Principles of Parasite Identification: Worms
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Why is diagnosis important?
Allows proper treatment
Understand where the infection came from
May help limit spread of infection (particularly in zoonotic cases)
Basis of diagnosis: Parasitological
Based on morphological characteristics of the parasite
Can be specific in some cases
Basis of diagnosis: Immunological
Based on presence of Ab or Ag
Antibodies are ________ specific; long lasting so do not indicate ___________
Less; infection, but rather exposure
Antigen tends to be ________ specific; indicates ___________
More ; active infection
Basis of diagnosis: Molecular
Based on PCR
Very specific!
Principles of diagnosis: Ideally a test should be:
Sensitive, specific, reliable
Samples for diagnosis that can be obtained from a live animal include
Blood, stool
Eggs may be concentrated from feces via
Flotation or sedimentation
Blood films are usually stained for what purpose?
To ID parasites
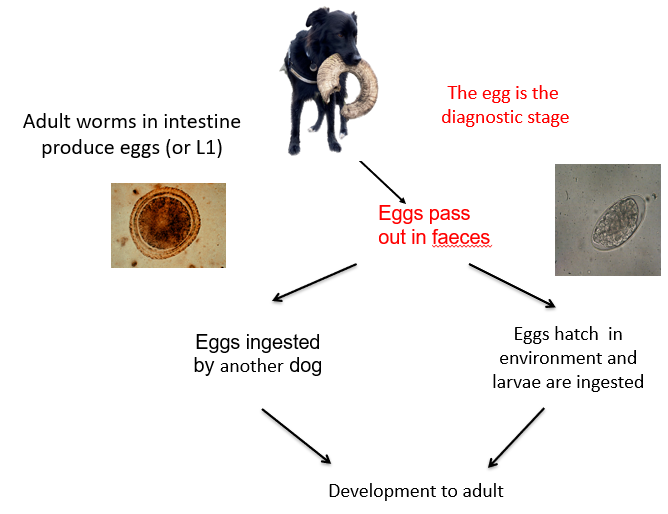
What is this an example of?
Direct nematode life cycle
Many gastro-intestinal worms are diagnosed via
detection of eggs in stool
Some worms are very fecund and eggs can be detected
In direct smear
Under some circumstances, may need to
Concentrate the eggs

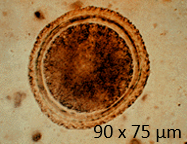
What type of egg is shown?
Smooth egg shell (Toxascaris leonina)
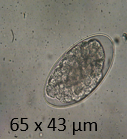
What type of egg is shown?
Rough pitted egg shell (Toxocara canis/cati)
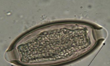
What type of egg is shown?
Strongyle egg (Hookworm, either Ancylostoma or Uncinaria)
What type of egg is shown?
Bipolar plugs (Trichuris egg)
Treatment options are often _____ for nematodes
The same
Easy to distinguish hookworms from ascarids via
Their eggs
Clinical signs of A. caninum infection
Anemic puppies
Clinical signs of T. canis
puppies with ill-thrift and swollen bellies
What is needed for concentration and quantification of eggs?
McMaster slide
Flotation of nematode eggs in saturated salt solution
Known volume added to each well on the slide
Why would we potentially need to culture nematode larvae from fecal samples?
If two species of eggs are identical
What is an example of two nematodes who may need culturing to distinguish?
Ancylostoma caninum and Uncinaria stenocephala
Nematode larvae found in feces: L1 of Angiostrongylus vasorum can be
detected in feces
Nematode larvae found in feces: Female worm in heart produce
Eggs, hatch rapidly, coughed and swallowed
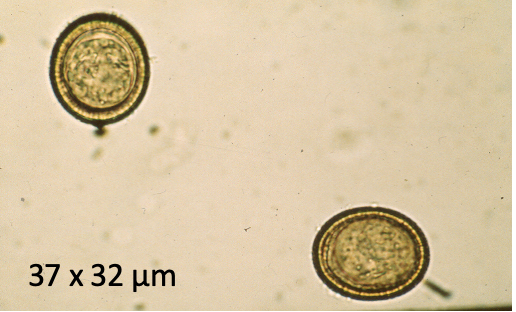
What does this image show?
