Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Autotrophic
An organism capable of synthesizing its own food from inorganic substances

Chloroplasts
Organelle that absorbs sunlight and uses it to drive the synthesis of glucose
Photosynthesis
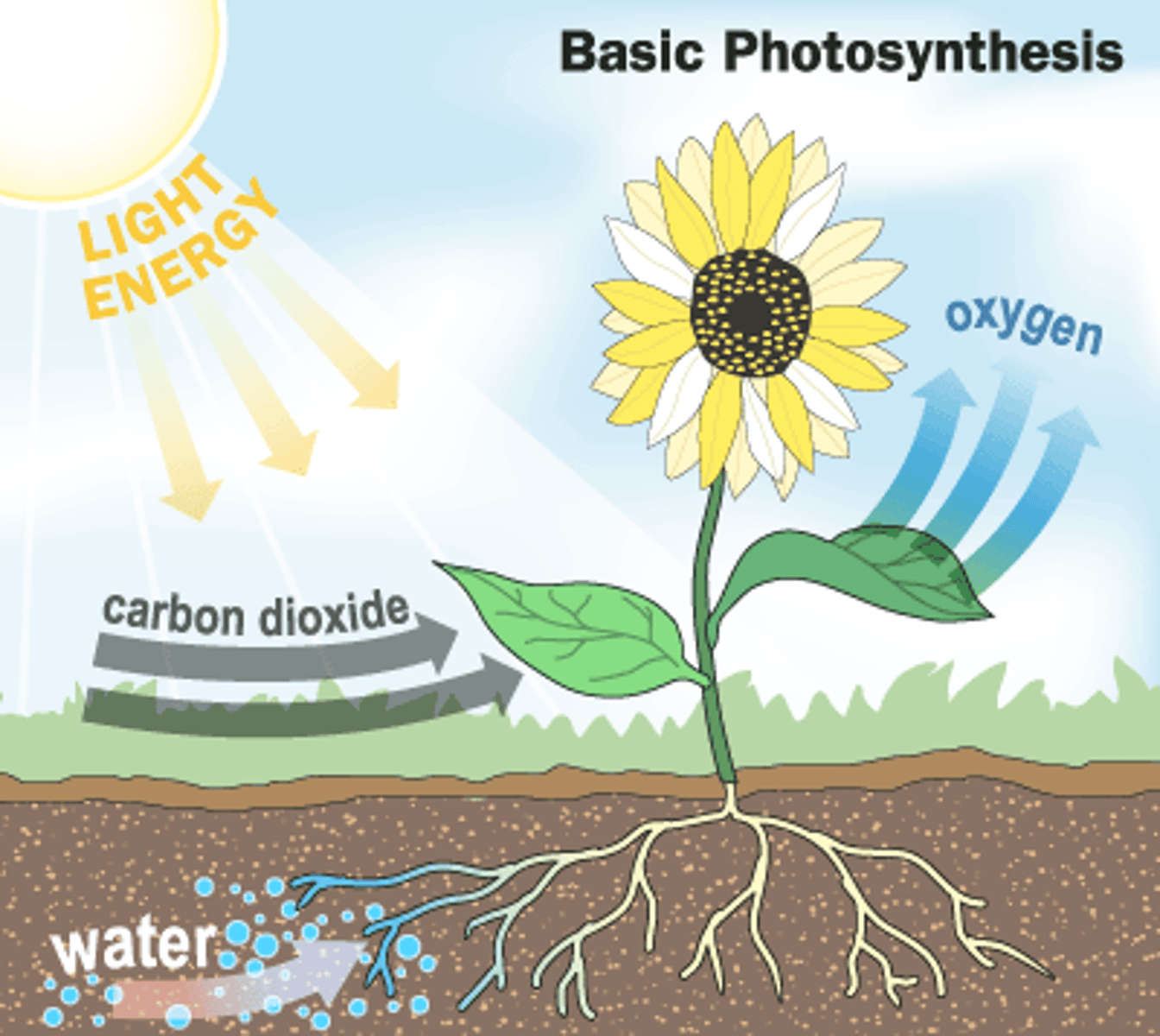
