Carbohydrates-Monosaccharides and Poly/Disaccharides
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is Polymerisation?
Monomers (usually carbon) link to form polymers (long chain of monomers)
Condensation Reaction
Water is removed to combine 2 molecules.
Hydrolysis Reaction
Water is added to break down a polymer into 2 monomers.
Monosaccharide
Sweet soluble substances (CH20) e.g glucose,fructose
What is the structure of an an alpha glucose molecule?
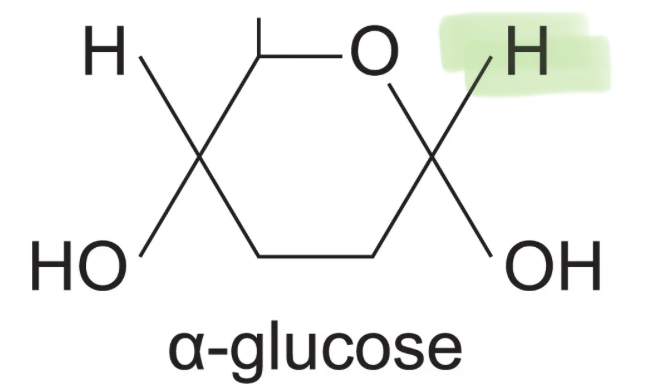
What is the structure of an an beta glucose molecule?
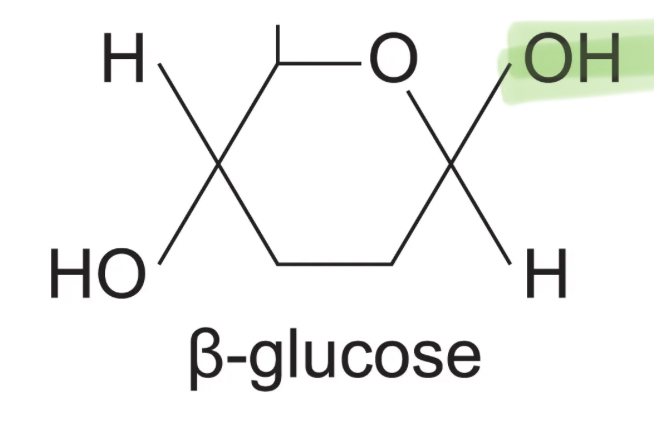
What is the test for reducing sugars?
Benedicts Reagent- alkaline copper sulfate solution that forms a red precipitate when heated with a reducing sugar
-Add 2cm³ of food sample (liquid form)
-Add equal vol of Benedicts Reagent
-Neutralise the solution
-Heat mixture in boiling water bath for 5 mins
How is maltose formed?
Glucose + Glucose
How is sucrose formed?
Glucose + Fructose
How is lactose formed?
Glucose + Galactose
What are the bonds called formed by a condensation reaction?
Glycosidic bonds
Polysacchaides
Formed by monosaccharides joined my glycosidic bonds they are all insoluble)
Amylose (Starch)
Found in plants,major energy source, formed from a glucose, straight chains that are coiled (1 to 4), very compact (can be stored in small spaces), insoluble and does not affect osmosis.
Amylopectin (Starch)
Formed from a glucose, branched chains (1 to 6), Large surface area (enzymes can work faster, hydrolyses faster), also insoluble.
Glycogen
Found in animals and bacteria (similar to starch), formed from a glucose (1 to 4 and 1 to 6), also insoluble and compact, more highly branched than Amylopectin and can be rapidly broken down (important for respiration as animals move more than plants).
Cellulose
Formed from B glucose (1 to 4), straight chains that run parallel with hydrogen bonds (forms fibrils between chains that add strength), used in plant cell walls.