Apes vocab, all units
1/122
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
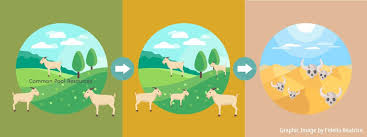
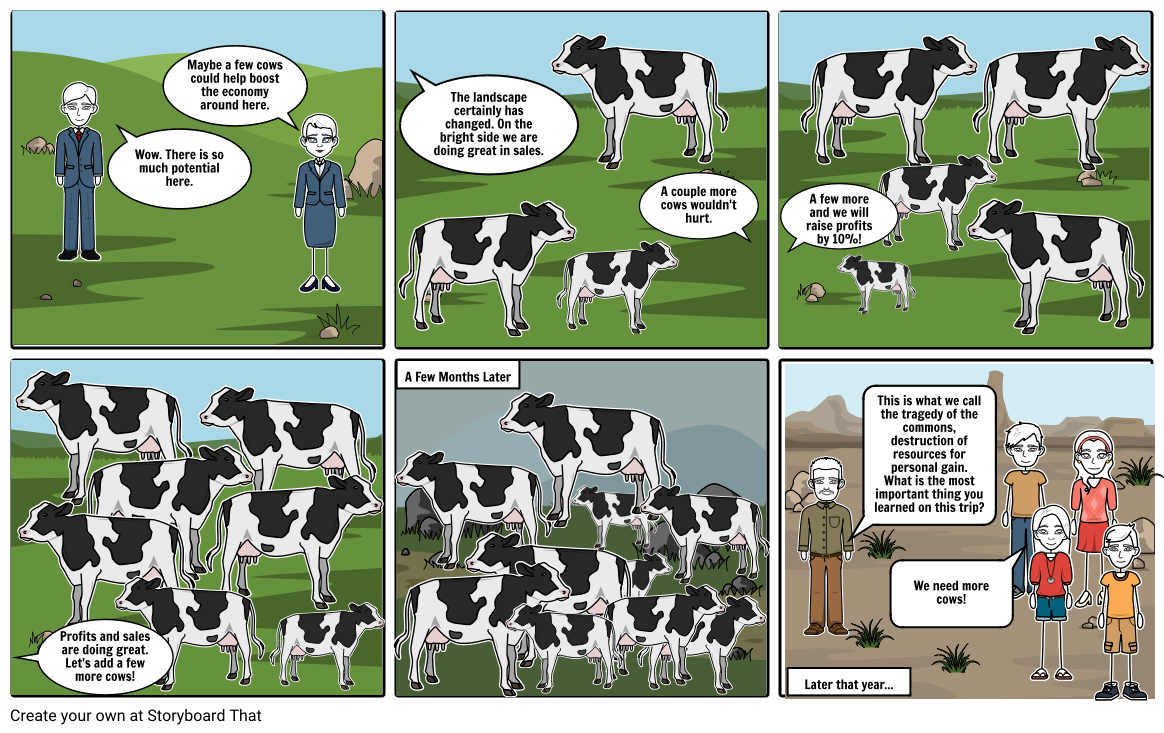
Tragedy of the commons
The tragedy of the commons summarizes a situation in which individuals over consume resources that are publicly accessible to satisfy their desires, which in result depletes that resource.

Sustainability
Sustainability is the capacity of the earth’s natural systems that support life and human social systems

Contour plowing
a farming practice where land is plowed and planted across a slope, following the natural curves of the land, rather than up and down the slope
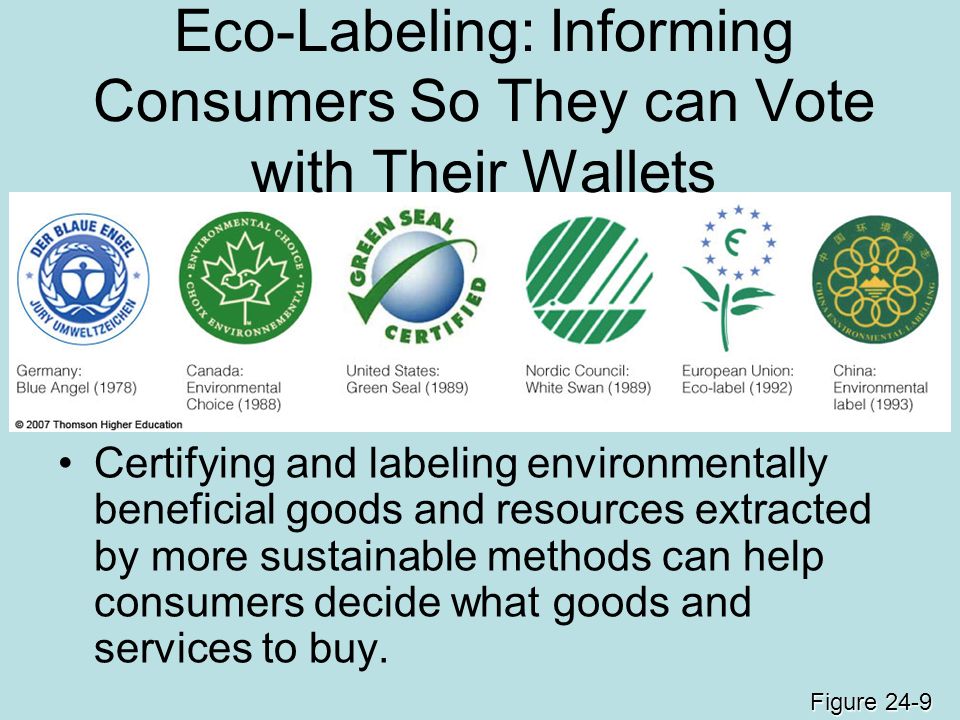
full cost pricing
full cost pricing is a practice that gives consumers information about the harmful environmental impacts of products that they buyv
Biodiversity
The variety of genes, species, ecosystems, and ecosystem processes.

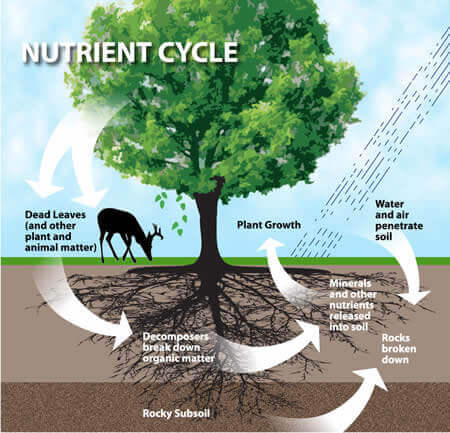
Chemical cycling
The circulation of chemicals/ nutrients needed to sustain life from the environment through various organisms and back to the envionment

Ecological footprint
The amount of biologically productive land and water needed to supply a population in an area

poverty
People lack enough money to fulfill their basic needs for food, water, shelter, health care, and education.