The process that converts light energy into chemical energy that is stored in glucose
Heterotrophs
An organism that obtains food by eating other organisms or substances derived from them.

Stroma
The fluid of the chloroplast- location of Light Independent/Calvin Cycle
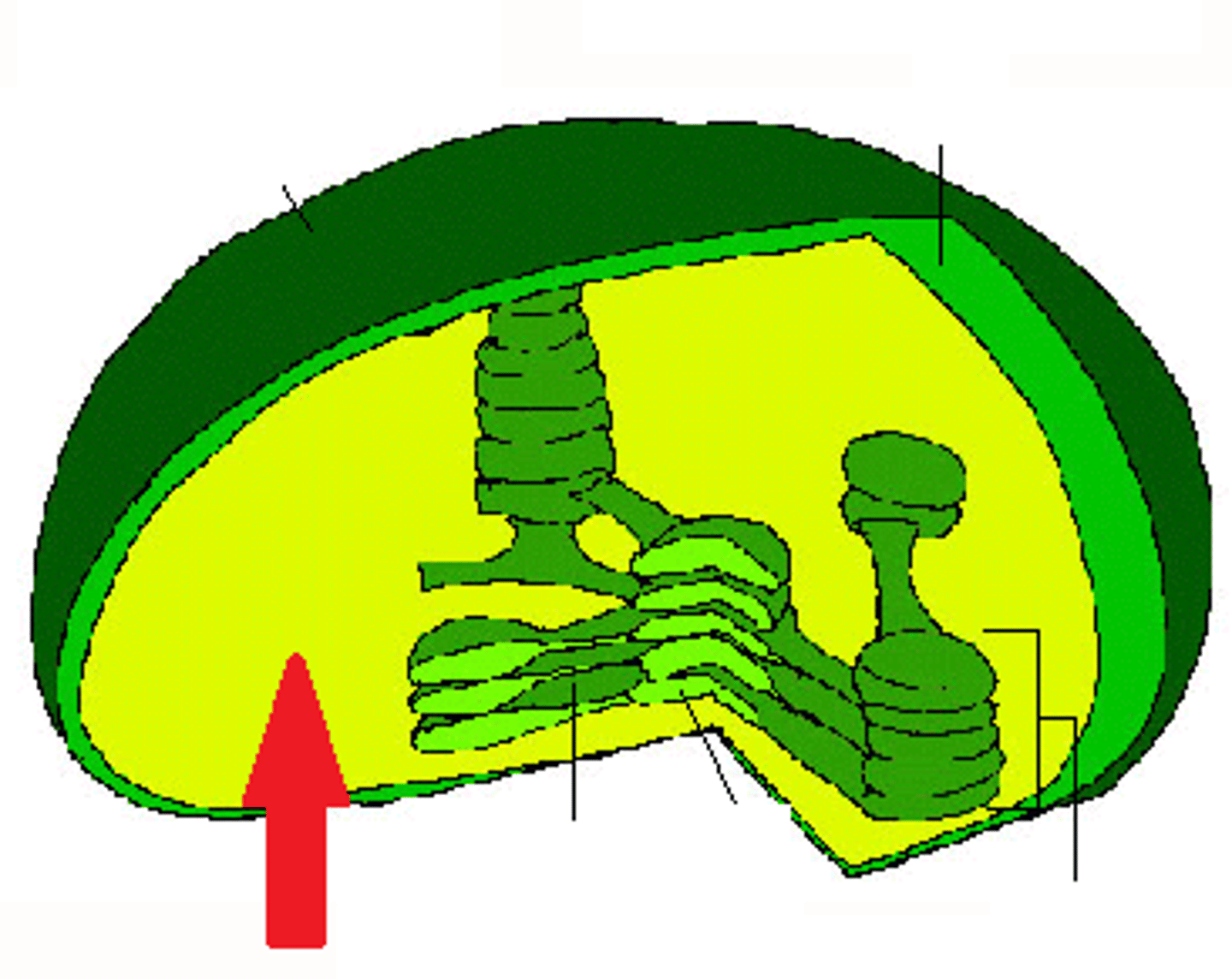
Thylakoids
