Human reproduction 2
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
zoology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
primary oocyte is formed______ and arrested in ___
formed before birth and arrested in diplotene of meiosis 1 till puberty
meiosis 1 in primary oocyte starts before birth
true false
true
secondary oocyte starts meiosis 2 and arrested in_____
arrested in metaphase 2
process of oogenesis
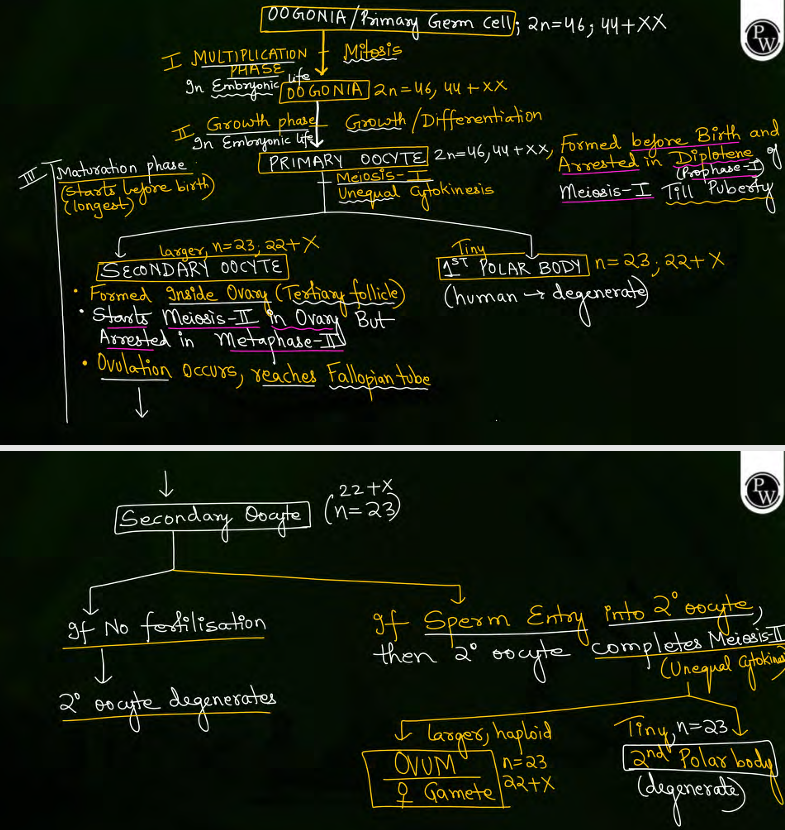
how many oogonia formed before birth and by how many weeks of preganancy
7 million/ couple of million acc to ncert formed before birth
by 20-22 weeks of pregnancy
no more oogonia are formed or added after birth
true false
true
primordial follicle number at birth and in puberty
birth= 2 million per ovary
puberty= 2 lac per ovary
primary follicle number at puberty
and structure
60,000- 80,000 per ovary
single layer of cuboidal follicular cells
primary follicle is present from birth till puberty
true false
false
primordial follicle present from birth till puberty
