms and molecules
cellular: study of cells
tissues: study of tissues, groups of cells that carry out a specialized function
organ:; multiple tissues working together for a specific function
organ systems: group of organs that work together for a common purpose
organismal: made up of many organ systems working together
what are teh 4 anatomy approaches
regional
systemic
microscopic
gross
what are these anatomy approaches descriptions
regional
systemic
microscopic
gross
regional: observes one body area
systemic: observes a body system
microscopic: anatomy seen with a microscope
gross: anatomy seen without a microscope
what are the names of the membranes that surround the lungs
Why are they there and what is their purpose
Visceral pleura surround the lungs themselves, parietal pleura surround the cavity that they sit in
these membranes secrete serous fluid between the membranes to reduce friction between neighboring organs
what is a lacunae
what is found inside the lacunae
lacunae are embedded cavities in hard bone matrix or cartilage
BONE: osteocyte in lacunae
CARTILAGE: chondrocyte in lacunae
ok
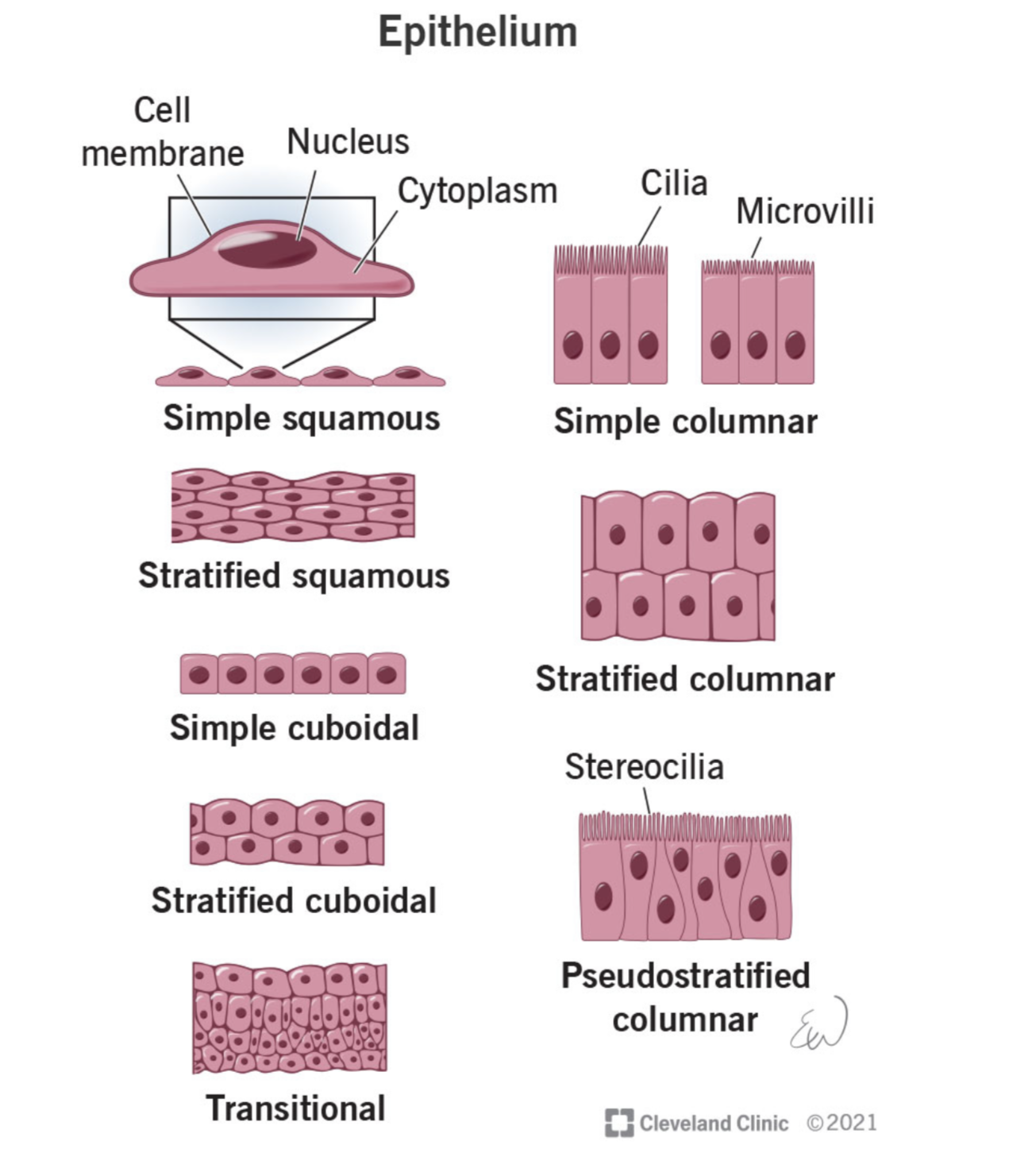
what is the purpose of epithelium, or what are the 5 characteristics of epithelium
protection
secretion
absorption
filtration
sensory receptor
MELANOCYTES
what are they
What layer of skin are they found
What do they secrete
a mature melanin-forming cell, especially in the skin.
