AP Psychology Unit 3 and 4 Test Review
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:01 AM on 10/31/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
1
New cards
Sensation
Your window to the world.
2
New cards
Perception
Interpreting what comes in your window.
3
New cards
Top-Down Processing
We perceive by filling in the gaps in what we sense. Based on our experiences and schemas.
I _ant ch_co_ate ic_ cr_am.
I _ant ch_co_ate ic_ cr_am.

4
New cards
Bottom-Up Processing
Uses features in the object itself to build a perception. (Takes longer than Top-Down Processing but is more accurate).
5
New cards
Selective Attention
Focusing conscious awareness on a particular stimulus. (Cocktail Party Effect)
6
New cards
Inattentional Blindness
Failing to see visible objects when our attention is directed elsewhere.

7
New cards
Change Blindness
When a stimulus undergoes a change without this being noticed by its observer.
8
New cards
Transduction
Transforming signals into neural impulses.
Information goes from the senses to the thalamus, then to the various areas of the brain.
Information goes from the senses to the thalamus, then to the various areas of the brain.
9
New cards
Psychophysis
Subfield of psychology devoted to the study of physical stimuli and their interaction with sensory systems.
10
New cards
Absolute Threshold
The smallest amount of stimuli we can detect about half of the time.

11
New cards
Signal Detection Theory
Absolute threshholds are not really absoulte. Things like motivation or physical stat can affect what we sense.
I can sleep through a war, but if I heard my baby I was up.
I can sleep through a war, but if I heard my baby I was up.
12
New cards
Subliminal Perception
Stimuli below our absolute threshold (Backmasking).
**SUBLIMINAL MESSAGES DO NOT WORK (If it seems it worked then it was probably a placebo effect)
**SUBLIMINAL MESSAGES DO NOT WORK (If it seems it worked then it was probably a placebo effect)
13
New cards
Priming
A phenomenon in which exposure to one stimulus influences how a person responds to a subsequent, related stimulus.
Ex: If a child sees a bag of candy next to a bench, they might begin looking for and/or thinking about candy the next time they see a bench.
Ex: If a child sees a bag of candy next to a bench, they might begin looking for and/or thinking about candy the next time they see a bench.
14
New cards
Difference Threshold
The smallest amount of change in a stimulus before we detect a change.

15
New cards
Weber's Law
The principle that, to be percieved as different, two stimuli must differ by a constant percentage (rather than a constant amount).
Ex: A person is much more likely to react to a quiet commercial that suddenly doubles in volume than a commercial that only slightly increases in volume.
Ex: A person is much more likely to react to a quiet commercial that suddenly doubles in volume than a commercial that only slightly increases in volume.
16
New cards
Sensory Adaptation
Decreased responsiveness to stimuli due to constant stimulation.
(Do you feel your underwear all day?)
(Do you feel your underwear all day?)
17
New cards
Perceptual Set
A mental predisposition to percieve or notice some aspects of the available sensory data and ignore others. (Influences nearly everything we perceive. Related to Top-Down Processing).

18
New cards
Extrasensory Perception (ESP)
Known as the sixth sense. A paranormal ability pertaining to reception of information not gained through the recognized physical senses, but sensed witht the mind.
(Telepathy, Clairvoyance, Precognition & Retrocognition).
(Telepathy, Clairvoyance, Precognition & Retrocognition).