new theca layer and multilayered follicular cells present in which follicle
secondary follicle
secondary follicle has____ oocyte
primary oocyte in diplotene stage
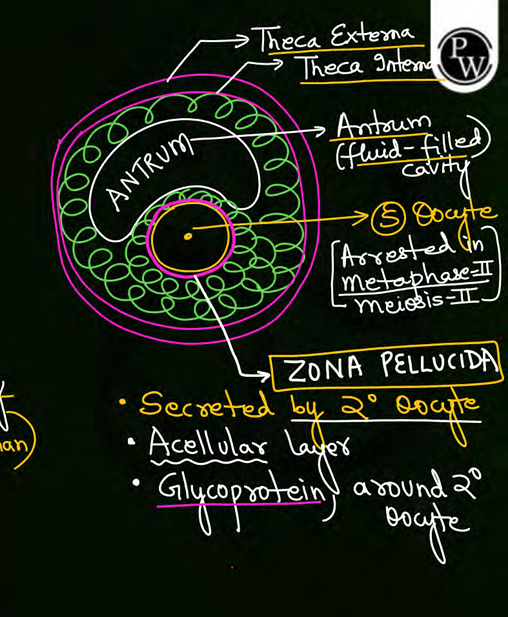
In tertiary follicle primary oocyte is in which stage
it completes meiosis 1 and forms secondary oocyte in metaphase 2
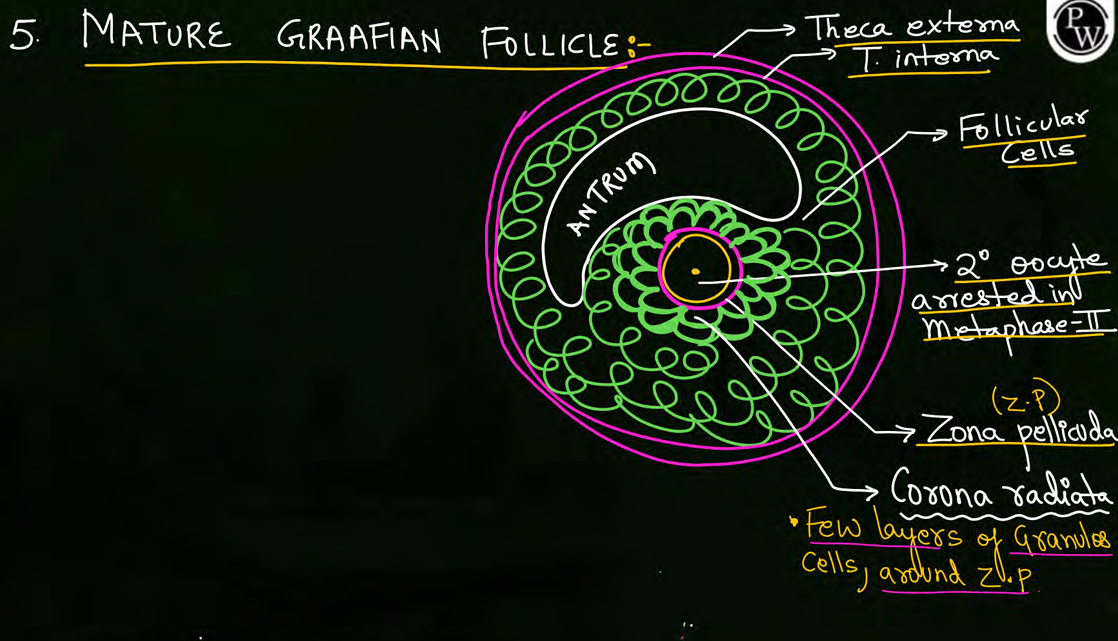
all layers in tertiary follicle
layers of mature graafian follicle
how secondary oocyte released from granulosa cells
granulosa cells secrete estrogen which is responsible for endometrium proliferation
endometrium proliferation leads to LH surge
this LH surge is responsible for secondary oocyte release
why unequal cell division occur in oogenesis
unequal cell division occurs to retain most of the cytoplasm in female gamete because sperm has very less amount of cytoplasm
ovum is formed only if fertilisation occurs
secondary oocyte formed every month
true false
true
colostrum is rich in ____ except_____
vitamins minerals and fats
except vitamin c and iron
colostrum has antibody
IgA

C
