Anatomy and Physiology II - Lab 12
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This goes over Lab 12: Fetal Pig Dissection 1. The specific course is Anatomy and Physiology II (BIOL-2402)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
eyelid
pigs are born with closed eyelids
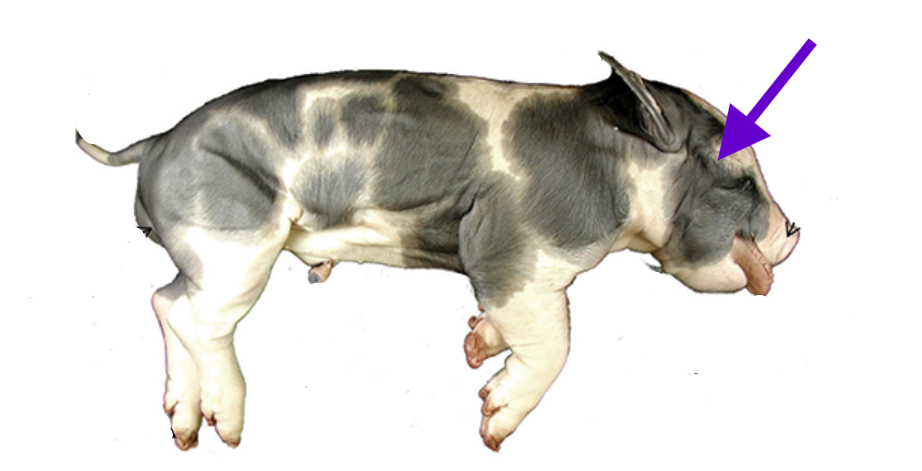

eyelid
pinna
external ear flap
gathers sound into the external auditory canal
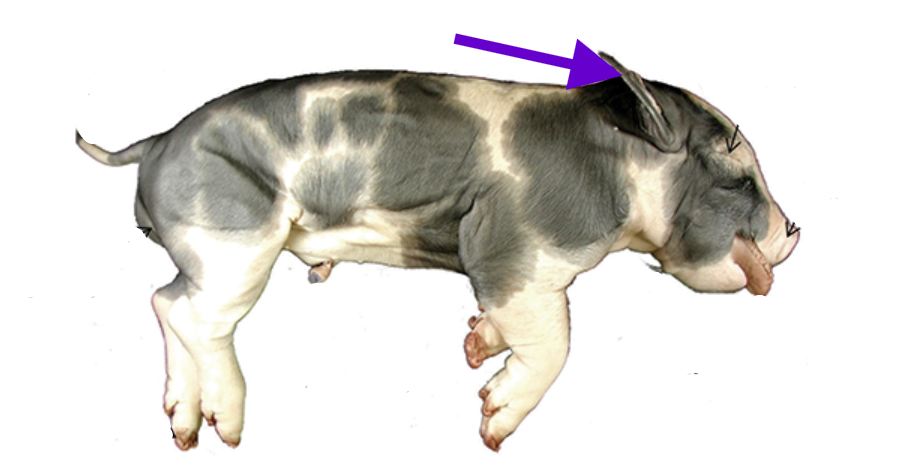
pinna
external nares
exterior openings of the nose
breathing
sense of smell

external nares
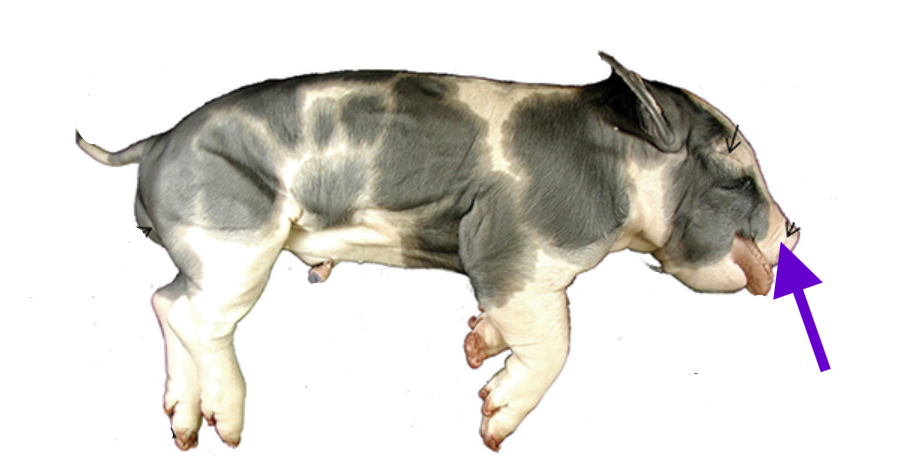
vibrissae
long, stiff hairs/whiskers
touch
vibrissae
digits
toes and hooves
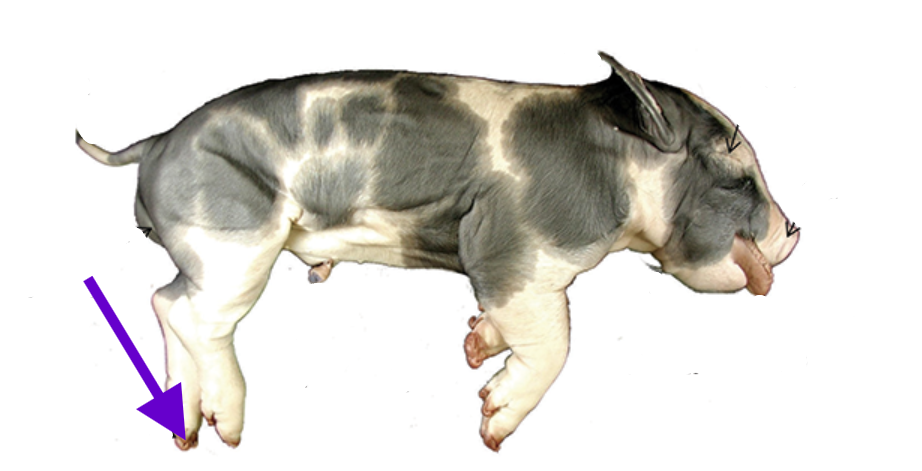

digits
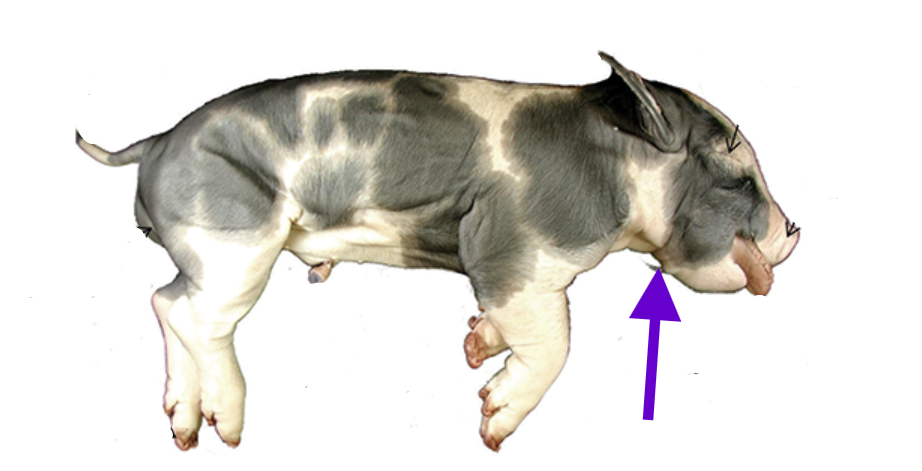