Location of Light Dependent Reactions
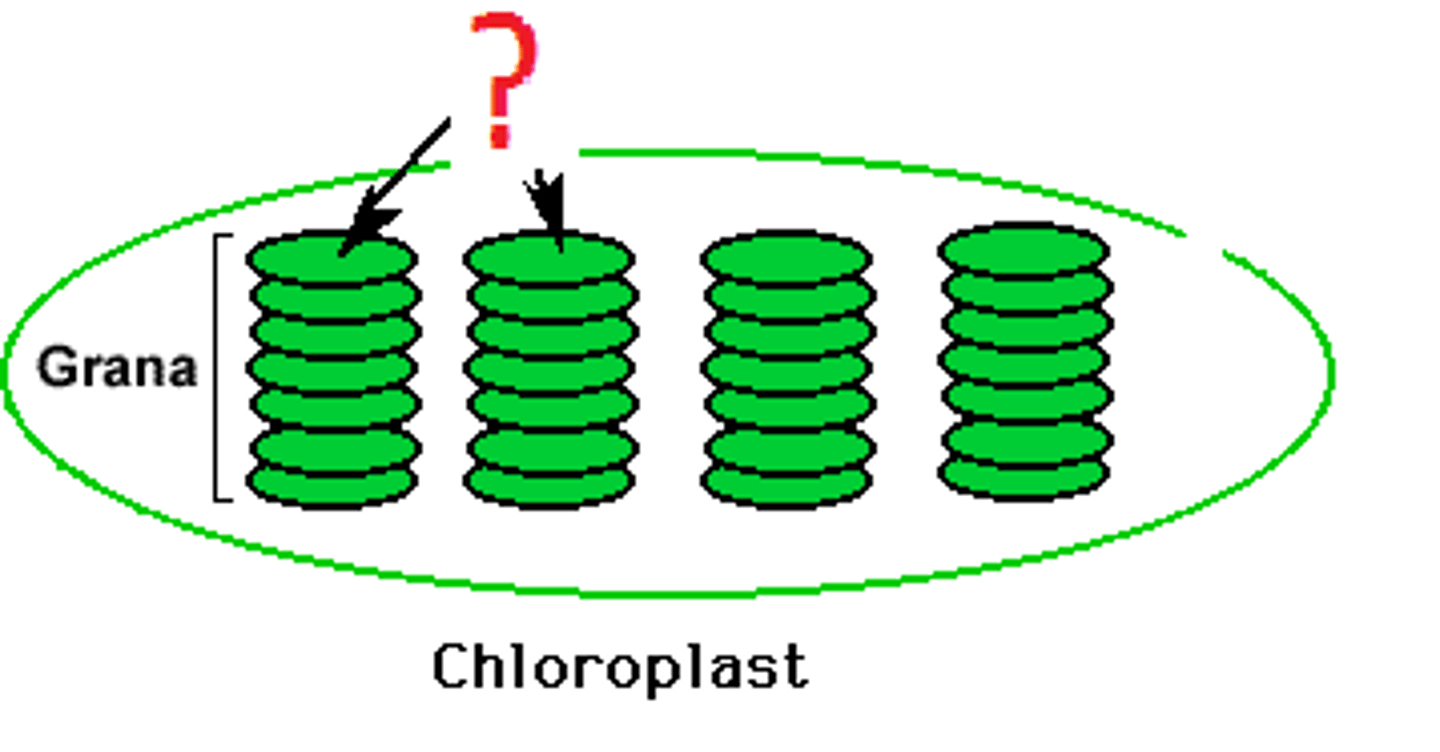
Chlorophyll
Green pigment located in chloroplasts.
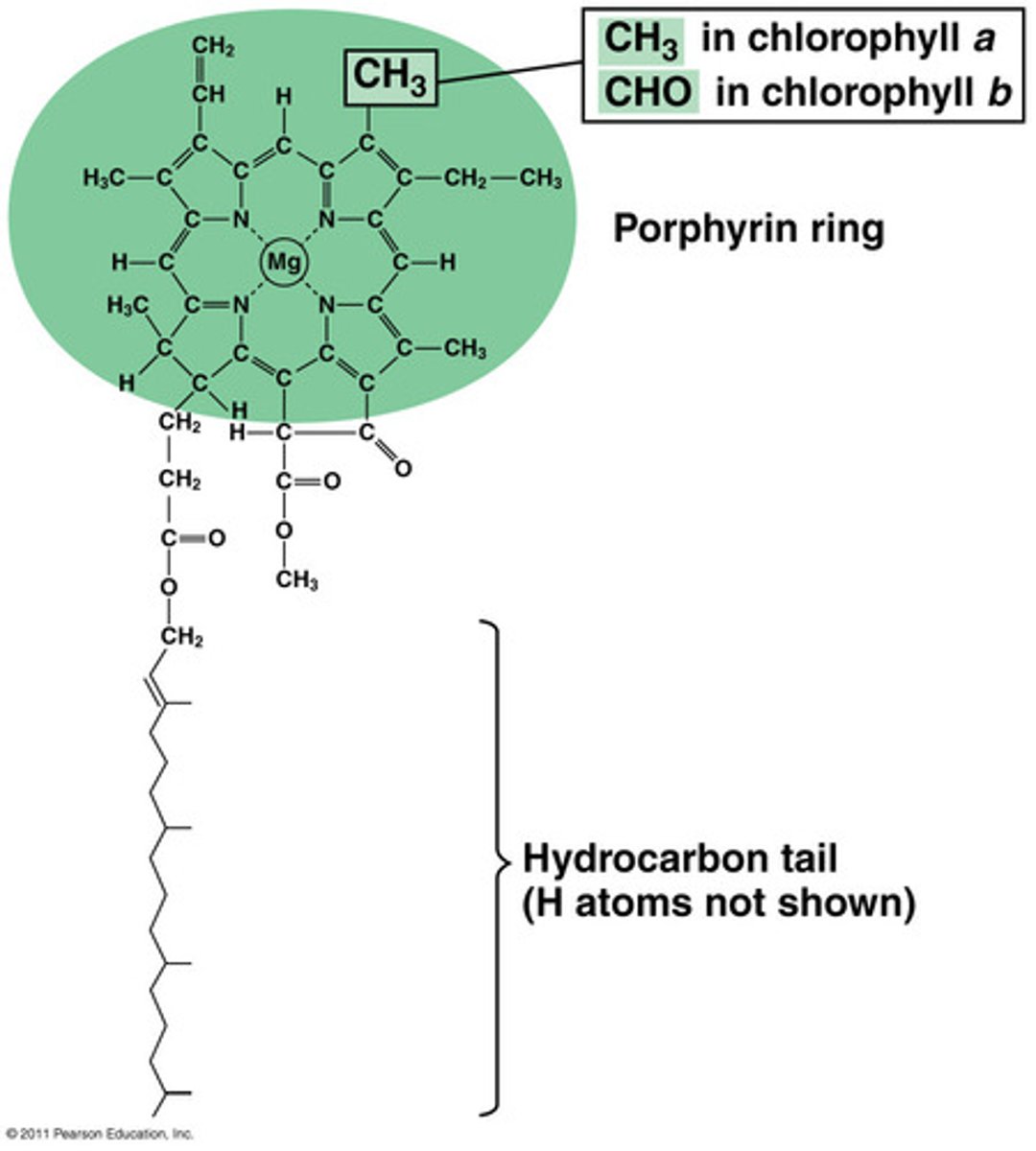
Light Dependent Reaction
occur on the thylakoids. convert solar energy to the chemical energy by splitting water while releasing oxygen