Tapeworm eggs (Taenia)
Echinococcus granulosus is
zoonotic
very similar egg to Taenia
Describe Taenia eggs
thick egg shell
radial striations
6-hooked (hexacanth) embryo inside
Antigen detection of parasites
ELISA test
Dipstick
Antigen detection relies on
good antibodies
DNA detection of parasites
PCR
PCR relies on
primers specific to parasite DNA
extremely sensitive → specific equipment
prone to contamination
many factors in stool can interfere
What is a staining profile of parasites used for
To distinguish pathogenic and nonpathogenic species of Dirofilaria
Serological tests for worms
Antibody is a measure of exposure and can be useful under some circumstances
Antigen detection in blood is very useful as indicated current infection
Ag detection test for heartworm
relies on detection of antigens release by adult female worms in the heart using a specific antibody to capture the Ag. color change denotes the presence of antigen in the blood
Not quantitative - need ELISA
Why is antigen testing for heartworm alone not useful in cats?
Only detects sexually mature female worms
level of antigen relates to number of worms
often contain few worms and not sexually mature
What in addition to antigen testing should you use for heartworm testing cats?
Antibody test
Antigen test for A. vasorum
detects antigen in the blood stream of infected dog
improvement over L1 in feces as these are shed intermittently
McMaster method: Large Animal
measure eggs per gram of feces (EPG)
McMaster method useful in
FECRT (fecal egg count reduction test) which measure the level of anthelmintic resistance in a worm population
Quantify eggs before vs eggs after treatment
Baermann test is used for
detecting L1 of cattle lungworm, D. viviparus
D. viviparus Baermann test
nematode larvae migrate from the fecal sample downward in water through the gauze and collect in the tubing above the clamp
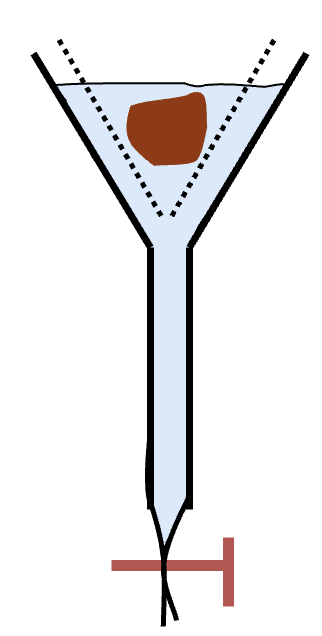
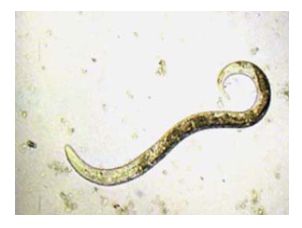
What does this image show?
Cattle lungworm, D. viviparus
Protozoan - Feco-oral tranmission/GI of host examples
Toxoplasma gondii
Giardia spp.
Cryptosporidium parvum
Protozoan - Vector borne examples
Babesia
Leishmania
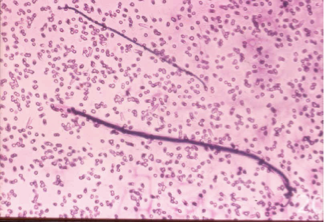
What does this image show?
Dirofilaria
Diagnosis of toxoplasmosis (Ovine): grossly
bright red placenta cotyledons
Diagnosis of toxoplasmosis (Ovine): microscopically
AB in fetal fluids/precolostral lamb serum
Ewe; AB test with paired samples or IgM detection
Immunohistochemcial/PCR detection of parasite (tissue cyst) in aborted (placenta) tissue (expensive)
Bradyzoite tissue cysts are
too small to be picked up in meat inspection
T. gondii - Diagnosis (Human): Pregnant mother
Serology - IgM detection + high igG titre (acute infection within las 3 months)
T. gondii - Diagnosis (Human): Congenital infection
prenatal - PCR of amniotic fluid/ultrasound
postnatal - CAT or MRI scan for brain lesions
T. gondii - Diagnosis (Human): immunocompromised (AIDS)
PCR on blod, cerebrospinal fluid and brain scans
Giardia clinical signs
Strong smelling, watery diarrhea/vomiting, weight loss
Giardia transmission
feco-oral via ingested cyst form
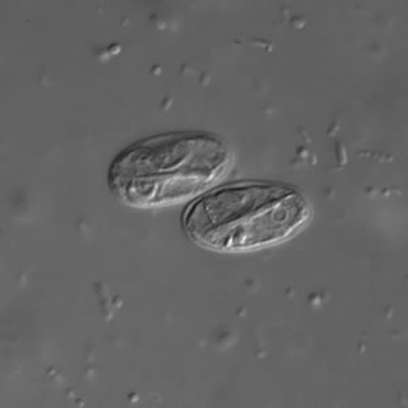
What does this image show?