Subsidy
A tax break given by the government to businesses to help them grow their business
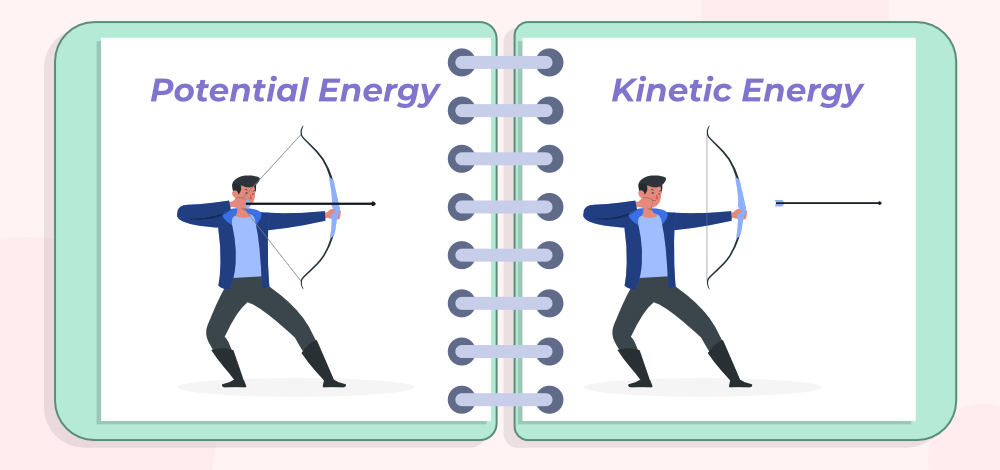
Kinetic energy Ex:flowing water, a car speeding down the highway, wind
Moving energy
Thermal energy
The total kinetic energy of all moving atoms, ions, or molecules in an object
Potential energy
Energy stored in an object due to its position or arrangement
Law of conservation of energy
When energy is converted from one form to another, no energy is created or destroyed
Second law of thermodynamics
When energy is converted from on form to anther, we end up with lower-quality or less-usable energy then we started with
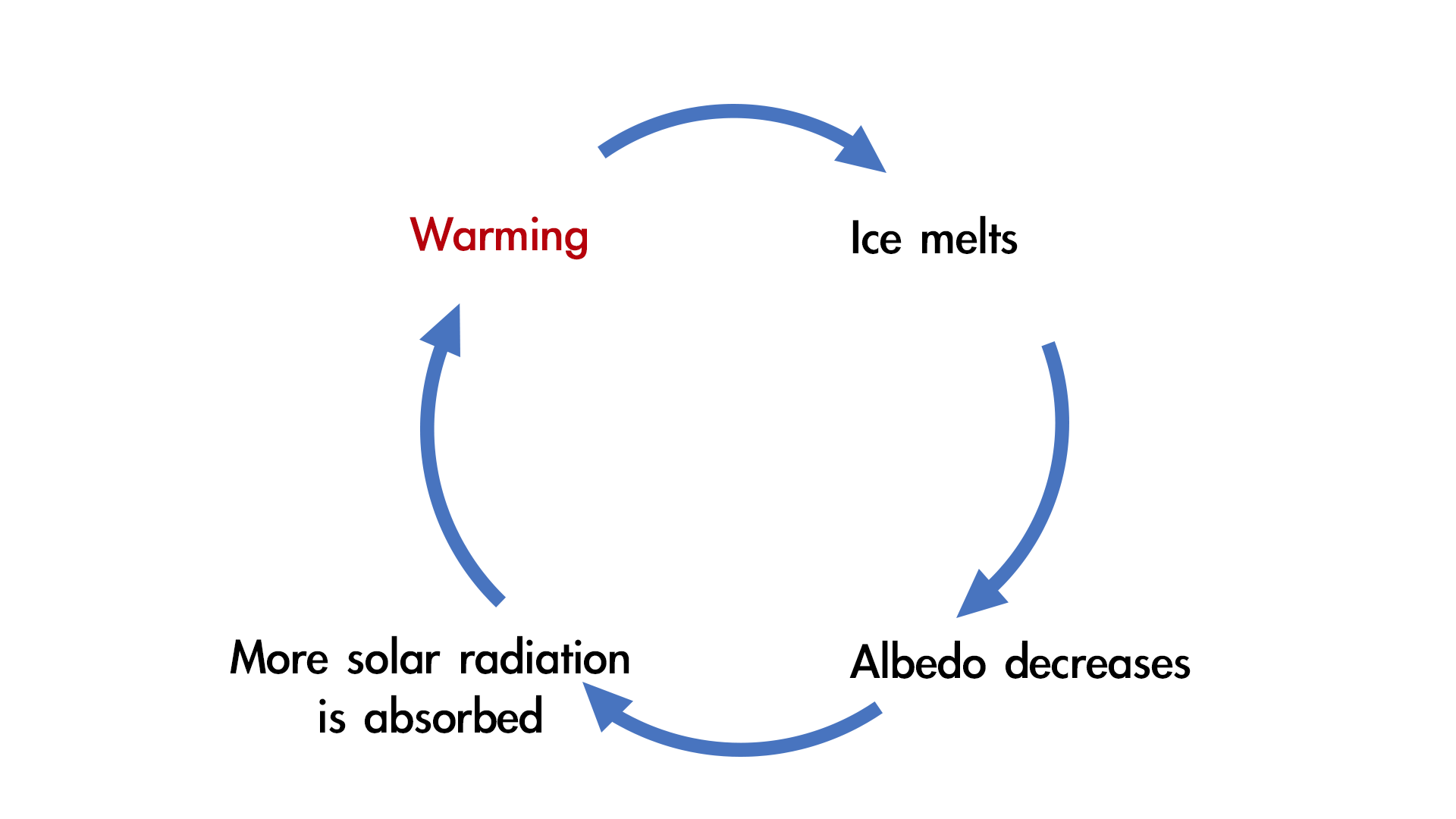
Positive feedback loop
the output of a process enhances or amplifies the input, leading to a continuous cycle of increasing or decreasing change.
negative feedback loop
the output of a system is used to reduce the initial input
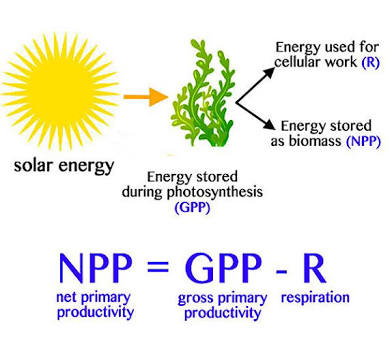
Gross primary productivity (GPP)
The rate at which an ecosystems producers convert solar energy into chemical energy stored in compounds found in their tissues
Net primary productivity
Rate at which producers use photosynthesis to produce and store chemical energy minus the rate at which they use some of the store chemical energy through aerobic respiration
Surface runoff
water flowing off the land into bodies of surface water
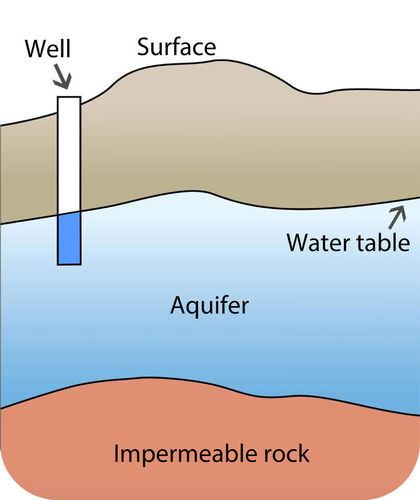
Aquifers
Water-saturated layers of sand, gravel, or bedrock that can yield an economically significant amount of water
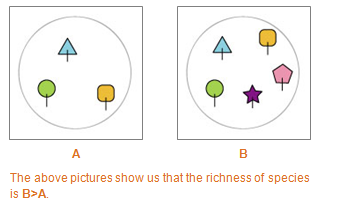
species richness
The number of different species in an ecosystem
Species evenness
A measure of the comparative abundance of all species in an ecosystem
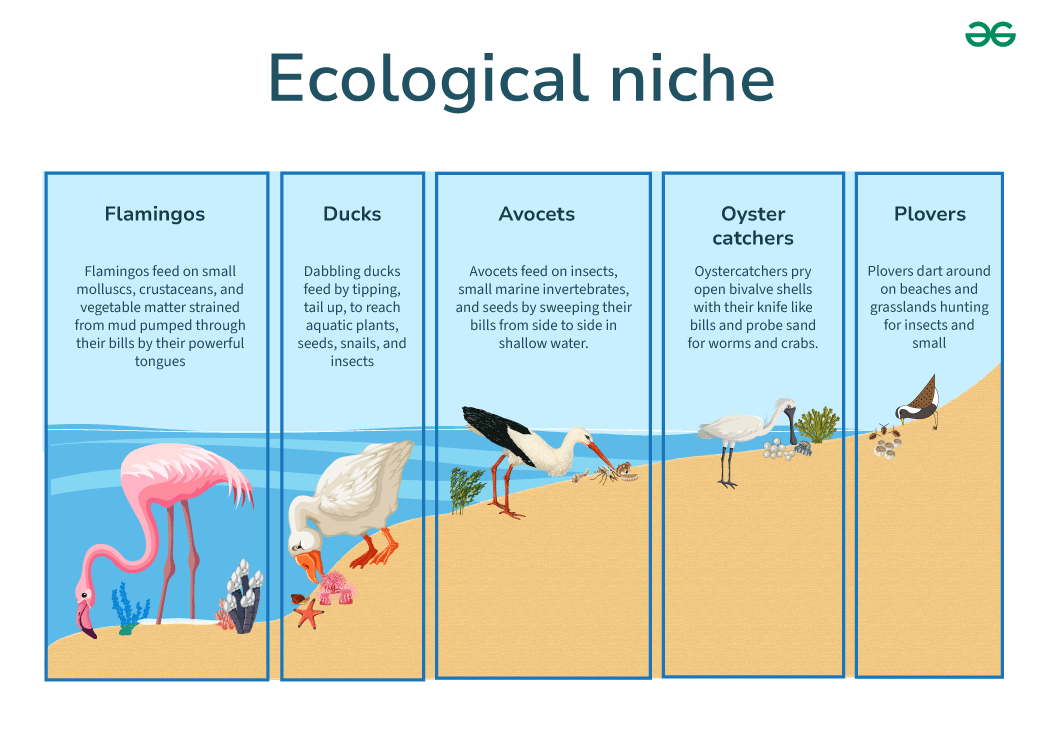
Ecological niche
A species way of life in its ecosystem and includes everything that affects its survival and reproduction