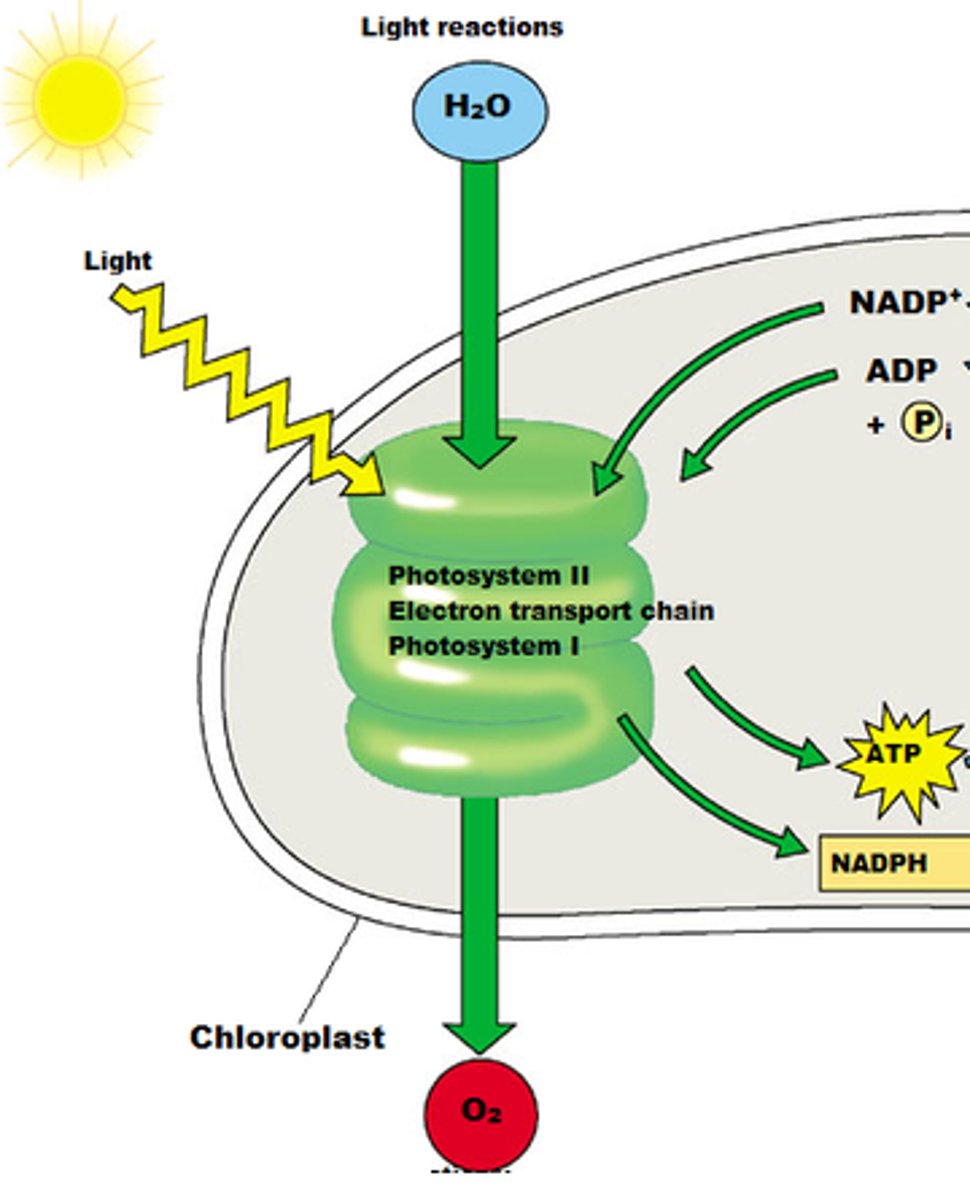
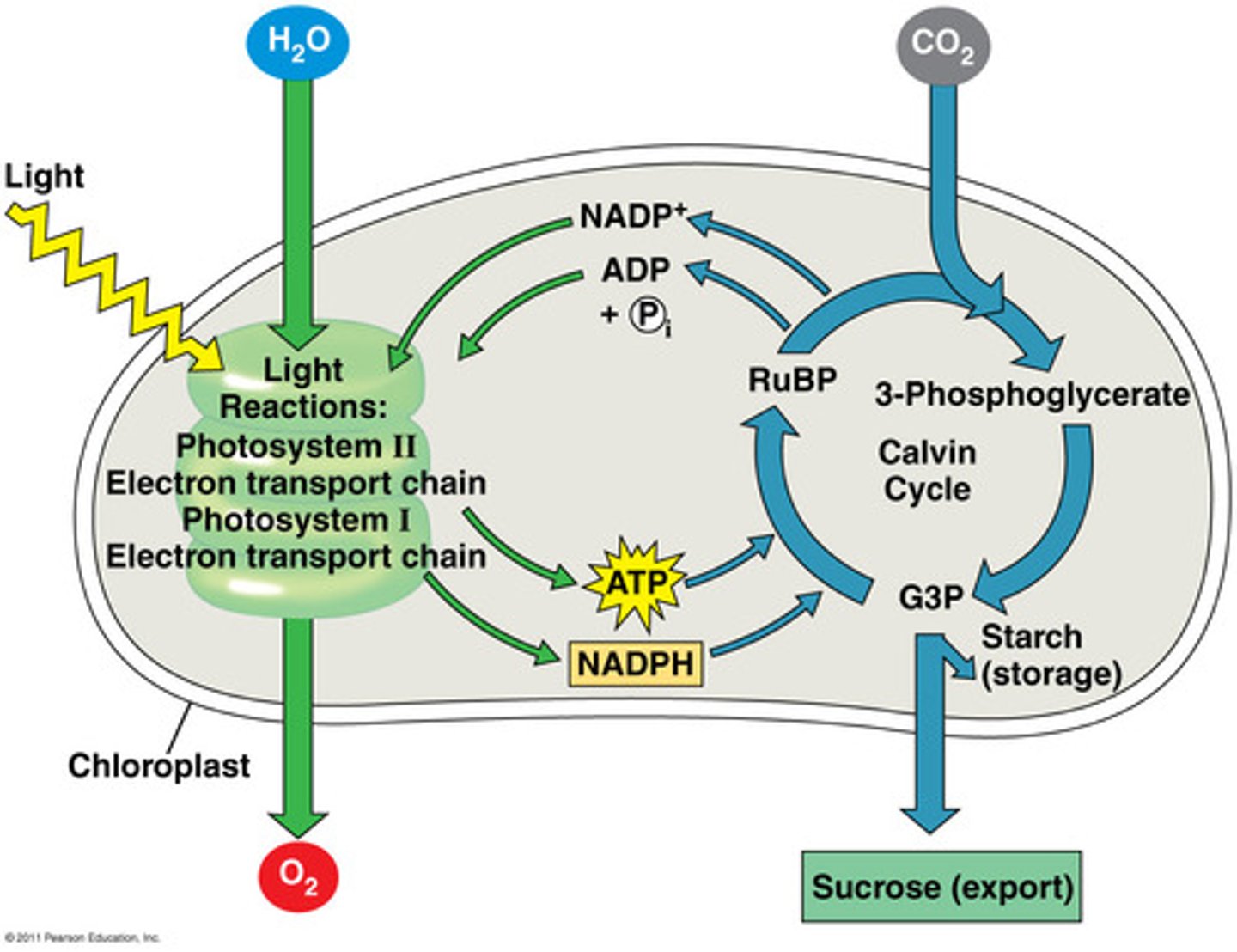
Light Independent/Calvin cycle
Second stage of photosynthesis breaking CO2 to produce glucose
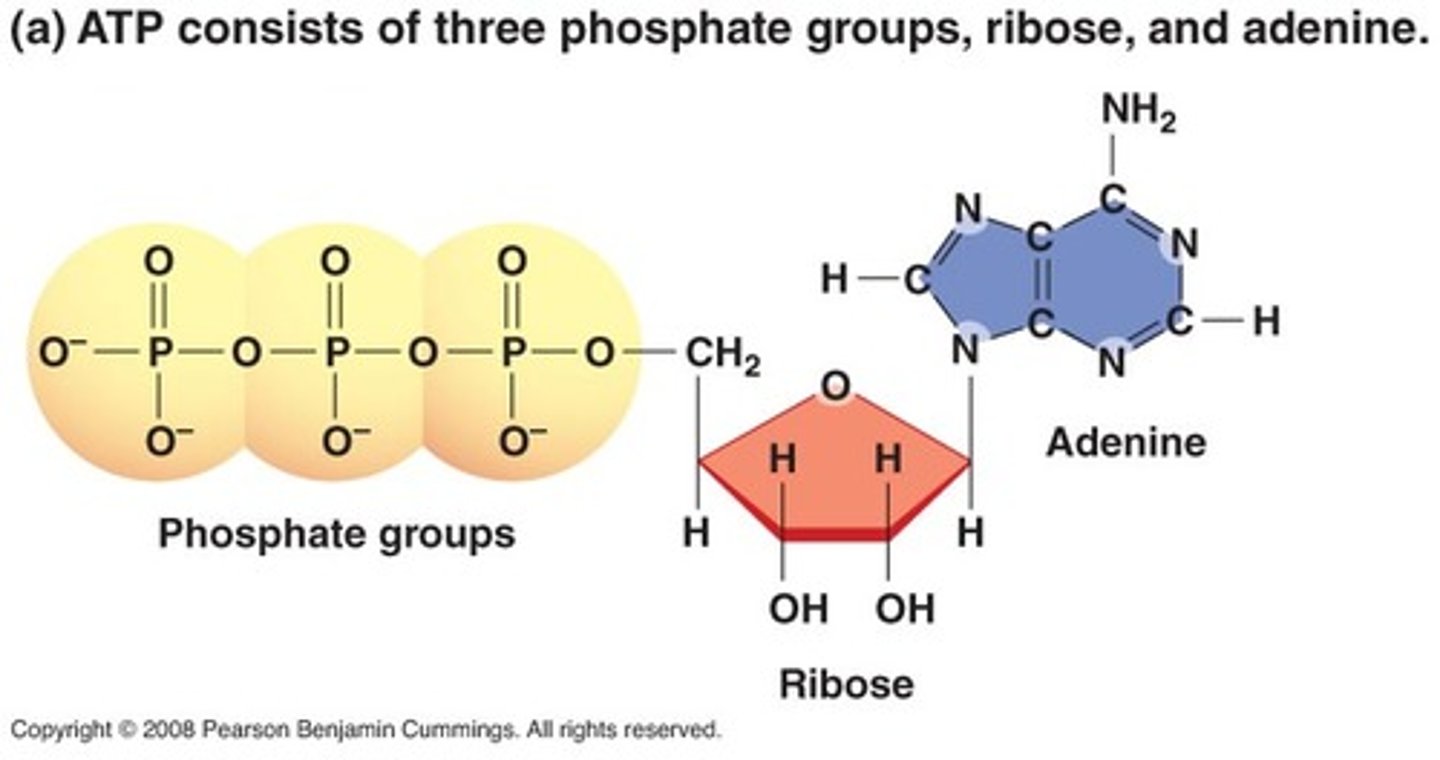
ATP
(Adenosine triphosphate molecule) main energy source that cells use for most of their work.