found in the basal layer of the skin
(C, L, G, S, B) -found in the deepest layer of the skin
they secrete melanin to produce the color of hair, skin, eyes.
also protects the skin against UV radiation
what is the order of the skin layer
stratum corneum
stratum lucidum
stratum granulosum
stratum spinosum
stratum basale
look up what is the last layer of skin to contain alive cells
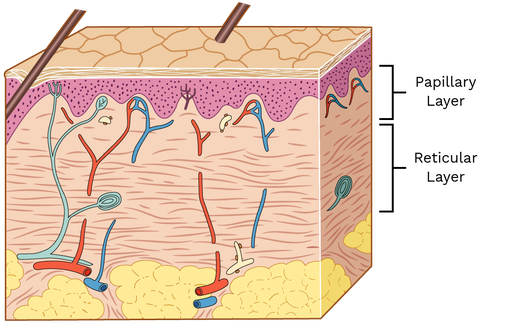
what are the two layers of the dermis
papillary
reticular

what is this layer of the dermis
thin layer of loose areolar CT propper
dermal papillae
papillary layer
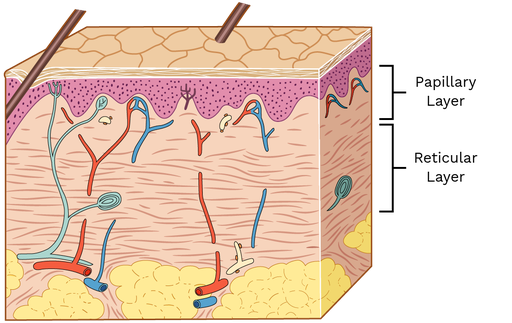
what layer of the dermis is this
thick layer of dense irregular CT
makes up the bulk of the dermis
reticular
what bones belong to the appendicular skeleton
everything else, the girdles, lower and upper limbs
what bones belong to the axial skeleton