Specialist species
Species with a narrow ecological niche; they are able to live in only one type of habitat, tolerate only a narrow range of climatic and other environmental conditions.

Generalists species
Species that can live in many different places, eat a variety of foods, and can tolerate a wide range of environmental conditions.
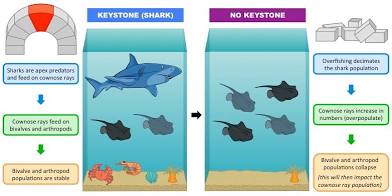
Keystone species
A species has a disproportionately large impact on a ecosystem
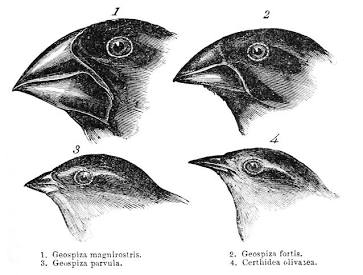
Biological evolution
The process by which the earth’s life forms change genetically over time.

endemic species
a plant or animal species that is exclusively found in a specific geographic area
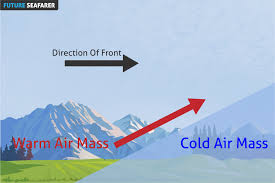
Warm front
The boundary between an advancing warm air mass and the cooler one
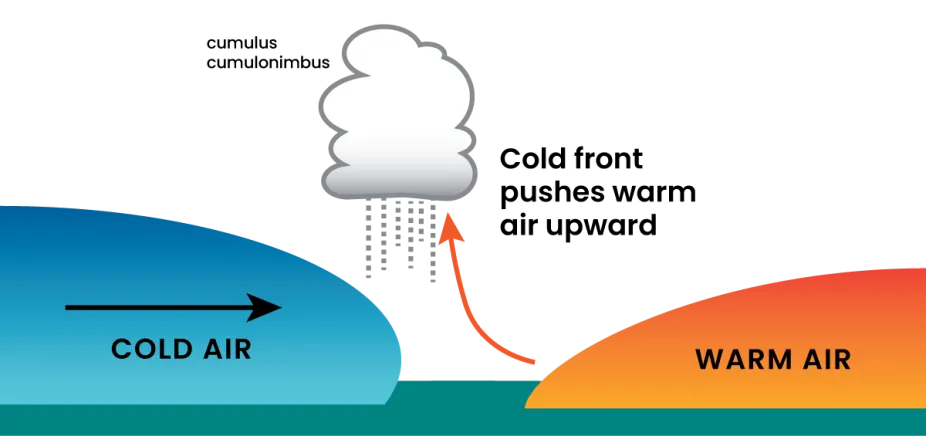
Cold front
The leading edge of an advancing mass of cold air
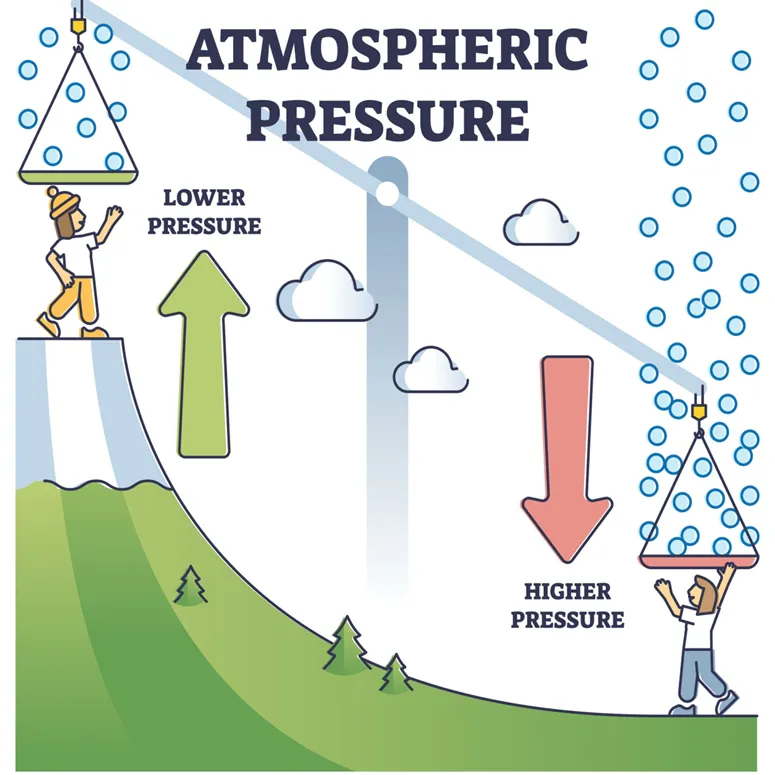
Atmospheric pressure
Molecules of gases in the atmosphere zipping around at very high speeds and bouncing off everything they encounter
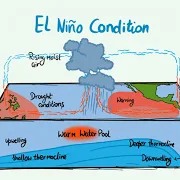
El Nino
Climate pattern where winds that usually blow more or less constantly from east to west weaken or reverse direction
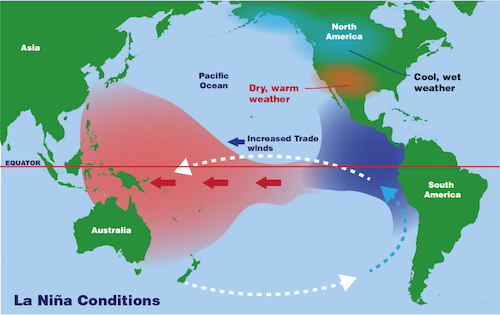
La Nina
La Niña is a natural climate pattern that involves large-scale cooling of the equatorial Pacific Ocean's surface temperatures, along with atmospheric changes.

