Bacterial Virulence Factors
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Define LD50.
Lethal dose required to kill 50% of inoculated test animals
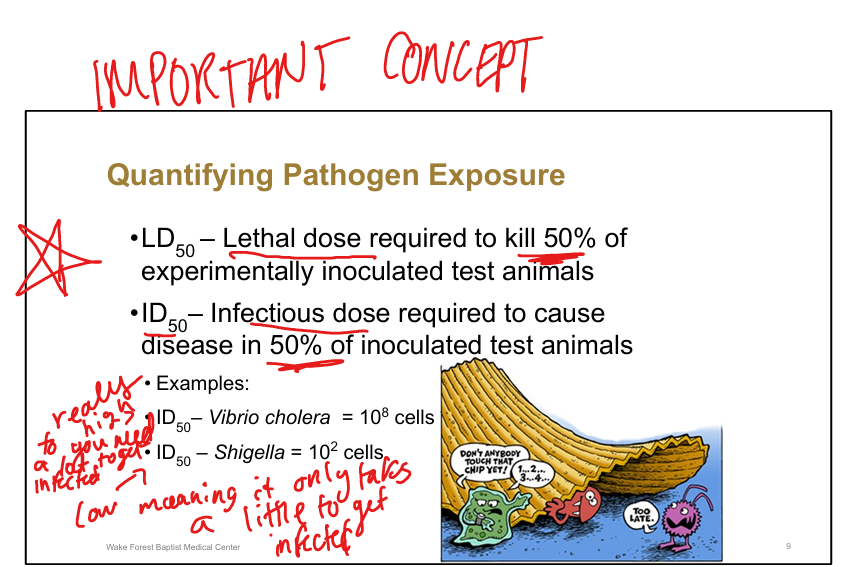

Define ID50.
Infectious dose required to cause disease in 50% of inoculated test animals
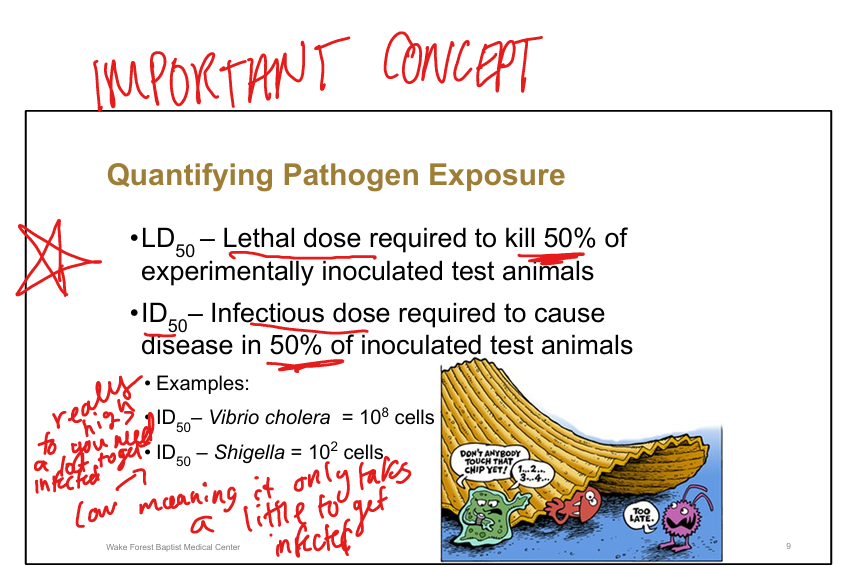

Example of high ID50 pathogen.
Vibrio cholerae (~10^8 cells)==> you need a lot of it to get infected
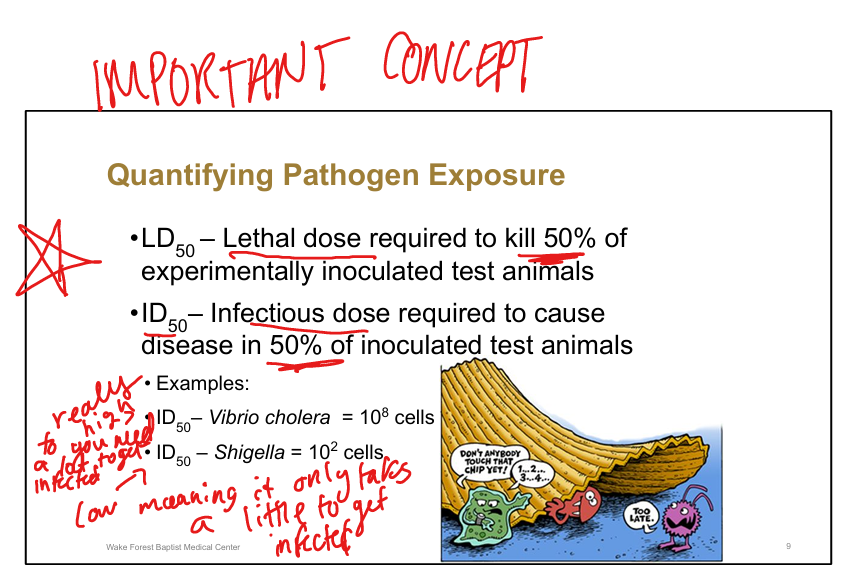

Example of low ID50 pathogen.
Shigella (~10^2 cells)»only need a little to get infected