mammary papilla
5-6 pairs in both sexes
females: develop into mammary glands
mammary papilla
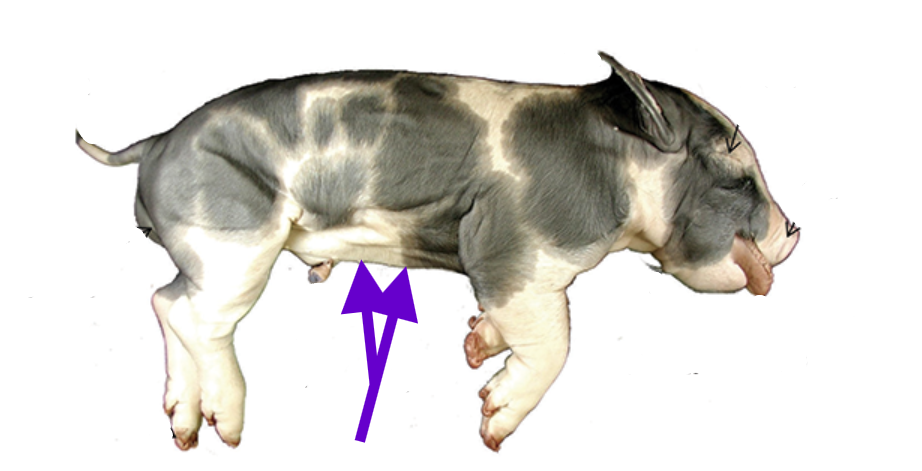
umbilical cord
2 umbilical arteries and 1 umbilical vein
vessels do nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between the fetus and maternal placenta
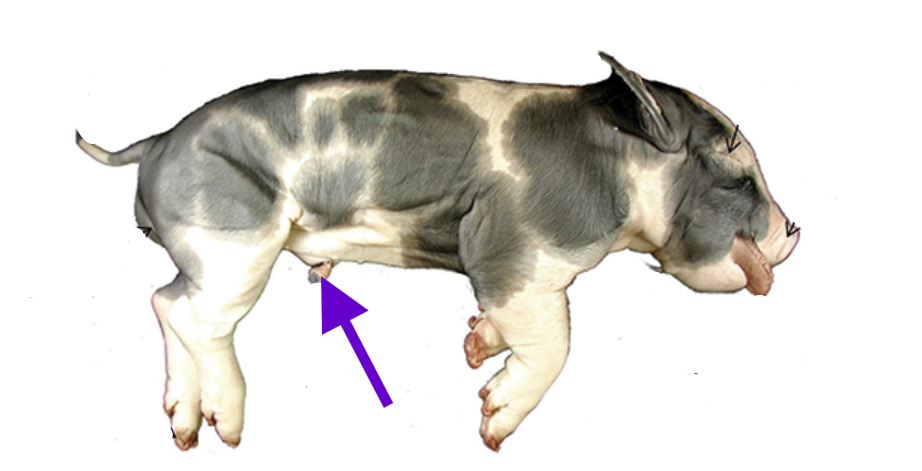
umbilical cord
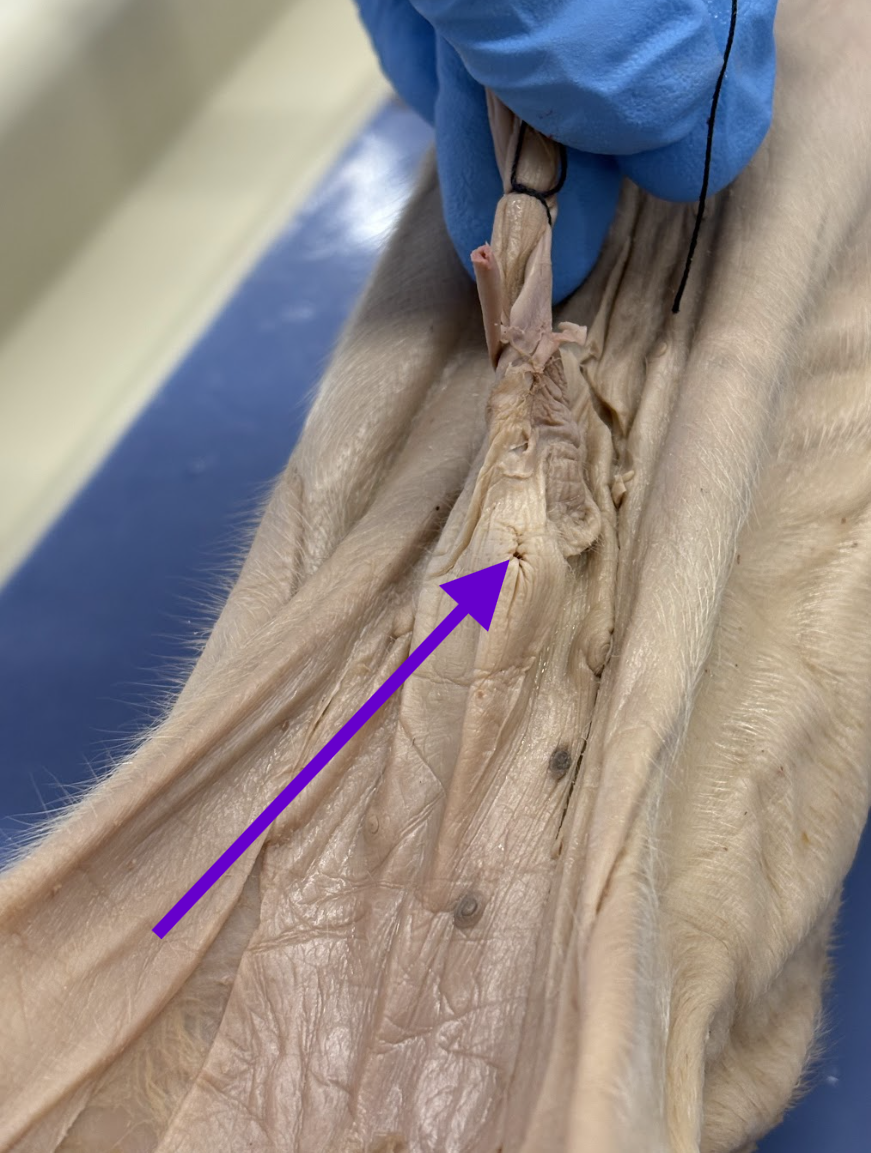
genital papilla
female only
like the human vulva
terminal ends of vagina and urethra
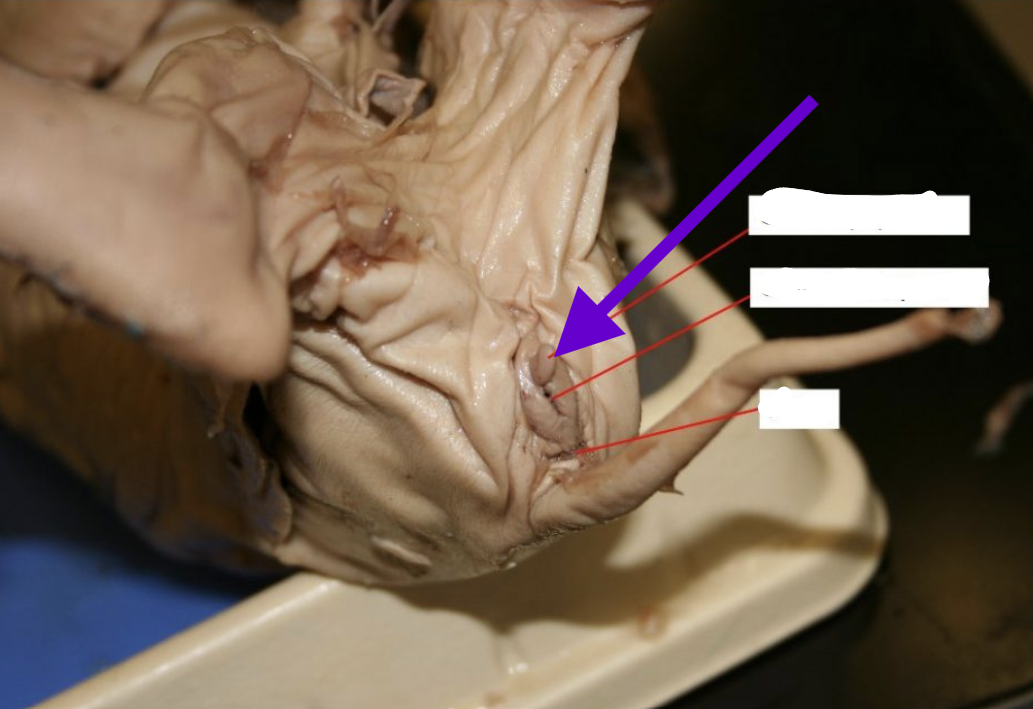
genital papilla
urogenital opening
male only
near the base of the umbilical cord
terminal end of the male urogenital tract/urethra
urogenital opening
scrotum
male only
sac of the testes