Tropical cyclones
a rapidly rotating storm system that forms over tropical or subtropical waters and is characterized by low pressure, strong winds, and heavy rain.
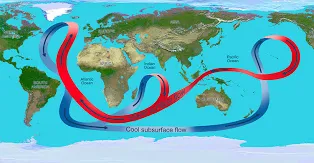
Ocean currents
large, predictable movements of seawater that flow along specific paths across the globe.
convection cell
a circular pattern of fluid movement caused by temperature differences, resulting in rising and sinking motions
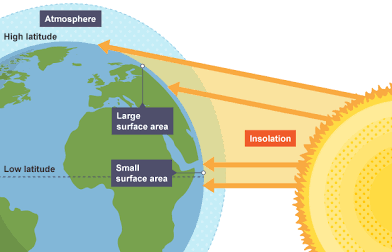
Insolation
The input of solar energy in a given area
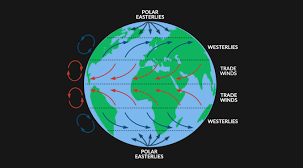
Coriolis effect
The deflection of an object’s path due to the rotation of the earth
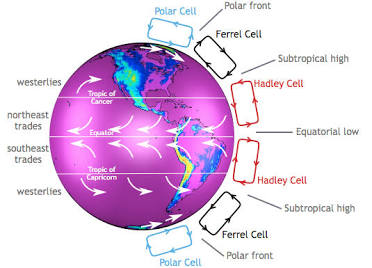
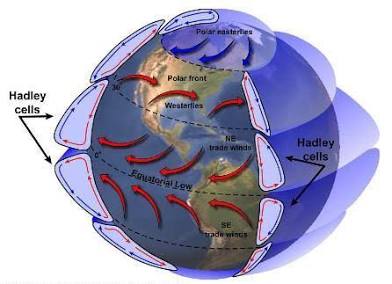
Hadley cell
large-scale atmospheric circulations that transport energy and momentum towards the poles
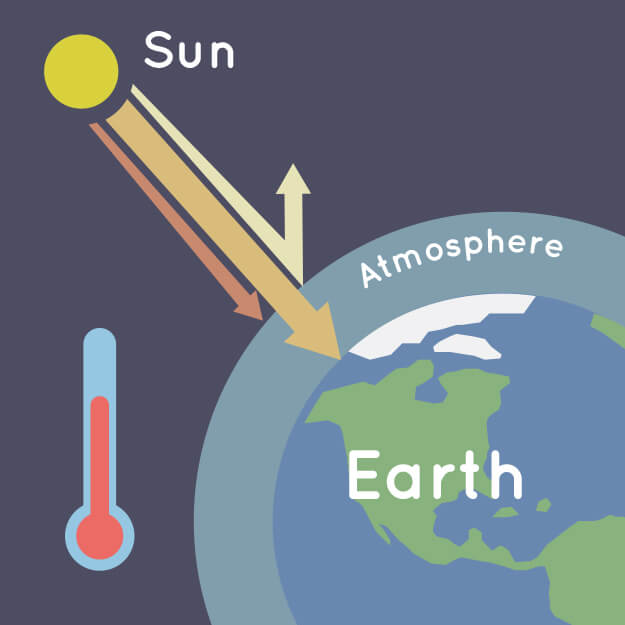
Greenhouse effect
a natural phenomenon where gases in the Earth's atmosphere trap heat, preventing it from escaping into space and warming the planet
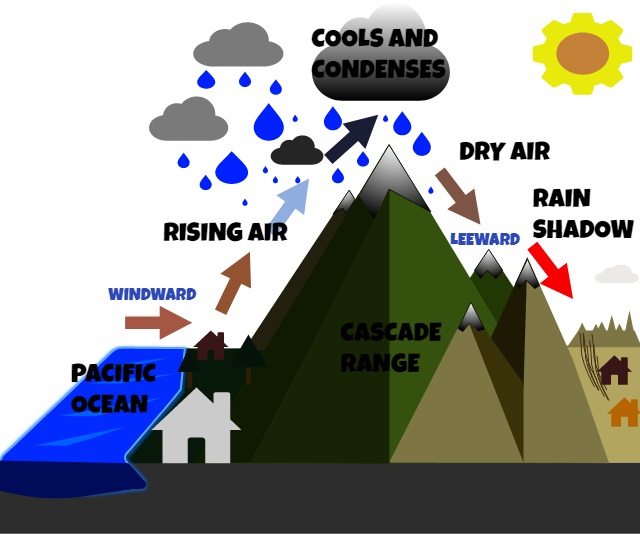
Rain shadow effect
a phenomenon where a region experiences significantly less rainfall on the leeward (downwind) side of a mountain range compared to the windward side