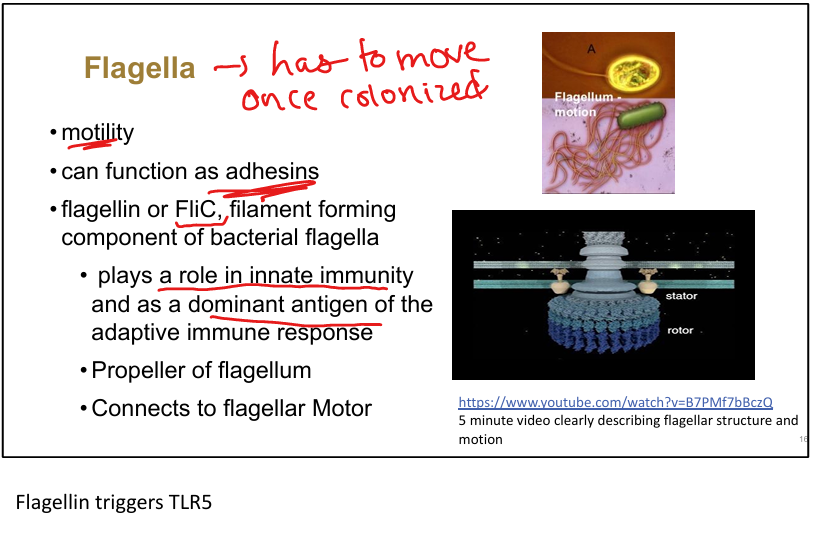
Role of flagella in virulence.
Provide motility, can function as adhesins, trigger innate immunity via TLR5
Main antigenic component of flagella.
Flagellin (FliC)

Type IV pili function.
Enable twitching motility, gliding, and “slingshotting” across surfaces
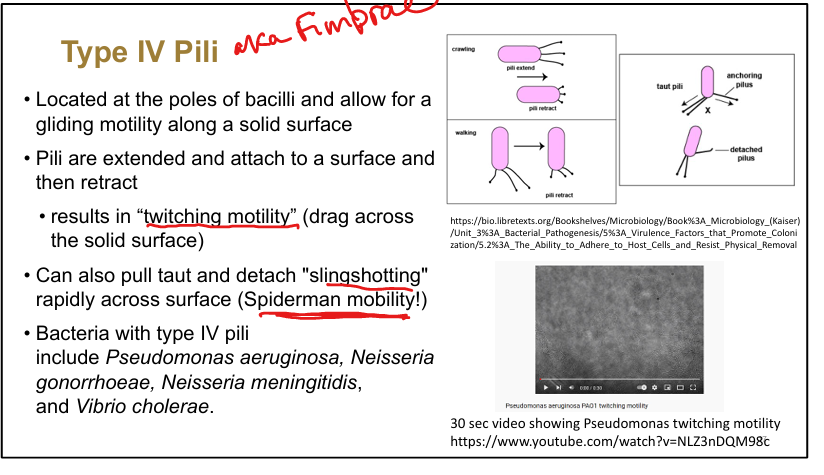

Examples of bacteria with type IV pili.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, Vibrio cholerae