19
New cards
Parasychology
The study of mental phenomena which are excluded from or inexplicable by orthodox scientific psychology. (Study of Extrasensory Perception).
20
New cards
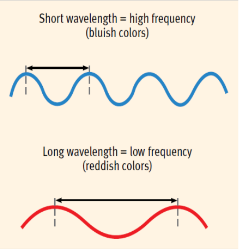
Wavelength
The distance from the peak of one light or sound wave to the next peak.
*Wavelengths in light waves determine the hue (color).
*Wavelengths in sound waves determine the pitch (sound).
*Wavelengths in light waves determine the hue (color).
*Wavelengths in sound waves determine the pitch (sound).
21
New cards
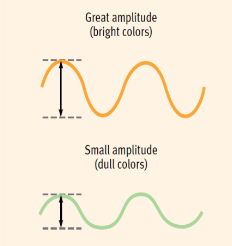
Amplitude
The wave's height, measures the intensity of the wave. Measured from the peak of the wave to the trough of the wave (top to bottom).
*Amplitude in light determines the brightness of the color.
*Amplitude in sound determines the volume.
*Amplitude in light determines the brightness of the color.
*Amplitude in sound determines the volume.
22
New cards
Hue
Subjective quality of color, which is determined primarly by wavelength and secondarily by amplitude.
23
New cards
Intensity
The quantitative value of a stimulus or sensation.
The strength of any behavior, such as an impulse or emotion.
The strength of any behavior, such as an impulse or emotion.
24
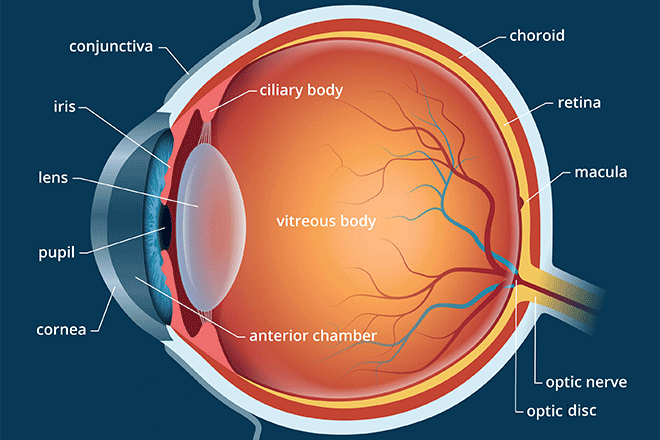
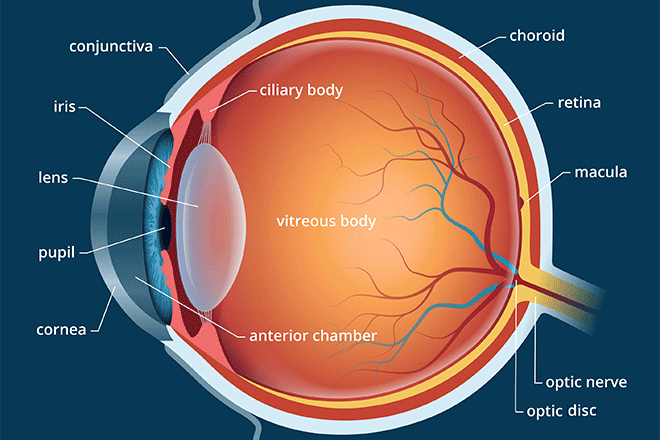
New cards
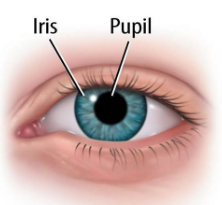
Pupil
The adjustable opening in the center of the eye though which light enters.
25
New cards
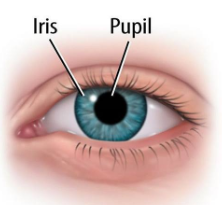
Iris
The ring of muscle tissue that forms the colored portion of the eye and controls the size of the pupil opening.
26
New cards
Lens
The transparent structure behind the pupil that changes the shape to help focus images on the retina.
27
New cards
Retina
the light-sensitive inner surface of the eye that contains the receptor rods and cones plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of transduction for vision
28
New cards
Accommodation
Process of the lens changing shape.
29
New cards
Rods
Retinal receptors that detect black, white, and shades of gray that are necessary for peripheral and twilight vision when cones don't respond.
30
New cards
Cones
Retinal receptors that are concentrated near the center of the retina that detect colors and details and that function in the daylight or in well-lit conditions.
31
New cards
Optic Nerve
The nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain.
32
New cards
Blind Spot
The point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye, creating a "blind" spot because there are no receptor cells located there.
33
New cards
Fovea
The central focal point in the retina, around which the eye's cones cluster.
34
New cards
Feature Detectors
Nerve cells in the brain that respond to specific features of the stimulus. (shape, angle, or movement).
35
New cards
Parallel Processing
The brain's natural mode of information processing many things at once, such as color, motion, form, and depth.
36
New cards
Trichromatic Theory
The theory that the retina contains three different color receptors (red, green, and blue) that when stimulated in combination can produce the perception of any color.
37
New cards
Opponent-Processing Theory (Gesalt)
The theory that opposing retinal processes enables color vision (red-green. yellow-blue, white-black).
38
New cards
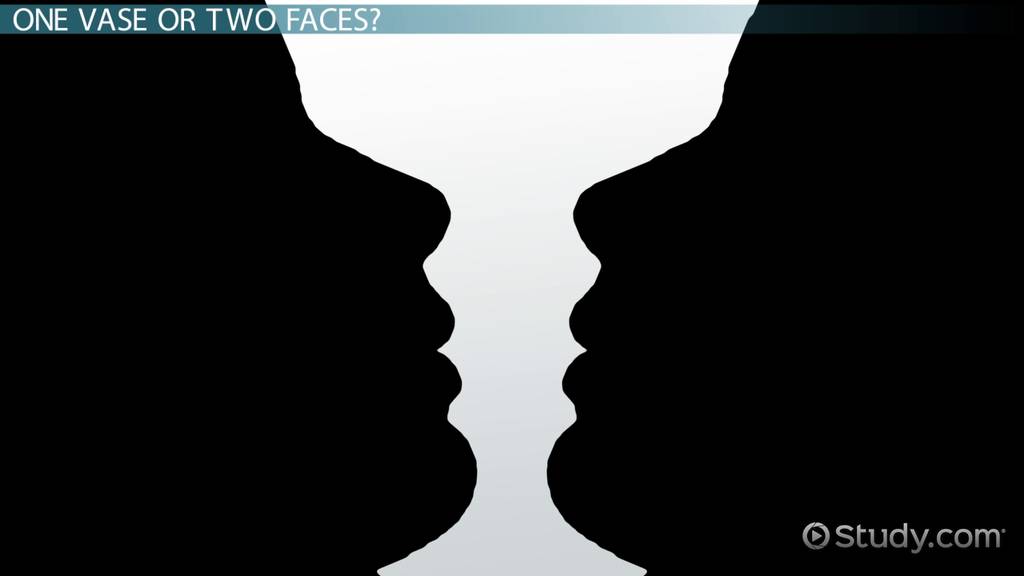
Figure-Ground
The organization of the visual field into objects that stand out from their surroundings.