Salinity
The amounts of various salts dissolved in a given volume of water

nekton (fish, turtles, and whales)
Strongly swimming consumers

Benthos (clams, worms, oysters, and sea stars)
Bottom dwellers; organisms that anchor themselves to ocean-bottom structures
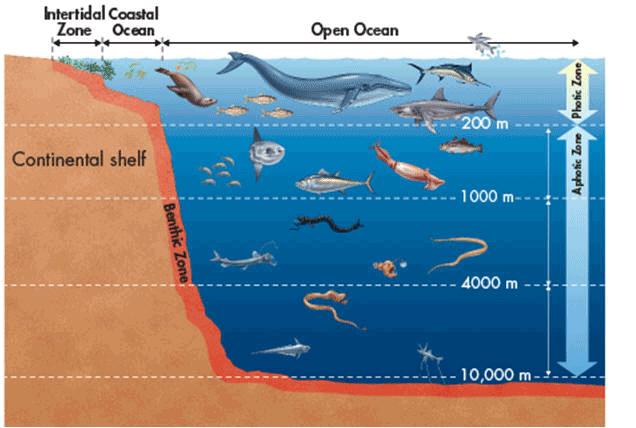
Coastal zone
Warm nutrient rich shallow water that extends from the high-tide mark on land to the shallow edge of the continental shelf.
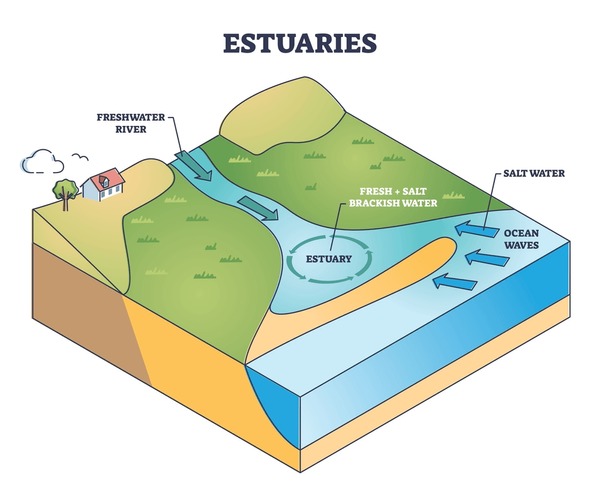
estuary (seawater mixes with fresh water)
Aquatic zone where a river meets the sea.
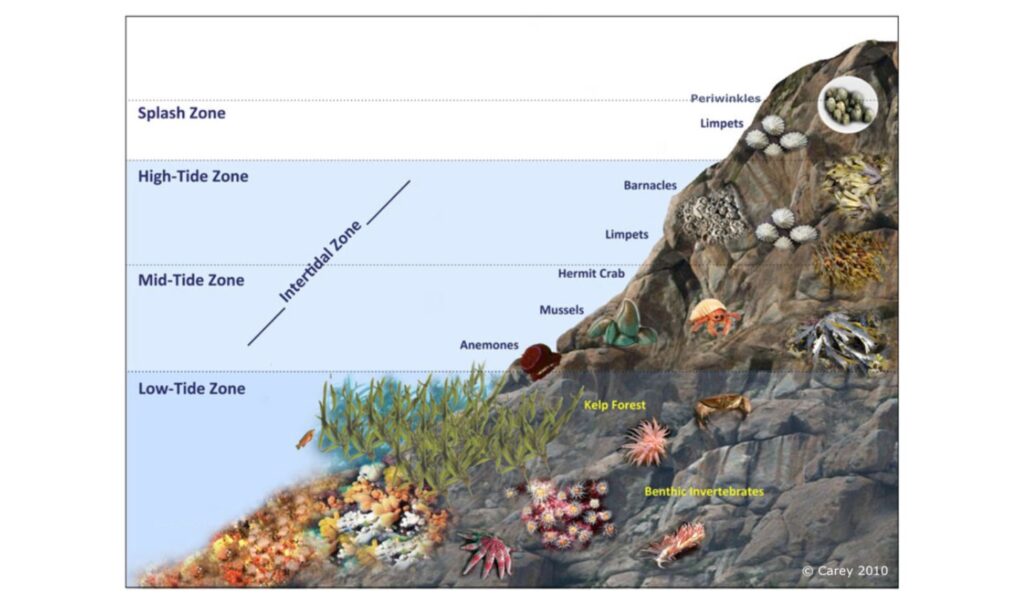
Intertidal zone
The area of shoreline between low and high tides.
Ocean acidification
The rising levels of acidity in ocean waters
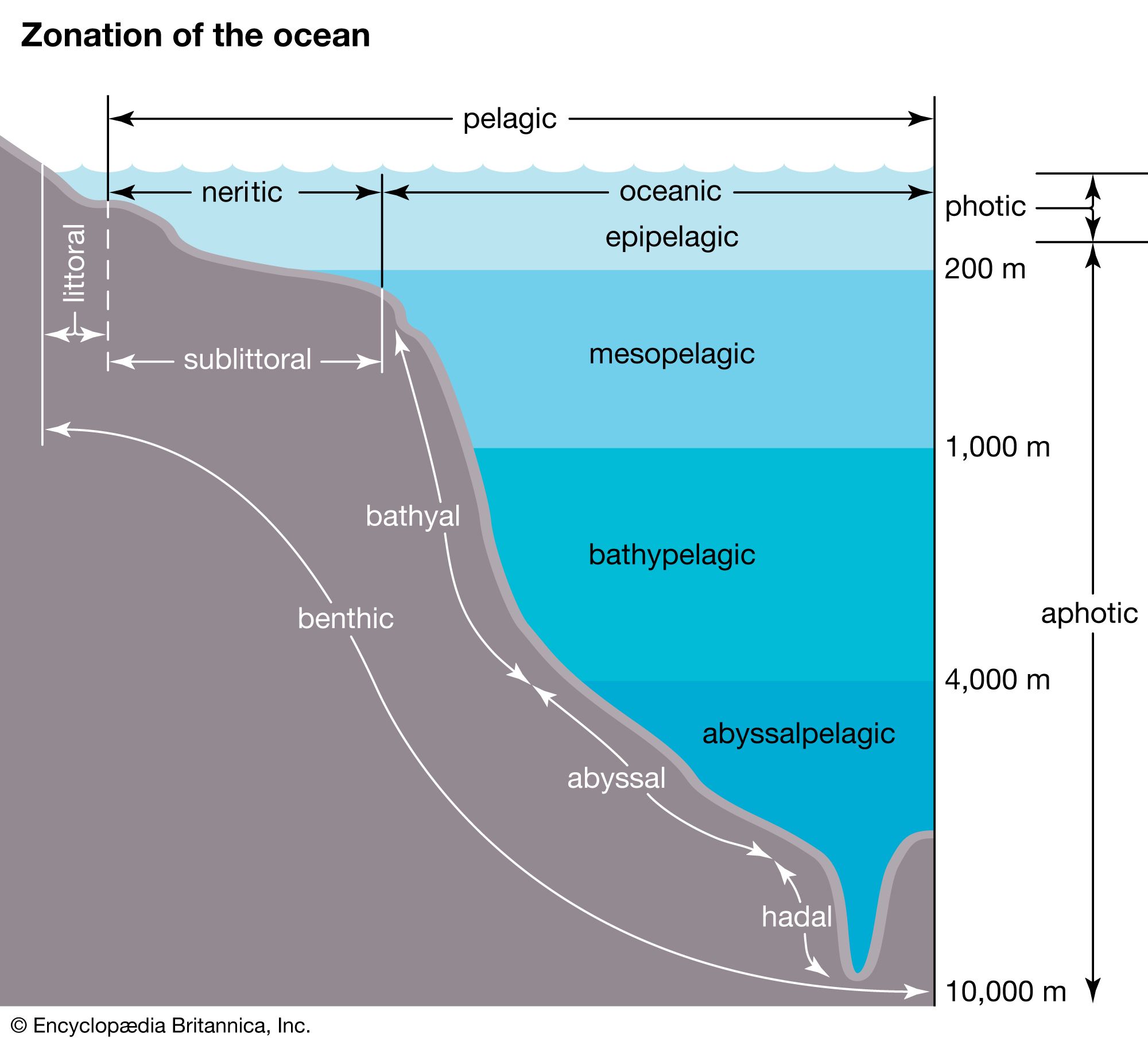
Pelagic zone/ open sea
Part of an ocean that lies beyond the continental shelf
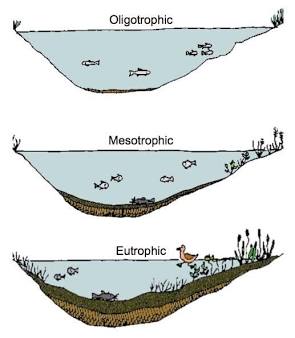
Oligotrophic lake
Lake with a low supply of plant nutrients
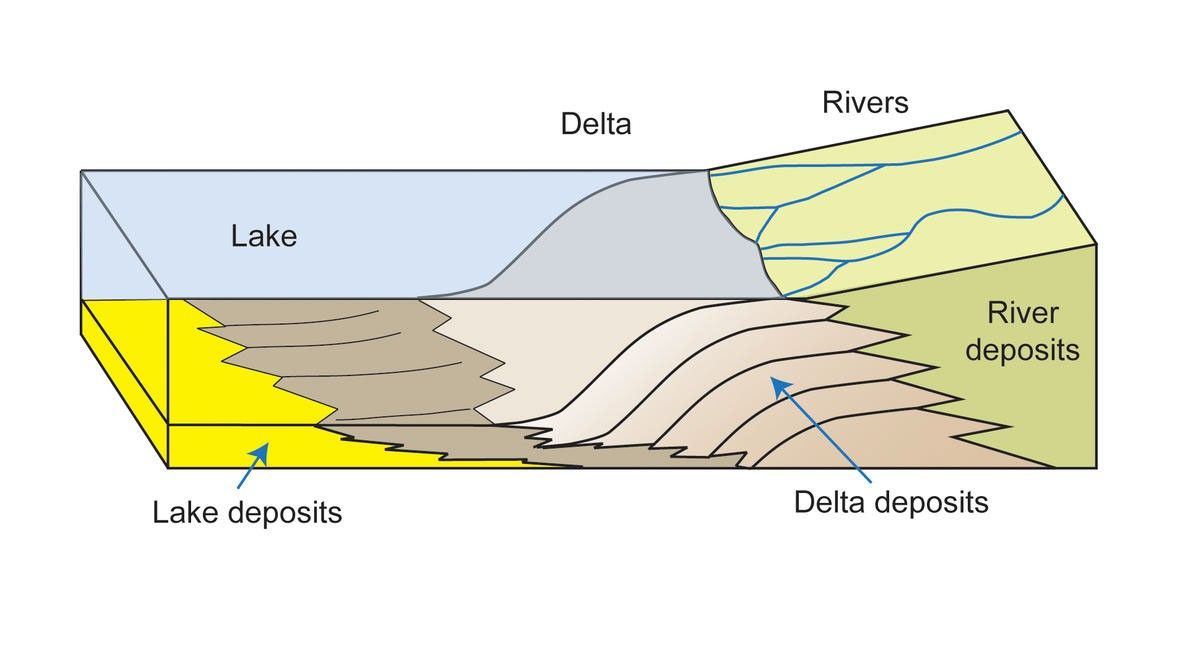
Delta
The area at the mouth of a river built up by deposited sediments, usually containing coastal wetlands and estuaries
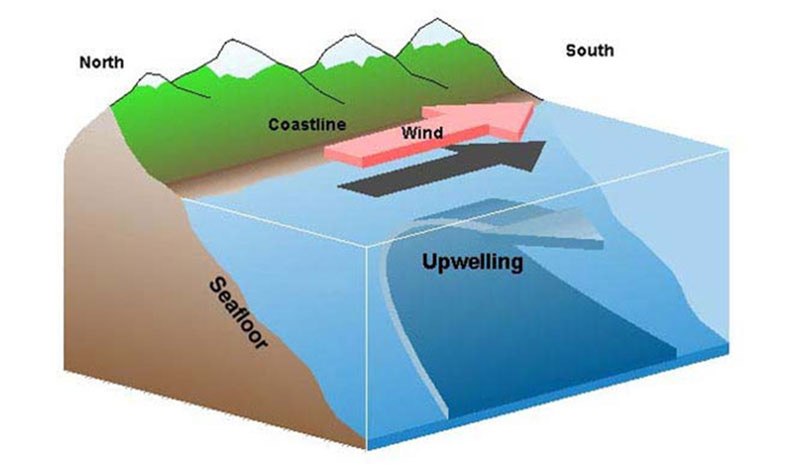
Upwelling
Movement of cold nutrient-rich bottom water to the ocean’s surface
Watershed
an area of land where all water drains into a common body of water, like a stream, lake, or ocean.