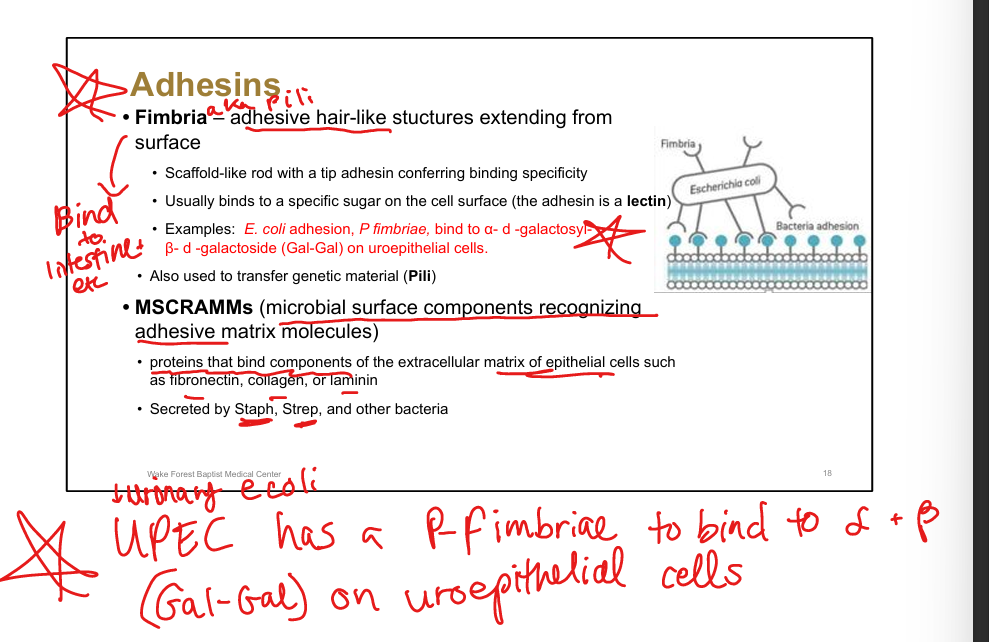
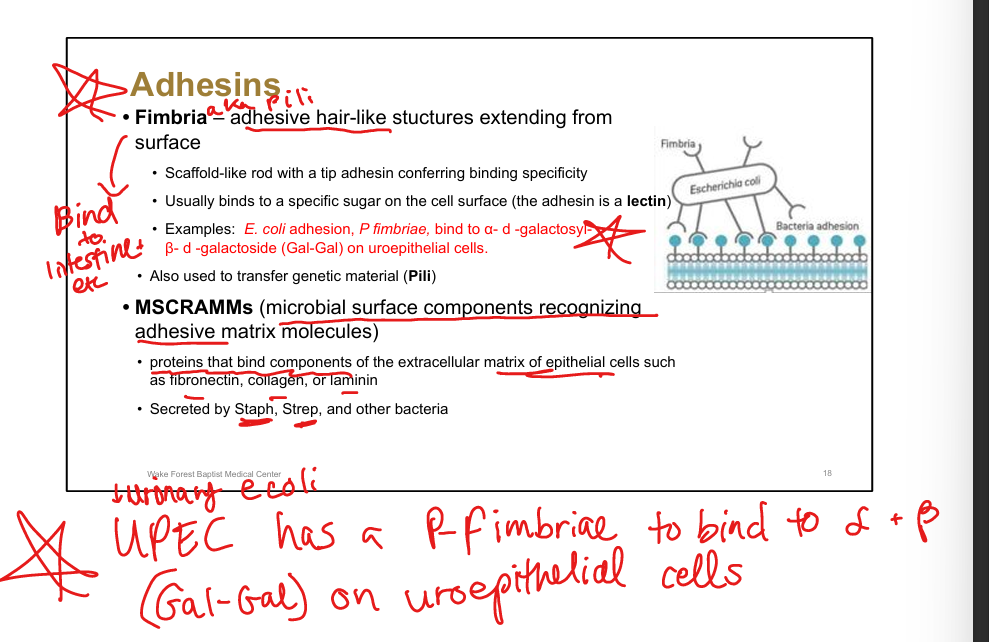
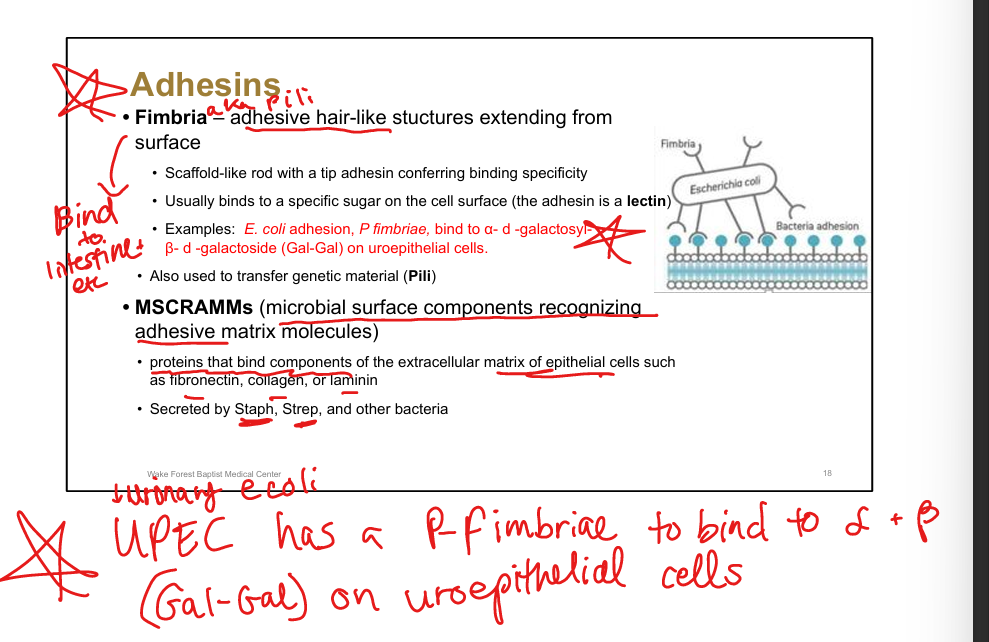
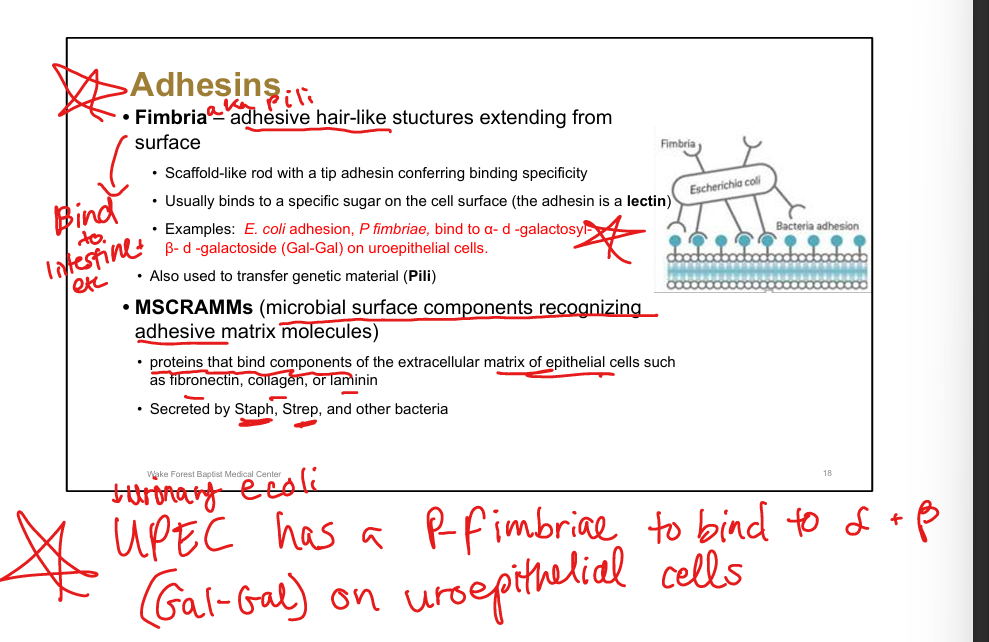
Define fimbriae.
Hair-like structures with tip adhesins conferring binding specificity
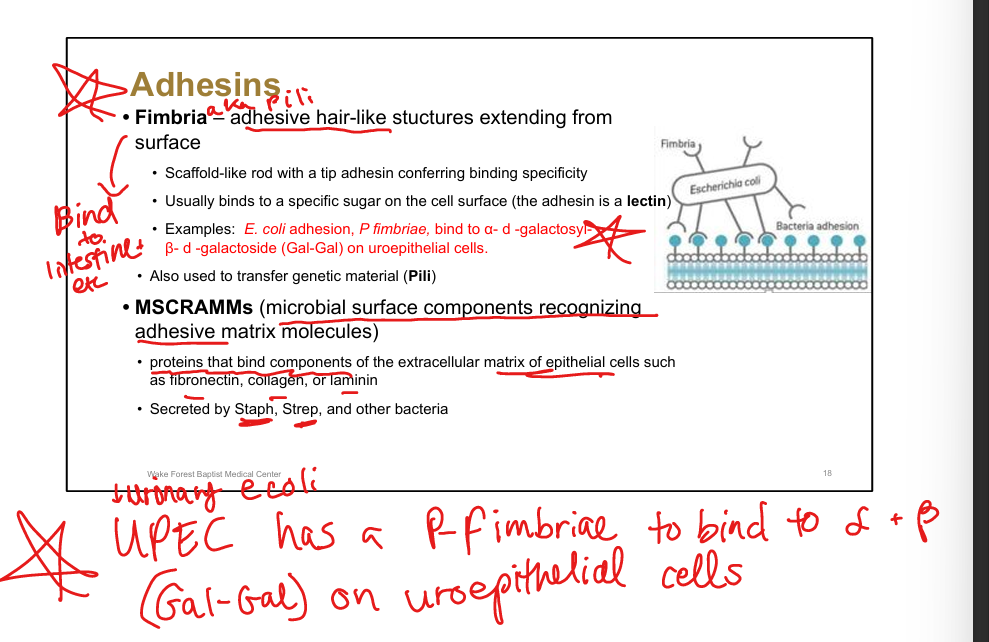