39
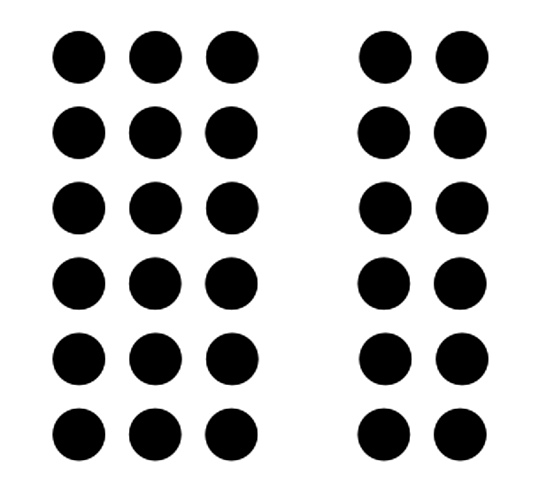
New cards
Grouping
Elements that are groups together within the same region of space tend to be grouped together.
40
New cards
Depth Perception
The ability to see objects in three dimensions although the images that stirke the retina are two-dimensional.
Allows us to judge distance.
Allows us to judge distance.
41
New cards
Visual Cliff
Experiment that tested depth perception on infants.
42
New cards
Binocular Cues
We use both of our eyes to judge distance.
43
New cards
Retinal Disparity
Each eye sees a slightly different image because they are abour 6cm apart. Your brain then puts the two imagaes together into a three-dimensional image.
44
New cards
Monocular Cues
Depth perception that requires only one eye.
45
New cards
Phi Phenomenon
(Stroboscopic Movement)
(Stroboscopic Movement)
An illusion of moevement created when two or more adjacent lights blink on and off in quick succession.
46
New cards
Perceptual Constancy
Our ability to percieve objects as unchanging even as changes may occur in distance, point of view, and illumination. Our brain makes adjustments and interpretation without our awareness to perceive the objects as the same, or else nothing would make sense.
47
New cards
Color Constancy
Perception that the color of an object remains the same even if lighting conditions change.
48
New cards
Perceptual Adaptation
The ability of the body to adapt to an environment by filtering out distractions.
49
New cards
Audition
The sense of hearing
50
New cards
Frequency
The number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time. (Determines the pitch).
51
New cards
Pitch
A tone's highness or lowness.
52
New cards
Outer Ear
The part of the ear that traps sound waves and channels them through the auditory canal to the eardrum.
53
New cards
Middle Ear
The part of the ear that transmits the eardrum's vibrations through a piston made of three tiny bones to the cochlea.
54
New cards
Inner Ear
The innermost part of the ear that contains the cochlea, semicircular canals, and vestibular sacs. (Where transduction happens for sound).
55
New cards
Cochlea
Hollow, spiral-shaped bone found in the inner ear that plays a key role in the process of auditory transduction.
56
New cards
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Hearing loss caused by damage of the cochlea's receptor cells or to the auditory nerves.
57
New cards
Conduction Hearing Loss
Hearing loss caused by damage to the mechanical system. (Hearing aids).
58
New cards
Cochlear Implant
A device for converting sounds into electrical signals and stimulating the auditory nerve through electrodes threaded into the cochlea.
59
New cards
Place Theory
Links pitch we hear with the place where the cochlea's membrane is stimulated.
60
New cards
Gate-Control Theory
The theory that the spinal cord contains a nerological gate that blocks pain signals or allows them to pass on to the brain.
61
New cards
Kinesthesis
The system for sensing the position and movement of individual body parts.
62
New cards
Vestibular Sense
The sense of body movements and position, including the sense of balance.
63
New cards
Sensory Interaction
The principle that one sense may influence another, as when the smell of food influences its taste.
64
New cards
Learning
The process of acquiring new and relatively enduring information or behaviors.
65
New cards
Habituation
Decreasing responsiveness with repeated stimulation.
66
New cards
Associative Learning
Learning that certain events occur together. The events may be two stimuli or a response and its consequences.
67
New cards
Stimulus
Event or situation that provokes a response.
68
New cards
Cognitive Learning
The acquisition of mental information, whether by observing events, by watching others, or through language.
69
New cards
Classical Conditioning
Conditioning that pairs a neutral stimulus with a stimulus that evokes a reflex; the stimulus that evokes the reflex is given whether or not the conditioned response occurs until eventually, the neutral stimulus comes to evoke the reflex.
70
New cards
Behaviorism
The view that psychology should be an objective science that studies behavior without reference to mental processes.
71
New cards
Neutral Stimulus (NS)
In classical conditioning, a stimulus that elicits no response before conditioning.
72
New cards
Unconditioned Response (UR)
In classical conditioning, an unlearned, naturally occurring response to an US.
73
New cards
Unconditioned Stimulus (US)
In classical conditioning, a stimulus that unconditionally triggers a response (UR).
74