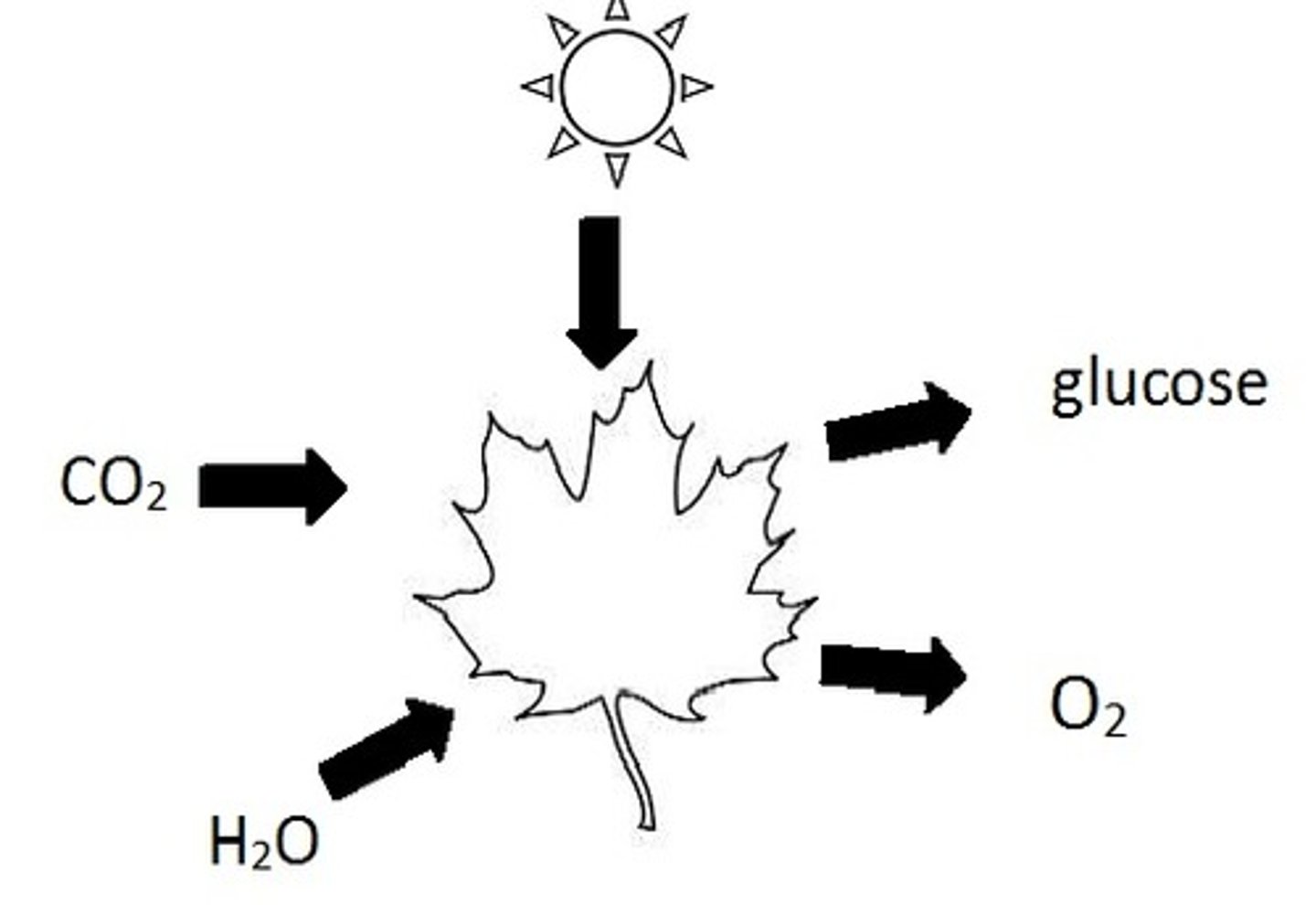
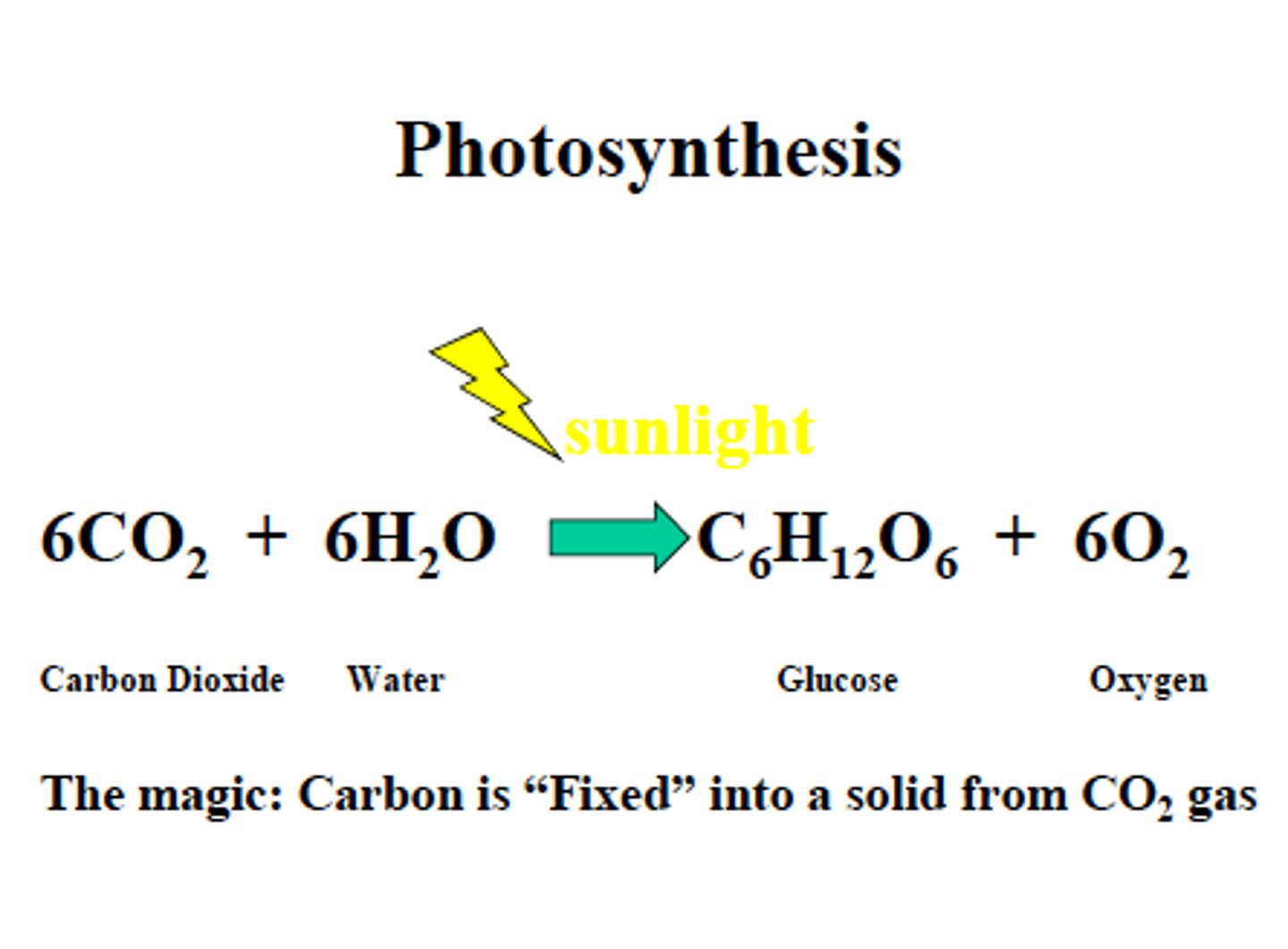
Photosynthesis Equation
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
reactants of photosynthesis
carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight
reactants of cell respiration
glucose and oxygen