Example of fimbrial adhesion.
UPEC(E coli) P fimbriae bind Gal-Gal on uroepithelial cells

Define MSCRAMMs.
Microbial surface components recognizing adhesive matrix molecules; bind fibronectin, collagen, laminin

Examples of adhesins in Streptococcus pyogenes.
Protein F, lipoteichoic acid, M protein

Clinical relevance of adhesins.
Enable colonization of mucous membranes (e.g., strep throat)

Define biofilm.
Irreversible attachment to surfaces with extracellular polymer (matrix) formation
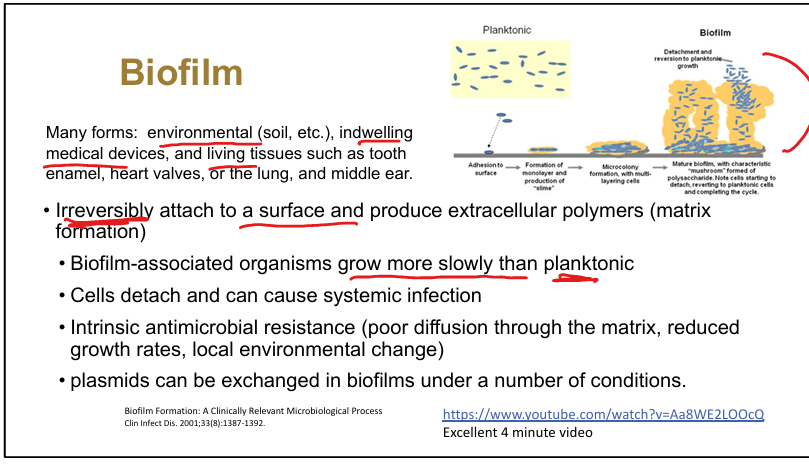

Clinical relevance of biofilms.
Resistant to antimicrobials, persistent infection source, harbor pathogens, allow plasmid exchange


Examples of biofilm-associated infections.
Tooth enamel, heart valves, lung, middle ear, indwelling medical devices
Define quorum sensing.
Cell-to-cell communication regulating gene expression based on population density
Gram-negative quorum sensing molecules.
Acyl-homoserine lactones (AHLs)


Gram-positive quorum sensing molecules.
Processed oligopeptides via two-component systems


Examples of virulence factors encoded.
Adhesins (pili, intimin), siderophores (yersiniabactin, aerobactin), exotoxins, invasion genes, secretion systems

Function of IgA protease.
Cleaves IgA, allowing adherence to mucosal surfaces


Examples of IgA protease producers.
Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae


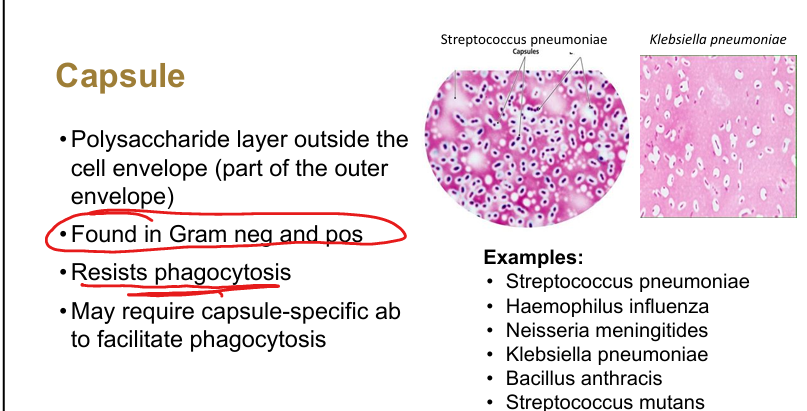
Function of capsules.
Polysaccharide layer resisting phagocytosis
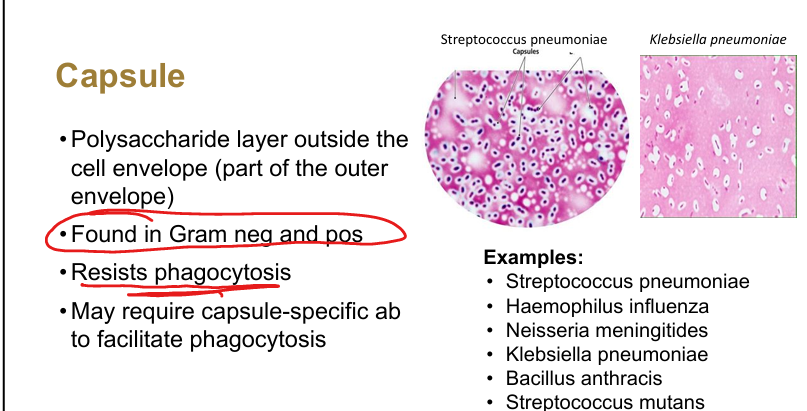

