Health and Human development VCE Unit 3 outcome 2
1/38
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Old public health
Government actions that focused on changing the physical environment to prevent the spread of disease, such as providing safe water, sanitation and sewage disposal, improved nutrition, improved housing conditions and better work conditions
Health promotion
The process of enabling people to increase control over, and to improve, their health.
Biomedical model of health
Focuses on the physical and biological aspects of disease and illness.
Build healthy public policy
This action area relates directly to decisions made by governments and organizations regarding laws and policies that discourage unhealthy behaviors and encourage healthier choices.
Strengthen community action
This action area focuses on building links between individuals and the community and centers on the community working together to achieve a common goal.
Social Model of Health
Aims to change unhealthy behaviors by addressing the sociocultural and environmental factors that contribute to inequities in health outcomes.
Create supportive environments
This action area is one that promotes health by being safe, stimulating, satisfying and enjoyable.
Reorient Health Services
This priority area refers to reorienting the health system so that it promotes health as opposed to only focusing on diagnosing and treating illness.
Advantage of Biomedical Approach
Disadvantage of biomedical approach
Public System
This includes all public-sector health services and schemes that are provided by the Australian, state/territory and local governments, and include:
•Public hospitals
•Medicare
•the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme
•National Disability Insurance Scheme
Medicare
Medicare is Australia’s universal health insurance scheme. Medicare is known as a universal health insurance scheme as it is available to all Australian residents, regardless of income, location, and culture.
Medicare service
Medicare bulk billing
term used when a service provider (GP, optometrist, etc.) chooses to charge the patient no more than the scheduled fee for their services.
Scheduled fee
The scheduled fee is the amount the government, via Medicare, contributes towards the costs of treatments and services. Essentially it works like a ‘recommended retail price’.
Co-payment
f the service provider chooses to charge more than the schedule fee for their service the patient will have to make up the difference. These charges are called ‘out-of-pocket’ expenses or patient co-payments.
Medicare Safety Net
The Medicare safety net aim to protect those who have a heavy reliance on medical services from high ‘out-of-pocket’ expenses.
Advantage and Disadvantage of Medicare
Medicare Funding
Pharmaceutical Benfefits Scheme(PBS)
The aim was to provide essential medicines to people who needed them, regardless of their ability to pay.
The purpose of the PBS remains the same today, but instead of being free, medicines are now subsidised and consumers must make a patient co-payment.
Provide essential medicines that are subsidised to reduce illness.
PBS Safety Net
In addition to the initial subsidy, individuals and families are further protected from large overall expenses for PBS-listed medicines through the
PBS Safety Net.
National Disability Insurance Scheme
he NDIS is a national insurance scheme that provides services and support for people with permanent, significant disabilities, and their families and carers.
Funded by the federal and state/territory governments, the NDIS works to assist individuals with disabilities to live an ordinary life.
NDIS Requirement
The residency requirements are two fold:
be an Australian citizen or hold a permanent visa or a Protected Special Category visa
live in Australia where the NDIS is available.
NDIS individualised plans
If the residency and disability requirements are met, the first step in accessing the NDIS is developing an individualised plan.
Private Health Insurance
Private health insurance is a type of insurance under which members pay a premium (or fee) in return for payment towards health-related costs not covered by Medicare.