New cards
Conditioned Response (CR)
In classical conditioning, a learned response to a previously neutral (now conditioned) stimulus (CS).
75
New cards
Conditioned Stimulus (CS)
In classical conditioning, an originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus (US), comes to trigger a conditioned response.
76
New cards
Acquisition
In classical conditioning, the initial stage, when one links a NS and an US so that the NS begins triggereing the CR.
In operant conditioning, the strengthening of a reinforced response.
In operant conditioning, the strengthening of a reinforced response.
77
New cards
High-Order Conditioning
A procedure in which the CS in one conditioning experience is paired with a new NS, creating a second CS.
Ex: A baby has learned that a light predicts that his mom is going to come, he then may learn that a tone predicts the light and start responding to the tone alone.
Ex: A baby has learned that a light predicts that his mom is going to come, he then may learn that a tone predicts the light and start responding to the tone alone.
78
New cards
Extinction
The diminishing of a conditioned response.
Occurs in classical conditioning when an US does not follow a CS.
Occurs in Operant conditioning when a response is no longer reinforced.
Occurs in classical conditioning when an US does not follow a CS.
Occurs in Operant conditioning when a response is no longer reinforced.
79
New cards
Spontaneous Recovery
The reappearance of an extinguished CR.
80
New cards
Generalization
The tendency, once a response has been conditioned, for stimuli similar to conditioned stimulus to elicit similar responses.
81
New cards
Discrimination
The learned ability to distinguish between a CS that does not signal an US.
82
New cards
Operant Conditioning
A type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcement or diminished if followed by a punisher.
83
New cards
Law of Effect
Thorndike's principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and that behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely.
84
New cards
Operant Chamber
(Skinner Box)
(Skinner Box)
A chamber containing a bar or key that an animal can manipulate to obtain a reinforcer; attached devices record the animal's rate of bat pressing or key pecking.
85
New cards
Reinforcement
In operant conditioning, any event that strengthens the behavior it follows.
86
New cards
Shaping
An operant conditioning procedure in which reinforcers guide behavior toward closer and closer approximations of the desired behavior.
87
New cards
Discriminative Stimulus
In operant conditioning, a stimulus that elicits a response after association with reinforcement.
88
New cards
Positive Reinforcement
Increasing behaviors by presenting positive reinforcers (a stimulus that when presented after a response strengthens the response).
89
New cards
Negative Reinforcement
Increasing behaviors by stopping or reducing negative stimuli (a stimulus that, when removed after a response, strengthens the response).
**NOT A PUNISHMENT
**NOT A PUNISHMENT
90
New cards
Primary Reinforcer
Innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need.
91
New cards
Conditioned Reinforcer
(Secondary Reinforcer)
(Secondary Reinforcer)
A stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its associetion with a primary reinforcer.
92
New cards
Reinforcement Schedule
Pattern that defines how often a desired response will be reinforced.
93
New cards
Continuous Reinforcement
Reinforcing the desired response every time it occurs.
94
New cards
Partial Reinforcement
(Intermittent Reinforcement)
(Intermittent Reinforcement)
Reinforcing a response only part of the time; results in slower acquisition of a rsponse but much greater resistance to extinction.
95
New cards
Fixed-Ratio Schedule
A reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response only after a specified number of responses.
96
New cards
Variable-Ratio Schedule
A reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response after an unpredictable number of responses.
97
New cards
Fixed-Interval Schedule
A reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response only after a specified time has elapsed.
98
New cards
Variable-Interval Schedule
A reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response at unpredictable time intervals.
99
New cards
Punishment
An event that tends to decrease the behavior that is follows.
100
New cards
Biofeedback
A system for electronically recording, amplifying, and feeding back information regarding a sublte physiological state, such as blood pressure or muscle tension.