Cognitive Development Theories: Piaget and Vygotsky
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
Who was Jean Piaget?
A Swiss philosopher known for his work on cognitive development.
What was Piaget's big question regarding knowledge?
What is knowledge and where does it come from?
What is the goal of Piaget's theory of cognitive development?
To achieve cognitive equilibrium.
What are the two processes involved in adaptation according to Piaget?
Assimilation and accommodation.
What is assimilation in Piaget's theory?
The process of integrating new information into existing schemas.
What is accommodation in Piaget's theory?
The process of modifying existing schemas to incorporate new information.
What is cognitive disequilibrium?
A state of discomfort caused by a mismatch between existing knowledge and new experiences.
What are schemes in Piaget's theory?
Organized patterns of thought or action that children construct to make sense of their experiences.
What is the significance of cognitive equilibration?
It is the process of achieving balance between what we know and what we experience.
What are the four stages of Piaget's cognitive development?
Sensorimotor, Preoperational, Concrete Operations, and Formal Operations.
What characterizes the Sensorimotor stage?
From birth to 2 years, where children transition from reflexive to symbolic thinking.
What occurs during the Preoperational stage?
Children aged 2-7 develop language and engage in symbolic play but lack logical reasoning.
What is a key feature of the Concrete Operations stage?
Children aged 7-11 can think logically about concrete events but struggle with abstract concepts.
What defines the Formal Operations stage?
From age 11 onwards, individuals can think abstractly and reason logically.
What is the role of trial and error in the Sensorimotor stage?
Children learn about the world through repeated actions and their consequences.
What is the importance of the term 'equilibration' in Piaget's theory?
It describes the process of balancing assimilation and accommodation to foster cognitive development.
How do children construct and modify their schemes?
By combining existing schemes and adapting to new information.
What is the Piagetian term for an organized pattern of thought?
Scheme.
What is the main motivation for cognitive development according to Piaget?
A sense of discomfort when the balance between knowledge and experience is disrupted.
What is an example of assimilation?
A child calling a cat a 'dog' because it has four legs and fur.
What is an example of accommodation?
A child learning that not all four-legged animals are dogs after seeing a cat.
What is the age range for the Preoperational Stage in Piaget's theory?
Ages 2-7
What cognitive ability is characterized by the use of words, gestures, maps, and models?
Symbolic function in the Preoperational Stage
What is animism in the context of Preoperational thought?
The attribution of lifelike qualities to inanimate objects
What is egocentrism in children's cognitive development?
The inability to understand perspectives other than one's own
What task is used to demonstrate egocentrism in children?
The Three Mountain Task