thermoregulation
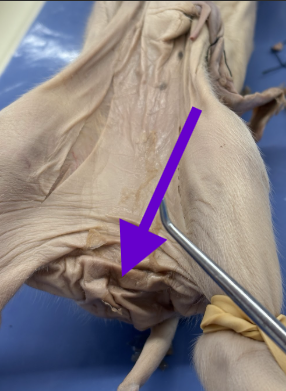
scrotum
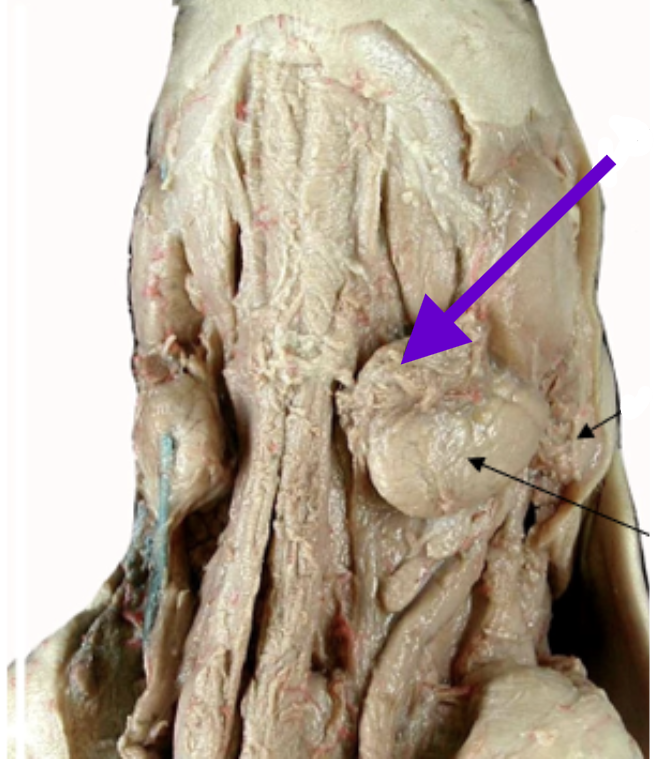
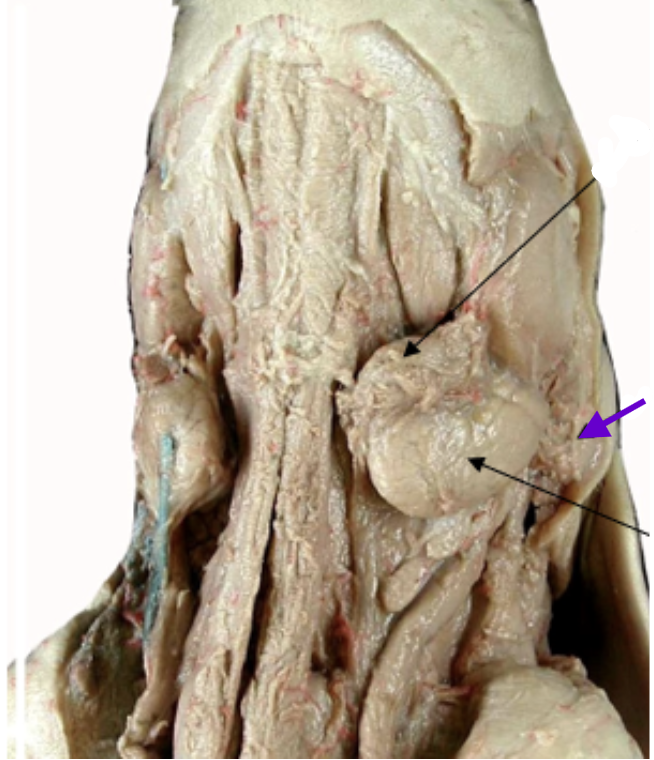
mandibular/submaxillary gland
lima bean shaped salivary gland
partially ventral to parotid gland, between parotid and angle of the jaw
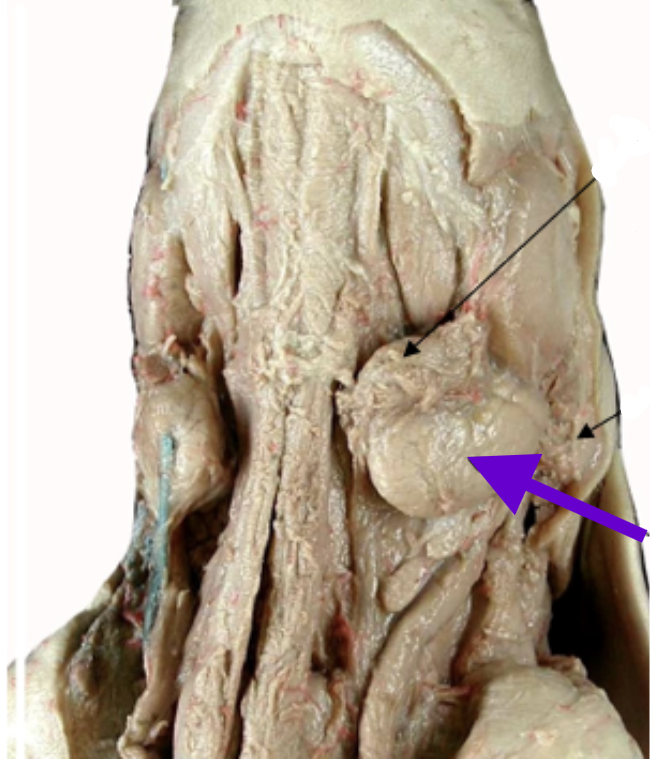
mandibular/submaxillary gland
sublingual gland
narrow and flat salivary gland
beneath the skin, medial to the lower jaw, next to the tongue
usually near mandibular gland’s medial edge
sublingual gland
parotid gland
large salivary gland
posterior and ventral to the masseter
near pinna base
parotid gland
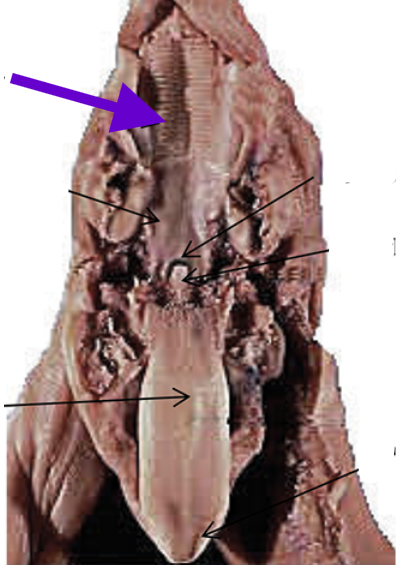
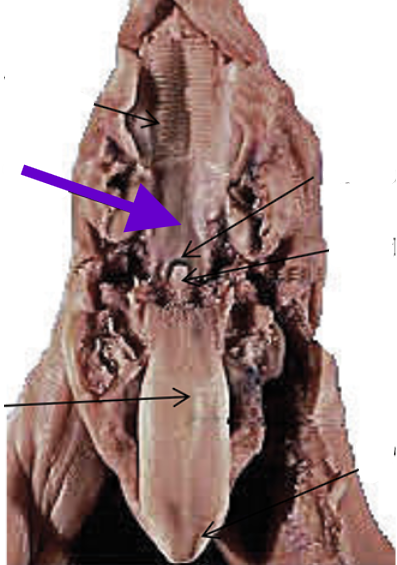
hard palate