only things in the axis
skill, ribs, vertebrae, sacrum, ribs, sternum, hyoid bone
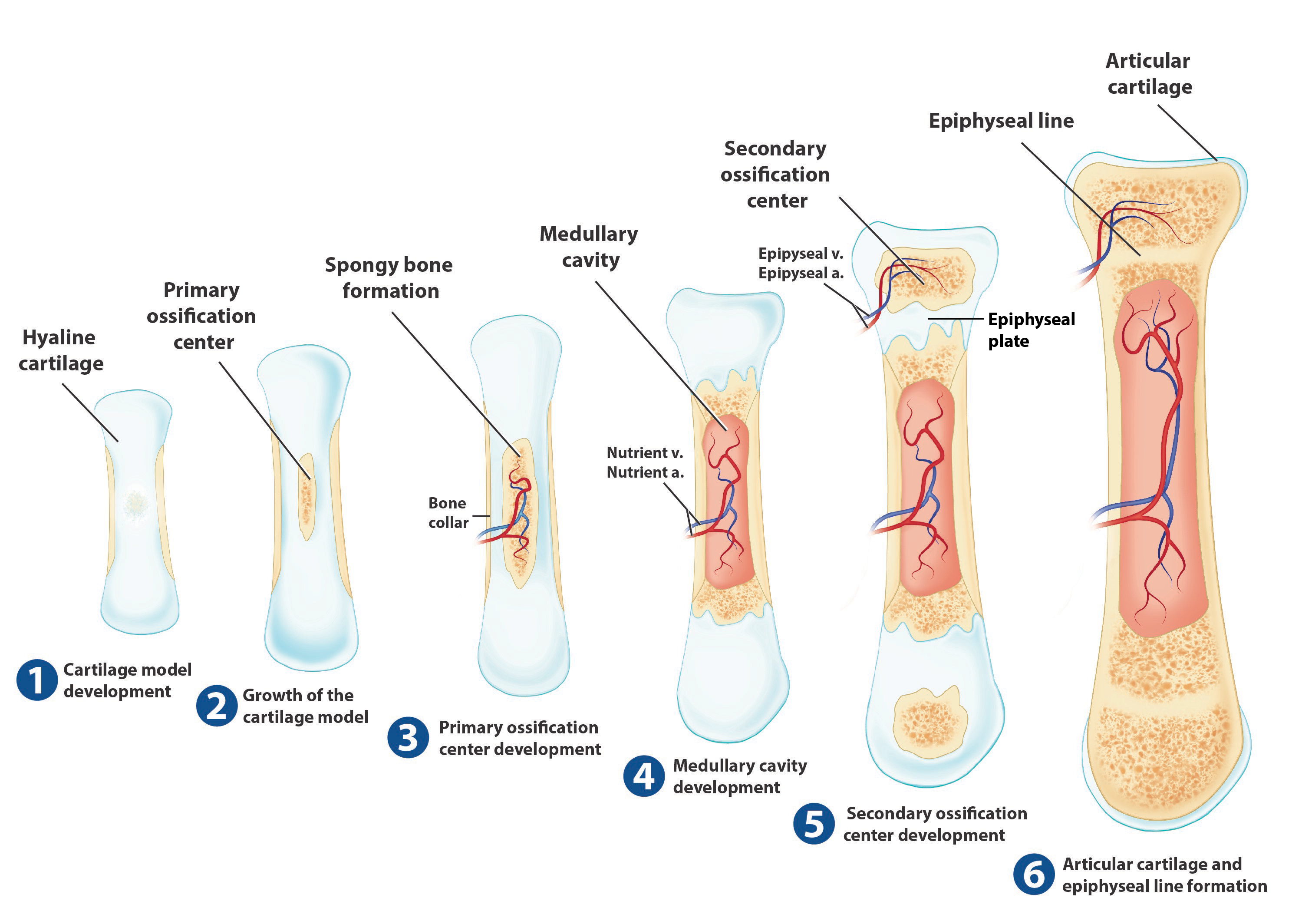
what is endochondral ossification, what forms and what is replaced, what type is it from.
occurs in all bones except for clavicles
cartilage forms first, then replaced by bone. Forms from hyaline cartilage
starts off with the medullary cavity
*. look up the steps perchance
what are the 4 types of bones classified by shape
long (humerus) limbs
short *talus)
flat( sternum)
irregular (vertebra)
description of long bones and what is unique to them, and examplkes
Longer than it is wide
medullary cavity with yellow bone
shaft
HUMERUS
FEMUR
description of short bones and examples
no diaphysis, epiphysis or medullary cavity. Includes CUBED bones
CARPALS
TARSALS
PATELLAE
description of flat bones and examples
no diaphysis, epiphysis or medullary cavities.