What is centration in cognitive development?
Focusing on one aspect of a situation while ignoring others
What is the significance of conservation tasks in cognitive development?
They assess a child's understanding that quantity remains the same despite changes in shape or arrangement
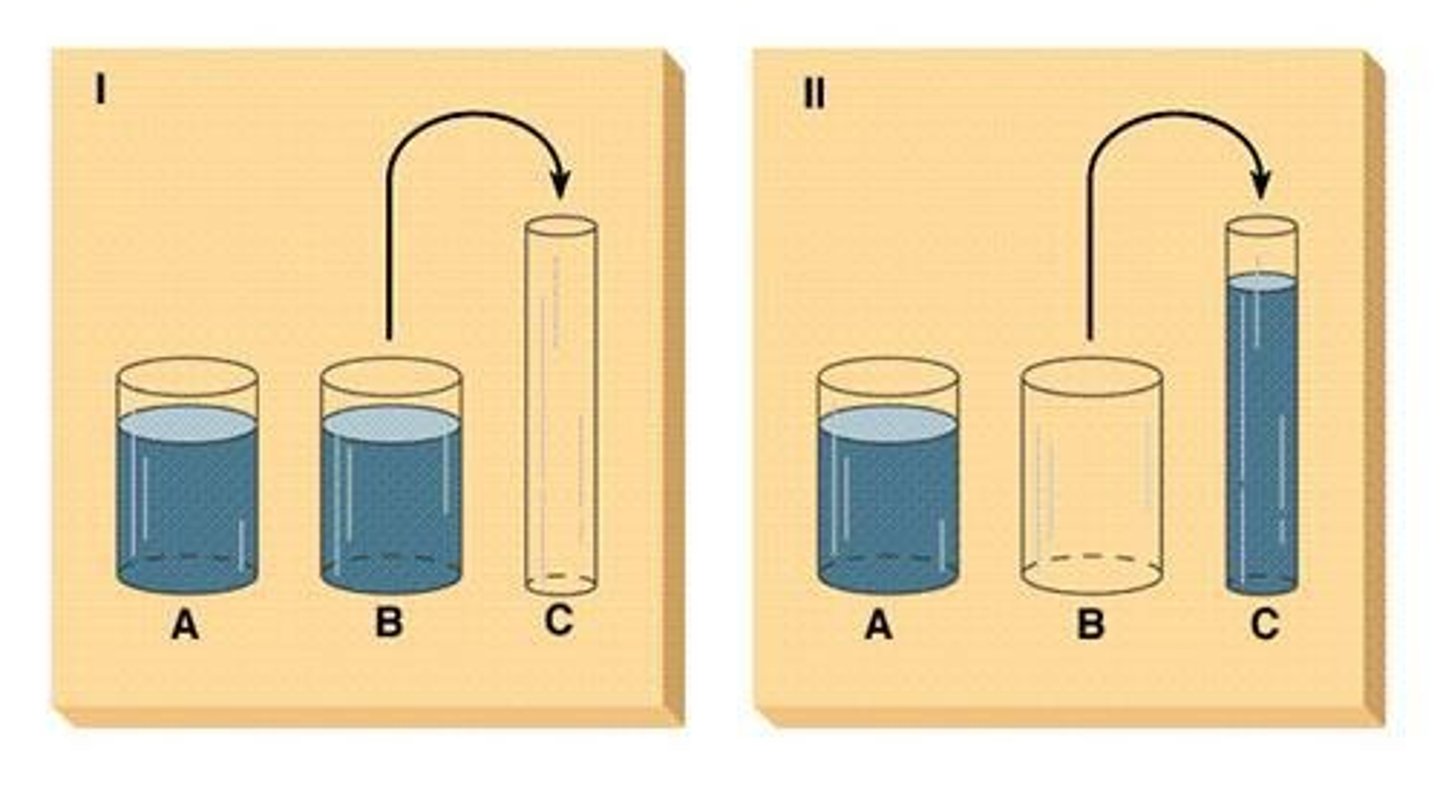
What stage of cognitive development is characterized by the ability to perform mental operations and understand reversibility?
Concrete Operational Stage (ages 7-11)
What is a key limitation of the Concrete Operational Stage?
Children can only apply logic to concrete, real-world objects and events
What is the Formal Operational Stage, and when does it occur?
The stage where abstract thinking and deductive reasoning develop, occurring from age 11 onward
What is systematic problem solving in the context of the Formal Operational Stage?
The ability to think logically and experiment while holding variables constant
What did Piaget contribute to the field of cognitive development?
He pioneered the study of cognitive development and emphasized constructivism
What are some weaknesses of Piaget's theory?
Lack of explanation for cognitive change mechanisms and undervaluing sociocultural influences
Who is Lev Vygotsky and what is his perspective on cognitive development?
A psychologist who emphasized the sociocultural context of development
What is the Zone of Proximal Development?
The difference between what a child can do independently and what they can achieve with guidance
What role does scaffolding play in cognitive development?
It provides support to help children achieve greater understanding and skills
What is private speech in the context of cognitive development?
Self-regulatory speech that helps children communicate with themselves during tasks
How does Vygotsky's view differ from Piaget's regarding children's learning?
Vygotsky emphasizes social interaction and cultural context, while Piaget focuses on individual exploration
What is the significance of inner speech in cognitive development?
It reflects a child's ability to self-regulate and communicate internally
What is the primary focus of the Preoperational Stage?
Symbolic thinking and the ability to engage in pretend play
What cognitive ability develops in the Concrete Operational Stage that is not present in the Preoperational Stage?
The ability to understand conservation and perform mental operations
What is a common misconception about children's abilities in the Formal Operational Stage?
That they can solve abstract problems as easily as concrete ones
What is the impact of cultural tools on cognitive development according to Vygotsky?
Cultural tools shape thought and influence cognitive activities
What is cognition?
The activity of knowing and the processes through which knowledge is acquired, including attending, perceiving, learning, thinking, and remembering.
What does cognitive development refer to?
Changes that occur in mental activities such as attending, perceiving, learning, thinking, and remembering.
Who is Jean Piaget?
A psychologist known for his work in developmental psychology and genetic epistemology, focusing on how knowledge develops in children.