ridged surface on the anterior of the mouth’s roof
hard palate
soft palate
smooth surface on the posterior of the mouth’s roof
soft palate
tongue
floor of the mouth, between the lower jaws
taste buds
food manipulation
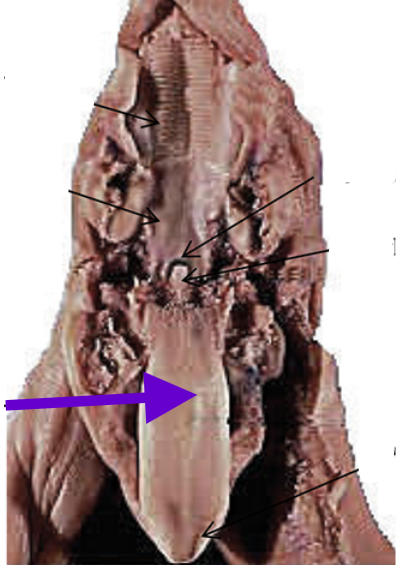
tongue
papillae of the tongue
small projections of the tongue
food manipulation
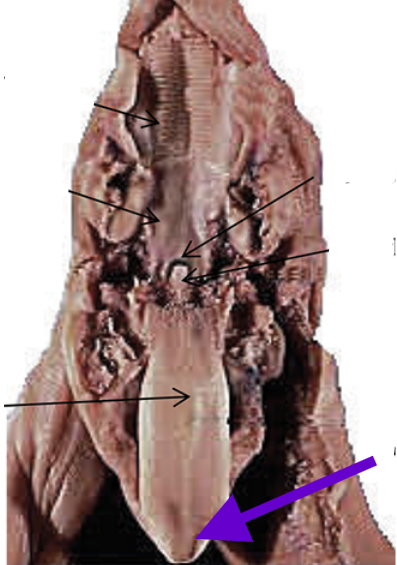
papillae of the tongue
pharynx
throat region that merges the respiratory and digestive systems
glottis
trachea opening
covered by epiglottis
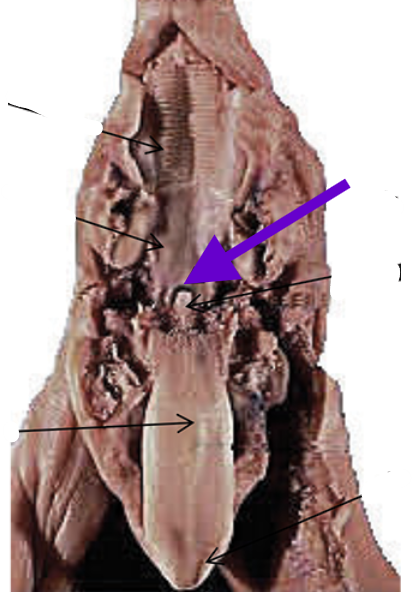

glottis
epiglottis
covers the glottis
separates esophagus from the trachea
prevents food from entering the respiratory system
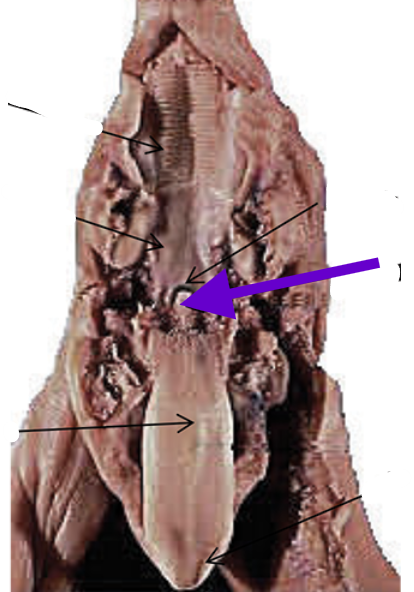

epiglottis