Examples of encapsulated bacteria.
Strep pneumoniae, H. influenzae, Neisseria meningitidis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Bacillus anthracis

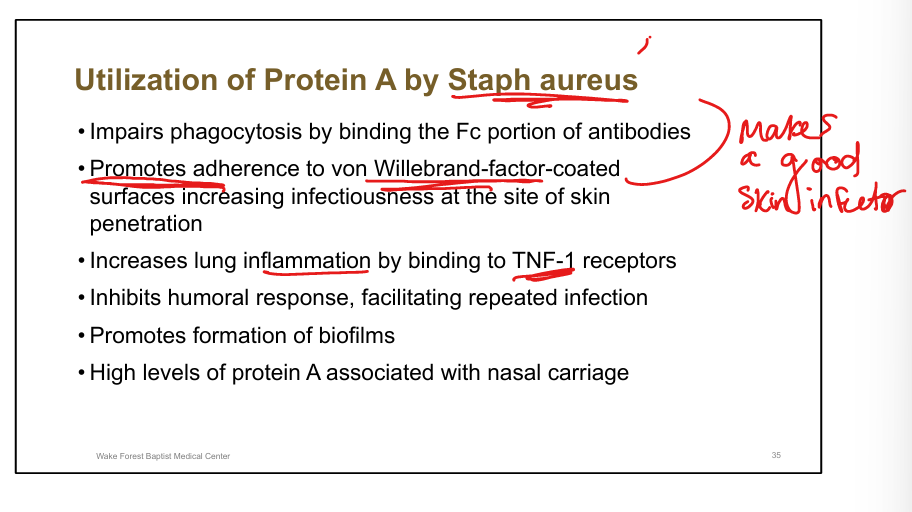
Function of Protein A (Staph aureus).
Binds Fc portion of antibodies, impairs opsonization, promotes biofilms, increases inflammation

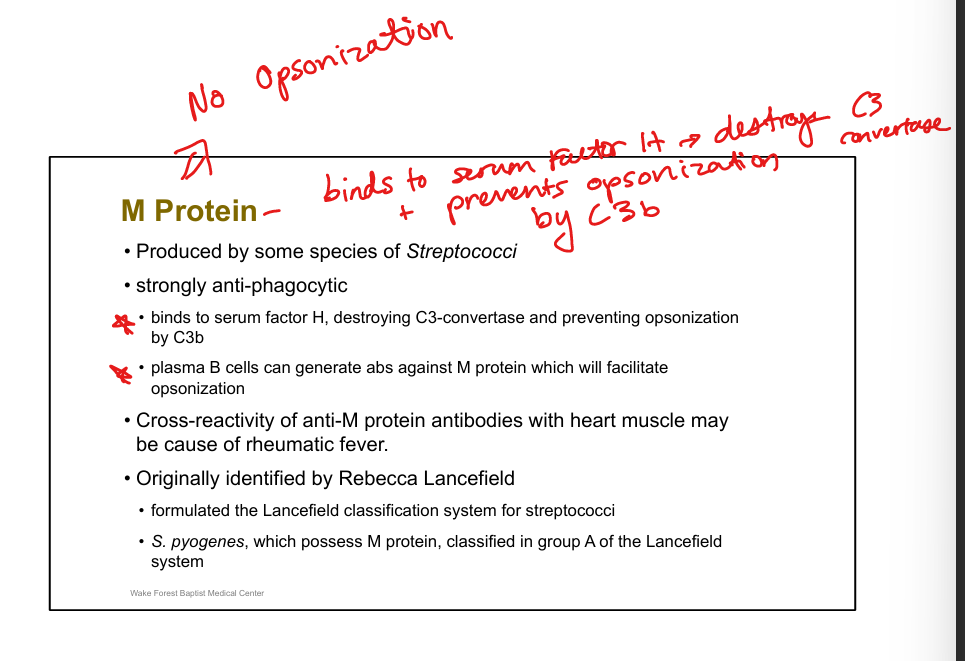
Function of M protein (Strep pyogenes).
Anti-phagocytic, binds factor H which destroys C3 convertase and prevents opsonization by C3b; cross-reactivity → rheumatic fever

Function of hyaluronidase.
Breaks down hyaluronic acid; “spreading factor”