products of photosynthesis
glucose and oxygen
products of cellular respiration
carbon dioxide, water, and ATP
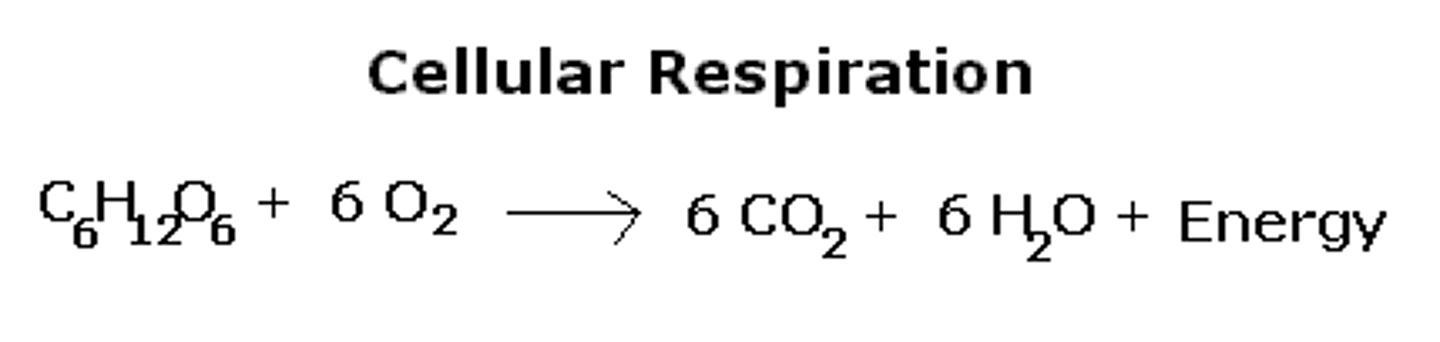
cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen
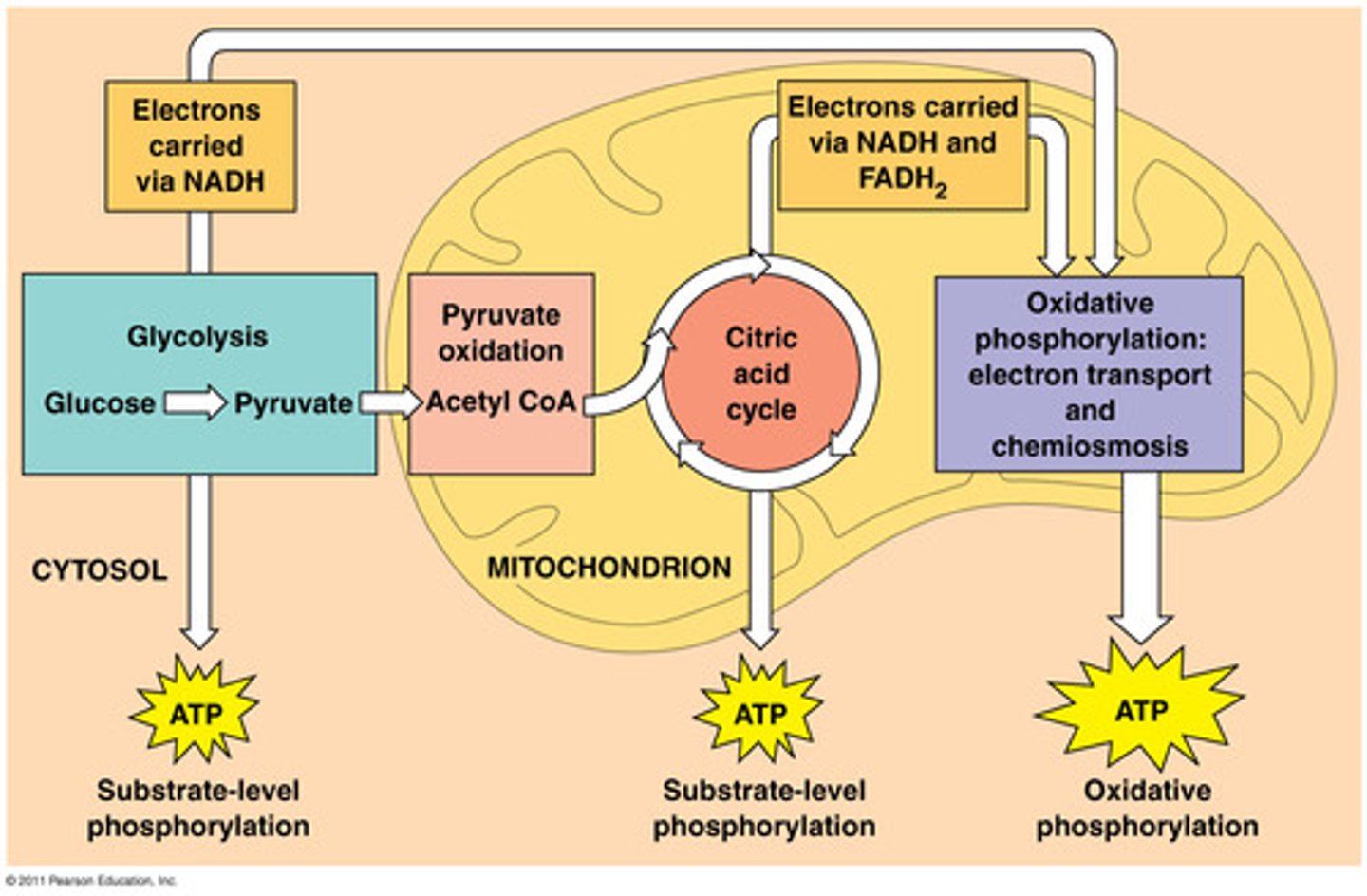
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production