Inland wetlands
Lands located away from coastal areas that are covered with freshwater all or part of the time.
Interspecific competition
Completion between different species

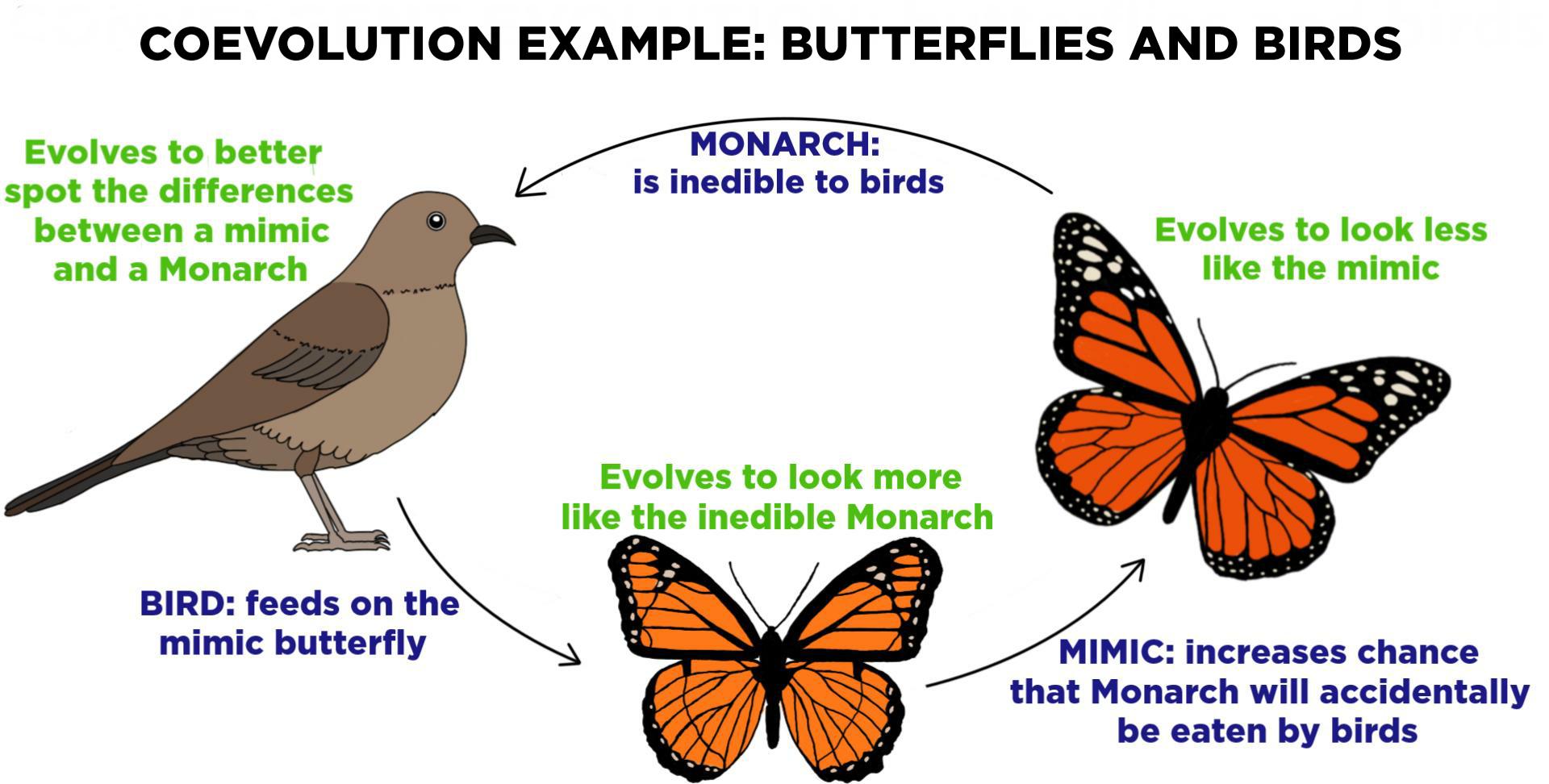
coevolution
A natural selection process in which changes in a gene pool leads to changes in the gene pool of another species
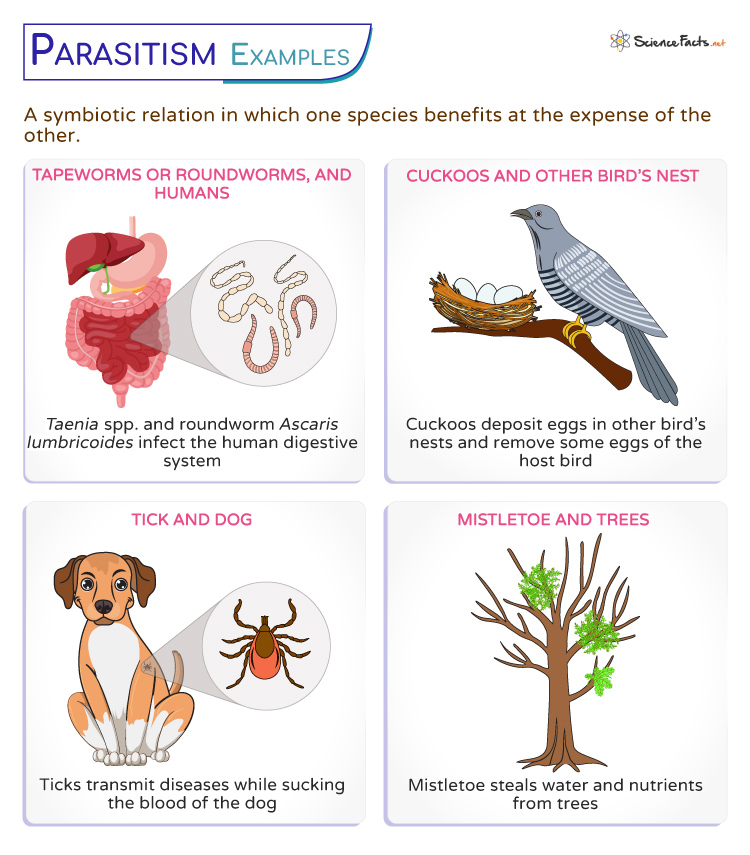
Parasitism (benefits, a parasite weakens its host but rarely kills it)
One species lives in or on another organism.