larynx
voice box
anteriorly connected to the glottis, posteriorly connected to the trachea
vocal cords
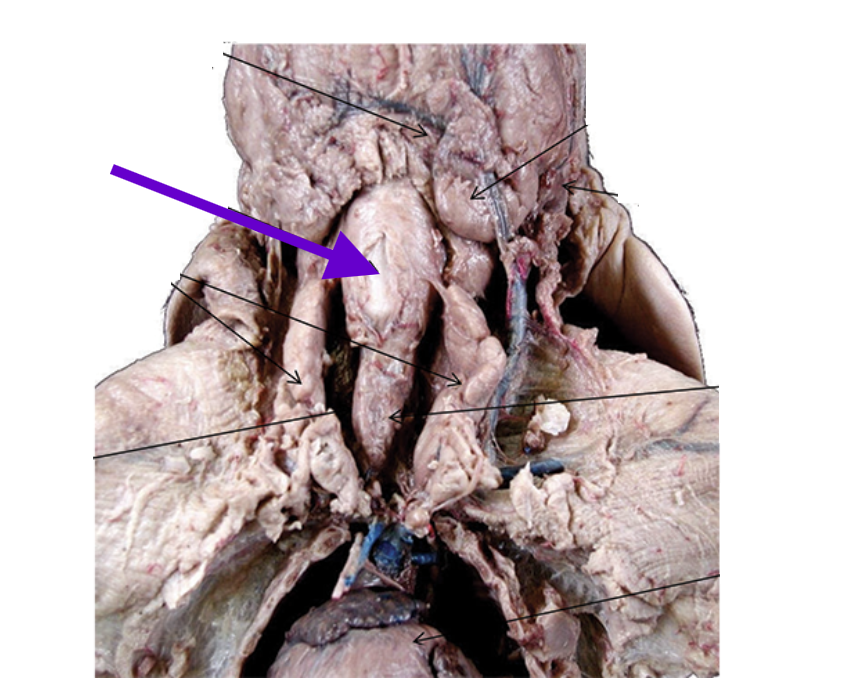
larynx
trachea
windpipe
tube from the larynx to the lungs
cartilage rings keep it open
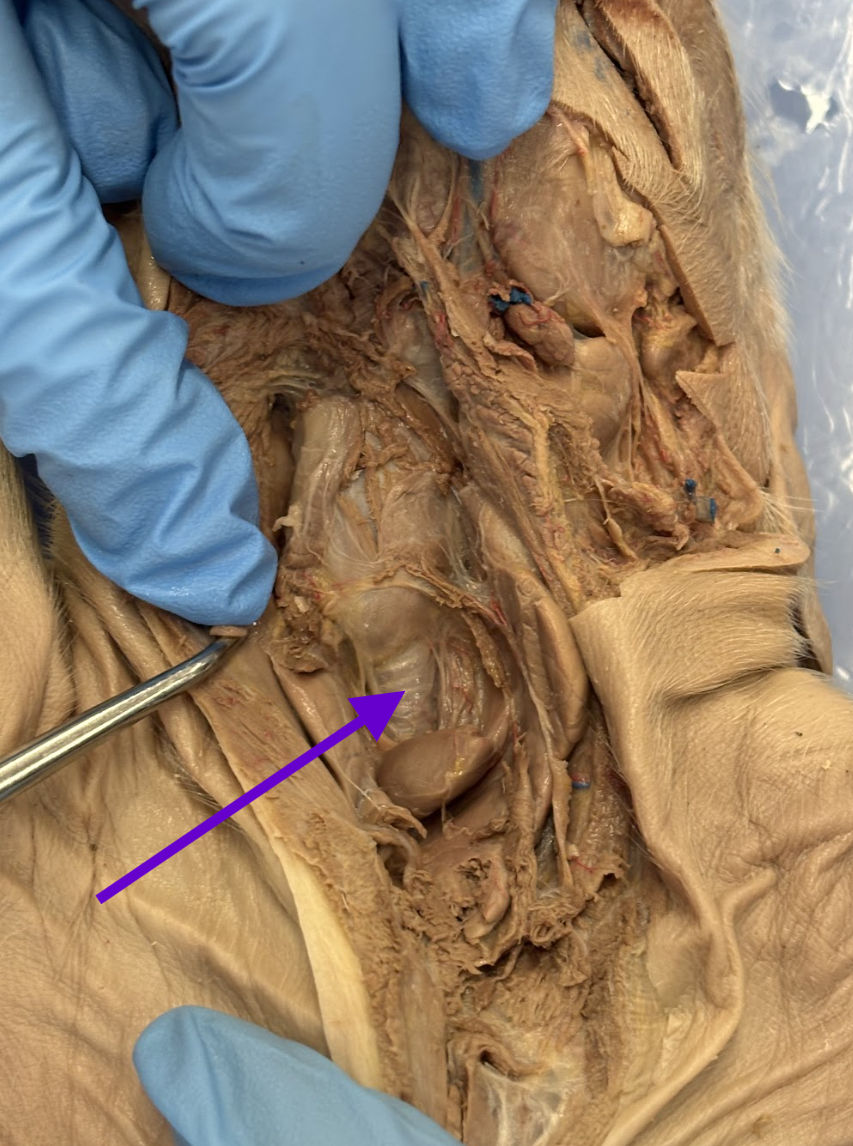
trachea
thymus gland
large and long endocrine gland
beneath the skin on each side of and over the trachea
extends down into the thoracic cavity, lying dorsally on the heart
early development of the immune system
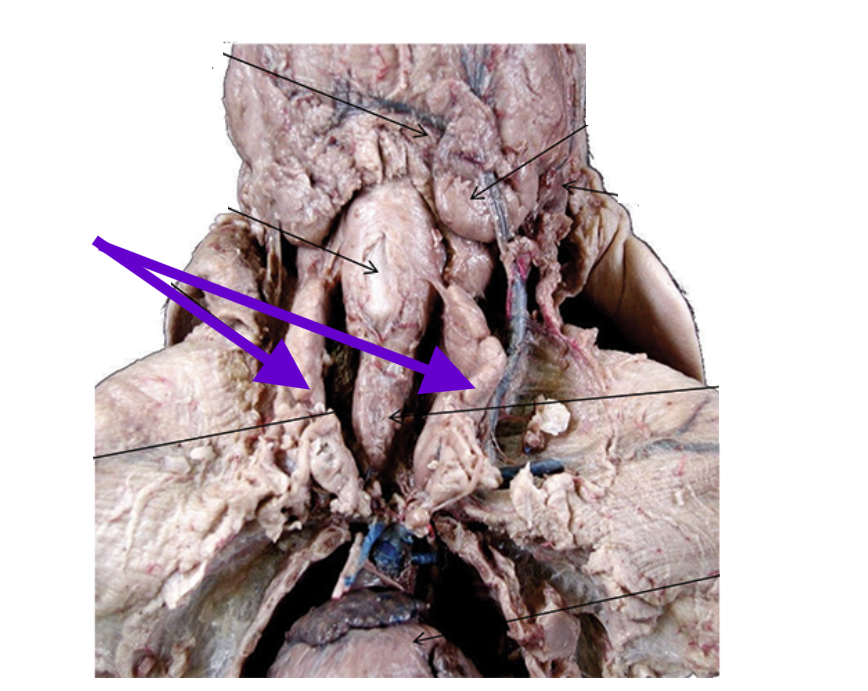
thymus gland
thyroid gland
small, dark, oval endocrine gland
between thymus gland, posterior to larynx, and ventral to trachea
covered by 2 sternohyoid muscles
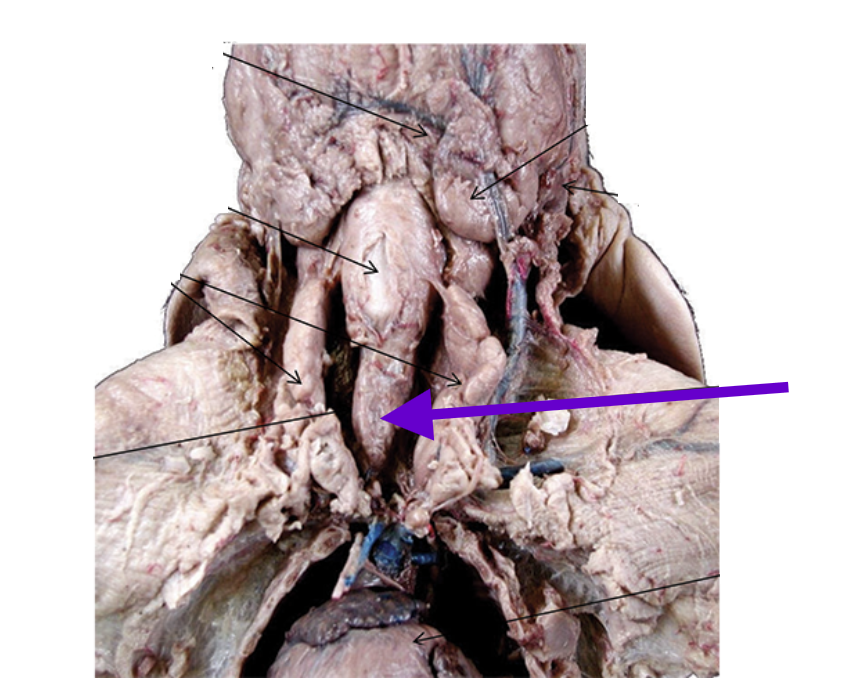