Function of collagenase.
Breaks down collagen; promotes tissue invasion


Function of streptokinase/staphylokinase.
Dissolve clots; promote bacteremia
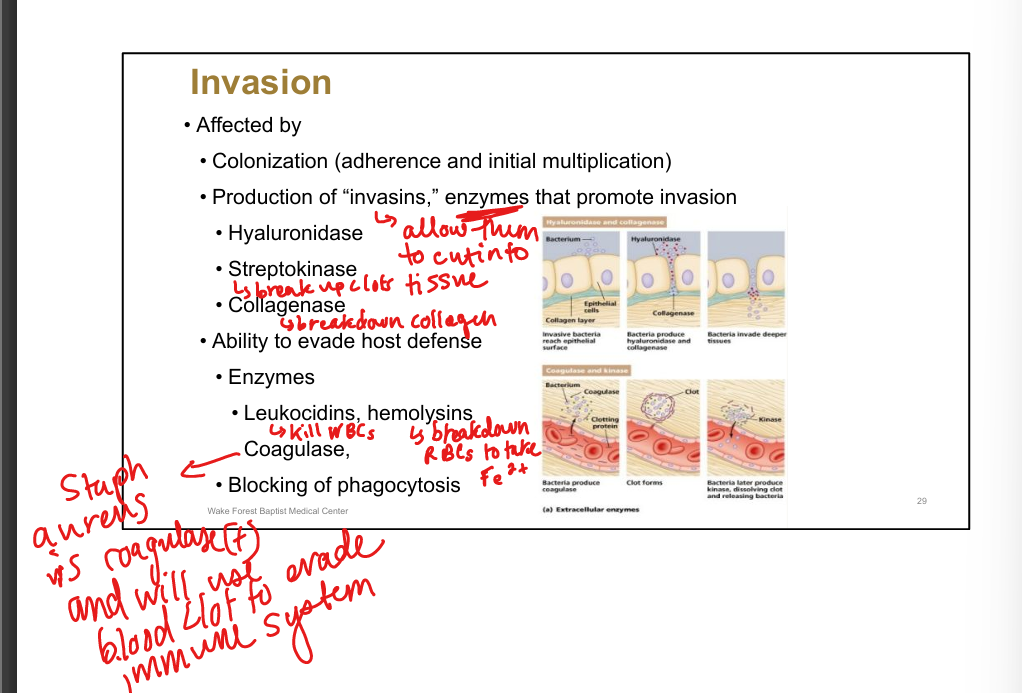

Function of coagulase.
Stimulates clotting; protects bacteria from phagocytosis (Staph aureus)


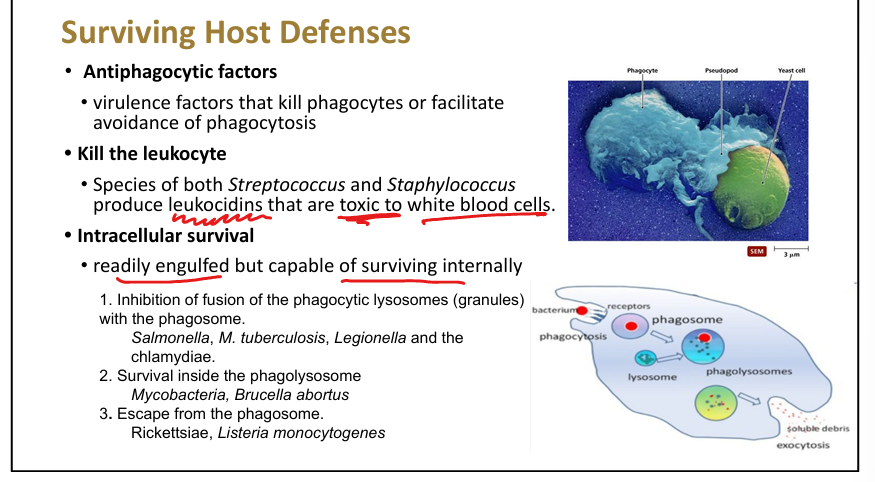
Function of leukocidins.
Kill WBCs; rupture lysosomes; tissue damage


Function of hemolysins.
Lyse RBCs; alpha/beta hemolysis (Strep, Staph)


Intracellular survival strategies.
Inhibit phagosome-lysosome fusion (Salmonella, TB, Legionella), survive inside phagolysosome (Mycobacteria, Brucella), escape phagosome (Rickettsia, Listeria)