corpus luteum is glandular because it secretes hormones like
lots of progesterone
little estrogen
relaxin hormone at end of pregnancy
inhibin hormone which inhibits fsh
inhibin hormone secreted by
corpus luteum
granulosa cells
sertoli cells
corpus luteum changes into____ if fertilisation does not occur
white, non-glandular corpus albicans
hormone regulation in females after forming fsh and lh
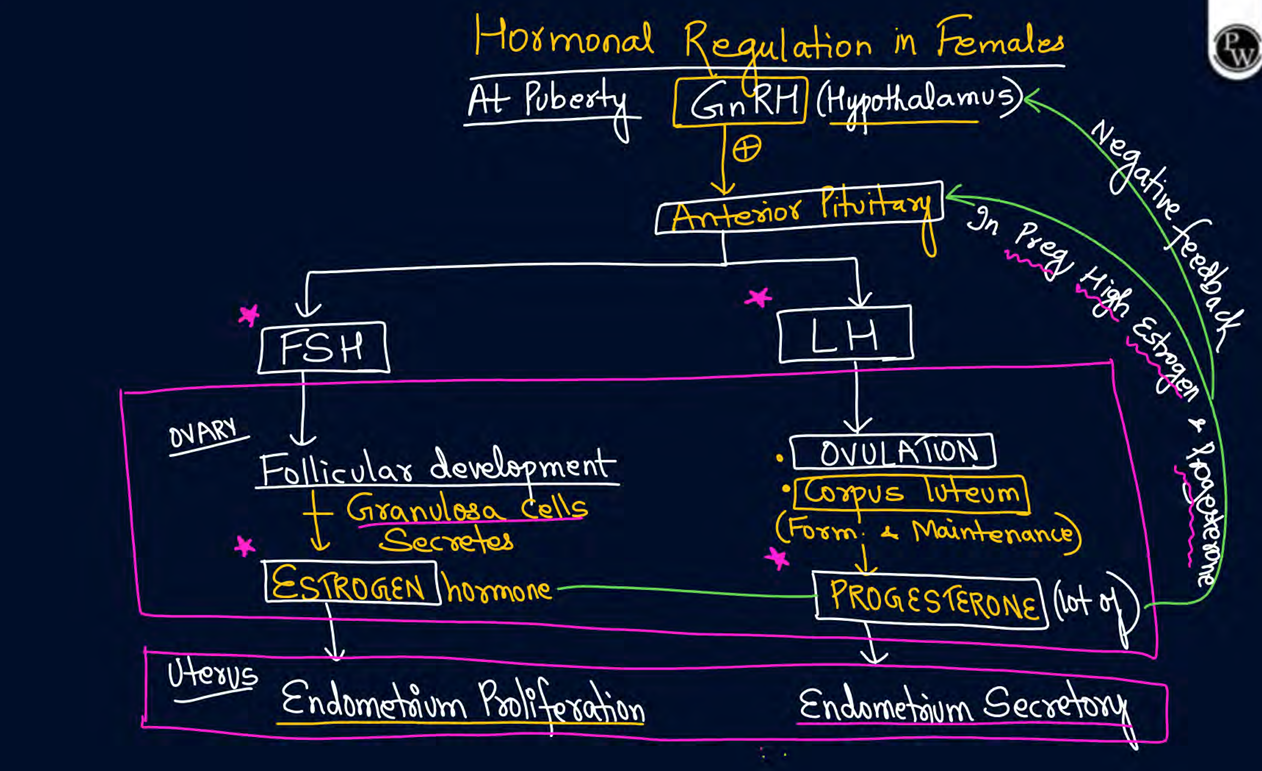
During pregnancy FSH and LH is high
true false
false
fsh and lh low
estrogen and progesterone high
How does LH maintain pregnancy
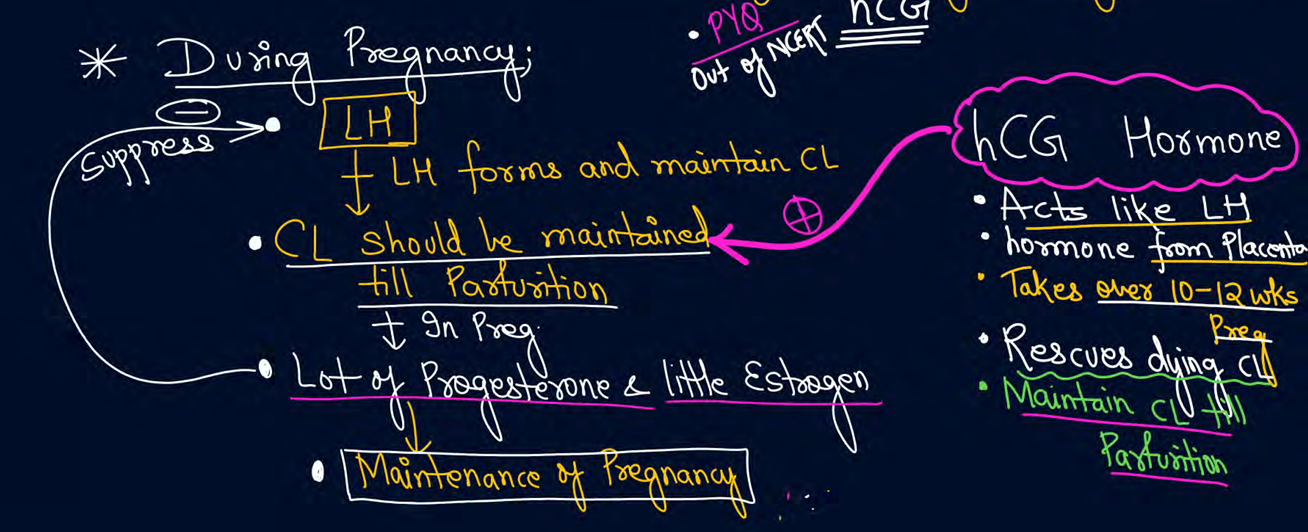
graafian follicles are formed from

growth of corpus luteum is initiated by
LH
sequence of layers of mammalian egg from outside to inside
corona radiata, zona pellucida, plasma membrane
during oogenesis each diploid cell produces
one functional egg and three polar bodies
how many eggs will be formed from 100 primary oocyte
100 eggs
how many mature eggs are produced by each ovary of a non pregnant woman each year
6


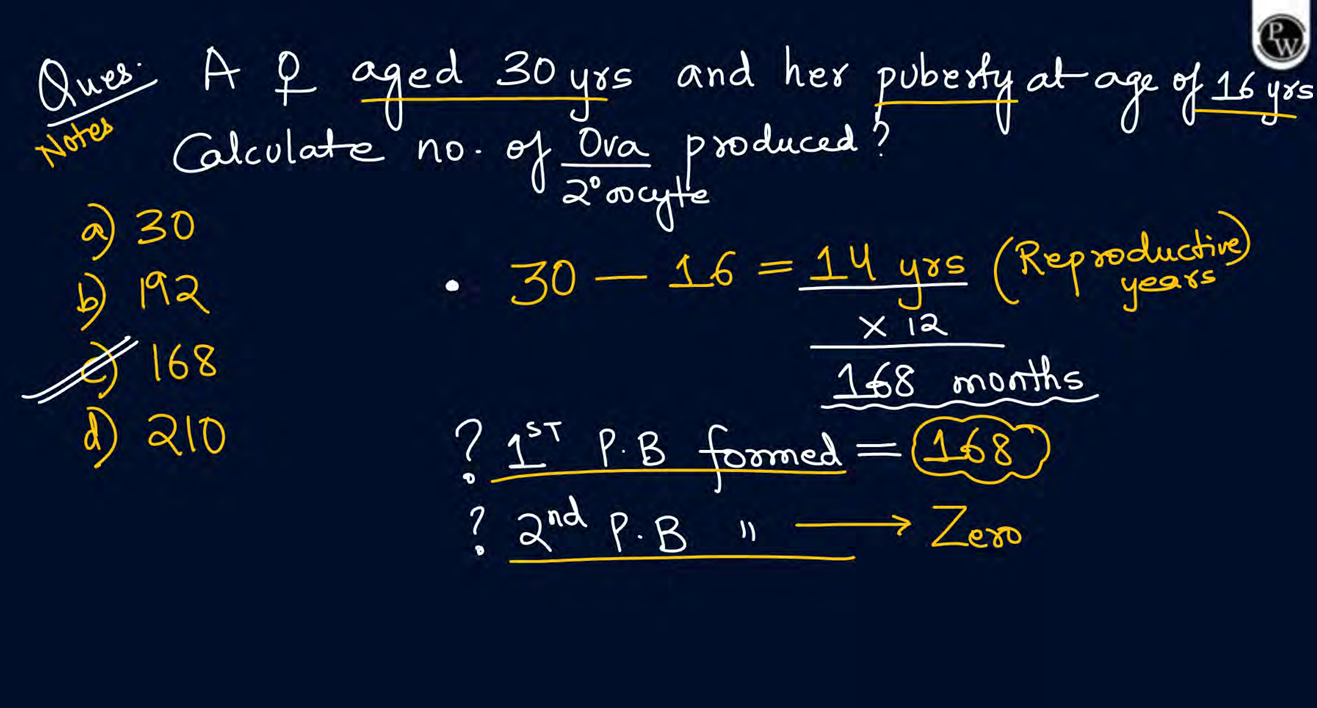