thyroid gland
lungs
large organ on lateral sides of the heart
gas exchange
diaphragm
skeletal muscle between lung and liver
breathing
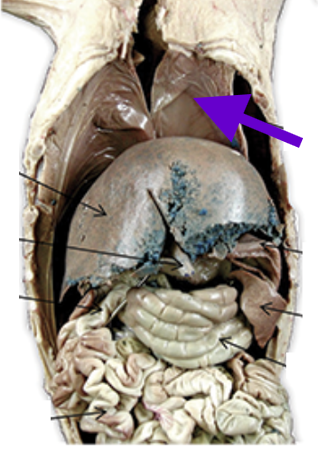
diaphragm
esophagus
tube from the pharynx to the stomach
travels through throat and diaphragm
stomach
digestive organ
posterior to the liver
breaks down food
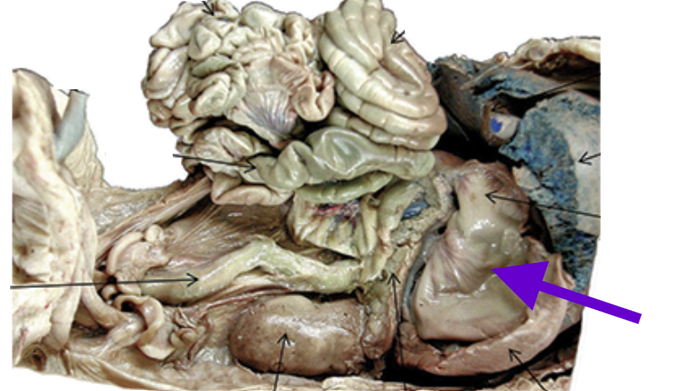
stomach
pyloric sphincter
donut-shaped smooth muscle
posterior end of the stomach
separates stomach and small intestine
pyloric sphincter
omentum
connective tissue that attaches and anchors the stomach
lesser omentum
inside, concave stomach curve
greater omentum
outside, convex stomach curve
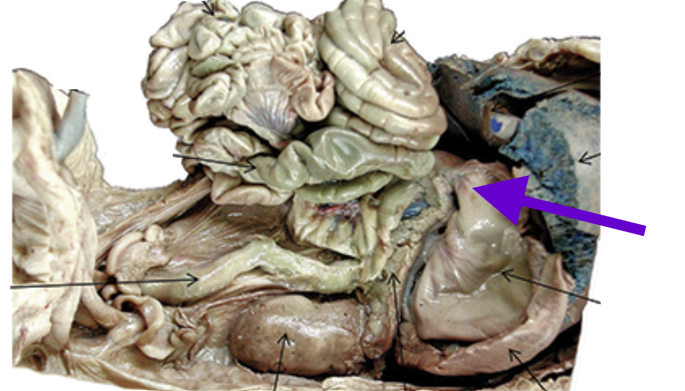
gall bladder
green bile sac