Giardia ovoid cysts 10-14 um
fecal smear for diagnosis
test x3 - 3-5days
firm stool

What does this image show?
Giardia trophozoites - loss stools
Giardia is elusive parasite to test use
SNAP (ELISA) plus flotation
if both +, 95% correct diagnosis
Cryptosporidium spp. clincally
zoonotic - acute gastroenteritis
infection from public water sources, contact with livestock
faulty water treatment
Cryptosporidium oocytes detection
difficult in unstained fecal samples due to small size
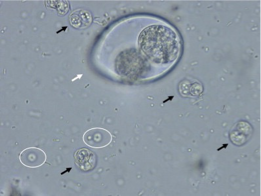
What does the white circle show?
Cryptosporidium parvum
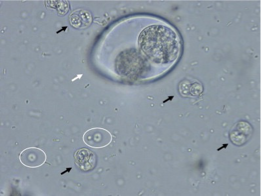
What does the black arrow show?
Toxoplasma gondii
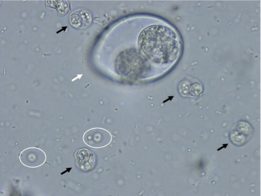
What does the white arrow show?
Isospora felis
Cryptosporidium detection Common
modified Ziehl-Nielsen (acid-fast) staining technique
poor sensitivity - but will detect acute cases
detection limi 5×105 oocysts/g feces following concentration of fecal sample
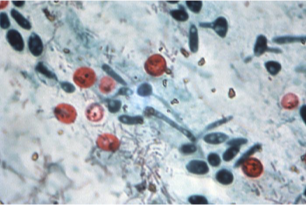
What does this image show?
Ziehl-Nielsen stain for detection of Cyptosporidium
Cryptosporidium detection Other
Immunofluorescent AB test (IFAT)
Antigens in feces detected by enzyme immunoassays
PCR
Cryptosporidium detection: Immunofluorescent antibody test (IFAT)
Microscopy based, fluorescently labeled Mab Ab
combined tests detect giardia
Sensitivity; 1x104 – 1x105 oocysts/g faeces (50x more than stained smears)
Municipal water monitored/filtered – Ab based oocyst capture
Cryptosporidium detection: Enzyme immunoassays
results inconsistent when applies to small animals
Cryptosporidium detection: PCR based assays
used for genotyping species ID
10x more cases positive
What parasites are detected via blood smear?
Trypanosomes, Leishmania, Theileria, Babesia
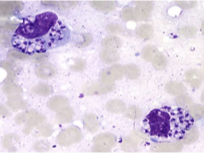
What does this image show?
Leishmania amastigotes in macrophages
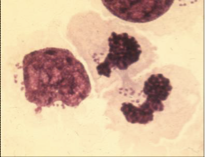
What does this image show?
Theileria macroschizonts in lymphocytes
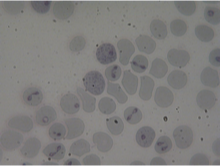
What does this image show?
Babesia piroplasms in RBC

What does this image show?
Trypamastigote of Trypanosoma
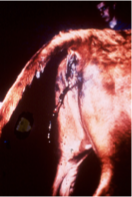
What does this image show?
Red water
Detection of blood-born protozoa excluding blood smear
Immunofluorescence
ELISA
PCR
PCR positives
very specific
very sensitive - needs small amounts of material
can differentiate mixed infections
PCR negatives
not that rapid/lab based
easy to contaminate, so need controls for false +s
for quantification need sophisticated thermal cycler
Antigen and PCR will
NOT always confirm the infection is viable
CAN generate over-estimation of risk