STERNUM
RIBS
SCAPULAE
ROOFING BONES
description of irregular bones and some examples
no diaphysis, epiphysis or medullary cavity
VERTABRAE
HIPBONES
CERTIAL FACIAL BONES AND CRANIAL BONES
What is the name of the neurotransmitter that operates at the neuromuscular junction
acetylcholine
Where is teh primary somatosensory cortex found
post central gyrus of parietal lobe
What is a sulcus
shallow groove that separates gyrus
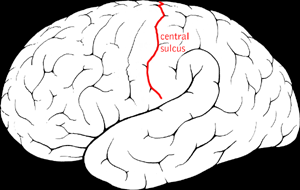
what is a gyrus
a ridge on the surface of the brain
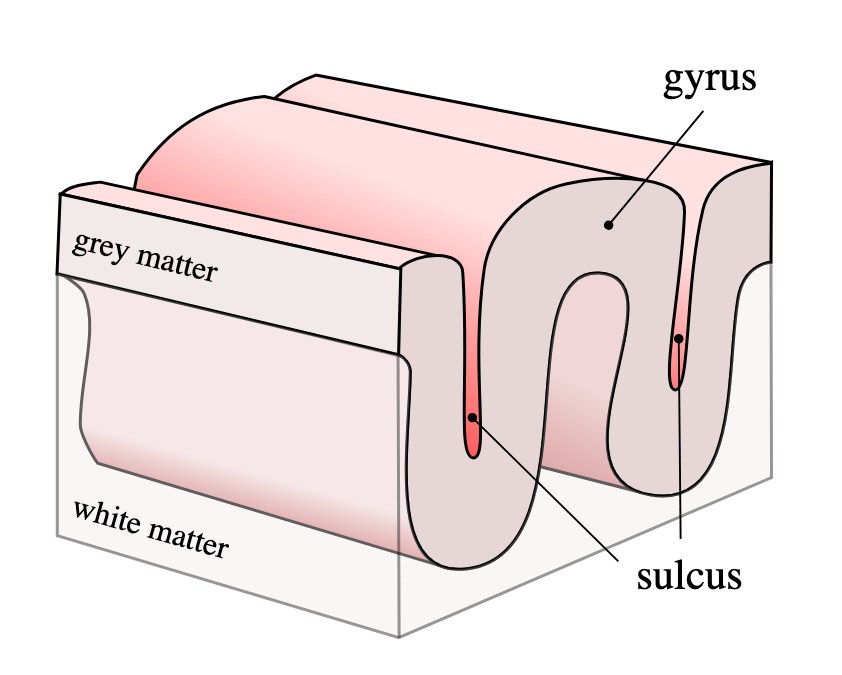
what is a fissure
deep groove that divides brain into lobes and hemispheres
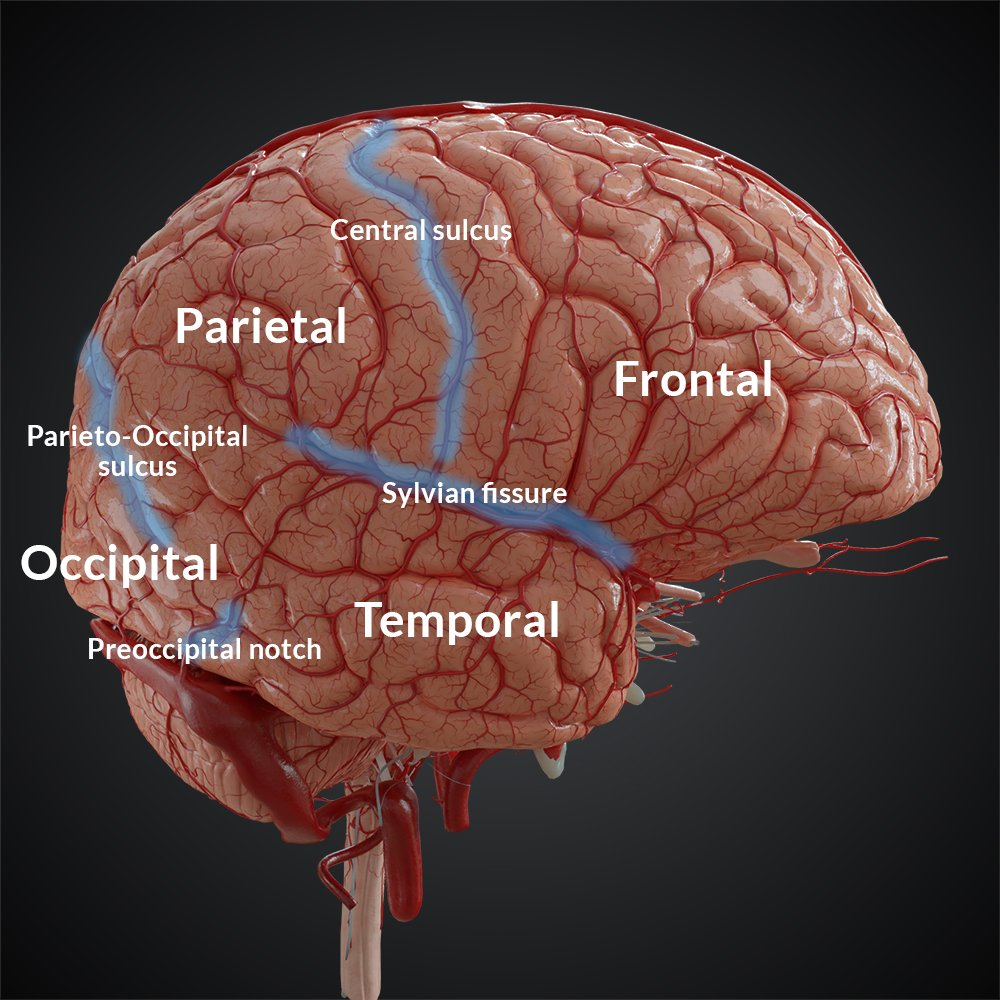
AREAS OF THE CNS
primary motor cortex
premotor cortex
visual association area
primary auditory cortex
primary motor cortex: located in precentral gyrus, initiates voluntary movements
premotor cortex: found in frontal lobe in front of primary motor cortex. involved in the repetitive learned motor skills
visual association area: located in occipital lobe and surrounds primary visual cortex. Interprets visual stimuli and makes sense of the information
primary auditory cortex: located in the temporal lobe
PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX
where is it located
what is its function
located in precentral gyrus
initiates voluntary movement of skeletal muscle
PREMOTOR CORTEX
where is it found
what is its function
found in the frontal lobe in front of primary motor cortex
involved in the repetitive learned motor skills