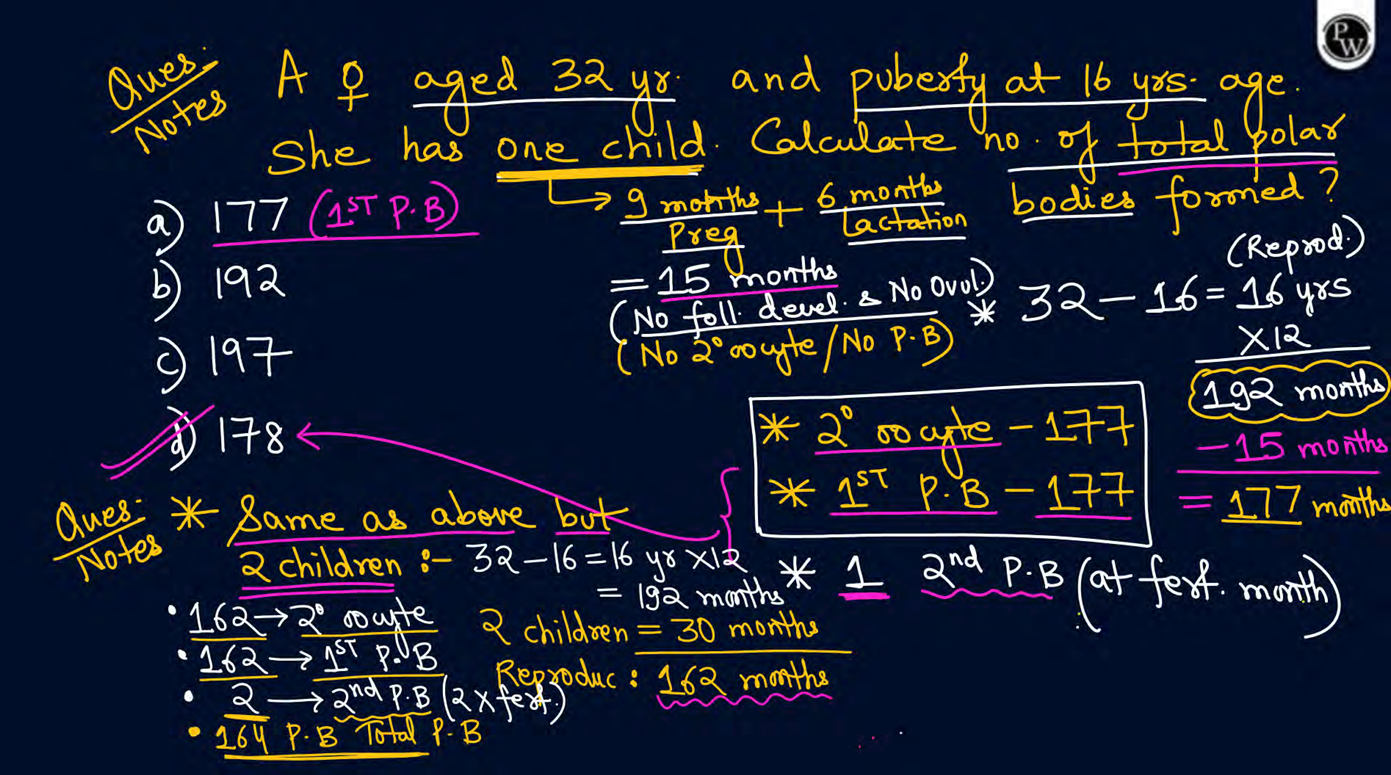
Ovarian events with their reason of occurence
FOL
follicular phase- due to increase in FSH
ovulatory phase- due to increase in LH
luteal phase- due to increase in LH
uterine events with their reason of occurence
MPS
menstrual phase- due to decrease in estrogen and progesterone
proliferative phase- due to increase in estrogen
secretory phase- increase in progesterone
FSH LH is at peak during
ovulation or ovulatory phase
estrogen and progesterone is at peak during
estrogen= ovulatory+ secrotory/luteal phase
progesterone= luteal phase
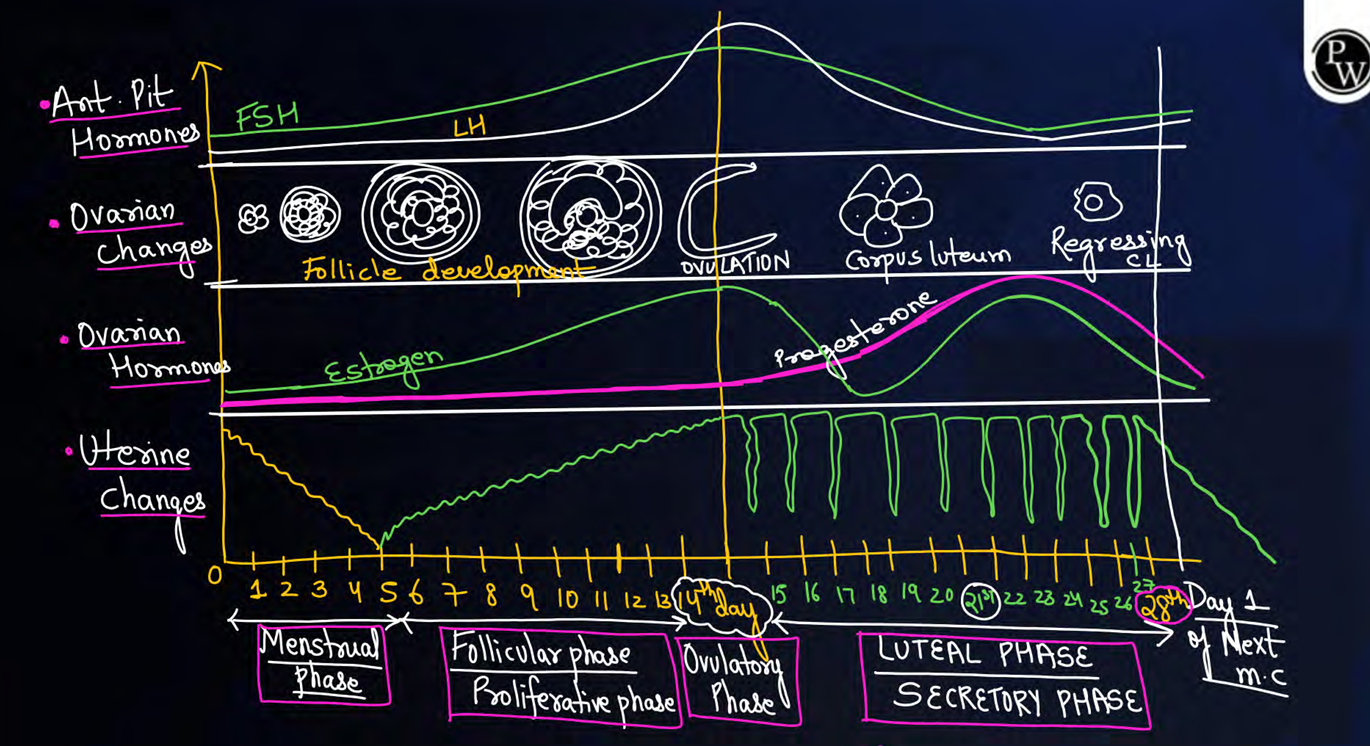
day of ovulation formula
menstrual cycle-14 days
after menopause
FSH, estrogen and progesterone levels increase or decrease
FSH increase
estrogen and progesterone decrease
corpus luteum secrete
lots of progesterone and little estrogen
egg viability is ___ hours
24-48 hours
or 1-2 days
sperm viability in female reproductive tract is
48-72 hours
upto 5 days
events of male and female gametes from gamete transfer to fertilisation is