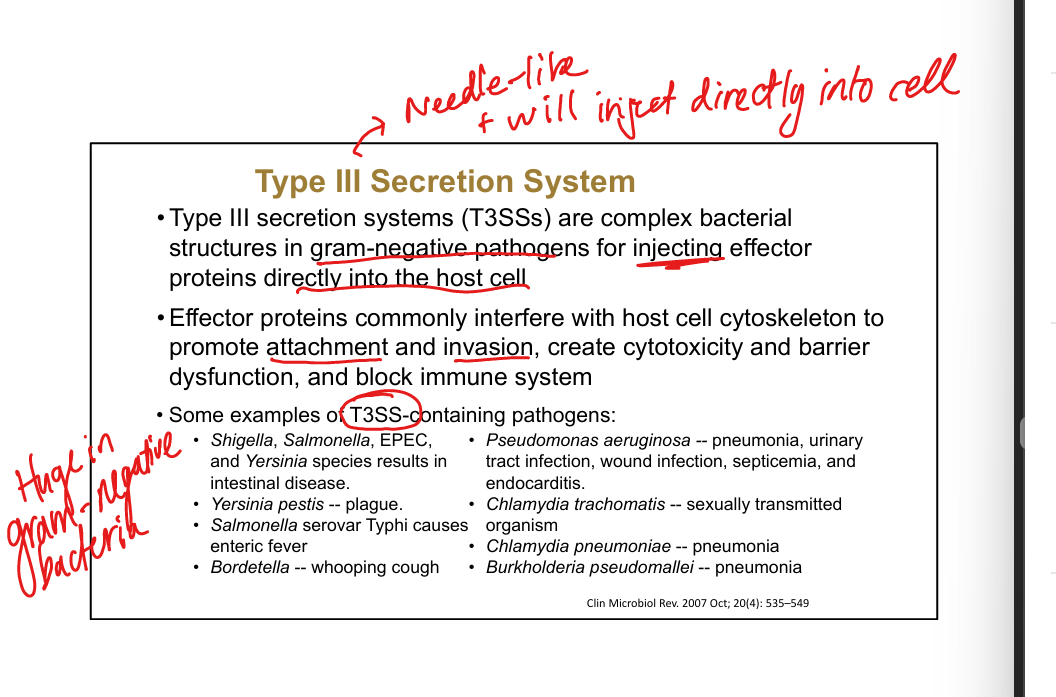
Type III secretion system.
Needle-like structure injecting effectors into host cells; major gram-negative virulence factor
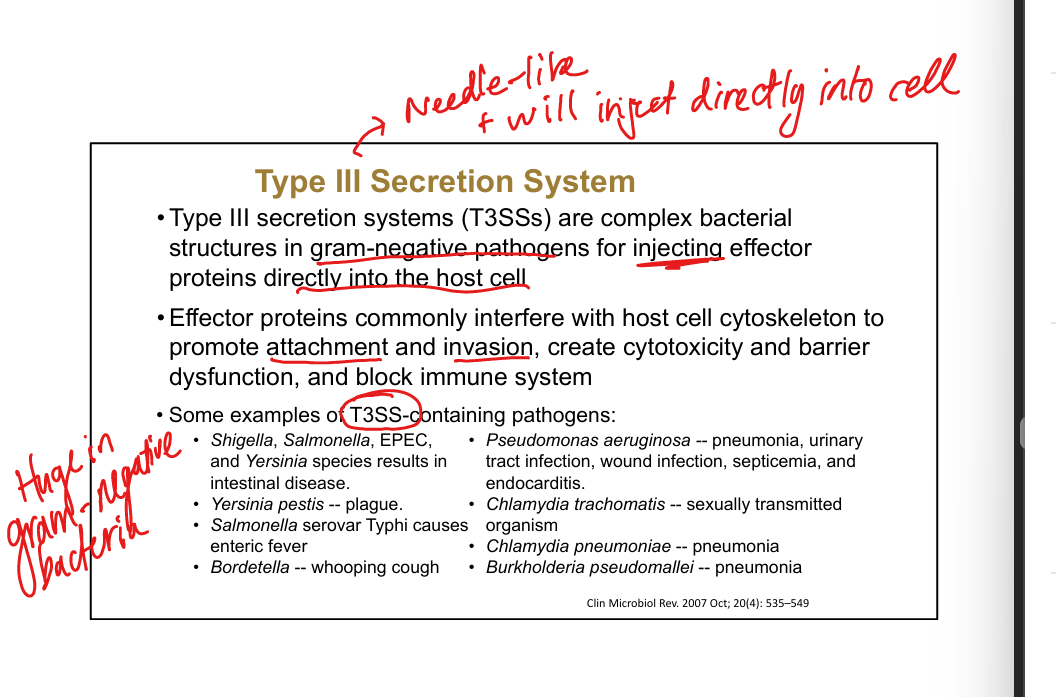

Examples of T3SS pathogens.
Shigella, Salmonella, EPEC, Yersinia, Pseudomonas, Chlamydia, Bordetella, Burkholderia

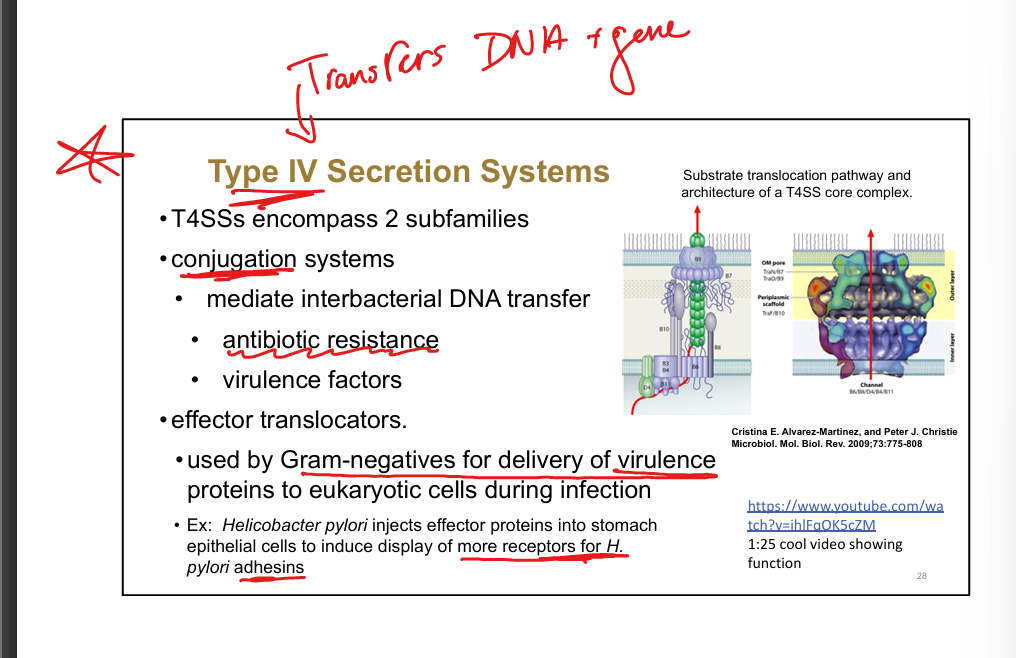
Type IV secretion system.
Transfers DNA/proteins; mediates conjugation, antibiotic resistance, virulence (e.g., H. pylori)