VISUAL ASSOCIATION AREA
where is it located
what is its function
located in the occipital lobe, surrounds primary visual cortex
interprets visual stimuli and makes sense of the information
PRIMARY AUDITORY CORTEX
where is it located
what is its function
located in the temporal lobe
receives input from inner ear for pitch, loudness, and sound localization
DORSAL COLUMN-MEDIAL LEMINSCAL PATHWAY
1st order neurons…
emerge from dorsal roots of spinal cord, synapse at medulla oblongata
DORSAL COLUMN-MEDIAL LEMINSCAL PATHWAY
1st order neurons emerge from the ___, and synapse at the ___
emerge from the dorsal roots of the spinal cord
synapse at the medulla oblongata
DORSAL COLUMN-MEDIAL LEMINSCAL PATHWAY
2nd order neurons, where do they emerge and synapse
emerge from medulla, synapse at thala,us
DORSAL COLUMN-MEDIAL LEMINSCAL PATHWAY
3rd order neurons, where do they emerge from and where do they synapse
emerge from the thalamus, synapse at primary somatosensory cortex
DORSAL COLUMN-MEDIAL LEMINSCAL PATHWAY
2nd order neurons emerge from the ___, and synapse at the ___
medulla; thalamus
DORSAL COLUMN-MEDIAL LEMINSCAL PATHWAY
3rd order neurons emerge from the ___, synapse at the ___
thalamus;primary somatosensory cortex
what is saltatory conductance
the rapid "leaping" of nerve impulses (action potentials) from one gap in the myelin sheath (Node of Ranvier) to the next along a myelinated axon
conduction of electrical signals across myelinated axons
what is the reason for saltatory conductance?