What is genetic epistemology?
The experimental study of the development of knowledge, developed by Jean Piaget.
How does Piaget define intelligence?
A basic life function that enables an organism to adapt to its environment.
What is cognitive equilibrium?
A balanced relationship between one's thought processes and the environment, achieved through the process of equilibration.
What is equilibration?
The process of achieving cognitive equilibrium by making mental adjustments in response to new experiences.
What is the interactionist model in Piaget's theory?
A model suggesting that mismatches between internal mental schemes and the external environment stimulate cognitive activity and intellectual growth.
What is organization in cognitive development?
The process by which children combine existing schemes into new and more complex intellectual schemes.
What is adaptation in cognitive development?
The process of adjusting to the demands of the environment, involving assimilation and accommodation.
What is assimilation?
The process by which children interpret new experiences in terms of their existing models of the world.
What is accommodation?
The process of modifying existing structures to account for new experiences.
What are the stages of cognitive development proposed by Piaget?
Sensorimotor Stage, Preoperational Stage, Concrete Operational Stage, and Formal Operational Stage.
What is object permanence?
The understanding that objects continue to exist even when they are not visible.
What is the A-not-B error?
The tendency of infants aged 8-12 months to search for a hidden object where they previously found it, even after seeing it moved.
What characterizes the Preoperational Stage?
Children think at a symbolic level but are not yet using cognitive operations, leading to intuitive and egocentric thinking.
What is symbolic function in the Preoperational Stage?
The ability to use symbols, such as images and words, to represent objects and experiences.
What is egocentrism in Piaget's theory?
The tendency to view the world from one's own perspective, failing to recognize that others may have different viewpoints.
What is animism?
The attribution of life and lifelike qualities to inanimate objects, common in preoperational children.
What is the appearance/reality distinction?
The ability to understand that the true properties of an object can differ from its deceptive appearance, which young children struggle with.
What is centered thinking in preoperational children?
The tendency to focus on one salient perceptual feature of a situation while ignoring other relevant aspects.
What is dual representation?
The ability to think about an object in two different ways, which develops significantly during the preschool years.
What is the concept of 'centred' in Piaget's theory?
The tendency of preoperational children to focus on one aspect of a situation while ignoring others.
Define conservation in the context of cognitive development.
The recognition that the properties of an object do not change when its appearance is altered superficially.
At what age do children typically begin to understand conservation?
Around 6 or 7 years old.
What are the two cognitive operations that help overcome perceptually based intuitive reasoning?
Decentration and reversibility.
What is decentration?
The ability to concentrate on more than one aspect of a problem at the same time.
What does reversibility refer to in cognitive development?
The ability to mentally undo or negate an action.
What is identity training in conservation tasks?
Teaching children that an object remains the same despite changes in appearance.
What is the Theory of Mind?
Children's developing understanding of mental activity and that behavior is based on beliefs and desires.
What is the false-belief task?
A task where a child must infer that another person does not possess knowledge that the child possesses.
What is executive function?
A set of processes involved in planning, executing, and inhibiting actions.
What age range does Piaget's Concrete Operations stage cover?
7 to 11 years.
What cognitive abilities do children acquire during the Concrete Operations stage?
They can solve conservation problems and apply relational logic.
What is horizontal décalage?
An inability to solve certain problems even though a child can solve similar problems requiring the same mental operations.
What age range does Piaget's Formal Operations stage cover?
11 years and older.
What is hypothetico-deductive reasoning?
The ability to think hypothetically and reason from general to specific.
What is inductive reasoning?
The type of thinking that generates hypotheses from specific observations.
What criticism did Piaget face regarding competence and performance?
He underestimated the cognitive capabilities of younger children and equated task performance with underlying concepts.
What is Vygotsky's view on cognitive development?
Cognitive growth occurs in a sociocultural context influenced by social interactions.
What is scaffolding in Vygotsky's theory?
The tailored support provided by more skilled partners to help novice learners.
What is guided participation?
Adult-child interactions that shape children's cognition through culturally relevant activities.
What is private speech according to Vygotsky?
Verbal utterances that serve a self-communicative function and guide a child's thinking.
How does Piaget's egocentric speech differ from Vygotsky's private speech?
Egocentric speech is nonsocial and not directed to others, while private speech serves a self-guidance function.
What is the main focus of contemporary research regarding Piaget and Vygotsky?
Contemporary research tends to support Vygotsky's theories over Piaget's.