Define exotoxins.
Secreted proteins (Gram+ > Gram–); specific actions; heat-labile; do not usually cause fever
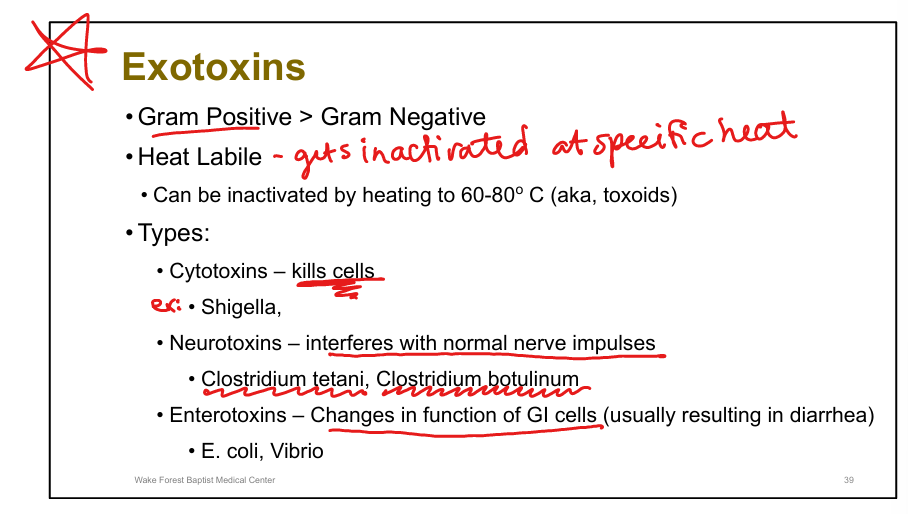

Types of exotoxins.
Cytotoxins (Shigella), Neurotoxins (C. tetani, C. botulinum), Enterotoxins (E. coli, Vibrio)

Define endotoxins.
LPS component of Gram– outer membrane; activity due to lipid A; heat-stable; pyrogenic(produces fever)


Examples of endotoxin-producing bacteria.
Salmonella, Shigella, E. coli, Neisseria


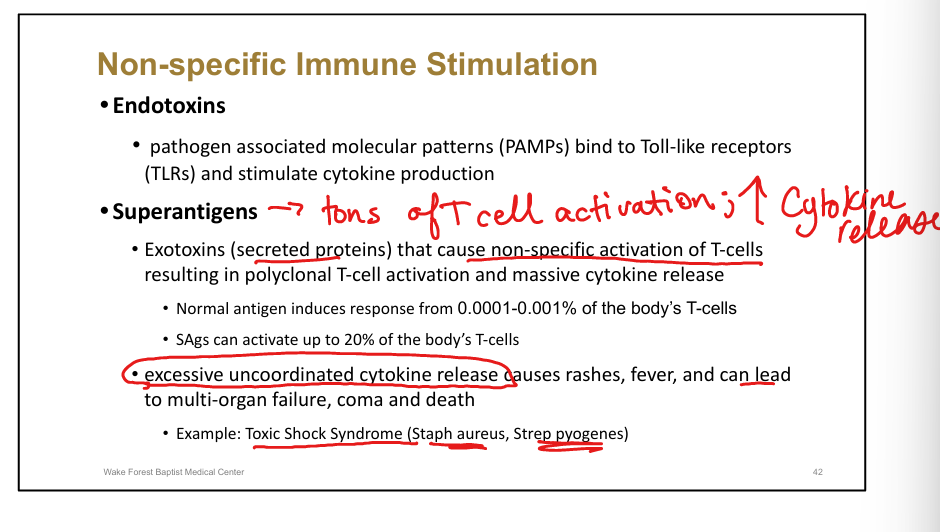
Define superantigens.
Exotoxins causing massive non-specific T-cell activation and cytokine release
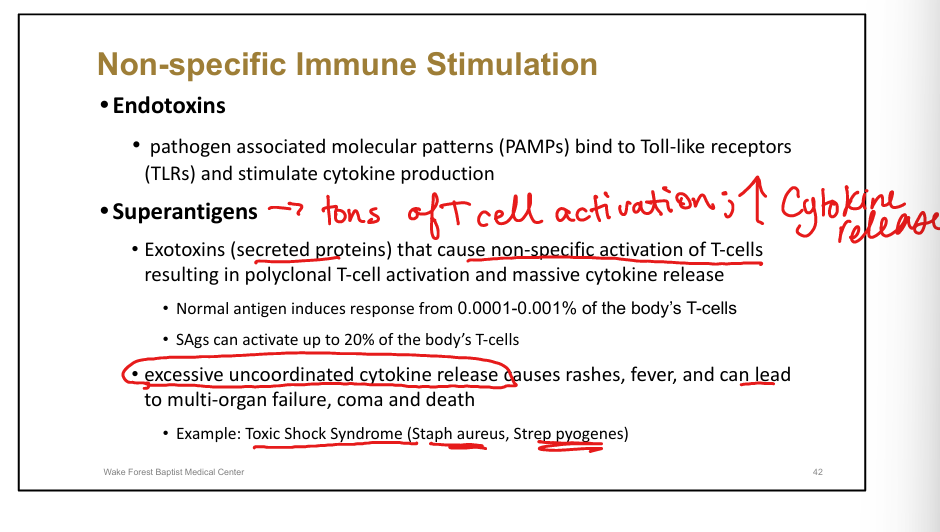

Clinical example of superantigen disease.
Toxic Shock Syndrome (Staph aureus, Strep pyogenes)