in middle lobe of liver
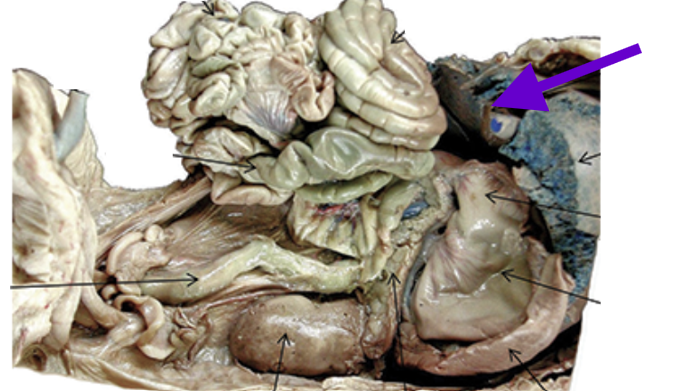
gall bladder
common bile duct
transports bile to the duodenum, in gallbladder
liver
largest gland
between stomach and diaphragm
filters blood
makes blood clotting proteins
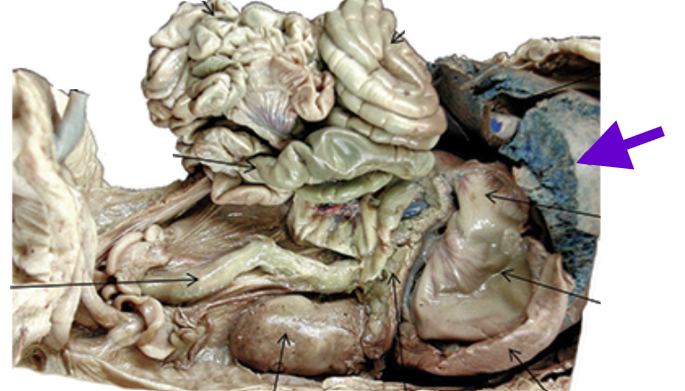
liver
spleen
long, flat, finger-like, dark red to purplish projection
left of stomach
stores blood
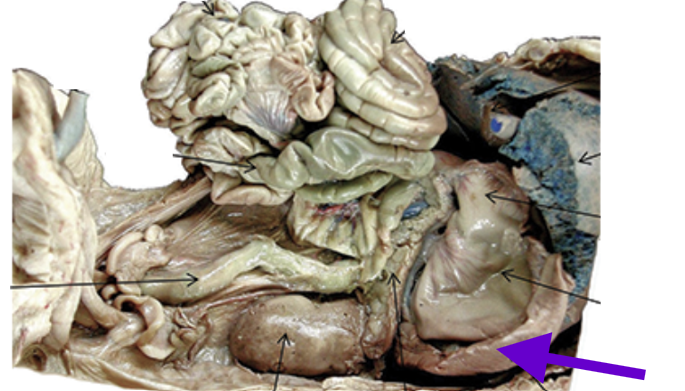
spleen
pancreas
looks like chewed gum
endocrine gland
stomach base
hormones control
blood sugar
digestive enzymes
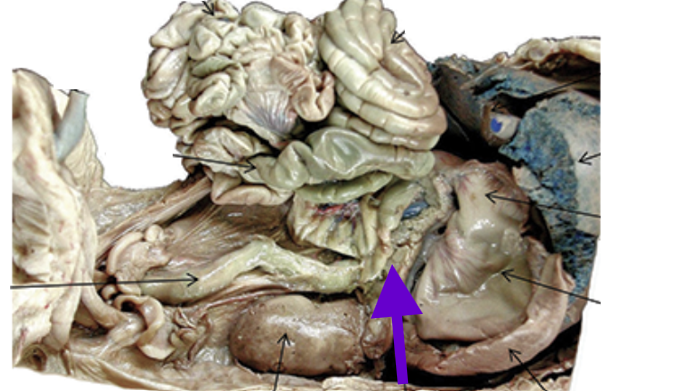
pancreas
small intestine
digestive part between stomach and large intestine
nutrient absorption
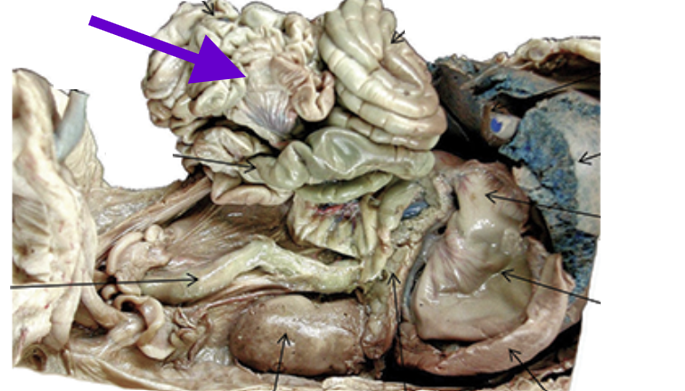
small intestine