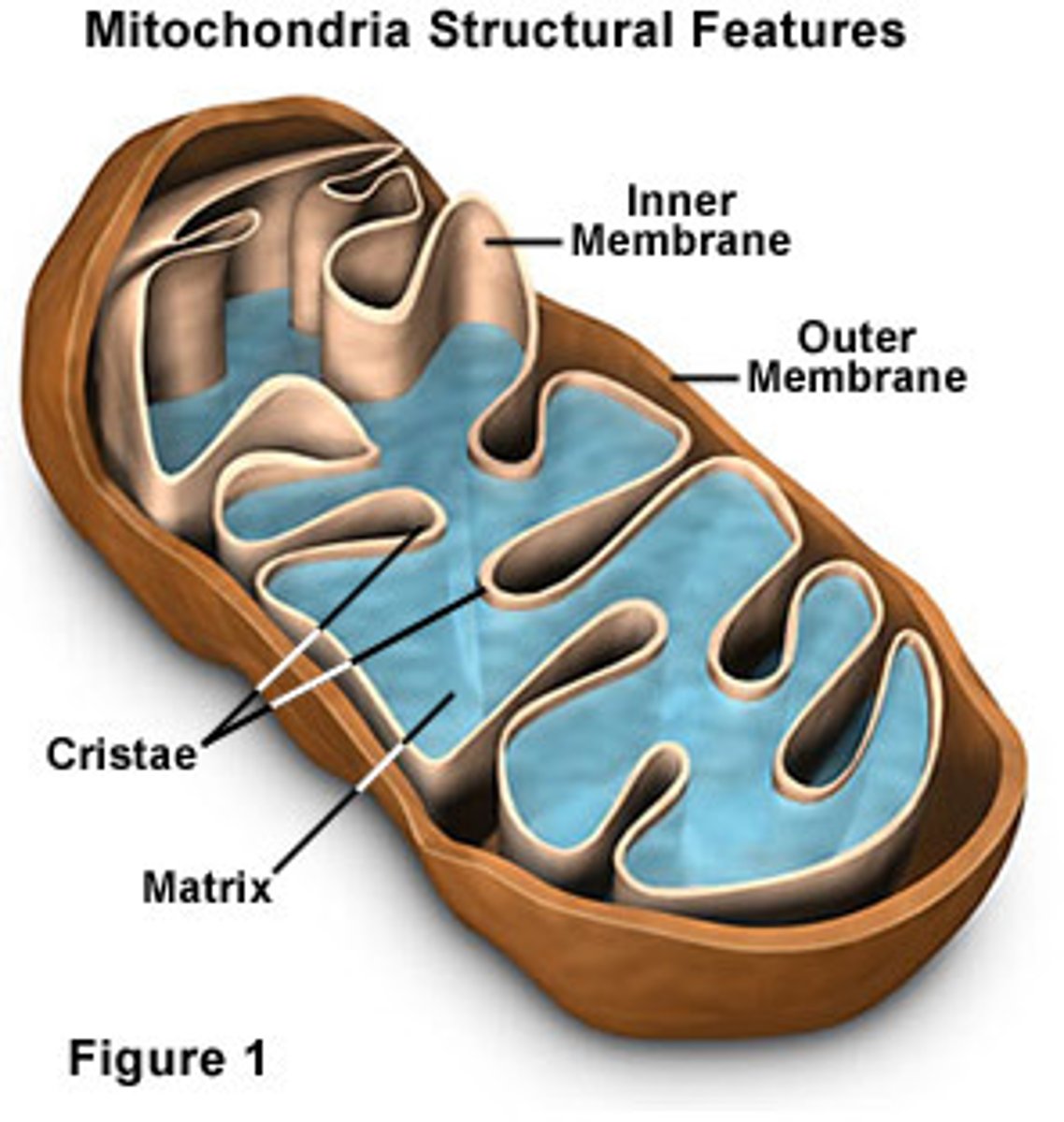
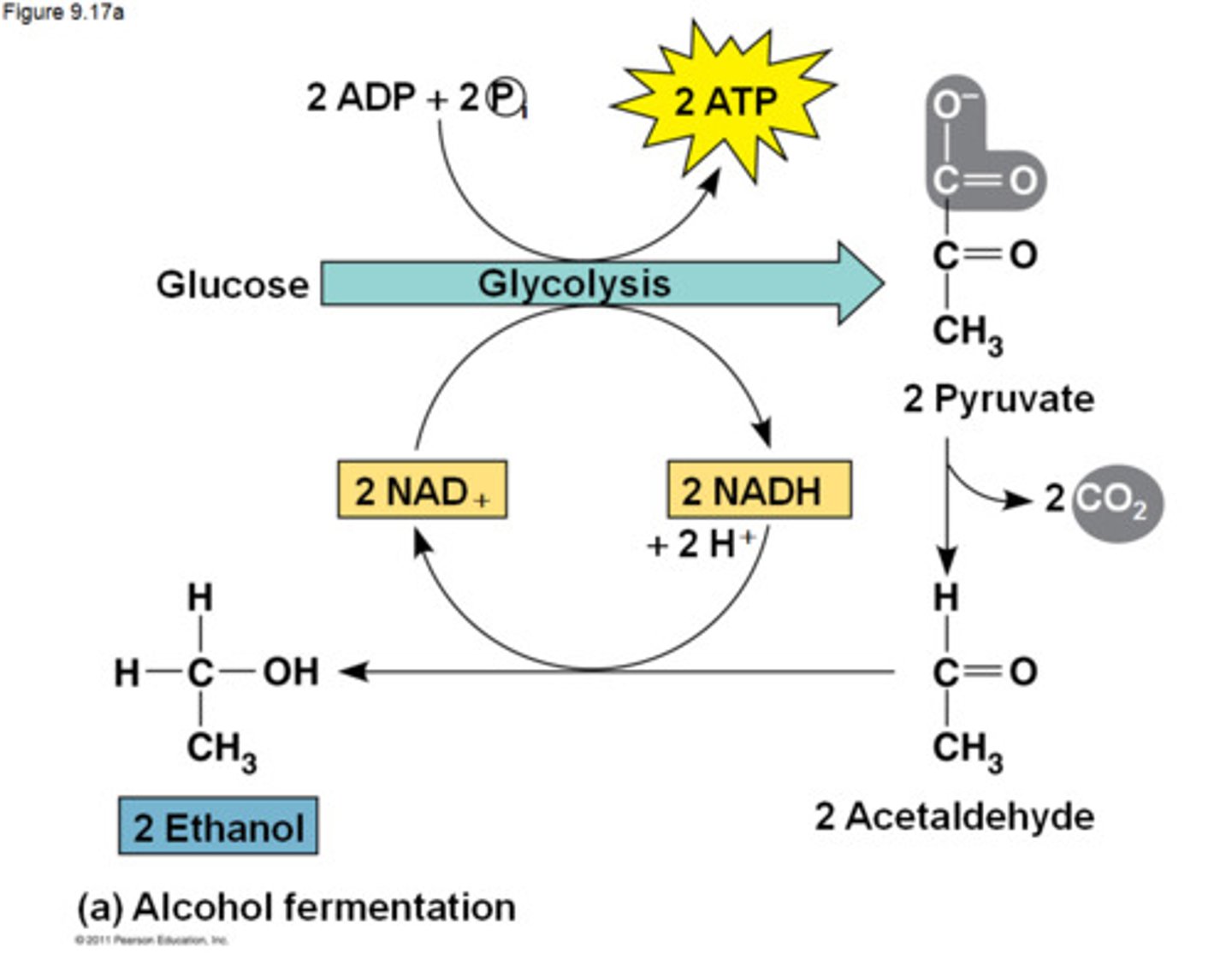
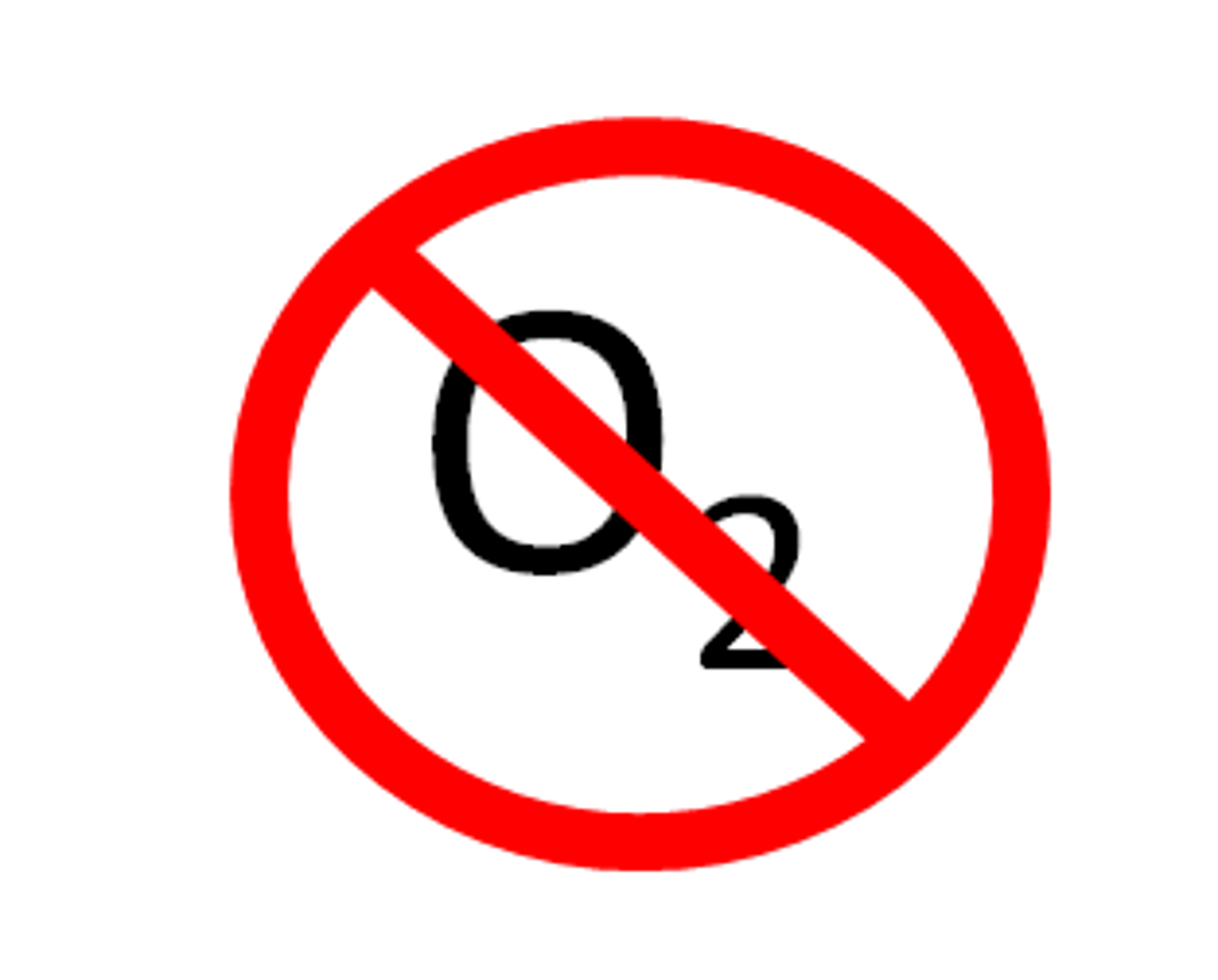
fermentation (anaerobic respiration)
Process by which cells release energy in the absence of oxygen

aerobic respiration
Respiration that requires oxygen
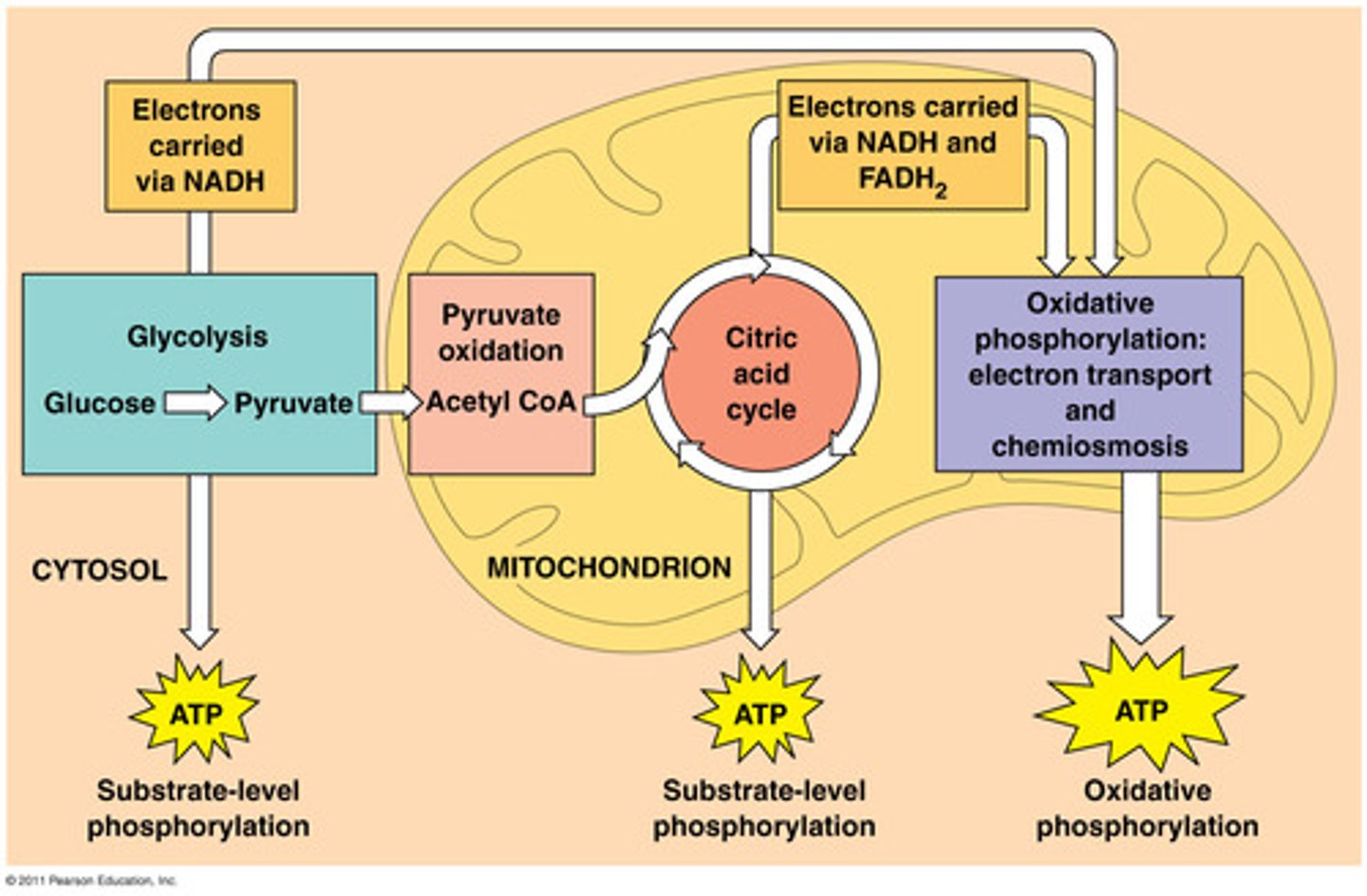