speeds up the rate AP’s travel for a quicker transmission of nerve signals
to speed up the transmission of nerve impulses along a neuron and make this process more energy-efficient
what allows for saltatory conductance
myelination and nodes of ranvier allows for rapid, jumpy, conduction
the myelin sheath (an insulating layer) and the Nodes of Ranvier (gaps in the sheath) on myelinated axons
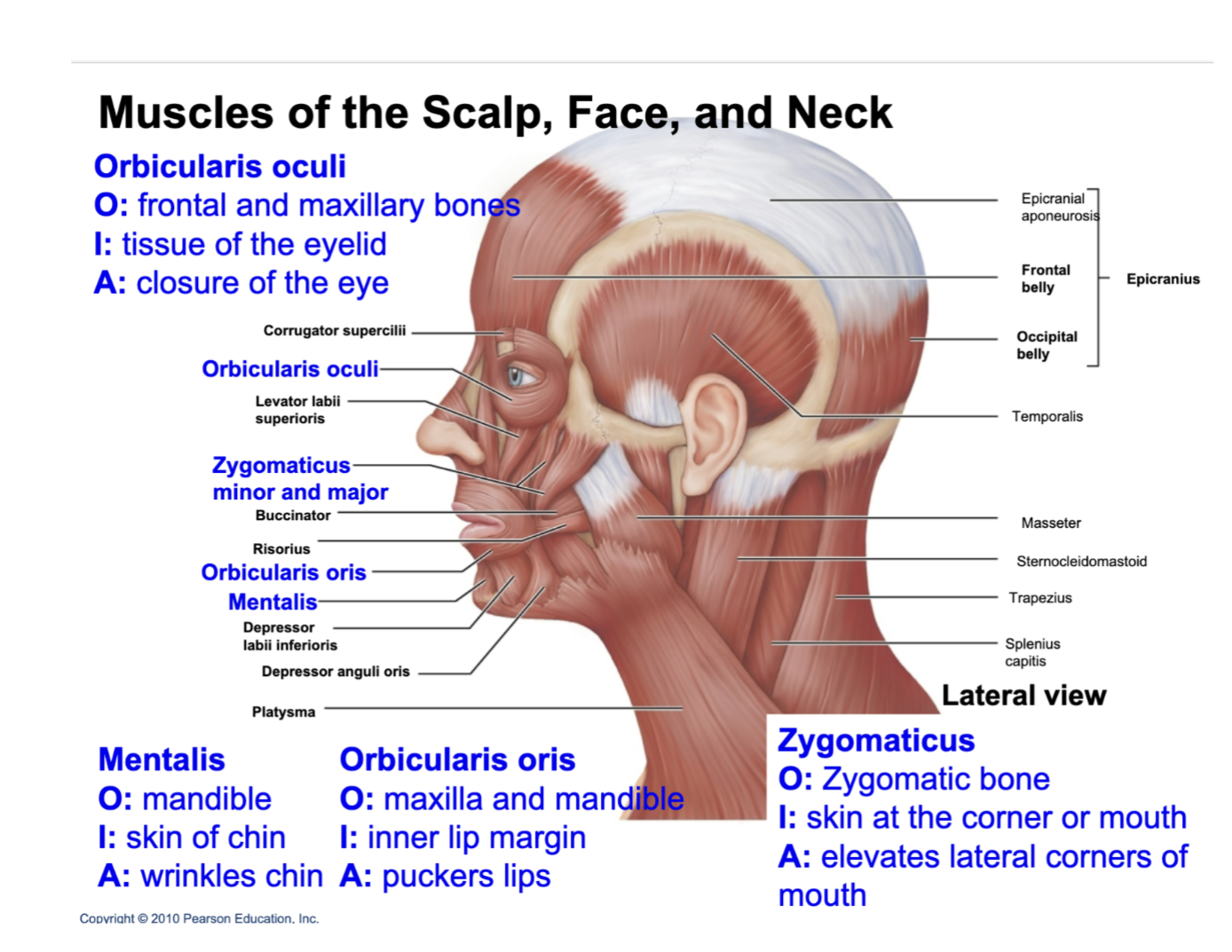
ok
what are the 5 structures of the CNS put int he correct order
spinal cord
medulla oblongata
pons
cerebellum
midbrain
cerebrum