capacitation-physiological maturation of the sperms so that they become competent to fertilize an oocyte
agglutination- sticking of sperms
Acrosomal reaction
fast and slow block to polyspermy
fertilisation
cementing layer between cells of corona radiata is formed by
hyaluronic acid (polysaccharids)
perivitteline space is space between
plasma membrane of 2’ oocyte and zona pellucida

luteal= sceretory= pre-menstrual

learn
which hormone stimulates the buildup of endometrium
estrogen
what is capacitation in terms of sperm
physiological maturation of sperm inside female reproductive tract
capacitation takes ___ hours to make sperms more capable to fertilize ovum
6-7 hours
capacitation has 2 processes namely
Ca+ influx= sperm motility increase
destablisation of plasma membrane= dissolution of cholestrol and removal of glycoprotein
agglutination is a process which ensures
that same species gamete fertilise each other
responsible for reproductive isolation
species specific
antifertilisin and fertilisin is present on ___ and __ respectively
antifertilisin and fertilisin is chemically ____and ____
sperm, ovum
acidic, glycoprotein
these two chemicals attract each other
what is acrosomal reaction process
sperm touches zona pellucida
acrosome burst and release sperm lysins
secretions of acrosomes help sperm pass through zona pellucida and plasma membrane
sperm lysin enzymes are
hyaluronidase= digest hyaluronic acid
corona penetrating enzyme= digest corona radiata cells
zona lysin= digest zona pellucida cells
what is fast block to polyspermy
temporary
when sperm comes in contact with plasma membrane
plasma membrane formes a fertilisation cone
Na+ influx into 2’ oocyte
depolarisation of plasma membrane(inner+, outer-)
what is slow block to polyspermy
permanent. cortical reaction
when membrane depolarised
induces ser to release Ca+ ions into cytoplasm
exocytosis of cortical granulles into perivitteline space
zona pellucida become hard and thick so no more sperm can fertilise
entry of sperm in cytoplasm of 2’ oocyte induces
completion of meiosis 2 in sec oocyte arrested in metaphase 2 of meiosis 2
pregnancy begins with