mutualism
Two species interact in ways that benefit both by providing each with food, shelter, or some other resource.
Commensalism
An interaction that benefits one species, but has little beneficial effects on the other
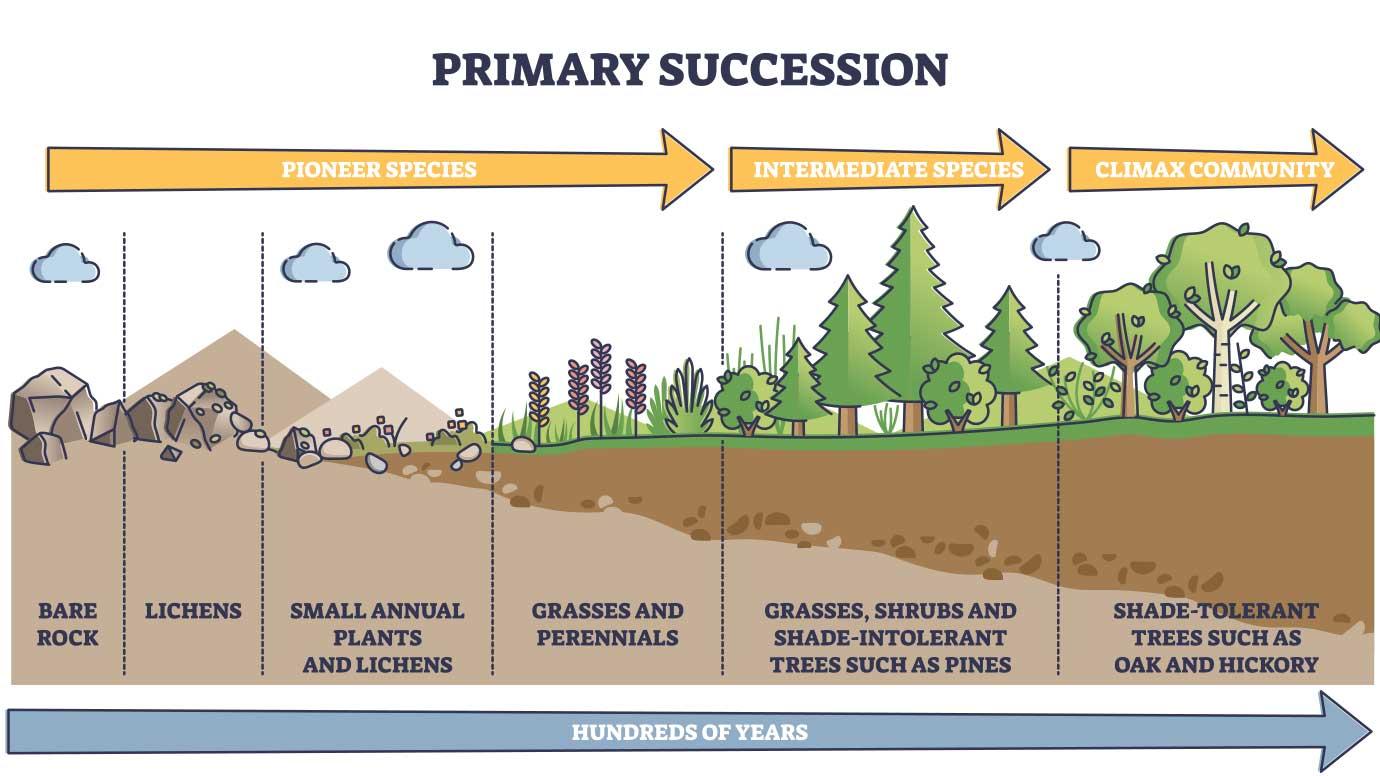
Ecological succession
Gradual change in species composition in a given terrestrial area or aquatic system
Pioneer species
The first species that began colonizing a site as the first stage of ecological succession.
Inertia/persistence
The ability for an ecosystem to survive moderate disturbance

Resilience
The ability of an ecosystem to be restored through secondary ecological succession after a severe disturbance
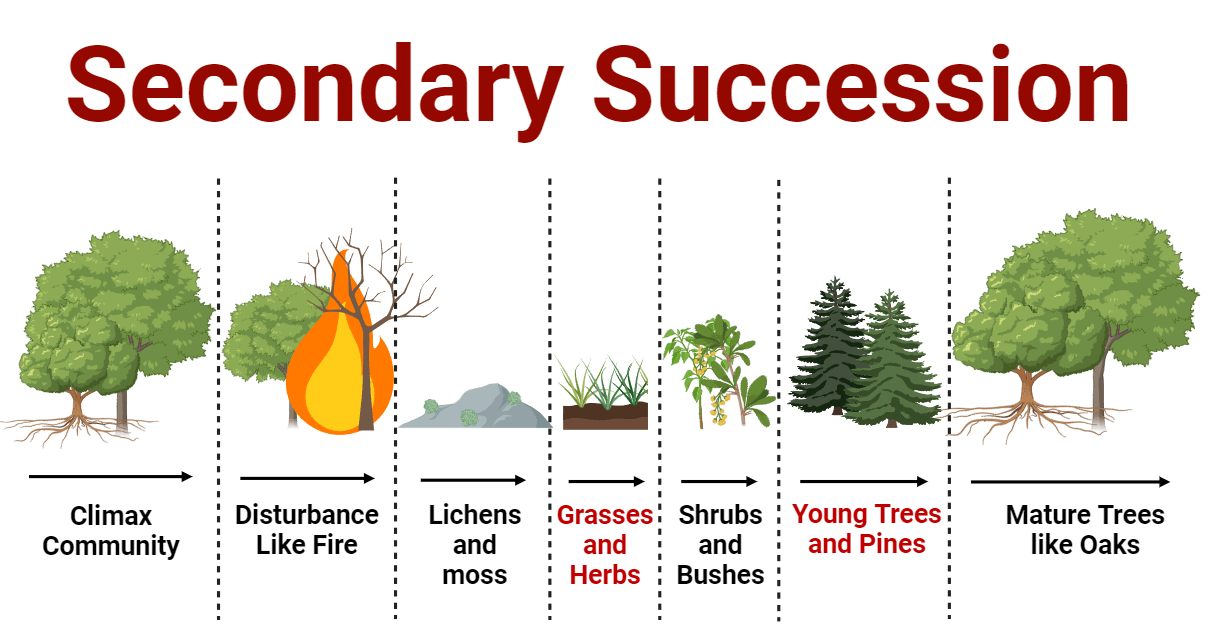
Secondary ecological succession (This type of succession occurs in an area where an ecosystem has been disturbed or destroyed)
A series of terrestrial communities or ecosystems within different species developed in places containing soil or bottom sediment
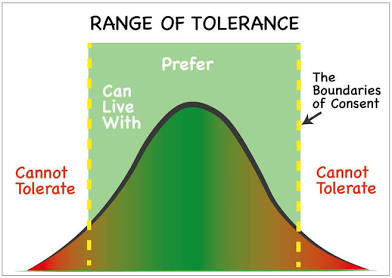
Range of tolerance
The environmental limits that allow a population to survive
Population density
The number of individuals in a population found within a defined area or volume
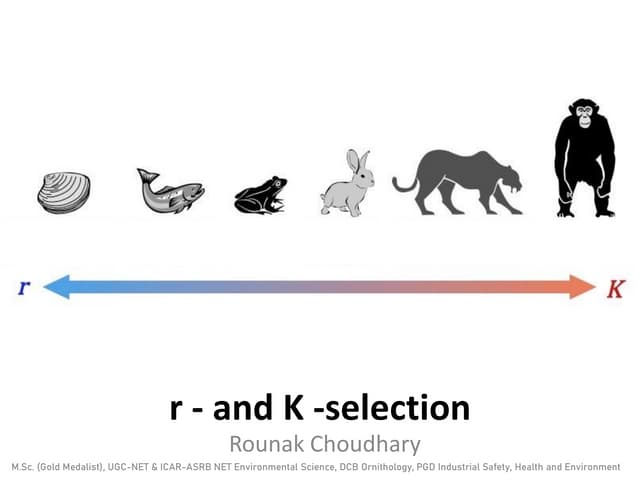
k-selected species (Humans)
Reproduce later in life, have few offspring, and have long life spans
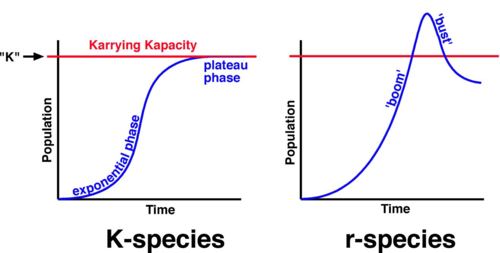
R-selected species (Short life spans and produce many small offspring)
Species with a capacity for a high rate of population growth
replacement level fertility rate
The average number of children that couples in a population must bear to replace themselves.

biological extinction
When a species can no longer be found anywhere on earth.
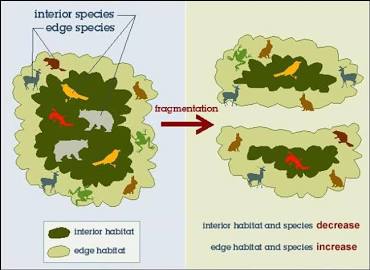
Habitat fragmentation
A large area of a habitat is divided into smaller isolated patches

Old growth forest
An uncut or regrown forest that has not been seriously disturbed by human activities or natural disasters for 200 years or more

Sedimentary rock
Rocks made of sediment, dead plants, animal remains, and particles of weathered and eroded rocks.