Funding
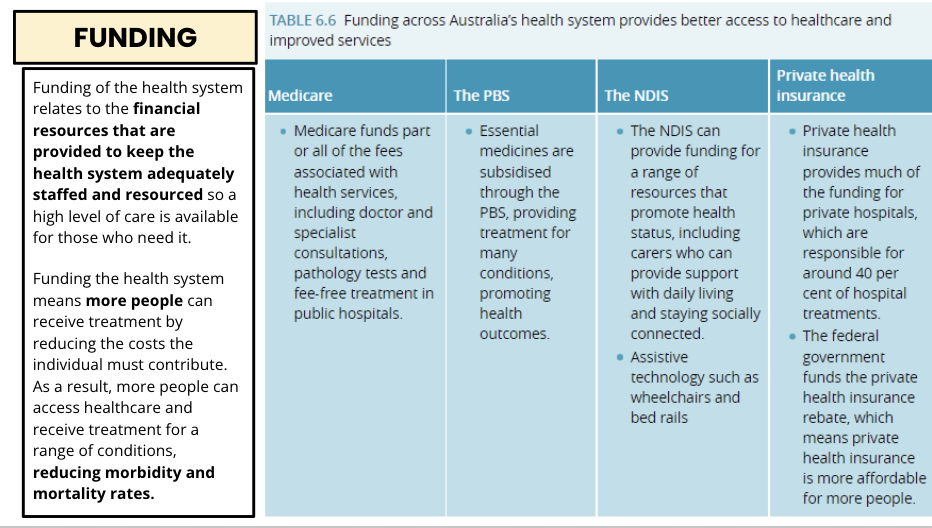

Sustainability
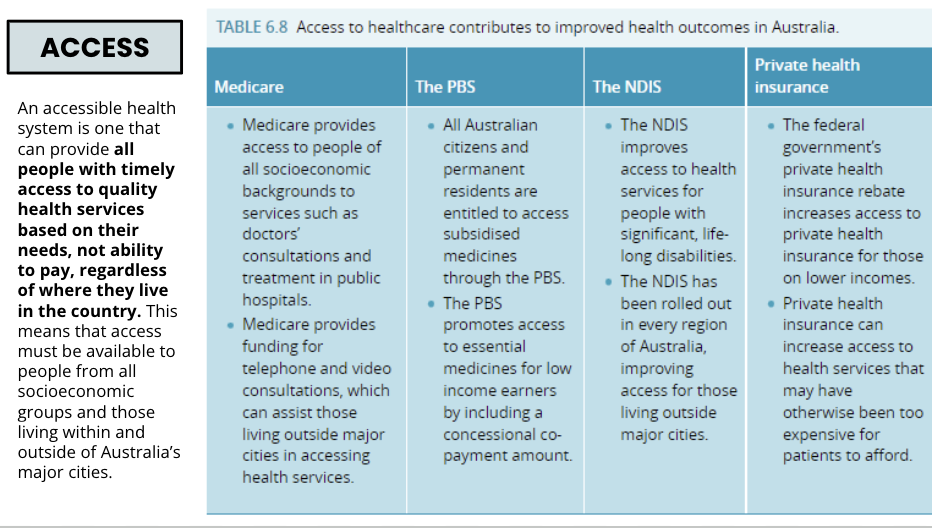
Access

Equity
Australian Dietary Guidelines
Guideline 1 - To achieve and maintain a healthy weight, be physically active and choose amounts of nutritious food and drinks to meet your energy needs.
Guideline 2 - Enjoy a wide variety of nutritious foods from the following five groups every day and drink plenty of water.
Guideline 3 - Limit intake of foods containing saturated fat, added salt, added sugars and alcohol.
Guideline 4 - Encourage, support and promote breastfeeding.
Guideline 5 - Care for your food; prepare and store it safely.
Social Model of Health
focuses on addressing the societal factors that influence health outcomes, rather than solely focusing on individual behaviors or biological factors.
Advantage of Social Model
Promotes good health and assists in the prevention of disease
Relatively inexpensive
Focuses on vulnerable population groups to improve equity in health
Disadvantage of Social Model
Not every condition can be prevented
It doesn't address the health concerns of individuals
Social Justice- Human Right
human rights — Human rights relate to the freedoms and conditions that every person is entitled to, regardless of factors such as race, religion, gender identity, sexual orientation, age and sex. Governments must work to ensure that all people have their human rights protected, respected and promoted.
Social Justice- Access
access — All people must have adequate access to the resources and opportunities they need to thrive, including food, safe water, shelter, education, employment, income and health care, and to participate in the decisions that affect their lives, such as if and when they get married or have children, or the sorts of jobs they do.
Social Justice- Particapation
participation — Everyone in society has the opportunity to participate in their community and have their voice represented.
Social Justice- Equity
equity — Disadvantaged individuals and groups need to have their specific challenges addressed, so they can achieve the same level of health and wellbeing as others in the population. In this sense, equity relates to providing more support for those who need it.