small intestine divisions
length of name corresponds to order (long → short)
duodenum
jejunum
ileum
mesentery
connective tissue attached to the intestines
cecum
finger-like projection of large intestines
junction of large and small intestines
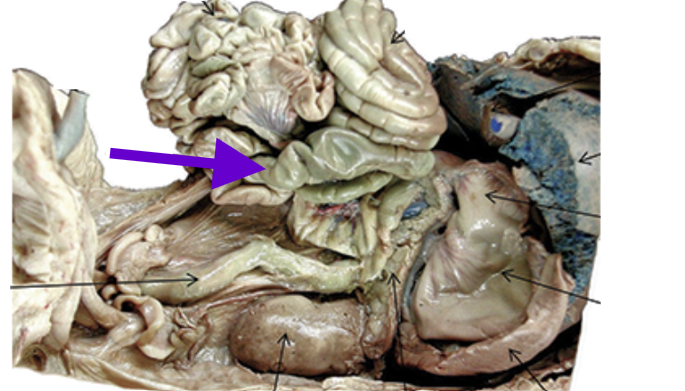
cecum
large intestine
posterior part of the intestines
absorbs water
prepares for waste elimination
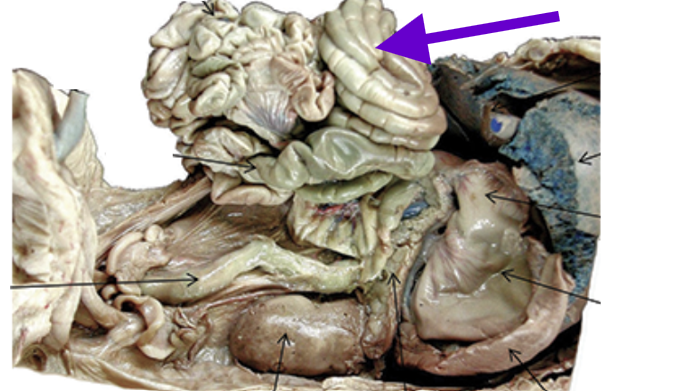
large intestine
large intestine divisions
Can All Teachers Drink Soda Regularly?
cecum
ascending colon
transverse colon
descending colon
sigmoid colons
rectum
rectum
final part of the large intestine
waste storage
anus
terminal opening of the digestive tract
eliminates waste from the rectum out of the body