Igneous rock
Rock formed below or on the earth’s surface under intense heat and pressure when magmas wells up from the earth’s mantle and then cools and hardens

Metamorphic rock
Rock formes when an existing rock is subjected to high temperatures, high pressures, and or chemically active fluids.
Weathering
Break down of bedrock into smaller pieces that will being the foundation of soil
High-grade ore
High grade ore has a high concentration of desired minerals and fewer impurities
Low-grade ore
Rock containing valuable minerals, but at a relatively low concentration
Reserves
Resources that have been identified and from which a usable mineral can be extracted profitably at present prices with current mining or extraction technology
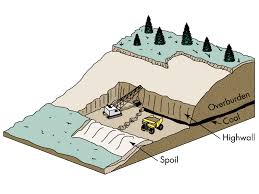
Strip mining
Extracting mineral deposits that lie in large horizontal beds close to earth’s surface
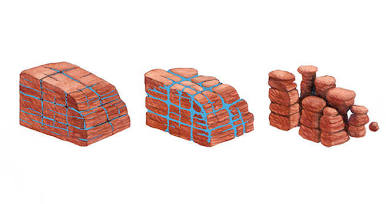
Contour strip mining
Used to mine coal and various mineral resources on hilly or mountainous terrain.
Mountaintop removal
Explosives are used to remove the top of a mountain to expose seams of coal
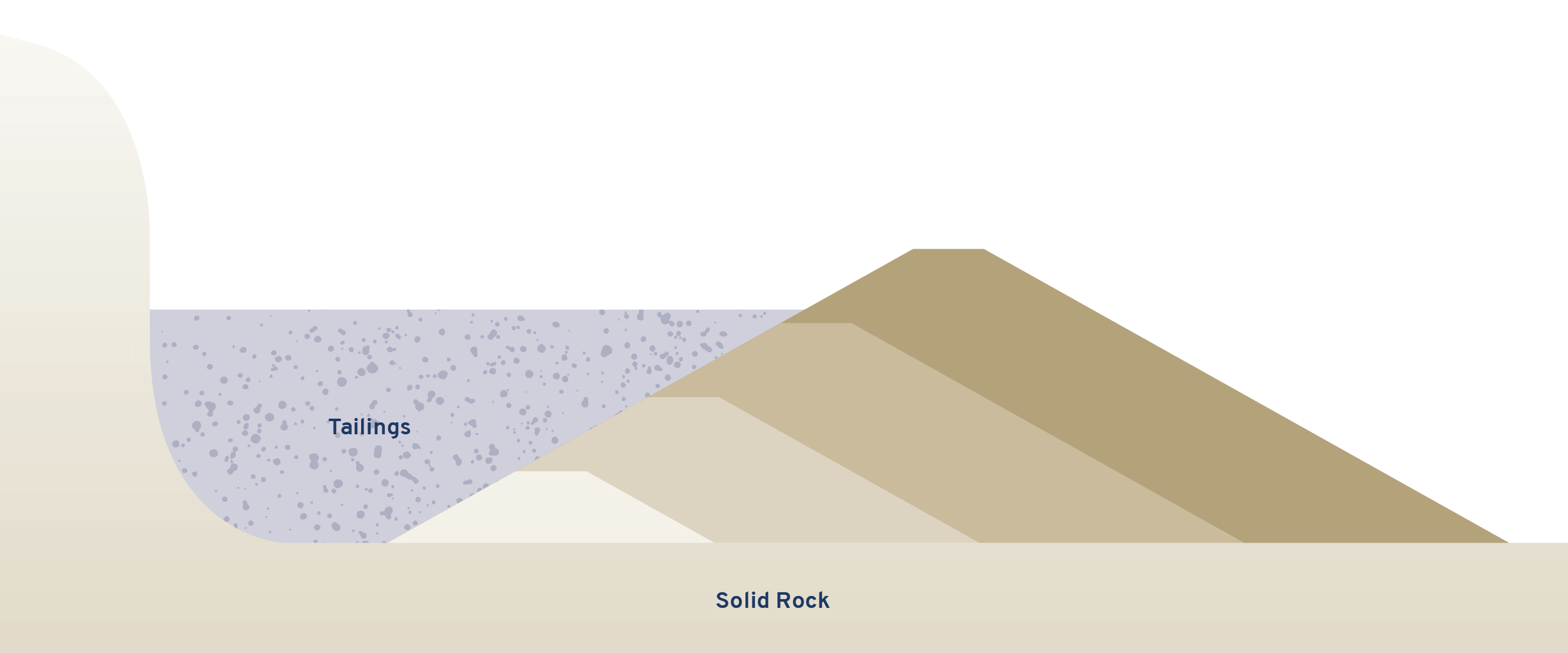
Tailings
Rock wastes that are left in piles or put into ponds where they settle out

Smelting
Heating ores to release metals
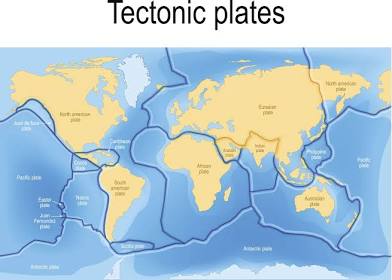
Tectonic plates
Earthquakes and volcanoes
Various-sized areas pf the earths lithosphere that move slowly around with the mantle’s asthenosphere
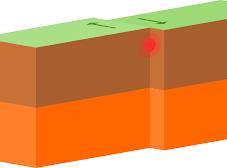
Transform plate boundary
Two tectonic plates slide past each other horizontally
Área where the earth’s lithospheric plates move parallel to each other in opposite directions.
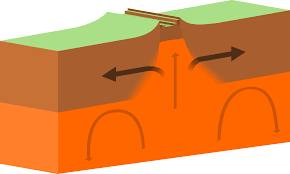
Divergent boundary
Magma flows up where the plates separate, sometimes hardening and forming new crust and sometimes breaking to the surface and causing volcanic eruptions
Two plates move away from each other
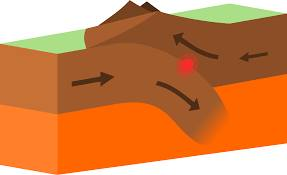
Convergent boundary
Mountain ranges
Two tectonic plates collide with each other Causing one plate to rise up and the other to fall beneath
Chronic malnutrition
A condition where people don’t get enough protein and other key nutrients
Famine
Severe shortage of food in an area which in result can cause mass starvation, death, and economic chaos

Irrigation
A mix of methods by which water is supplied to crops by artificial means
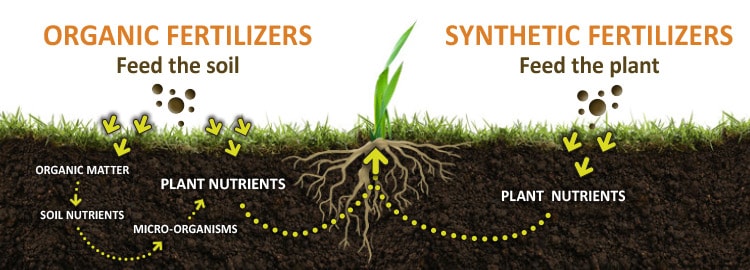
Synthetic fertilizers
Manufactured chemicals that contain nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and several other chemicals.

Synthetic pesticides
Chemical manufactured to kill or control populations of organisms that interfere with crop production

Industrialized agriculture
Heavy equipment and large amounts of financial capital, fossil fuels, water, commercial inorganic fertilizers, and pesticides to produce single cops or monocultures
Yield
The amount of food produced per unit of land.

Traditional subsistence agriculture
Method in which combines energy from the sun with the labor of humans and draft animals to produce enough crops for a farm family’s survival, with little left over to sell or store.

Polyculture
This method relies on solar energy and natural fertilizers such as animal manure
Complex form of intercropping in which a large number of different plants maturing at different times are planted together
Organic agriculture
Crops are grown without the use of synthetic pesticides, synthetic inorganic fertilizers, or genetically engineered seed varieties
farm subsidies
Government payments and tax breaks intended to help farmers stay in business and increase their yields.
Soil erosion
The movement of soil components from one place to another by the actions of wind and water