lactic acid fermentation
the chemical breakdown of carbohydrates that produces lactic acid as the main end product
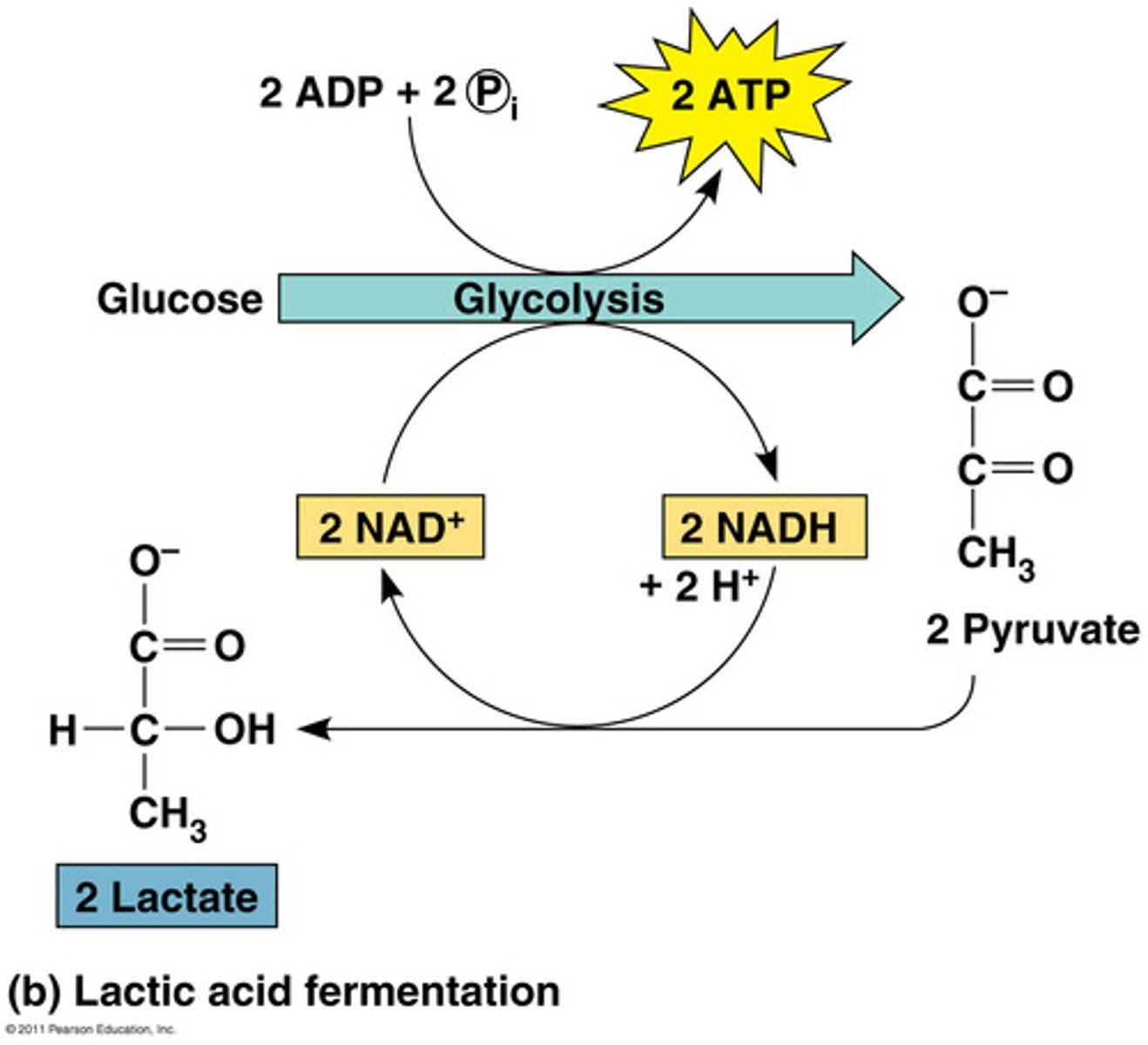
alcoholic fermentation
the anaerobic process by which yeasts and other microorganisms break down sugars to form carbon dioxide and ethanol