1.2.4 Aggregate Supply (Micro)
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
THE THEORY OF SUPPLY
Supply is defined as the quantity of a good or service that producers are willing and able to supply at a given price in each time period.
The law of supply is that as the price of a product rises, so businesses expand supply. Higher prices provide a profit incentive for firms to expand production
SUPPLY CURVE
A supply curve shows a relationship between market price and how much a firm is willing and able to sell.
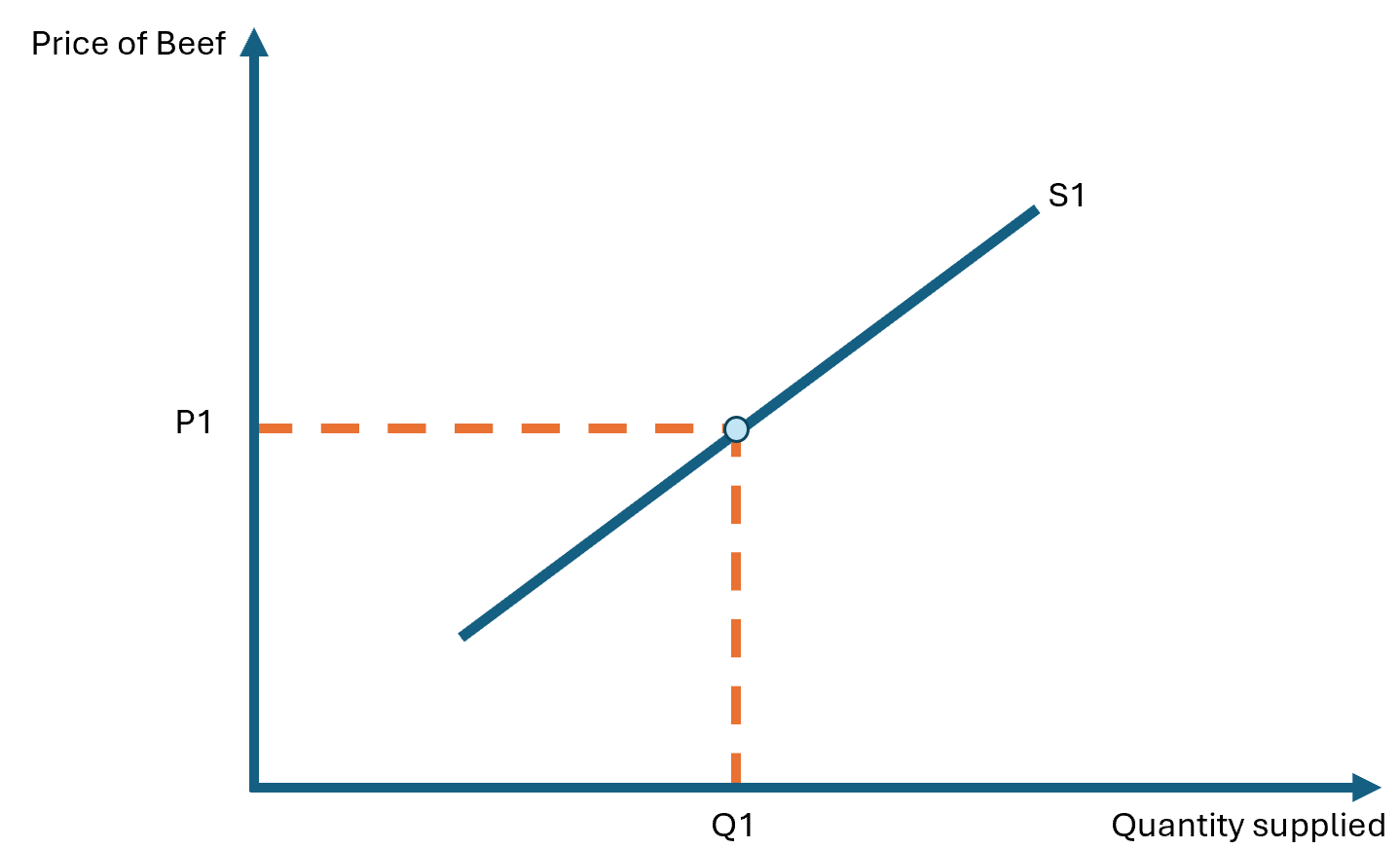
WHY IS THE SUPPLY CURVE SLOPPING UPWARDS
Standard theory assumes that rational firms choose an output and price that aims to maximize profits. If the price of a good or service rises, it will become more profitable to sell that good or service.
If there are greater potential profits, it is reasonable to expect that producers will wish to produce more. Therefore a rise in price will lead to an increase in the quantity supplied.
CAUSES OF SHIFTS IN MARKET SUPPLY CURVE
Changes in the unit costs of production
Lower unit costs mean a business can supply more at each price
Higher unit costs cause an inward shift of supply perhaps due to a rise in wage rates or an increase in prices of raw materials
A fall (depreciation) in the exchange rate causes an increase in the prices of imported components and raw materials
Advances in production technologies – causes outward shift of supply