implantation of blastocyst
high level of hcG stimulates the synthesis of
estrogen and progesterone
zygote to blastocyst stages with time taken
day1= fertilisation
day2 or 30 hours after fertilization= 2 celled
day2 or 40 hours after fertilization= 4 celled
day 3 or 72 hours after fertilization= 8 celled morula
day4= 16 celled morula
32 celled blastocyst at day 5
cleavage division starts when
zygote moves through isthmus into uterus as 2/4/8/16 daughter cell or blastomeres
size of blastomere goes on___
size of embryo____
decreasing
constant
total dna in embryo is increasing
DNA in each blastomere is same
true false
true both
because blastomeres are increasing so total dna increasing
4 points on morula
solid mulberry like
8-16 celled embryo
formed in fallopian tube 3-4 days after fertilisation
zona pellucida intact
3 points blastocyst
formed in uterus at day 5 of fertilisation
hollow with cavity called blastocoel
differentiates into inner cell mass and trophoblast
inner cell mass differentiates to form____
embyro
____ forms foetal part of placenta
trophoblast
hCG hormone function
rescue dying corpus luteum
acts like LH
trophoblast secrete which enzyme and hormone
enzyme for digestion of zona pellucida
hCG hormone

blatula has blatocoel
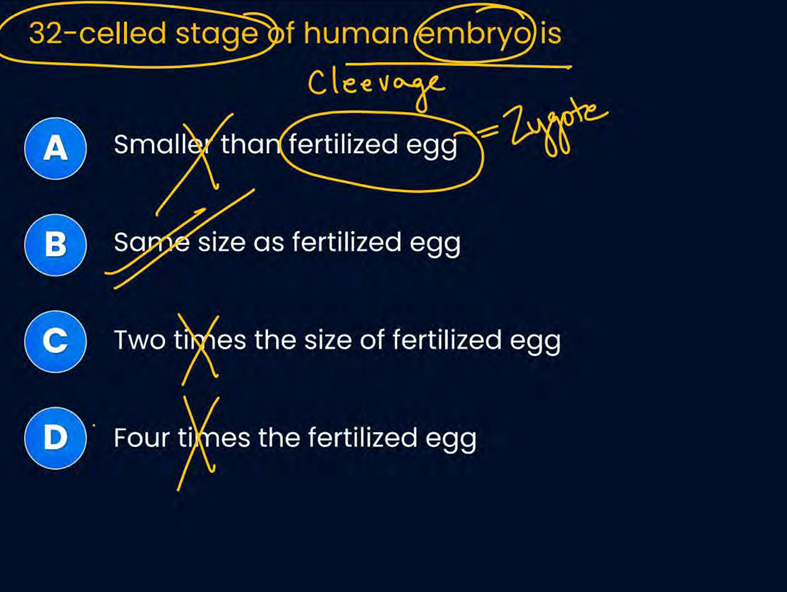
32 celled stage of embryo is larger than size of fertilised egg
true false
false
32 celled stage is same size as fertilised egg
morula has same amount of cytoplasm and dna as in zyote
true false
false
same cytoplasm more dna
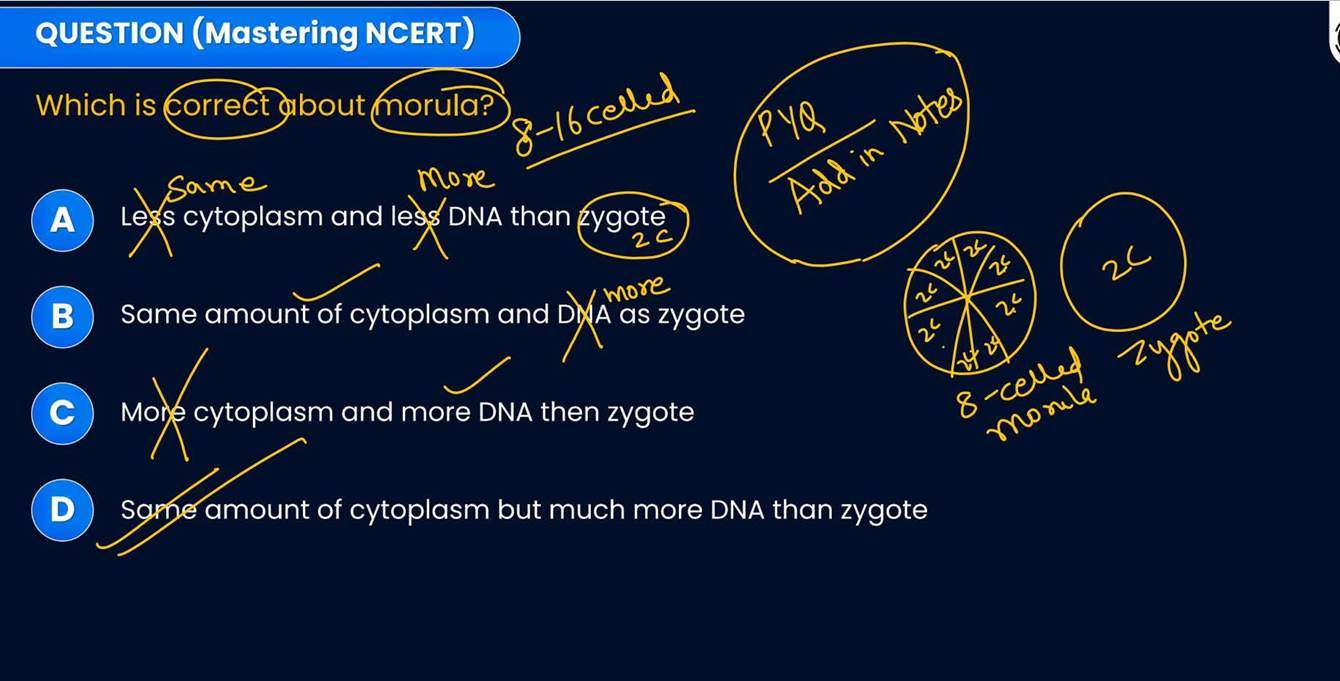

repeat all four lines
implantation occurs on day_____
6-7 days after fertilisation
which hormone is basis for pregnancy test
hCG
if 2 pregnant women has ovarian cyst. one of them has gestation period less than 3 months and other more than 3 months then
less than 3 months abortion is to be done after removing ovaries because progesterone secreted only by corpus luteum of ovary
more than 3 months can continue after removing ovary because progesterone secreted by both corpus luteum and placenta
formation of extra embryonic membranes start from
2nd week