what are the orders of muscle organization
LARGEST TO SMALLEST:
muscle
fascicles
muscle fibers
myofibrils
myofilaments
in an OIA, which one is stationary/stable, and how do they move
origin is stationary
insertion site moves TOWARD the origin site when the muscle contracts

identify a cranial nerve in yellow
t/f
know the OIA of the extensor carpi radialis
O: medial epicondyle of humerus
I: 2nd and 3rd metacarpals
A: flex the hand
t/f
OIA for extensor digitorum longus
O: fibula
I: middle and distal phalanges of lateral 4 digits
A: extends the toes
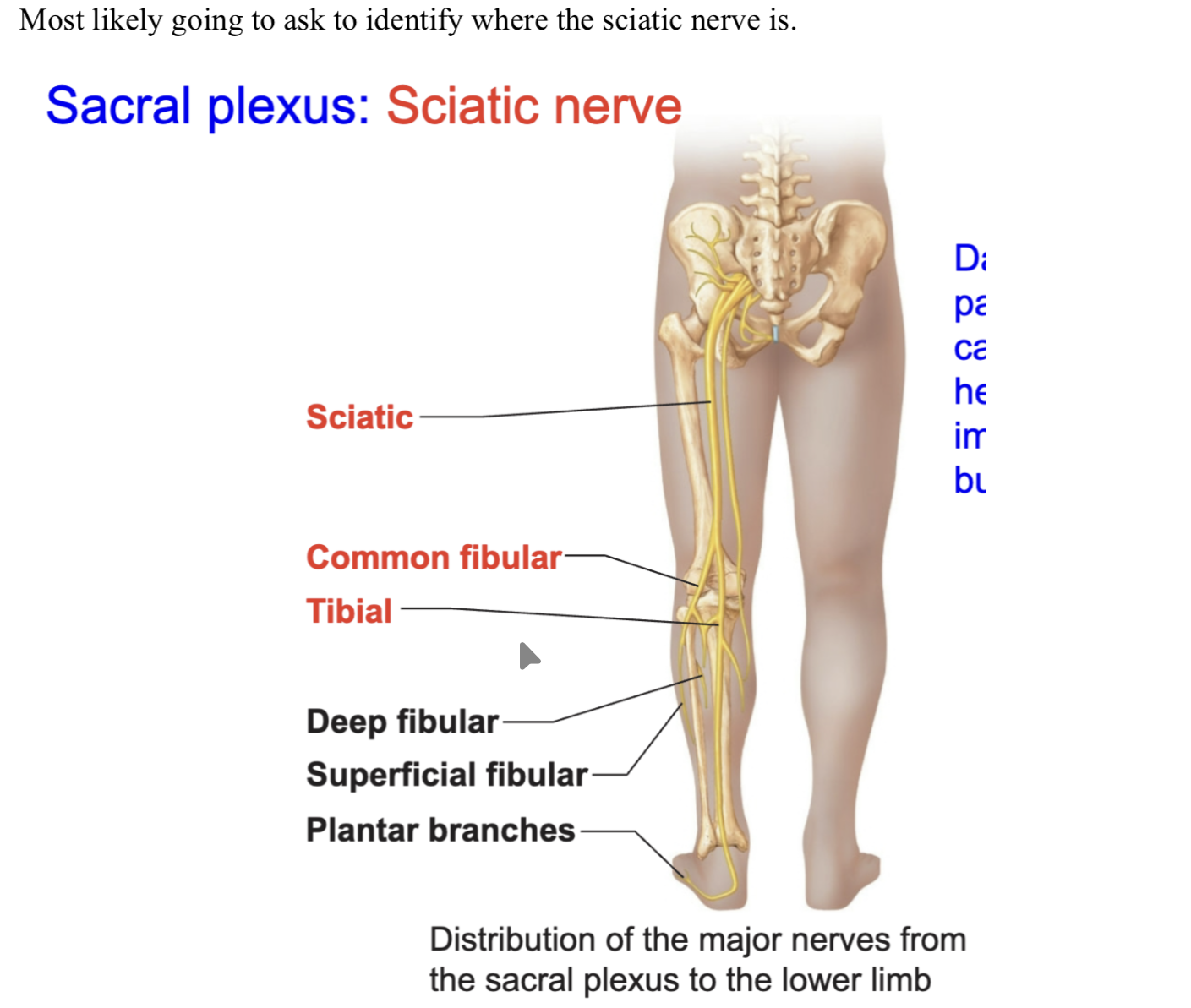
ogi